
Medication
What You Can Do to Prevent Atherosclerosis
- Kick Your Smoking Habit. If you smoke, quitting is the single most important step you can take to reduce your risk for atherosclerosis and other heart disease risk factors, according ...
- Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet. ...
- Get Enough Exercise. ...
- Keep Track of Your Numbers. ...
Procedures
What causes atherosclerosis?
- High cholesterol. Cholesterol is a waxy, yellow substance that’s found naturally in the body as well as in certain foods you eat.
- Diet. It’s important to eat a healthy diet. ...
- Aging. As you age, your heart and blood vessels work harder to pump and receive blood. ...
Self-care
- Sores on the feet or legs that won’t heal
- Cramping or pain in the thigh or calf when walking that resolves with rest
- Fatigue
- Weakness in the arms or legs after exercise or exertion
- Loss of hair on the legs or arms
- Pale or bluish skin on the legs or arms
- Leg pain at night or while resting
- Poor toenail or fingernail growth
- Cold and painful legs or arms i
Nutrition
Quitting smoking is the best thing you can do to keep your arteries healthy and prevent atherosclerosis complications. Exercise most days of the week. Regular exercise improves blood flow, lowers blood pressure, and reduces your risk of conditions that increase the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
What you can do to prevent atherosclerosis?
What is atherosclerosis and how you can prevent it?
What is the difference between PVD and atherosclerosis?
What can be done to prevent atherosclerosis?
Is there any cure for atherosclerosis?
Bits of plaque can break loose and cause blood clots that may lead to heart attack or stroke. There is currently no cure for atherosclerosis, but the condition can be slowed with statin drugs and dietary changes.
What is the main cause of atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is thickening or hardening of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery. Risk factors may include high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, physical activity, and eating saturated fats.
What are three symptoms of atherosclerosis?
If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to your brain, you may have signs and symptoms such as sudden numbness or weakness in your arms or legs, difficulty speaking or slurred speech, temporary loss of vision in one eye, or drooping muscles in your face.
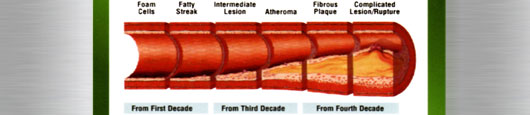
What are the 4 stages of atherosclerosis?
Atherogenesis can be divided into five key steps, which are 1) endothelial dysfunction, 2) formation of lipid layer or fatty streak within the intima, 3) migration of leukocytes and smooth muscle cells into the vessel wall, 4) foam cell formation and 5) degradation of extracellular matrix.
What foods should you avoid if you have atherosclerosis?
Avoid fruits canned in heavy sugar-based syrup, and frozen fruits with sugar added. Grains Whole grains should form the basis of your grain intake....Avoid or limit the following items:Fatty or marbled meats.Spareribs.Chicken wings.Hot dogs and sausages.Lunchmeat.Bacon.Breaded or fried meat, fish, or poultry.
Can you live a long life with atherosclerosis?
Living healthy with atherosclerosis is possible with proper management, so take steps toward better heart health now. Atherosclerosis doesn't have to be a losing battle. In fact, the disease can be reversed through lifestyle changes, according to the American College of Cardiology.
How do you test for arteriosclerosis?
Your doctor may order a heart imaging test to take pictures of your heart and find problems in blood flow in the heart or coronary arteries. Examples of heart imaging tests used to diagnose atherosclerosis appear below. Angiography is a special type of X-ray using a dye.
Can you reverse atherosclerosis?
Medical treatment, regular exercise, and dietary changes can be used to keep atherosclerosis from getting worse and stabilize the plaque, but they aren't able to reverse the disease.
How to reduce risk of atherosclerosis?
Lose extra pounds and maintain a healthy weight. If you're overweight, losing even just a few pounds can reduce your risk of high blood pressure and high cholesterol, two of the major risk factors for developing atherosclerosis. Ask your doctor what your target weight should be. Eat healthy foods.
What is the best test for atherosclerosis?
High levels of blood sugar and cholesterol raise your risk of atherosclerosis. A C-reactive protein (CRP) test also may be done to check for a protein linked to inflammation of the arteries. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This simple and painless test records the electrical signals in your heart. Exercise stress test.
How to tell if you have atherosclerosis?
This test can tell if you have atherosclerosis in the arteries in your legs and feet. During an ABI test, your doctor compares the blood pressure in your ankle with the blood pressure in your arm. An abnormal difference may be a sign of peripheral vascular disease, which is usually caused by atherosclerosis.
How to reduce the risk of heart disease?
Regular exercise improves blood flow, lowers blood pressure, and reduces your risk of conditions that increase the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. Aim to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. If you can't fit it all into one session, try breaking it up into 10-minute intervals.
