What are the treatment options for breast abscess and masses?
Breast Abscesses and Masses Treatment & Management 1 Emergency Department Care. Definitive diagnosis of the etiology can only be made by pathologic... 2 Consultations. Patients with breast masses require a general surgeon for definitive treatment. 3 Long-Term Monitoring. For breast cancer screening guidelines, see the Guidelines section.
What are the treatments for breast cancer?
Once a malignant tumor has been diagnosed in the breast, your doctor will recommend a treatment plan tailored to your unique situation. This plan could include surgery, hormone therapy, radiation, and chemotherapy: 3 Surgery: The doctor will remove cancerous tissue from the affected area.
How do you treat benign breast disease?
Maintain a healthy weight. Exercise regularly. Eat a nutritious diet. Drink alcohol in moderation or not at all. Quit smoking. Reconsider the use of hormone replacement therapy. Switch to a non-hormonal birth control option. What is the prognosis (outlook) for people with benign breast disease?
What do I need to know about a breast mass?
What do I need to know about a breast mass? A breast mass is a lump or growth in your breast or underarm. A cyst (fluid-filled pocket), an injury, or changes in your breast tissue are the most common causes. A breast mass can also be caused by cancer. You must follow up as directed to find the cause of your breast mass.
See more

Does a breast mass need to be removed?
If your doctor is reasonably certain that your breast lump is a fibroadenoma — based on the results of the clinical breast exam, imaging test and biopsy — you might not need surgery. You might decide against surgery because: Surgery can distort the shape and texture of the breast.
What happens if they find a mass in your breast?
A lump or mass in the breast is the most common symptom of breast cancer. Lumps are often hard and painless, although some are painful. However, not all lumps are cancer. Benign breast conditions (like cysts) that can also cause lumps.
How do you treat benign breast mass?
How is benign breast disease managed or treated?Fine needle aspiration to drain fluid-filled cysts.Surgery to remove lumps (lumpectomy).Oral antibiotics for infections like mastitis.
What are the causes of breast mass?
Causes include infection, trauma, fibroadenoma, cyst, fat necrosis, or fibrocystic breasts. Breast lumps may develop in both males and females, but they are much more common in females....Possible causes of breast lumps include:an abscess or infection.adenoma or fibroadenoma.cysts.fat necrosis.lipoma.breast cancer.
How painful is a breast biopsy?
You will be awake during your biopsy and should have little discomfort. Many women report little pain and no scarring on the breast. However, certain patients, including those with dense breast tissue or abnormalities near the chest wall or behind the nipple, may be more sensitive during the procedure.
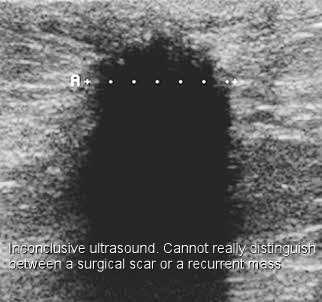
Can you tell if a mass is cancerous from an ultrasound?
Ultrasound images are not as detailed as those from CT or MRI scans. Ultrasound cannot tell whether a tumor is cancer. Its use is also limited in some parts of the body because the sound waves can't go through air (such as in the lungs) or through bone.
Can breast lump be treated without surgery?
If you have been diagnosed as having a non-cancerous lump in your breast, you don't have to live with it. You can have it removed, without surgery. The breast specialists of Bedford Breast Center offer the finest, most comprehensive fibroadenoma treatment in Los Angeles.
Can a 5 cm breast mass be benign?
These can grow to larger than 2 inches (5 centimeters). They might need to be removed because they can press on or replace other breast tissue. Phyllodes tumor. Although usually benign, some phyllodes tumors can become cancerous (malignant).
Can a 2 cm breast mass be benign?
In conclusion, US-CNB of probably benign breast lesions with benign biopsy results 2 cm or larger was accurate (98.6%) enough to rule out malignancy. But, it was difficult to rule out borderline lesions even after they were diagnosed as benign through US-CNB.
What is the difference between a breast cyst and a mass?
