
What foods must I avoid with microalbuminuria?
- Slow carbohydrate foods: porridge oats, beans, brown rice, pasta, lentils, carrots, sweet potatoes, and asparagus.
- Low protein food: bread and cereals, pasta, lettuce, celery, sprouts, cucumber, parsley, tofu, fish and lean meats.
- Low fat and low sodium foods: eat nothing fried (use olive oil if need be) and skip the salt. ...
What are the causes and treatments for a high level of microalbumin?
Elevated microalbumin levels in the urine indicate that your kidneys are leaking protein. There are many conditions that can cause this, and for all of these it is really important to speak to your doctor about this result. The most common causes of elevated protein in the urine is diabetes or high blood pressure (hypertension).
How to cure or prevent microalbuminuria?
Treatment
- Lifestyle Interventions. Lifestyle interventions are an important part of treatment. ...
- Medications. In general, if you have medical conditions that may be worsening your kidney function (like diabetes), it’s helpful to get those under better control.
- Treatment Goals. ...
- Microalbuminuria and Cardiovascular Disease. ...
- A Word From Verywell. ...
When to treat microalbuminuria?
Know what the results mean.
- The normal result is less than 30 mg
- 30 to 300 mg is indicative of early kidney disease
- More than 300 mg is indicative of more advanced kidney disease Appropriate discussion with your healthcare provider about the test result is necessary to make prompt treatment and management. ...
See more
Can albuminuria be reversed?
Yes, your level of albumin may return to normal after you get treatment and may stay at a normal level for years. If you start treatment and make lifestyle changes straight away, you'll have a better chance of reversing any damage to your kidneys from microalbuminuria, or at least slow down its progression.
How serious is albumin in urine?
An ACR shows whether you have albumin in your urine. A normal amount of albumin in your urine is less than 30 mg/g. Anything above 30 mg/g may mean you have kidney disease, even if your GFR number is above 60.
How can I reduce protein in my urine?
Possible treatment includes:Changes to your diet. If high levels of protein are caused by kidney disease, diabetes, or high blood pressure, your doctor will give you specific diet changes.Weight loss. ... Blood pressure medication. ... Diabetes medication. ... Dialysis.
Can protein in urine be cured?
Can proteinuria be prevented? Proteinuria cannot be prevented, but it can be controlled. Many of the causes of proteinuria can be treated (diabetes, high blood pressure, preeclampsia and kidney disease), allowing your healthcare provider to improve the condition.
Can albuminuria be cured?
There is no treatment for albuminuria itself, as it is not a disease. Rather, it's a side effect (of diabetes or hypertension, for instance) or a symptom (of kidney disease). Dealing with excess protein in urine will depend on the cause.
What foods reduce protein in urine?
Diet For ProteinuriaOranges and orange juice.Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and greens (collard and kale)Potatoes.
Can drinking water reduce protein in urine?
Drinking water will not treat the cause of protein in your urine unless you are dehydrated. Drinking water will dilute your urine (water down the amount of protein and everything else in your urine), but will not stop the cause of your kidneys leaking protein.
Is protein in urine always serious?
Protein in the urine is not usually obvious, but can be detected by a simple dip- stick test, or sometimes by more sensitive lab tests. The presence of protein in the urine can act as a warning signal that not all is well with the kidneys. Usually there are no symptoms.
How long can you live with proteinuria?
For example, the life expectancies of 40-year-old men and women with no proteinuria were 15.2 and 17.4 years longer, respectively, than those with heavy proteinuria. Proteinuria-free men and women also outlived those with mild proteinuria by 8.2 years and 10.5 years, respectively.
How Do I Know If I Have Protein in My urine?
You can have a simple urine test. This is part of a routine exam. You will be asked to pee into a clean cup called a “specimen cup.” Only a small a...
What’S Wrong With Having Albumin (Protein) in My urine?
One of the main jobs of your kidneys is to filter your blood. Your kidneys keep important things your body needs inside your blood, like protein. T...
If I Have Albuminuria, Does It Mean I Have Kidney Disease?
It may be an early sign of kidney disease, but your doctor will check you again to make sure albuminuria is not caused by something else, like not...
