- Stop transfusion as soon as a reaction is suspected
- Replace the donor blood with normal saline
- Examine the blood to determine if the patient was the intended recipient and then send the unit back to the blood bank
- Furosemide may be administered to increase renal blood flow
- Low-dose dopamine may be considered to improve renal blood flow
- Make efforts to maintain urine output at 30-100 mL/h
What should I do after a blood transfusion?
After a blood transfusion, most people are perfectly fine and experience mild or no side effects. These patients will not need to do anything different or out of the ordinary. Rarely, some people can react badly to the transfused blood, meaning that the transfusion may need to be aborted and the patient may need other types of medical care.
What illnesses can blood transfusion help treat?
Blood transfusions to treat anemia. A blood cell transfusion is a safe and a common way to treat anemia in people with cancer. It can help the patient feel better and helps oxygen get to vital organs. While blood transfusions can help symptoms very quickly, sometimes the relief is temporary depending on the cause of anemia.
Can you eat before getting a blood transfusion?
Can you eat before getting a blood transfusion? There are generally no special restrictions on eating, though it does make sense to be well hydrated. There are also no restrictions on activities before or during the transfusion, as long as it doesn’t interfere with the IV if the line is already placed.
Should blood be warmed before a transfusion?
Warming blood products before a transfusion is not normally required. If you receive a blood transfusion of 1 or 2 units, the blood is approximately 10 degrees C when it is infused. However, there are two indications for the use of a special “blood warmer” in transfusions:
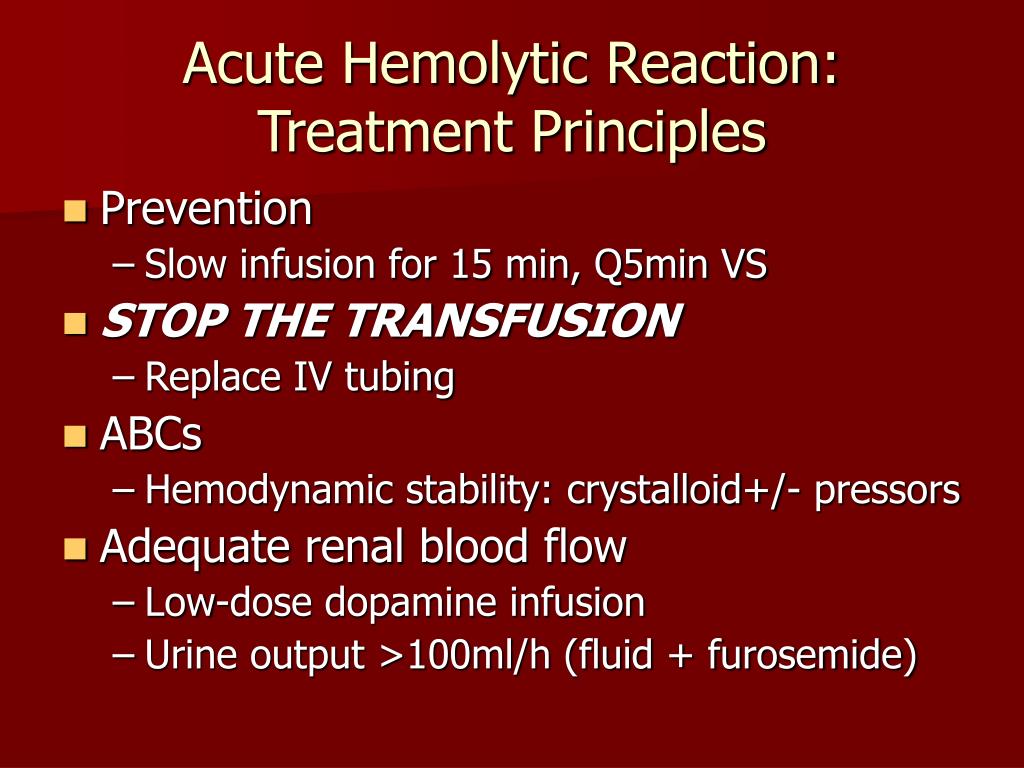
What medication is given for blood transfusion reaction?
Febrile non-hemolytic and allergic reactions are the most common transfusion reactions, but usually do not cause significant morbidity. In an attempt to prevent these reactions, US physicians prescribe acetaminophen or diphenhydramine premedication before more than 50% of blood component transfusions.
What is the treatment for severe allergic transfusion reactions?
Symptoms are usually controlled by slowing the transfusion and giving antihistamine, and the transfusion may be continued if there is no progression at 30 minutes. Pre-treatment with chlorphenamine should be given when a patient has experienced repeated allergic reactions to transfusion.