The bottom line Breast cysts are fluid-filled sacs. They're quite common, especially for people in their 40s who were assigned female at birth. Most of the time breast cysts turn out to be benign, and don't need treatment. A tumor can be cancerous or noncancerous, and usually requires treatment.
Where are breast masses most frequently found?
Commonly developing from the mammary glands or ducts, such malignant lumps generally (about 50 percent) appear in the upper, outer quadrant of the breast, extending into the armpit, where tissue is thicker than elsewhere.
What percent of breast masses are cancerous?
Your genes and stage of life, from puberty to menopause, can all affect how your breasts develop, look, and feel. Sometimes breast lumps develop that are benign (noncancerous). Only 3% to 6% of breast lumps are due to breast cancer.
Which Treatments Are Used For Breast Cancer?
There are several ways to treat breast cancer, depending on its type and stage.Local treatments: Some treatments are local, meaning they treat the...
How Is Breast Cancer Typically Treated?
Most women with breast cancer will have some type of surgery to remove the tumor. Depending on the type of breast cancer and how advanced it is, yo...
Who Treats Breast Cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team might include: 1. A breast surgeon or surgical oncologist: a doctor who uses surgery to treat breast cancer 2...
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi...
Help Getting Through Breast Cancer Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are many places you can get more help if you need it. Hospita...
What is a breast mass?
Breast Masses (Breast Lumps) The term breast mass is preferred over lump for a palpably discrete area of any size. A breast mass may be discovered by patients incidentally or during breast self-examination or by the clinician during routine physical examination. Masses may be painless or painful and are sometimes accompanied by nipple discharge ...
How do you know if you have a breast mass?
A breast mass may be discovered by patients incidentally or during breast self-examination or by the clinician during routine physical examination. Masses may be painless or painful and are sometimes accompanied by nipple discharge or skin changes.
What is fibroadenomas in breast?
Fibroadenomas. Fibrocystic changes (previously, fibrocystic disease) is a catchall term that refers to mastalgia, breast cysts, and nondescript masses (usually in the upper outer part of the breast); these findings may occur in isolation or together. Breasts have a nodular and dense texture and are frequently tender when palpated.
Why do my breasts feel heavy?
The breasts may feel heavy and uncomfortable. Women may feel a burning pain in the breasts. Symptoms tend to subside after menopause. Fibrocystic changes cause the most commonly reported breast symptoms and have many causes.
What is the mass palpated for?
The mass is palpated for size, tenderness, consistency (ie, hard or soft, smooth or irregular), and mobility (whether it feels freely mobile or fixed to the skin or chest wall). The axillary, supraclavicular, and infraclavicular areas are palpated for masses and adenopathy.
Can a mastitis cause pain in the breast?
They may occur after breast surgery. Puerperal mastitis, usually due to Staphylococcus aureus, can cause massive inflammation and severe breast pain, sometimes with an abscess. If infection occurs under other circumstances, an underlying cancer should be sought promptly.
Does fibroadenomas increase risk of breast cancer?
Juvenile fibroadenoma, a variant, occurs in adolescents, and unlike fibroadenomas in older women, these fibroadenomas continue to grow over time. Simple fibroadenoma does not appear to increase risk of breast cancer; complex fibroadenoma may increase risk slightly. Breast Mass (Fibroadenoma)
What is the treatment for stage 1 breast cancer?
Local therapy (surgery and radiation therapy) Surgery is the main treatment for stage I breast cancer. These cancers can be treated with either breast-conserving surgery (BCS; sometimes called lumpectomy or partial mastectomy) or mastectomy.
Why do you need radiation after breast surgery?
If BCS is done, radiation therapy is usually given after surgery to lower the chance of the cancer coming back in the breast and to also help people live longer.
How long does it take to get rid of HER2 cancer?
Many women with HER2-positive cancers will be treated with trastuzumab (with or without pertuzumab) followed by surgery and more trastuzumab (with or without pertuzumab) for up to 1 year. If after neoadjuvant therapy, residual cancer is found during surgery, trastuzumab may be changed to a different drug, called ado-trastuzumab emtansine, which is given every 3 weeks for 14 doses. If hormone receptor-positive cancer is found in the lymph nodes, your doctor might recommend one year of trastuzumab followed by additional treatment with an oral drug called neratinib for 1 year.