How Often Do I Need to Have A Test For Albuminuria (Proteinuria)?
People who are at increased risk for kidney disease should have this test as part of routine checkups by a healthcare provider. Those at increased...
If I Have Albuminuria, Will I Need Treatment?
If kidney disease is confirmed, your healthcare provider will create a treatment plan. You may also be asked to see a special kidney doctor called...
How to prevent albuminuria?
Lose excess weight. to reduce the risk of diabetes and high blood pressure. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the pressure on your kidney and prevent albuminuria. Including physical activities like the exercise in daily life can improve the blood circulation to the body.
How does albuminuria work?
It will help you understand the problem better. The kidney act like a filter in your body. When the blood passes through the organ, it can separate the waste products. So, the waster along with the excess water from the urine. So, you pass the urine from the body to eliminate the waste. The kidneys have filters known as glomeruli. It can segregate the waste from your body. Usually, the protein cannot pass through the filter. It is due to the large size of the protein. But, the abnormal or damaged kidney can leak the albumin into your urine.
What does low albumin mean?
But, the frequent low levels of albumin can indicate chronic kidney disease. It is the earliest symptoms of kidney disease.
What protein seeps into urine?
The two terms mean more or less the same. The abnormal levels of albumin in the urine refer to albuminuria. The albumin is the most common protein that can seep into the urine. But, the urine also has other proteins that can seep into the urine like: Immunoglobulin (low molecular weight) Insulin. Lysozyme.
What does albuminuria mean?
We may receive a commission for purchases made through these links. Albuminuria, as the name suggests, is the issue that causes the albumin to seep into the urine. So, the condition causes the protein to pass from the blood to your urine. It signifies the underlying kidney disease.
Why is my urine a lot of albumin?
Main Causes Of Albuminuria. The normal urine may have trace amounts of proteins in it. The albumin seeping into the urine in very small amount needs no medical attention. But, some health conditions can trigger the excess albumin concentration in the urine. The cause of the condition is either temporary or permanent.
What happens if you have high albumin levels?
It is one of the most common risks associated with high albumin levels. The high levels of sugar in the blood can put pressure on the kidneys. It can lead to kidneys malfunctioning, which can cause albuminuria.
How to reduce albuminuria?
You may also be able to protect your kidneys and reduce albuminuria by working with a registered dietitian who can help you plan meals and change your eating habits. The meal plan may help you. lose weight, if you are overweight. avoid foods high in sodium or salt. eat the right amounts and types of protein.
What is albuminuria?
Albuminuria is a sign of kidney disease and means that you have too much albumin in your urine. Albumin is a protein found in the blood. A healthy kidney doesn’t let albumin pass from the blood into the urine. A damaged kidney lets some albumin pass into the urine. The less albumin in your urine, the better.
How is albuminuria detected?
A health care provider often tests for albuminuria using a urine dipstick test followed by a urine albumin and creatinine measurement.
What is the ratio of albumin to creatinine in urine?
Creatinine is a waste product that is filtered in the kidneys and excreted in the urine. Health care providers consider a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio above 30 mg/g higher than normal.
What does it mean when your albumin level stays the same?
A urine albumin level that stays the same or goes down may mean that treatments are working. Treatment that lowers the urine albumin level may lower the chances that kidney disease will progress to kidney failure.
Can albumin pass through kidneys?
Sometimes albuminuria is also called proteinuria. A healthy kidney doesn’t let albumin pass into the urine . A damaged kidney lets some albumin pass into the urine. More information is provided in the NIDDK health topics, Diabetic Kidney Disease and High Blood Pressure and Kidney Disease.
Why do diabetics have proteinuria?
The first is long-term hyperglycemia —higher-than-normal levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. 3 Excess glucose can damage capillaries in the kidneys called glomeruli.
How to manage diabetes?
For most people, managing diabetes involves a combination of adhering to a medically-approved diet, embarking on a regular exercise routine, taking medication to help control blood sugar, and self-testing glucose levels regularly. Lifestyle Changes for Type 2 Diabetes.
How to treat diabetes with type 2 diabetes?