Which would the nurse do first if an allergic reaction to a blood transfusion occurs?
When a transfusion reaction is suspected, the transfusion should be immediately stopped, and the intravenous line should be kept open using appropriate fluids (usually 0.9% saline). A clerical check should be performed by examining the product bag and confirming the patient's identification.
How do you treat a delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction?
Symptomatic patients experiencing DHTR can be immediately treated with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg), adding erythropoietin (EPO) if the DHTR is also associated with reticulocytopenia. Prophylactic anticoagulation is administered to lower the risk of thrombosis associated with EPO administration.
What Is A Blood Transfusion reaction?
A blood transfusion reaction is a harmful immune system response to donor blood. Reactions can occur right away or much later, and can be mild or s...
What Causes A Blood Transfusion reaction?
Your immune system can react to anything in the donor blood. One of the most serious reactions is called ABO incompatibility. The 4 main blood type...
What Increases My Risk For A Blood Transfusion reaction?
1. You had a blood transfusion before. Your immune system will attack donor blood the next time you get a transfusion. 2. You have been pregnant. Y...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of An Immediate reaction?
Healthcare providers will stop the transfusion if you have any of the following: 1. A strong feeling of dread or that something is wrong 2. Faintin...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of A Delayed reaction?
A delayed blood transfusion reaction can begin within 3 to 10 days. You may also have a reaction the next time you receive blood. 1. A high fever a...
How Is A Blood Transfusion Reaction Diagnosed and Treated?
Your blood and urine will be tested for signs of kidney failure or destroyed red blood cells. You may need any of the following to treat a reaction...
How Can I Help Prevent Another Blood Transfusion reaction?
1. Give complete health information. Tell your healthcare providers about your health conditions, transfusions, and pregnancies. 2. Alert your heal...
Call 911 For Any of The Following
1. You have a skin rash, hives, swelling, or itching. 2. You have trouble breathing, shortness of breath, wheezing, or coughing. 3. Your throat tig...
When Should I Seek Immediate Care?
1. You have a seizure. 2. You have a headache or double vision. 3. You are lightheaded, confused, or feel like you are going to faint. 4. You have...
What is a blood transfusion reaction?
A blood transfusion reaction is a harmful immune system response to donor blood. Reactions can occur right away or much later, and can be mild or severe.
How to stop a transfusion?
Alert your healthcare providers about any problems. Tell your healthcare providers right away if something feels wrong. They will stop the transfusion and treat your symptoms.
What does it mean when you feel like you have a blood transfusion?
A strong feeling of dread or that something is wrong. Fainting or breathing problems. Fever and chills. Itching, hives, or swelling. Pain or burning in your abdomen, chest, or back, or at the transfusion site. Swelling and a large bruise at the transfusion site. Blood in your urine. Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Why do you stop a blood transfusion?
Pain, nausea, itching, or a large bruise at the transfusion site are good reasons to stop the transfusion. Ask if you can use your own blood. You may be able to get your own blood during surgery. Your blood will need to be drawn and stored a few weeks before a scheduled surgery. Carry medical alert identification.
How long does it take for a delayed blood transfusion to occur?
A delayed blood transfusion reaction can begin within 3 to 10 days. You may also have a reaction the next time you receive blood. Yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes.
What are the different types of blood?
The 4 main blood types are A, B, O, and AB. Your immune system will try to destroy donor cells that are the wrong type for you. Another reaction happens when you are allergic to something in the donor blood. Allergic reactions are usually mild but can become a life-threatening reaction called anaphylaxis.
Why do you need medicine for a fever?
You may also need medicine to relax muscles in your throat and chest to help you breathe, or to raise your blood pressure. Medicine may also be given to lower a fever. Fluids may be given through your IV to prevent your blood pressure from falling too low.
Why do we need blood transfusions?
You may need a blood transfusion if you've lost blood from an injury or during surgery, or if you have certain medical conditions including: Anemia. Certain cancers. Hemophilia.
How long does it take for a blood transfusion to take place?
Most transfusions take between one and three hours. Talk to your healthcare provider for more specifics about your needs.
How long does it take to check blood pressure after a blood transfusion?
Make sure that the supplied blood is the product ordered by your doctor and is labeled with your name. During your transfusion, your nurse will: Recheck your blood pressure and pulse after 15 minutes.
Why is blood important?
Blood is important. If you don’t have enough blood or one of the components of blood, you could face a life-threatening situation. Blood and the components of blood benefit the body in these ways: Red blood cells carry oxygen through your body to your heart and brain. Adequate oxygen is very important to maintain life.
How many transfusions are contaminated by bacteria?
