
Medication
For some people, Barrett's esophagus can heal, per Cedars Sinai, though it's typically a permanent condition. Tip If you have severe or frequent GERD symptoms or take heartburn medicine more than twice a week, visit your doctor to get treatment and check for Barrett's esophagus, per the Mayo Clinic.
Procedures
Between 10 and 15 percent of people with GERD develop Barrett's esophagus. 4. Obesity-specifically high levels of belly fat-and smoking also increase your chances of developing Barrett's esophagus. Some studies suggest that your genetics, or inherited genes, may play a role in whether or not you develop Barrett's esophagus. What factors decrease a person's chances of developing Barrett's esophagus? Having a Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection may decrease your chances of ...
Therapy
In GERD, stomach contents wash back into the esophagus, damaging esophagus tissue. As the esophagus tries to heal itself, the cells can change to the type of cells found in Barrett's esophagus. However, some people diagnosed with Barrett's esophagus have never experienced heartburn or acid reflux.
Self-care
Those who asked “can Barrett’s esophagus be cured?” and find that the answer is “no” can at least take relief in the fact that management and treatment of Barrett’s are possible, and can greatly improve your quality of life.
Nutrition
Does Barretts esophagus ever heal?
What are the chances of getting Barrett's esophagus?
Can Barrett's esophagus heal itself?
Does Barretts esophagus get better?
How long can you live with Barrett's esophagus cancer?
RESULTS: The mean age at diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus was 61.6 years in males and 67.3 years in females. The mean life expectancy at diagnosis was 23.1 years in males, 20.7 years in females and 22.2 years overall.
How fast does Barrett's esophagus progress to cancer?
4. How long does it take for Barrett's esophagus to develop into cancer? Barrett's esophagus increases your risk of developing adenocarcinoma, the most common type of esophageal cancer. But if Barrett's esophagus does turn into cancer, it is a slow process that takes several years.
How common is cancer with Barrett's esophagus?
The risk of esophageal cancer in patients with Barrett's esophagus is quite low, approximately 0.5 percent per year (or 1 out of 200). Therefore, the diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus should not be a reason for alarm. It is, however, a reason for periodic endoscopies.
How often does Barrett's esophagus turn into esophageal cancer?
Barrett's esophagus is a complication of gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD). An estimated 10-15 percent of patients with GERD will develop Barrett's esophagus. Approximately one in 860 Barrett's esophagus patients will develop esophageal cancer, meaning the risk is statistically low.
What are the symptoms of Barrett's esophagus cancer?
What are the symptoms of Barrett's esophagus?Heartburn that worsens or wakes you from sleep.Painful or difficult swallowing.Sensation of food stuck in your esophagus.Constant sore throat, sour taste in your mouth or bad breath.Unintentional weight loss.Blood in stool.Vomiting.
What are the four stages of Barrett's esophagus?
The stages, or grades, of Barrett's are: Non-dysplastic, Indefinite, Low grade Dysplasia, and High Grade Dysplasia, which can lead to Intramucosal Carcinoma.
What are the signs that Barrett's esophagus is getting worse?
The development of Barrett's esophagus is most often attributed to long-standing GERD , which may include these signs and symptoms:Frequent heartburn and regurgitation of stomach contents.Difficulty swallowing food.Less commonly, chest pain.
Is Barrett's esophagus a death sentence?
Those who are diagnosed with Barrett's Esophagus can expect to live a normal life. This condition is treatable and doesn't hold any risk of premature death. However, Barrett's Esophagus is a serious condition and should be under the treatment guidelines recommended to you by a gastroenterologist.
Can esophageal cancer be reversed?
Esophageal cancer is often in an advanced stage when it is diagnosed. At later stages, esophageal cancer can be treated but rarely can be cured. Taking part in one of the clinical trials being done to improve treatment should be considered.
What type of cancer is associated with Barrett's esophagus?
Barrett's esophagus (BE) is the only known precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), whose incidence has increased sharply in the last 4 decades. The annual conversion rate of BE to cancer is significant, but small. The identification of patients at a higher risk of cancer therefore poses a clinical conundrum.
Is esophageal cancer fast growing?