What are the stages of breast cancer?
Most women with breast cancer in stages I to III will get some kind of drug therapy as part of their treatment. This may include: 1 Chemotherapy 2 Hormone therapy (tamoxifen, an aromatase inhibitor, or one followed by the other) 3 HER2 targeted drugs, such as trastuzumab (Herceptin) and pertuzumab (Perjeta) 4 Some combination of these
What is the treatment for BCS?
Women who have BCS are treated with radiation therapy after surgery. Women who have a mastectomy are typically treated with radiation if the cancer is found in the lymph nodes.
What stage of breast cancer do you get drug therapy?
Most women with breast cancer in stages I to III will get some kind of drug therapy as part of their treatment. This may include:
Can breast reconstruction be done at the same time as breast surgery?
In some cases, breast reconstruction can be done at the same time as the surgery to remove the cancer.
What do I need to know about a breast mass?
A breast mass is a lump or growth in your breast or underarm. A cyst (fluid-filled pocket), an injury, or changes in your breast tissue are the most common causes. A breast mass can also be caused by cancer. You must follow up as directed to find the cause of your breast mass.
What to tell your healthcare provider about breast mass?
Your healthcare provider will perform a breast exam to feel the mass. Tell him or her when you noticed the breast mass, and if it has changed in size. Tell him or her if you have any other symptoms, such as pain, fever, or nipple discharge. He or she will ask if you have a personal or family history of breast disease or cancer.
Why is it important to continue breast self-exams?
Check your breast for changes in size , shape, or feel of the breast tissue. Check under your arms and all around your breasts. If you have monthly periods, examine your breasts after your period is over. Contact your healthcare provider if you notice any changes in your breasts. If you have questions, ask for more information on how to do a breast self-exam.
What causes a mass in the breast?
A breast mass is a lump or growth in your breast or underarm. A cyst (fluid-filled pocket), an injury, or changes in your breast tissue are the most common causes. A breast mass can also be caused by cancer. You must follow up as directed to find the cause of your breast mass.
Does breast mass return?
Your breast mass returns or grows larger.
What is spiculated breast mass?
A spiculated breast mass, which has spikes extending out from the main mass, is often highly suggestive of cancer.
What does a benign breast mass feel like?
Palpation of Benign Breast Masses. In contrast to breast cancer tumors, benign lumps are often squishy or feel like a soft rubber ball with well-defined margins. They're often easy to move around (mobile) and may be tender. 4 . Breast infections can cause redness and swelling.
What tests can be done to detect breast lumps?
Ultrasound. MRI. Biopsy. Noncancerous and cancerous breast lumps can be very different from each other when it comes to how they feel during a breast exam and what they look like in imaging tests.
What is the ultrasound of breast cancer?
On ultrasound, a breast cancer tumor is often seen as hypoechoic, has irregular borders, and may appear spiculated. Other ultrasound findings that suggest breast cancer include: Non-parallel orientation (not parallel to the skin) A mass that is taller than it is wide.
How accurate is breast palpation?
In one study, palpation (feeling the lump) had an overall accuracy of around 90%. 1 .
What is a breast tumor on an ultrasound?
On ultrasound, a breast cancer tumor is often seen as hypoechoic, has irregular borders, and may appear spiculated. Other ultrasound findings that suggest breast cancer include:
Where do breast tumors grow?
Breast tumors can grow in the mammary glands, or the milk ducts. They begin as tiny as a seed and may not be felt or detected by a physical exam, mammogram, MRI, or ultrasound until they grow larger.
What to do with a large breast abscess?
Consider admitting patients with large or complex breast abscesses for pain management, parenteral antibiotic therapy, and definitive management . Admit patients with sepsis due to mastitis. Consider diabetic ketoacidosis in patients with nonpuerperal breast abscess.
How to treat granulomatous mastitis?
Treatment of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis usually involves corticosteroids and methotrexate, with or without surgery. Consider admitting patients with large or complex breast abscesses for pain management, parenteral antibiotic therapy, and definitive management. Admit patients with sepsis due to mastitis.
What is the best treatment for a persistent abscess?