Bacterial contamination: 1 in 100,000 transfusions. You’re more likely to get struck by lightning than to get a disease from a transfusion. The precautions healthcare workers take have helped make transfusions very safe.
What does it feel like to have a hemolytic reaction?
Most people don’t have any of these reactions. When they do happen, they often feel like allergies. If you experience unusual symptoms during a transfusion, tell your healthcare provider.
What questions do blood banks ask?
Blood banks ask potential donor s questions about their health, behavior and travel history. Only the people who pass the blood donor requirements can donate blood. Donated blood is tested according to national guidelines. If there is any question that the blood is not safe, it is thrown away.
What are the symptoms of a transfusion reaction?
The most common signs and symptoms include fever, chills, urticaria (hives), and itching. Some symptoms resolve with little or no treatment. However, respiratory distress, high fever, hypotension (low blood pressure), and red urine (hemoglobinuria) can indicate a more serious reaction. Transfusion reactions are defined as adverse events associated ...
Why do blood transfusions cause death?
The majority of blood transfusion reactions occur because of a clerical/nursing error. While some reactions can be severe and lead to death, many transfusion reactions are benign. Anaphylactic reactions from a blood transfusion are very rare but often result in a fatality.
Can transfusion reactions occur during a transfusion?
They range in severity from minor to life-threatening and can occur during a transfusion, termed acute transfusion reactions, or days to weeks later, termed delayed transfusion reactions. Transfusion reactions may be difficult to diagnose as they can present with non-specific, often overlapping symptoms.
Can a transfusion reaction be life threatening?
These may range in severity from minor to life-threatening. Reactions can occur during the transfusion (acute transfusion reactions) or days to weeks later (delayed transfusion reactions) and may be immunologic or non-immunologic. A reaction may be difficult to diagnose as it can present with non-specific, often overlapping symptoms.
Can antihistamines be given for febrile transfusion?
For example, antihistamines (such as diphenhydramine) can be given for a mild allergic reaction, or an antipyretic can be given for a non-hemolytic febrile transfusion reaction. [9][15] Differential Diagnosis. Anaphylaxis.
Is transfusion reaction common?
Transfusion reactions range in frequency from relatively common, (mild allergic and febrile non-hemolytic reactions) to rare (anaphylaxis, acute hemolytic, and sepsis). Fatal adverse events have been reported to occur most commonly with TRALI, and long-term or later adverse events are typically the result of disease transmission.
What are blood products?
There are multiple different blood products that are transfused within the hospital, and each one can have adverse reactions called blood transfusion reactions.
Why are Blood products Given?
Blood products are given whenever the blood levels are too low, or when there is acute bleeding. While this will depend on each specific patient and clinician, blood products are generally given when:
Blood Transfusion Reactions
As with any medication or fluid, there are possible adverse reactions that can occur and that you need to monitor for.
Acute Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
An acute hemolytic transfusion reaction is a rare life-threatening blood transfusion reaction to receiving blood, specifically PRBCs.
Anaphylactic Transfusion Reaction
An anaphylactic transfusion reaction is a severe allergic reaction to something within the blood product. These are rare, with an estimated 1 in 20-50K transfusions.
Urticarial Transfusion Reaction
An urticarial transfusion reaction is a less severe allergic reaction to a component within the blood products, but much more common, occurring in 1-3% of blood transfusions. This is an antigen-antibody interaction, usually with donor serum proteins.
What is the most common type of blood transfusion reaction?
Immune-related reactions include: Nonhemolytic fever is the most common type of blood transfusion reactions and is likely to recur with a patient who has had more than one blood transfusion. The reaction does not destroy the red blood cells.
What is a transfusion reaction?
Transfusion Reactions: Adverse Effects, Causes and Treatment. A blood transfusion or putting donated blood into a patient’s bloodstream is a procedure used to save lives. It is performed in people undergoing surgery, or in cases of serious loss of blood. A blood transfusion is a delicate procedure that should involve matching blood types ...
What happens when the immune system mistakenly identifies transfused blood components as harmful and begins to attack them
This reaction is combated by thorough screening before transfusion. Hemolytic transfusion reactions involve the destruction of red blood cells.
Why does hemolytic transfusion cause a reaction?
This causes the recipient body’s immune system to attack the transfused blood, destroying the red blood cells, Mild hemolytic transfusion reactions are caused by a mismatch in one or more of the 100 minor blood types. They are not as serious as a mismatch between blood types or rhesus factors. ...
Why does blood transfusion take longer?
The procedure can take longer if more blood is needs to be transfused. A blood transfusion is stopped immediately if the following adverse reactions occur: A large swelling at the point of transfusion. Apart from the large swelling, the transfusion point will be painful, and you have a burning sensation.
