
What is decompression sickness and how can you treat it?
What to do
- Contact emergency services. Watch for symptoms of decompression sickness. ...
- Contact DAN. You can also contact DAN, which operates an emergency phone line 24 hours a day. ...
- Concentrated oxygen. In more mild cases, you may not notice symptoms until a few hours or even days after a dive. ...
- Recompression therapy. ...
Does mild decompression sickness go away on its own?
This DCI denial is considered as one of the first symptoms of decompression illness and often leads to a delay in seeking medical advice. Sometimes these symptoms remain mild and go away by themselves, however, they often continue to persist or even increase in severity and medical advice will need to be sought.
How do you treat decompression sickness?
What causes Decompression Sickness?
- Dive well rested (especially if you are planning on doing one of those BIG dives on your bucket list!).
- Give yourself plenty of surface time in between dives to get rid of extra nitrogen.
- Maintain a reasonable level of fitness for the sort of diving you want to do, get a medical check-up regularly and stay hydrated.
How serious is decompression sickness?
These symptoms do not threaten life but may precede more dangerous problems. The more severe type of decompression sickness most commonly results in neurologic symptoms, which range from mild numbness to paralysis and death. The spinal cord is especially vulnerable.

What causes decompression sickness and how is it treated?
When a diver swims to the surface too quickly (a rapid ascent), the nitrogen can form tiny bubbles in the blood and/or body tissues, causing decompression sickness (DCS). DCS may occur even if a person dives within the limits of their dive computer or decompression tables and even if they complete a safety stop.
What is the remedy for victims who have developed decompression sickness?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is the primary treatment for DCS. It immediately reduces the amount of bubbles in the bloodstream, fills the tissues with oxygen, and reduces dangerous swelling. In most instances, it's critical to get treatment as soon as possible, because the symptoms of DCS can be life-threatening.
How do doctors treat someone with decompression sickness or the bends?
The bends are treated in a hyperbaric recompression chamber. The doctor will first treat immediate life threats, such as breathing problems or shock, if present. The diver will need high-flow oxygen and IV fluids.
How do Emts treat decompression sickness?
The definitive treatment for DCS is hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy, or the delivery of pure oxygen at a pressure substantially higher than that of atmospheric pressure.
Why does oxygen help with decompression sickness?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used to treat decompression sickness in scuba divers. During these treatments, you breathe pressurized oxygen while you lie inside a clear plastic tube. This helps your body remove the nitrogen that can build up during a dive and make you sick. Side effects from the treatment are rare.
Can decompression sickness go away on its own?
In some cases, symptoms may remain mild or even go away by themselves. Often, however, they strengthen in severity until you must seek medical attention, and they may have longer-term repercussions.
How is lung barotrauma treated?
No specific treatment is required for pneumomediastinum; symptoms usually resolve spontaneously within hours to days. After a few hours of observation, most patients can be treated as outpatients; high-flow 100% oxygen is recommended to hasten resorption of extra-alveolar gas in these patients.
How do you treat a divers ear?
TreatmentChewing gum, sucking on a lozenge, swallowing, or yawning. Using the mouth helps to open up the eustachian tube.Taking an over-the-counter (OTC) nasal decongestant, antihistamine, or both. ... Stopping a diving descent at the first sign of ear discomfort to allow time for equalizing.
What is the treatment for nitrogen narcosis?
The main treatment for nitrogen narcosis is simply getting yourself to the water's surface. If your symptoms are mild, you can stay in shallower waters with your dive partner or team while you wait for them to clear. Once your symptoms have cleared, you can resume your dive at that shallower depth.
Why do dolphins not get the bends?
When dolphins dive deep below the water's surface, they avoid succumbing to decompression sickness, or "the bends," likely because the massive sea creatures have collapsible lungs, a new study finds. These lungs allow dolphins to inhale and exhale two to three times quicker than humans.
What happens if a diver does not decompress?
Commonly referred to as the bends, caisson disease, or divers sickness / disease, decompression sickness or DCS is what happens to divers when nitrogen bubbles build up in the body and are not properly dissolved before resurfacing, leading to symptoms such as joint pain, dizziness, extreme fatigue, paralysis, and ...
How can we prevent ear squeeze in diving?
The key to safe equalizing is to get air to flow from the throat to the ears through the opening of the normally closed eustachian tubes. Most divers are taught to equalize by pinching their nose and blowing gently. This gentle pressure opens the eustachian tube and flows air gently to the middle ear.
What is the treatment for DCS?
The definitive treatment for DCS is hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy, or the delivery of pure oxygen at a pressure substantially higher than that of atmospheric pressure. HBO therapy reduces the size of any bubbles and improves gradients which promote oxygen delivery and inert gas elimination. HBO therapy is typically delivered in recompression chambers.