For persistent lesions, treatment options may include ultrasound-guided needle aspiration, [ 20] percutaneous drainage catheter, [ 77] and/or surgical drainage. Ultrasound-guided needle aspirations are more successful for abscesses smaller than 3 cm and for puerperal abscesses. [ 8, 71, 72, 73, 87] Loculations are associated with failure of resolution with aspiration, regardless of abscess volume. [ 74] Nonpuerperal abscesses have a higher recurrence rate and often require multiple drainage attempts. [ 8] Regardless of the underlying organism, the need for repeat aspiration is common in patients treated with aspiration versus incision and drainage. [ 75] In a US cohort of 54 abscess cases treated with needle-guided aspiration, the median number of drainage procedures was 2 (interquartile range, 1.0-4.0), with 24% requiring 5 or more drainage procedures. [ 43]
How long does it take for mastitis to heal?
In general, mastitis is treated with antibiotic therapy for 10-14 days, warm or cold compresses, and continued breast emptying via breastfeeding or breast pumping every 2 hours or when engorged. Antibiotic therapy with continued breast emptying has been shown to be superior to breast emptying alone for resolving symptoms, ...
How far apart do you get a cranial mammogram?
Craniocaudal mammograms obtained 1 year apart demonstrate a newly developing mass in the outer part of the breast.
Is there a difference in clinical characteristics between breast abscesses infected by methicillin-resistant?
In one study, there was no difference in clinical characteristics between breast abscesses infected by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), and the authors recommended no change in interventional treatment based on a positive MRSA culture result. [ 89]
Do you need a general surgeon for breast mass?
Patients with breast masses require a general surgeon for definitive treatment. Immediate consultation in the ED is not mandatory, but it may help facilitate faster follow-up care once patients are discharged from the hospital.
Benign and Malignant Tumors
Healthcare providers may opt to leave a benign tumor alone rather than remove it. If you are experiencing discomfort, irritation, or pressure, talk with your practitioner, who may refer you to a surgeon to remove it and improve your comfort.
Tumor Levels
Malignant tumors are evaluated and classified according to a designated system based on severity. Your healthcare provider will evaluate how similar the cells are to healthy cells and the shape and size of the cells. He or she will also look for indications of how quickly the cells split and multiply.
Malignant Tumors and Other Cancers
If a malignant tumor sheds cells into your bloodstream or lymph system, those cells will carry cancer to other parts of the body, which may include:
Treatment
Once a malignant tumor has been diagnosed in the breast, your healthcare provider will recommend a treatment plan tailored to your unique situation. This plan could include surgery, hormone therapy, radiation, and chemotherapy: 3
What is the procedure to remove lumps from breast?
During fine-needle aspiration, a special needle is inserted into a breast lump, and any fluid is removed (aspirated). Ultrasound — a procedure that uses sound waves to create images of your breast on a monitor — might be used to help place the needle.
What to do if breast lump doesn't disappear?
If the fluid appears bloody or the breast lump doesn't disappear, your doctor may send a sample of the fluid for lab testing and refer you to a breast surgeon or to a radiologist — a doctor trained to perform imaging exams and procedures — for follow-up.
What to do if you don't have fluid in your breast?
If no fluid is withdrawn, your doctor will likely recommend an imaging test, such as a diagnostic mammogram or ultrasound. The lack of fluid or a breast lump that doesn't disappear after aspiration suggests that the breast lump — or at least a portion of it — is solid. A sample of the tissue may be collected to check for cancer.
What test can you do to see if you have a lump in your breast?
Large cysts and clusters of small cysts can usually be seen with mammography. But microcysts can be difficult or impossible to see on a mammogram. Breast ultrasound. This test can help your doctor determine whether a breast lump is fluid filled or solid.
What does a solid lump in breast mean?
A fluid-filled area usually indicates a breast cyst. A solid-appearing mass most likely is a noncancerous lump, such as a fibroadenoma, but solid lumps also could be breast cancer. Your doctor may recommend a biopsy to further evaluate a mass that appears solid. If your doctor can easily feel a breast lump, he or she may skip imaging tests ...
How to get rid of cysts on breast?