Lifestyle Changes for Type 2 Diabetes. Treatment for chronic kidney disease associated with diabetes also includes controlling blood glucose levels, as well as taking measures to lower blood pressure, such as losing weight, eating less salt, cutting out alcohol, quitting smoking, and increasing activity levels.
How much urine do you need to test for protein?
Only a couple of tablespoons of urine are necessary. Usually, it will be tested right away using a small plastic dipstick that will change colors in response to the presence of protein. (This initial test can also detect other suspicious substances in urine, such as bacteria, glucose, and blood cells—any of which can be a sign of a medical problem.)
Can diabetes cause albuminuria?
Albuminuria in diabetes also can result from hypertension —high blood pressure that's a common complication of diabetes. 3 . High Blood Pressure and Diabetes.
Is albuminuria a disease?
Because albuminuria is not a disease itself but rather a side effect (of diabetes or hypertension, for instance) or a symptom (of kidney disease), there's no treatment per se for the condition. Rather, dealing with the excess protein in urine will depend on the specific situation.
Why is albumin important for kidneys?
Albumin is a protein which helps to prevent water from leaking out of the blood into other tissues. If high blood sugar levels over a number of years damage the kidneys, they may allow too much albumin to be lost from the blood. Proteinuria is a sign therefore that the kidneys have become damaged.
What is proteinuria in diabetes?
Proteinuria (albuminuria) is a condition of having too much protein in the urine which results from damage within the kidneys. Proteinuria in diabetes will usually be the result of either long term hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels) or hypertension (high blood pressure).
How do you know if you have proteinuria?
Symptoms of proteinuria. The signs of proteinuria will only become noticeable once the kidneys have become very damaged and levels of protein in the urine are high . If this happens, the symptoms may present as swelling of the ankles, hands, tummy or the face.
What to do if fluid is accumulating in ankles?
If fluid is accumulating in your ankles or around the lungs, you may be given water tablets, a diuretic medication that helps to remove water from the body. If the level of kidney damage is severe, you may need to undergo kidney dialysis or a kidney transplant.
What to do if you have kidney damage?
If the level of kidney damage is severe, you may need to undergo kidney dialysis or a kidney transplant.
What causes protein in urine?
High blood pressure can also lead to the development of kidney damage. Pre-eclampsia, a condition which can affect pregnant women, includes very high blood pressure and is another potential cause of protein in the urine.
Causes and Symptoms of Albumin in Urine
The albumin in urine can be due to one or more or of these causes. Each cause has different symptoms. A person might experience symptoms from various causes and a doctor should be consulted at the earliest. The causes of albumin in urine are:
Tests to Diagnose Albuminin in Urea
The best and most prescribed way to test whether a person has a normal albumin level in urine is via the urine test. The patient will get the result within 24 hours and a consultation with the doctor will help to know the best treatment method. The normal albumin level depends highly on a person’s age.
Treatment for Albumin in Urine
A person may not need any treatment if the symptoms are mild since it is temporary in most cases and a slight fluctuation of albumin in urine is normal. However, the doctor may prescribe some lifestyle changes for an underlying condition which may complement the presence of albumin in the urine. These include:
Is microalbuminuria a cost effective treatment?
Because of the growing evidence that treatment of microalbum inuria in individuals without diabetes may offer a cost-effective benefit to prevent cardiovascular disease, nephrologists and other health care providers should pay more attention to the early detection and subsequent treatment of individuals with microalbuminuria.
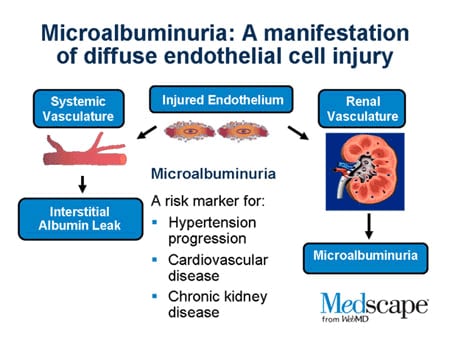
Is microalbuminuria a sign of renal disease?