What is in water recompression?
In-water recompression may be an alternative to chamber recompression in remote locations, if there is neither a nearby chamber nor the means to quickly transport the patient to a chamber elsewhere. The technique involves bringing the diver underwater again, to drive gas bubbles back into solution to reduce symptoms and then slowly decompress in a way that maintains an orderly elimination of the excess gas.
What is the first aid measure for DCS?
The foundation of first aid is basic life support. The primary first aid measure for DCS is delivery of supplemental oxygen in the highest concentration, or fraction, that is practical (Longphre et al. 2007). High oxygen fractions, if provided rapidly and over a sustained period, can reduce or even eliminate symptoms of DCS, albeit often only temporarily if definitive treatment is not secured. Continuous-flow oxygen systems, using non-rebreather or pocket masks, are frequently available in diving environs; however, such equipment delivers modest oxygen fractions. Much higher fractions can be achieved with demand masks, though they are appropriate only for conscious individuals able to breathe on their own.
What is the best way to manage DCS?
There are several elements to the effective management of DCS, specifically on-the-scene evaluation and first aid, transport and definitive medical evaluation and treatment. Anyone who has suffered DCS should seek appropriate evaluation, and possibly ongoing care, from a physician well informed about diving-related medical issues.
What is the key point to remember when establishing contact with emergency medical services and DAN?
The key point to remember is that establishing contact with emergency medical services and DAN can ensure timely and appropriate case management. When in doubt, call.
Can DCS be resolved with HBO?
A full resolution of DCS symptoms can often be achieved with one or sometimes multiple HBO treatments. In some cases, however, resolution will be incomplete, even after many treatments. The normal clinical approach is to continue the treatments until no further improvement is seen in the patient’s symptoms.
What is decompression sickness?
Decompression sickness (DCS) occurs when dissolved gasses (usually nitrogen or helium, used in mixed gas diving) exit solution and form bubbles inside the body on depressurization. DCS occurs from underwater diving decompression (ascent), working in a caisson, flying in an unpressurized aircraft, and extra-vehicular activity from spacecraft. Proper decompression procedures during diving can help decrease DCS. Experts have classified DCS as Type I with symptoms involving only the skin, musculoskeletal system, or lymphatic systems; and Type II with symptoms that involve the central nervous system.
What is the difference between DCS and decompression sickness?
Experts have classified DCS as Type I with symptoms involving only the skin, musculoskeletal system, or lymphatic systems; and Type II with symptoms that involve the central nervous system. Decompression sickness (DCS) occurs when dissolved gasses (usually nitrogen or helium, used in mixed gas diving) exit solution and form bubbles inside ...
How to treat DCS?
The treatment of DCS is with 100% oxygen, followed by recompression in a hyperbaric chamber. [8] In most cases, this will prevent long-term effects. However, permanent injury from DCS is possible. To prevent the excess formation of bubbles leading to decompression sickness, divers limit their ascent rate. The recommended ascent rate used by popular decompression models is about 10 meters (33 ft) per minute.
How many cases of decompression sickness are there in a 10,000 dive?
The incidence of decompression sickness, fortunately, is rare. Estimates for sports diving are three cases per 10,000 dives. The incidence among commercial divers can be higher ranging from 1.5-10 per 10,000 dives. As expected, the incidence depends on the length and depth of the dive.[3] The risk for DCS is 2.5 times greater for males than females.
Can decompression cause vertigo?
Vertigo can indicate inner ear or vestibular decompression sickness wherein bubbles form in the perilymph fluid of the cochlea.[6] However, other diving-related causes merit consideration, as recompression and hyperbaric oxygen can cause worsening of some of these conditions. Inner ear barotrauma, in particular, would be a contraindication to compression as high-pressure gas may be forced into the cochlea causing further trauma on decompression. Alternobaric and caloric vertigo should be differentiated from decompression sickness by history. Cerebral arterial gas embolism affecting the midbrain or cerebellum can also present as inner ear decompression sickness but receives similar treatment. [1]
Is decompression sickness a risk factor?
Having had decompression sickness may place patients at increased risk for future similar events. Prognosis is severity dependent and also dependent on such factors as the time to recompression, availability and time to surface oxygen, and supportive care.
What is the end point of decompression sickness?
If this event gives rise to immediate symptoms, recompression is remarkably effective. This end-point is characteristic of joint pain, that is, Type 1 decompression sickness.
Is recompression effective for joint pain?
If this event gives rise to immediate symptoms, recompression is remarkably effective. This end-point is characteristic of joint pain, that is, Type 1 decompression sickness. Unfortunately the onset of serious Type 2 decompression sickness may be insidious and the delay may be associated with blood-brain barrier dysfunction.
What is decompression sickness?