Esophageal cancer grows slowly and may grow for many years before the symptoms are felt. However, once the symptoms develop, esophageal cancer progresses rapidly. As the tumor grows, it can seep into the deep tissues and organs near the esophagus.
What is the best medication for Barrett's esophagus?
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are drugs that block the three major pathways for acid production. PPIs suppress acid production much more effectively than H2 blockers. PPIs are the most effective medication for healing erosive esophagitis and providing long-term control of GERD symptoms.
What is the best treatment for esophageal cancer?
But, given the risk of esophageal cancer, treatment may be recommended if the diagnosis is confirmed. Preferred treatments include: Endoscopic resection , which uses an endoscope to remove damaged cells to aid in the detection of dysplasia and cancer. Radiofrequency ablation, which uses heat to remove abnormal esophagus tissue.
What is the screening for Barrett's esophagus?
Screening for Barrett's esophagus. Barrett's esophagus has a distinct appearance when viewed during an endoscopy exam. During endoscopy, the doctor passes a flexible tube with a video camera at the tip (endoscope) down your throat and into the swallowing tube (your esophagus).
What is the best way to remove abnormal esophagus tissue?
Radiofrequency ablation, which uses heat to remove abnormal esophagus tissue. Radiofrequency ablation may be recommended after endoscopic resection. Cryotherapy, which uses an endoscope to apply a cold liquid or gas to abnormal cells in the esophagus. The cells are allowed to warm up and then are frozen again.
How to treat GERD?
Treatment for GERD. Medication and lifestyle changes can ease your signs and symptoms. Surgery or endoscopy procedures to correct a hiatal hernia or to tighten the lower esophageal sphincter that controls the flow of stomach acid may be an option.
Is Barrett's esophagus a low grade or high grade?
No dysplasia, if Barrett's esophagus is present but no precancerous changes are found in the cells. Low-grade dysplasia, if cells show small signs of precancerous changes. High-grade dysplasia, if cells show many changes. High-grade dysplasia is thought to be the final step before cells change into esophageal cancer.
Can acid back up in the esophagus?
This reinforces the lower esophageal sphincter, making it less likely that acid will back up in the esophagus. High-grade dysplasia is generally thought to be a precursor to esophageal cancer. For this reason, your doctor may recommend endoscopic resection, radiofrequency ablation or cryotherapy.
Can a woman have Barrett's esophagus?
Being over 50. Being a current or past smoker. Having a lot of abdominal fat. While women are significantly less likely to have Barrett's esophagus, women should be screened if they have uncontrolled reflux or have other risk factors for Barrett's esophagus.
What is the treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
If you have Barrett’s esophagus and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), your doctor will treat you with acid-suppressing medicines called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). These medicines can prevent further damage to your esophagus and, in some cases, heal existing damage.
How does Barrett's mucosal resection work?
In endoscopic mucosal resection, your doctor lifts the Barrett’s tissue, injects a solution underneath or applies suction to the tissue, and then cuts the tissue off. The doctor then removes the tissue with an endoscope. Gastroenterologists perform this procedure at certain hospitals and outpatient centers. You will receive local anesthesia to numb your throat and a sedative to help you relax and stay comfortable.
What is endoscopic ablative therapy?
Endoscopic ablative therapies use different techniques to destroy the dysplasia in your esophagus. After the therapies, your body should begin making normal esophageal cells. A doctor, usually a gastroenterologist or surgeon, performs these procedures at certain hospitals and outpatient centers.
What is the procedure to numb your throat?
You will receive local anesthesia to numb your throat and a sedative to help you relax and stay comfortable. Before performing an endoscopic mucosal resection for cancer, your doctor will do an endoscopic ultrasound. Complications can include bleeding or tearing of your esophagus.
How long does it take to recover from esophageal surgery?
The surgery is performed at a hospital. You’ll receive general anesthesia, and you’ll stay in the hospital for 7 to 14 days after the surgery to recover.
Can a doctor do an endoscopy with a biopsy?
Your doctor may use upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with a biopsy periodically to watch for signs of cancer development. Doctors call this approach surveillance. Experts aren’t sure how often doctors should perform surveillance endoscopies. Talk with your doctor about what level of surveillance is best for you.
Can you have anti-reflux surgery for GERD?