How to control blood pressure and cholesterol?
Eat healthy foods. A heart-healthy diet full of fruits, vegetables and whole grains — and low in refined carbohydrates, sugars, saturated fat and sodium — can help you control your weight, blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar. Try substituting whole-grain bread in place of white bread.
Does statin help with fatty deposits?
Aggressively lowering your low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol — the bad cholesterol — can slow, stop or even reverse the buildup of fatty deposits in your arteries. Statins are commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol, improve artery health and prevent atherosclerosis.
Does herbal medicine help with high cholesterol?
It's thought that some foods and herbal supplements can help reduce your high cholesterol level and high blood pressure, two major risk factors for developing atherosclerosis. With your doctor's OK, you might consider these supplements and products:
What are the medications that help reduce cholesterol?
Cholesterol Medication Drugs known as statins and fibrates can reduce your LDL (low-density lipoprotein, or "bad") cholesterol, which can help stop or even reverse the buildup of plaque in your arteries. In addition to regulating your cholesterol, statins can help stabilize the lining of your heart arteries and prevent atherosclerosis.
How does a surgeon treat atherosclerosis?
Surgical procedures used to treat atherosclerosis include: Angioplasty In angioplasty, a surgeon inserts a narrow tube into the blocked or narrowed artery and passes a second tube containing a deflated balloon tip through it. The balloon is then inflated, which pushes the blockage open against your artery walls.
How to control risk factors for atherosclerosis?
You can help control risk factors for atherosclerosis and heart disease — such as your weight, blood pressure, and blood cholesterol and glucose levels — by focusing on eating certain foods while avoiding others.
What is the best medicine for blood pressure?
Diuretics (Water Pills) Diuretics help lower your blood pressure by reducing fluid retention throughout your body. Other Drugs Your doctor may prescribe medication to control specific risk factors for atherosclerosis — like diabetes — or symptoms of atherosclerosis, like leg pain during exercise.
How does ACE inhibitor help with atherosclerosis?
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors ACE inhibitors may help slow the progression of atherosclerosis by lowering your blood pressure and relaxing your blood vessels. They also reduce your risk of having multiple heart attacks.
What are the treatments for atherosclerosis?
Medically Reviewed. Prescription drugs, surgery, and heart-healthy lifestyle changes are treatment options for atherosclerosis. Shutterstock (2) Atherosclerosis occurs when fat-containing deposits called plaque form in your arteries, causing them to harden and narrow. This can reduce blood flow to different areas of your body, ...
How to stop atherosclerosis?
Stop smoking. Smoking — or using tobacco in another form — damages your arteries. If you’re a smoker, quitting is the single most effective way to stop your atherosclerosis from getting worse and reduce your risk of complications, according to the Mayo Clinic. (2) Get enough exercise.
What is the difference between a healthy artery and an atherosclerotic artery?
A healthy artery is like a clean pipe: It has a smooth lining and is free of blockages that interfere with blood flow. Atherosclerosis is the buildup of cholesterol-filled deposits called plaque on the inner walls of arteries. Plaque narrows the vessels and slows down blood flow.
Why is aspirin important?
Taking a low-dose aspirin every day is also important. By making blood less likely to clot, aspirin reduces the chances of having a heart attack among men and women with coronary artery disease or those with significant risk factors for it .
What is the result of platelets from the bloodstream gathering at the site?
Whatever causes the initial damage, the result is that platelets from the bloodstream gather at the site, soon to be joined by a gruel-like mixture of cholesterol and other fats, calcium deposits, and cell debris. Cells from the wall of the artery gradually surround the mixture.
How to prevent atherosclerosis?
You can do this with lifestyle changes such as exercising every day; eating a heart-healthy diet; not smoking; and controlling high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and high blood sugar. Taking a low-dose aspirin every day is also important.
What happens to the white blood cells in the artery wall?
Cells from the wall of the artery gradually surround the mixture. The artery wall becomes inflamed; white blood cells become activated, race to the injured area, and try unsuccessfully to heal the damage. Over time, a fibrous cap forms over the fatty deposit.
Where does atherosclerosis occur?
Atherosclerosis can occur in any artery in the body, from those nourishing the heart (coronary arteries) to those supplying the brain, intestines, kidneys, and legs. Atherosclerosis begins as microscopic damage to the inner lining of an artery wall.
Does statin help with heart disease?
Taking a cholesterol-lowering statin can keep atherosclerosis from getting worse, and can also pull cholesterol out of artery-clogging plaque. Statins can also help stabilize atherosclerotic plaques and keep them from breaking open—the event that triggers most heart attacks and strokes.
What are the best medications for atherosclerosis?
Medications for treating atherosclerosis include: cholesterol-lowering medications, including statins and fibrates. angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which may help prevent narrowing of your arteries. beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers to lower your blood pressure.