Why do non-immune blood transfusions happen?
Nonimmune blood transfusion reactions usually happen because there is too much fluid caused by transfusion. It mostly happens to first-time patients of a blood transfusion. The condition is treated by putting the patient on medication to increase urination and thereby rid the body of the excess fluid.
What are the symptoms of delayed blood transfusion?
Watch out for the following symptoms: Headaches, blurred vision, and seizures. Yellowish eyes and skin. Fatigue and body weakness. Difficulty in breathing.
How long does it take for diuresis to resolve?
In febrile, nonhemolytic reactions, fever usually resolves in 15-30 minutes without specific treatment.
Can you take acetaminophen with fever?
If fever causes discomfort, oral acetaminophen (325-500 mg) may be administered. Avoid aspirin because of its prolonged adverse effect on platelet function. In allergic reactions, diphenhydramine is usually effective for relieving pruritus that is associated with hives or a rash. The route (oral or intravenous) and the dose (25-100 mg) ...
What is blood transfusion?
Overview. A blood transfusion is a routine medical procedure in which donated blood is provided to you through a narrow tube placed within a vein in your arm. This potentially life-saving procedure can help replace blood lost due to surgery or injury. A blood transfusion also can help if an illness prevents your body from making blood or some ...
Why do people need blood transfusions?
A blood transfusion also can help if an illness prevents your body from making blood or some of your blood's components correctly. Blood transfusions usually occur without complications. When complications do occur, they're typically mild.
Why does the immune system attack the transfused red blood cells?
Your immune system attacks the transfused red blood cells because the donor blood type is not a good match. The attacked cells release a substance into your blood that harms your kidneys. Delayed hemolytic reaction. Similar to an acute immune hemolytic reaction, this reaction occurs more slowly.
How long does it take for blood to decrease?
It can take one to four weeks to notice a decrease in red blood cell levels. Graft-versus-host disease. In this condition, transfused white blood cells attack your bone marrow. Usually fatal, it's more likely to affect people with severely weakened immune systems, such as those being treated for leukemia or lymphoma.
How long does it take to get IV blood?
You'll be seated or lying down for the procedure, which usually takes one to four hours.
Can you donate blood before surgery?
In some cases, you can donate blood for yourself before elective surgery, but most transfusions involve blood donated by strangers. An identification check will ensure you receive the correct blood.
Is it safe to give blood after a blood transfusion?
Blood transfusions are generally considered safe, but there is some risk of complications. Mild complications and rarely severe ones can occur during the transfusion or several days or more after.
What is a transfusion?
Introduction. A transfusion is defined as an infusion of whole blood or any one of its components. Transfusions like any other medical intervention have benefits and risks. Hemolytic transfusion reactions are one of the possible complications from transfusions. Hemolysis is described as rupture of red blood cells and leakage of their contents.
What are the symptoms of hemolytic transfusion?
Classically, acute hemolytic transfusion reaction is described as a triad of symptoms; fever, flank pain, and red or brown urine. However, this classic presentation is not seen often. Other symptoms are chills, hypotension, renal failure, back pain, or signs of disseminated intravascular coagulation.
What is extravascular hemolysis?
Extravascular hemolysis is hemolysis produced when the antibody to the RBC antigen can opsonize the RBC, which leads to their sequestration and phagocytosis by macrophages and other phagocytes of the reticuloendothelial system (liver and spleen).
What is hemolysis in blood?
Hemolysis is described as rupture of red blood cells and leakage of their contents. The site of hemolysis can be intravascular (in circulation) or extravascular (in reticuloendothelial system). Hemolytic transfusion reactions can be immune or non-immune mediated. [1][2][3]
What is the term for the rupture of red blood cells?
Hemolysis is the rupture of red blood cells, and can occur intravascularly, or in the circulation, or extravascularly, or in the reticuloendothelial system. Hemolytic transfusion reactions can be immune or non-immune mediated. Immune hemolytic transfusions reactions occur due to mismatch or incompatibility of the patient with the donor products.
How long does it take for a hemolytic reaction to occur?
Immune hemolytic transfusion reactions are divided into acute versus delayed hemolytic reactions. Acute hemolytic reactions happen within 24 hours of transfusion and delayed hemolytic reactions happen after 24 hours. Delayed reactions usually occur two weeks after but can go up to 30 days post transfusion.
What is hemolysis in transfusion?
Hemolytic transfusion reactions are one of the possible complications from transfusions. Hemolysis is described as rupture of red blood cells and leakage of their contents. The site of hemolysis can be intravascular (in circulation) or extravascular (in reticuloendothelial system).