Lifestyle and home remedies. To minimize discomfort associated with breast cysts, you might try these measures: Wear a supportive bra. Supporting your breasts with a bra that fits well may help relieve some discomfort. Apply a compress. Either a warm compress or an ice pack can help relieve pain. Avoid caffeine.
When is it necessary to remove a cyst from breast?
Surgery to remove a breast cyst is necessary only in unusual circumstances. Surgery may be considered if an uncomfortable breast cyst recurs month after month or if a breast cyst contains blood-tinged fluid or shows other worrisome signs.
Why do you have to remove breast tissue?
If you have atypical hyperplasia, your healthcare provider may recommend surgically removing affected breast tissue because the condition may make you more prone to breast cancer. Intraductal papilloma: These small, wart-like growths form inside the mammary duct near the nipple.
How to lower the risk of breast cancer?
These actions may lower cancer risk and help detect disease early when it’s most treatable: Get regular mammogram screenings. Perform self-exams to get familiar with how your breasts look and feel. Maintain a healthy weight. Exercise regularly.
What does it mean when you feel a lump in your breast?
If you feel a lump in your breast, your first thought may be that you have breast cancer. Fortunately, a majority of breast lumps are benign, meaning they’re not cancerous. Both women and men can develop benign (noncancerous) breast lumps. This condition is known as benign breast disease. While these breast changes aren’t cancerous ...
What is the most common breast cancer?
Fibroadenomas: These are the most common noncancerous solid breast tumors found in women ages 15 to 35. Fibroadenomas don’t increase cancer risk and often go away on their own. Fibrocystic breast changes: Fluctuating hormone levels can make breasts feel lumpy, dense and tender, especially right before menstruation.
What age group is most likely to have fibrocystic breasts?
Women ages 30 to 50 are more likely to experience fibrocystic breast changes, which go away without treatment. Hyperplasia: This condition occurs from an overgrowth of cells that line mammary ducts or glands. A condition called usual hyperplasia doesn’t increase cancer risk and doesn’t require treatment.
What is a tumor in breast that is damaged by radiation?
Traumatic fat necrosis: These breast lumps form when scar tissue replaces breast tissue that’s been damaged by an injury, surgery or radiation therapy. These lumps don’t raise cancer risk and don’t need treatment.
Can you get treatment for benign breast cancer?
Most types of benign breast disease don’t require treatment. Your healthcare provider may recommend treatment if you have atypical hyperplasia or a different kind of benign breast disease that increases your future risk of breast cancer. If you experience pain or discomfort or have an increased cancer risk, these treatments can help:
What is the procedure to remove a lump from breast?
Fine-needle aspiration. Through a thin needle inserted into your breast, your doctor attempts to withdraw the contents of the breast lump. If fluid comes out, the lump is likely a cyst. Core needle biopsy. A radiologist with guidance from an ultrasound usually performs this procedure.
What to do when you have a breast appointment?
What you can do. When you make the appointment, ask if there's anything you need to do in advance, such as restrict your diet. Make a list of: Your symptoms, including any that seem unrelated to your breast changes, and when they began.
What is a breast ultrasound?
A breast ultrasound can help your doctor determine whether a breast lump is solid or filled with fluid. A solid mass is more likely a fibroadenoma; a fluid-filled mass is more likely a cyst.
What is the best way to see if you have a lump in your breast?
Breast ultrasound. This technology uses sound waves to produce pictures of the inside of the breast. Your doctor might recommend a breast ultrasound in addition to a mammogram to evaluate a breast lump if you have dense breast tissue. For women younger than 30 who have a breast lump, the doctor likely will order a breast ultrasound first ...
How to remove fibroadenoma?
Cryoablation. Your doctor inserts a thin, wand-like device (cryoprobe) through your skin to the fibroadenoma.
What to do if you have a lump that can be felt?
If you have a lump that can be felt (palpable), your doctor might recommend certain tests or procedures, depending on your age and the characteristics of the lump.
Can fibroadenoma be removed?
Your doctor might recommend surgery to remove the fibroadenoma if one of your tests — the clinical breast exam, an imaging test or a biopsy — is abnormal or if the fibroadenoma is extremely large, gets bigger or causes symptoms.