How do you know if you have atherosclerosis?
Most symptoms of atherosclerosis don’t show up until a blockage occurs. Common symptoms include: chest pain or angina. pain in your leg, arm, and anywhere else that has a blocked artery. shortness of breath. fatigue. confusion, which occurs if the blockage affects circulation to your brain.
What is the narrowing of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque?
What is atherosclerosis ? Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque. Arteries are the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body. As you get older, fats, cholesterol, and calcium can collect in your arteries and form plaque.
What happens to your arteries as you get older?
As you get older, fats, cholesterol, and calcium can collect in your arteries and form plaque. The buildup of plaque makes it difficult for blood to flow through your arteries. This buildup may occur in any artery in your body, including your heart, legs, and kidneys. It can result in a shortage of blood and oxygen in various tissues of your body.
Why do arteries become less elastic?
As you age, your heart and blood vessels work harder to pump and receive blood. Your arteries may weaken and become less elastic, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
How to lower cholesterol?
If you need to lower your blood cholesterol, reduce saturated fat to no more than 5 to 6 percent of total calories. For someone eating 2,000 calories a day, that’s about 13 grams of saturated fat.
What are the medical emergencies for a heart attack?
loss of balance. sudden, severe headache. Heart attack and stroke are both medical emergencies. Call 911 or your local emergency services and get to a hospital’s emergency room as soon as possible if you experience symptoms of a heart attack or stroke.
How do you know if you have an atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis Signs and Symptoms. You might not have symptoms until your artery is nearly closed or until you have a heart attack or stroke. Signs can also depend on which artery is narrowed or blocked. Pain or pressure in your upper body, including your chest, arms, neck, or jaw.
How many chances of getting atherosclerosis in your lifetime?
Research has found that even teenagers can have signs. If you’re 40 and generally healthy, you have about a 50% chance of getting serious atherosclerosis in your lifetime. The risk goes up as you get older. Most adults older than 60 have some atherosclerosis, but most don’t have noticeable symptoms.
What is the term for the hardening and narrowing of the arteries?
Atherosclerosis is a hardening and narrowing of your arteries. It can put blood flow at risk as your arteries become blocked. You might hear it called arteriosclerosis or atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. It’s the usual cause of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral vascular disease -- what together are called cardiovascular disease.
What is the blood vessel that keeps blood flowing?
They're lined by a thin layer of cells called the endothelium. It keeps the inside of your arteries in shape and smooth, which keeps blood flowing. Atherosclerosis begins with damage to the endothelium.
How to stop plaques?
But with medication and lifestyle changes, you can slow or stop plaques. They may even shrink slightly with aggressive treatment. Lifestyle changes: You can slow or stop atherosclerosis by taking care of the risk factors. That means a healthy diet, exercise, and no smoking.
Can a doctor open a blockage in your leg?
They could also lower your risk of hearts attack and strokes. Your doctor can use more invasive techniques to open blockages from atherosclerosis or go around them: Angiography and stenting: Your doctor puts a thin tube into an artery in your leg or arm to get to diseased arteries .
Can a balloon tip open a blocked artery?
Angioplasty (using a catheter with a balloon tip) and stenting can often open a blocked artery. Stenting helps ease symptoms, but it does not prevent heart attacks. Bypass surgery: Your doctor takes a healthy blood vessel, often from your leg or chest, and uses it to go around a blocked segment.
Why does the heart weaken when you have atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis can become a serious condition: the heart may weaken because of a lack of oxygen, and the cholesterol buildup can rupture, damaging the walls of the artery. However, treatment options can vary and it's important to find a doctor who understands how to treat atherosclerosis at the root of the problem.
What happens when cholesterol builds up in the walls of the arteries?
When cholesterol and other debris collect in the walls of your arteries, they harden, reducing blood flow to the heart. When this series of events occurs in the coronary artery, doctors call the plaque accumulation coronary atherosclerosis, or coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis can become a serious condition: the heart may weaken because of a lack of oxygen, and the cholesterol buildup can rupture, damaging the walls of the artery.
What is the procedure called when a patient doesn't respond to medicine?
One common option, a stent, is simply a small tube placed inside an artery that keeps it open to blood flow. This procedure is called an angioplasty. Newer stents can include drugs that prevent the cholesterol buildup.
Is it better to reduce risk factors for atherosclerosis?
The patient isn’t dictated to, Dr. Cleman says. “You’re still the boss.". Still, when it comes to atherosclerosis, reducing all possible risk factors is better than treating the condition itself. “You want to not smoke, keep your blood pressure and cholesterol controlled, and exercise,” he says.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising, are the first treatment for atherosclerosis — and may be all that you need to treat your atherosclerosis. But sometimes, medication or surgical procedures may be needed.