Your doctor may consider anti-reflux surgery if you have GERD symptoms and don’t respond to medicines. However, research has not shown that medicines or surgery for GERD and Barrett’s esophagus lower your chances of developing dysplasia or esophageal adenocarcinoma. .
How to diagnose Barrett's esophagus?
How is Barrett's esophagus diagnosed? The only way to confirm the diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus is with a test called an upper endoscopy. This involves inserting a small lighted tube (endoscope) through the throat and into the esophagus to look for a change in the lining of the esophagus.
What is Barrett's esophagus?
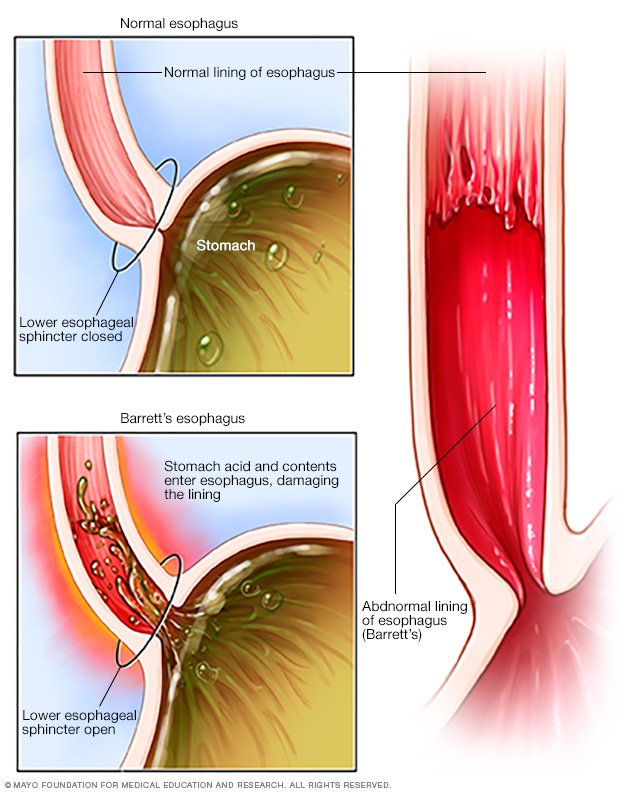
Barrett’s esophagus is a change in the tissue lining your esophagus, the tube in your throat that carries food to your stomach. For reasons no one understands completely, cells in the esophageal lining sometimes become more like intestinal cells. Researchers suspect that having acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) ...
How to keep esophagus healthy?
The best way to keep the lining of your esophagus healthy is to address heartburn or GERD symptoms. People with ongoing, untreated heartburn are much more likely to develop Barrett’s esophagus. Untreated heartburn raises the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma by 64 times.
What is the procedure to remove a spot on the esophagus?
Surgery: If you have severe dysplasia or esophageal cancer, your provider may recommend an esophagectomy, a surgery to remove all or part of the esophagus.
What is the most common procedure for esophageal sloughing?
Radiofrequency ablation: This is the most common procedure. It burns off abnormal tissue using radio waves, which generate heat. Cryotherapy: Healthcare providers use liquid nitrogen to freeze diseased parts of the esophagus lining so it will slough off (shed).
Is Barrett's esophagus a precancerous condition?
Barrett’s esophagus is a precancerous condition that may lead to esophageal adenocarcinoma. This type of cancer is rare. Most people with Barrett’s esophagus don’t have to worry — over 90% won’t develop esophageal adenocarcinoma. However, it’s important to monitor the condition.
Does Barrett's esophagus produce symptoms?
How common is Barrett’s esophagus? On its own, Barrett’s esophagus doesn’t produce symptoms. You may discover you have it only after seeing your healthcare provider for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms or after developing esophageal cancer. Because of the lack of symptoms, no one is sure how common it is.
What is Barrett's esophagus?
Barrett’s esophagus is a condition that can arise from acid reflux and increase your risk of developing esophageal cancer. Esophageal cancer occurs inside the esophagus, which is the tube in the throat that moves food from the mouth to the stomach. Barrett’s esophagus occurs when the cells in the lining of your esophagus are damaged ...
How many people with GERD develop Barrett's esophagus?