What Is It? Decompression sickness, also called generalized barotrauma or the bends, refers to injuries caused by a rapid decrease in the pressure that surrounds you, of either air or water.
What happens when you scuba dive with compressed air?
Your body uses the oxygen, but the nitrogen is dissolved into your blood, where it remains during your dive. As you swim back toward the surface after a deep dive, the water pressure around you decreases.
What is decompression sickness?
Decompression sickness is a type of injury that occurs when there’s a rapid decrease in pressure surrounding the body. It usually occurs in deep-sea divers who ascend to the surface too quickly. But it can also occur in hikers descending from a high altitude, astronauts returning to Earth, or in tunnel workers who are in an environment ...
How long does it take for decompression sickness to appear?
The symptoms of decompression sickness may appear rapidly. For scuba divers, they may start within an hour after a dive. You or your companion may appear visibly ill. Look out for:
What is DCS treatment?
The treatment for more serious cases of DCS involves recompression therapy, which is also known as hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Can you get physical therapy for a neurological condition?
For severe cases, there may also be long-term neurological effects. In this case, physical therapy may be required. Work with your doctor, and keep them informed about any lasting side effects. Together, you can determine a care plan that’s right for you.
Can you get decompression sickness from high altitudes?
Your risk for decompression sickness increases if you: In general, decompression sickness becomes more of a risk the deeper you dive.
What is a decompression illness?
Decompression illness, or DCI, is associated with a reduction in the ambient pressure surrounding the body. DCI encompasses two diseases, decompression sickness (DCS) and arterial gas embolism (AGE). DCS results from bubbles in body tissues causing local damage.
What are the risk factors for decompression illness?
Decompression illness affects scuba divers, aviators, astronauts and compressed-air workers. The main risk factor for DCI is a reduction in ambient pressure, but other risk factors will increase the likelihood of DCI occurring. The known risk factors for divers are deep or long dives, cold water, heavy exercise at depth, and rapid ascents.
How long does it take to detect decompression?
Make an initial evaluation at the dive site. You can suspect decompression illness if you notice any of the signs or symptoms listed above within 24 hours of surfacing from a dive. While waiting for professional medical care or evacuation, take as detailed a history as possible and try to evaluate and record the diver’s neurological status. Base your response on one of these three categories depending upon the symptoms: emergency, urgent or timely.
What is DCS in medical terms?
DCS (also called the bends or caisson disease) results from inadequate decompression following exposure to increased pressure. In some cases, it is mild and not an immediate threat. In other cases, a serious injury occurs. The sooner the treatment of an injury begins, the better the chance for a full recovery.
What Is Decompression Sickness?
- Decompression sickness, also called generalized barotrauma or the bends, refers to injuries caused by a rapid decrease in the pressure that surrounds you, of either air or water. It occurs most commonly in scuba or deep-sea divers, although it also can occur during high-altitude or u…
Symptoms
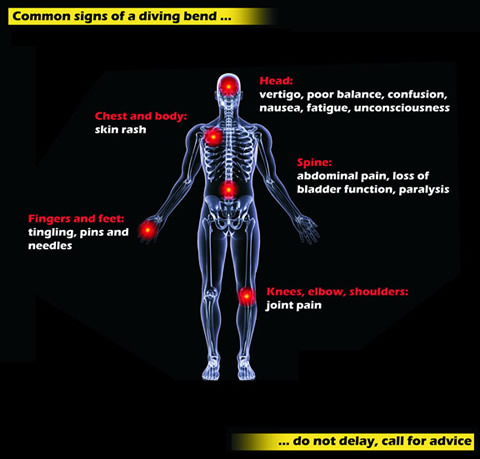
- Symptoms of decompression sickness include: 1. Joint pain 2. Dizziness 3. Headache 4. Difficulty thinking clearly 5. Extreme fatigue 6. Tingling or numbness 7. Weakness in arms or legs 8. A skin rash
Diagnosis
- Your diving history and symptoms are key factors in diagnosing decompression sickness. Blood tests and joint X-rays usually do not show any signs of the problem.
Prevention
- To minimize the risk of decompression sickness while diving: 1. Dive and rise slowly in the water, and don't stay at your deepest depth longer than recommended. Scuba divers typically use dive tables that show how long you can remain at a given depth. 2. Do not fly within 24 hours after diving. 3. Don't drink alcohol before diving. 4. Avoid hot tubs, saunas or hot baths after diving. 5. …
When to Call A Professional
- If you experience symptoms of decompression sickness after scuba diving or flying, get to a doctor as soon as you can. Hyperbaric treatment is most successful if given within several hours after symptoms start.
Prognosis
- Most cases of decompression sickness respond well to a single treatment with hyperbaric oxygen. Your doctor may suggest repeated treatments if you continue to experience symptoms, especially neurological symptoms.
Further Information
- Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Medical Disclaimer