Microalbuminuria is an early sign of progressive cardiovascular and renal disease in individuals with and without diabetes. Despite compelling data, at present only a minority of patients with diabetes and rarely individuals without diabetes are screened for albuminuria in a systematic way. All of the criteria to implement systematic albuminuria screening are fulfilled in diabetes, and most are nearly fulfilled for microalbuminuria screening in individuals without diabetes. Because of the growing evidence that treatment of microalbuminuria in individuals without diabetes may offer a cost-effective benefit to prevent cardiovascular disease, nephrologists and other health care providers should pay more attention to the early detection and subsequent treatment of individuals with microalbuminuria.
What type of diabetes is treated with microalbuminuria?
Treatment of microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
How long does it take for microalbuminuria to occur?
In patients who progress to overt nephropathy, microalbuminuria usually precedes macroalbuminuria by an interval of 5 to 10 years. In patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, blood pressure increases and renal function declines after the onset of macroalbuminuria. However, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, ...
What is the ratio of albumin to creatinine?
Microalbuminuria refers to a subclinical increase in urinary albumin excretion. By definition it corresponds to an albumin excretion rate of 20 to 200 microg/min (30 to 300 mg/day) or an albumin to creatinine ratio (mg/mmol) of 2.5 to 25 in males and 3.5 to 35 in females.
Does antihypertensive therapy slow the progression of renal disease?
There is accumulating evidence to suggest that the use of antihypertensive agents which target the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) can slow the progression of renal disease and provide cardioprotection in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria.
Is microalbuminuria a risk factor for renal disease?
In particular, the finding of microalbuminuria should provoke an intensified modification of the common risk factors for renal and cardiovascular disease, that is hyperglycemia, hypertension, dyslipidemia and smoking. Antihypertensive therapy in patients with microalbuminuria and type 2 diabetes mellitus should be initiated with angiotensin ...
How to reduce microalbumin?
The affected kidney can no longer filter ethanol from the alcohol efficiently, which increases the risk of prolonged high microalbumin levels. To combat this, cut out the alcohol and replace it with water, teas, and unsweetened juices.
What happens if you have too much albumin in your urine?
Studies show that if there are excessive amounts of albumin, or a globular protein produced by your liver, in your urine, it could be an indicator of kidney damage. This can increase your risk for conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or kidney disease.
What does it mean when you have too much albumin in your blood?
When you have excessive albumin in your blood, it's called microalbuminuria. A microalbumin result of 30-300 mg/dL indicates that your kidneys are not able to filter protein properly. However, experts note that with lifestyle changes and proper medical treatment, you can lower your microalbumin levels. [2]
Why is albumin elevated?
If you currently have diabetes, the albumin levels in your body will be elevated because unmanaged blood sugar damages your kidney function. 180 mg/dl is the average threshold of the kidneys for diabetics in the 2 hours after a meal.
How to help kidneys heal faster?
Focus your diet on slow-carb, low-protein, and low-sugar foods. Damaged kidneys cannot process proteins normally, so give your kidneys time to rest by reducing your protein intake. You should eat foods that compromise of slow carbohydrates (where your glucose levels don't spike), low amounts of protein, fat, sodium and sugar. Here are some healthy options:
What is the normal albumin level?
Having unmanaged high blood pressure can be a factor of why your albumin levels are high. Normal blood pressure ranges from below 120/80 (mmHg) to 130/80. Blood pressure that is equal to or more than 140 (mmhg) is considered to be high.
How to help kidneys not overwork?
Also, avoid binge eating instead eat small frequent meals. These will help your kidney not to overwork and strain itself from filtering all the waste products.
Albuminuria Symptoms
Causes
- Try losing extra weight
- Exercise regularly
- Stop smoking
- Foamy, frothy or bubbly- looking urine
- Needing to urinate more often
- Hiccups
- Fatigue (feeling tired)
- Trouble sleeping
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dry, itchy skin
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Swelling in your hands, feet, abdomen or face
- Shortness of breath
Diagnosis
Treatment
A Word from Verywell
- There are two reasons a person with diabetes might develop proteinuria: 1. Long-term hyperglycemia, higher-than-normal levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood: Excess glucose can damage capillaries in the kidneys called glomeruli. These tiny blood vessels are bundled together to form the glomerular membrane, the structure that filters waste from the blood into the urine …