An estimated 10-15 percent of patients with GERD will develop Barrett’s esophagus. Approximately one in 860 Barrett’s esophagus patients will develop esophageal cancer, meaning the risk is statistically low.
Is Barrett's esophagus reversible?
Barrett’s esophagus, while not reversible, is treatable and should be monitored closely by a trained specialist to minimize your risk of developing cancer.
What is the treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
Gastroenterologists at Johns Hopkins developed the use of cryoablation therapy, an effective treatment for Barrett's esophagus. Ablation therapy may cause Barrett's esophagus to regress. Medications will be given to suppress your stomach acid. Then, during an endoscopy, thermal injury is administered to the abnormal mucous lining.
What is the name of the doctor who treats Barrett's esophagus?
Doctors at Johns Hopkins are at the forefront of diagnosing and treating Barrett's esophagus. In fact, gastroenterologists at Hopkins pioneered the use of cryoablation, a revolutionary new therapy, to treat Barrett's esophagus.
How often do you need an endoscopy for Barrett's?
Patients with low-grade dysplasia may need an endoscopy every three to six months. Patients with high-grade dysplasia may need to undergo an esophagectomy (removal of the esophagus) because of the increased risk of cancer.
What is the goal of surgery for reflux disease?
Some patients prefer a surgical approach as an alternative to a lifetime of taking medications. The goal of surgery for reflux disease is to strengthen the anti-reflux barrier.
What is endoscopic surveillance?
This means that you undergo periodic endoscopic examinations to evaluate whether the condition has evolved into cancer. Your doctor looks for increasing degrees of dysplasia, the abnormal growth of cells, and may perform a biopsy on the area to check for cancerous tissue.
What is the best treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
Endoscopic Therapie s for Barrett’s Esophagus. If we find that your esophagus has precancerous cells or cancerous cells just in the superficial lining of your esophagus (noninvasive cancer), we may recommend endoscopic therapy or surgery.
What is the tube called that looks at the lining of the esophagus?
In this test, a gastroenterologist puts a thin, flexible tube with a light and a camera at the tip, called an endoscope, through the throat to look at the lining of the esophagus. To make patients more comfortable, they are sedated with an anesthetic that wears off quickly once the test is done.
What tests are used to check for GERD?
However, if tests show that your cells have changed, we will likely recommend more tests, such as endoscopic ultrasound and maybe an endoscopic mucosal resection (a procedure in which abnormal tissue is shaved off).
Where is endoscopy done?
Endoscopy is done in a doctor’s office while under sedation, or in the hospital. Screening helps doctors figure out if you have Barrett’s esophagus or cancer. If you do have Barrett’s esophagus, we may recommend regular endoscopy exams.
Is Barrett's esophagus a precancerous lesion?
Barrett’s esophagus is considered a precancerous lesion and increases the risk for esophageal cancer. Only a small percentage of patients with Barrett’s esophagus end up developing cancer, but we monitor all of our patients and look for early warning signs. For those patients, we have a number of effective therapies that can reverse the progression.
Can Barrett's esophagus be cancer?
Barrett’s is a way the esophagus defends itself: The cells in the lining of the esophagus start to change because they’ve been exposed to acid for many years. Barrett’s esophagus is considered a precancerous lesion and increases the risk for esophageal cancer. Only a small percentage of patients with Barrett’s esophagus end up developing cancer, but we monitor all of our patients and look for early warning signs. For those patients, we have a number of effective therapies that can reverse the progression.
Can GERD cause Barrett's esophagus?
Risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal cancer include having had severe gastroesophageal reflux disease for a long time, being male, and being overweight or obese. Most people with GERD do not get Barrett’s esophagus, and only a small portion of people who have Barrett’s esophagus will develop esophageal cancer — about 1 percent each ...
What is Barrett's esophagus?
In Barrett’s esophagus, the normal tissue lining the esophagus — the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach — changes to tissue that resembles the lining of the intestine.
Does Barrett's esophagus lead to specific therapy?
“Approach Considerations- The diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus does not lead to specific therapy. Little evidence supports the assumption that antisecretory agents or antireflux surgery prevents the occurrence of adenocarcinoma or leads to regression of Barrett’s esophagus. [ 13]

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment