Medication
The choice of treatment method will depend on:
- Your general condition
- Your doctor's expertise with various techniques
- Personal choice
- Prior treatments
Procedures
The herb most commonly used in natural remedies for Achalasia and one of the most important herbs used to improve circulation is Ginkgo Biloba. Natural remedies for Achalasia can include herbs that help with the uptake of nutrients, minerals, and vitamins like calcium, magnesium, etc.
Self-care
- Myotomy versus non-surgical treatment
- Laparoscopic myotomy with or without fundoplication
- Technique (laparoscopic, open, robotic, thoracoscopic, other)
- Revisional surgery
- Predictors of success
- Outcome
- Epiphrenic diverticula
- Other articles
Nutrition
While there is no cure currently available, there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms. Achalasia is a progressive disease meaning patients will gradually develop increasing severity of difficulty when swallowing. Medical treatment may alleviate symptoms but they do not provide a long term solution.
What are the natural ways to treat achalasia?
Is there any natural treatment for achalasia?
What are the surgical options for achalasia?
Does achalasia have a cure?
What is the best treatment for achalasia?
Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy and Fundoplication The most effective treatment for achalasia is Heller myotomy (esophagomyotomy), a procedure in which the muscle fibers of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) are divided.
Can achalasia be treated?
There's no cure for achalasia. Once the esophagus is paralyzed, the muscle cannot work properly again. But symptoms can usually be managed with endoscopy, minimally invasive therapy or surgery.
What is the latest treatment for achalasia?
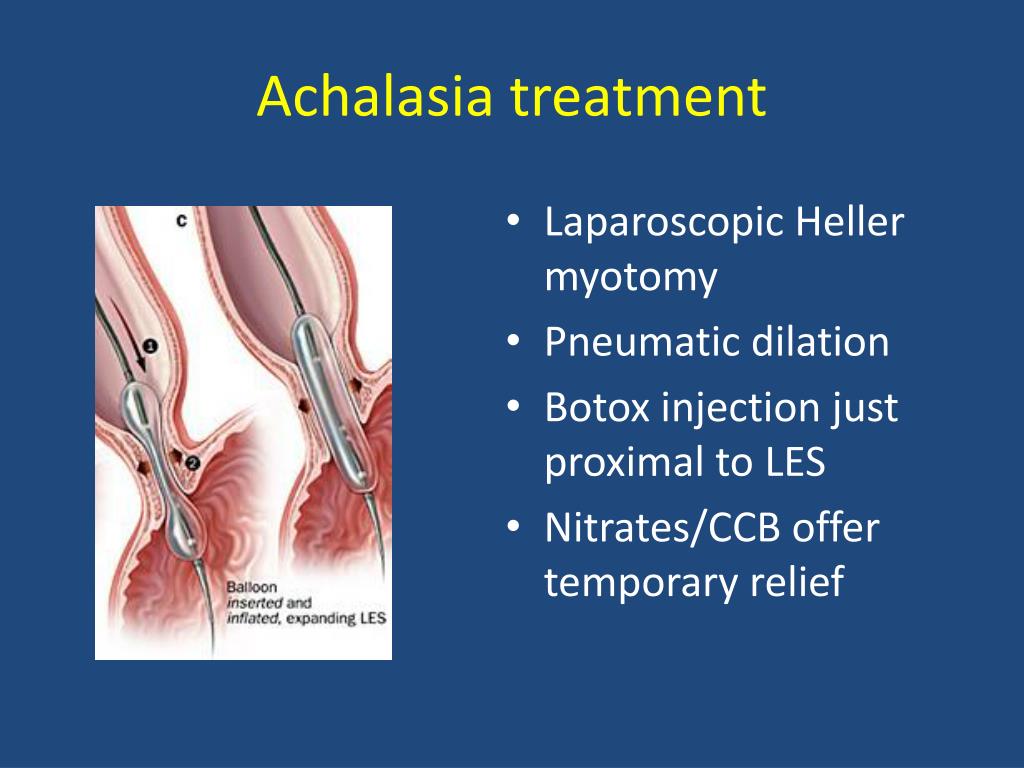
Pneumatic dilation is currently the most effective nonsurgical option for treatment of achalasia. Pneumatic dilation is generally performed under sedation with fluoroscopic guidance to accurately position the balloon across the LES.
How do you treat achalasia without surgery?
Nonsurgical options include:Pneumatic dilation. A balloon is inserted by endoscopy into the center of the esophageal sphincter and inflated to enlarge the opening. ... Botox (botulinum toxin type A). This muscle relaxant can be injected directly into the esophageal sphincter with an endoscopic needle. ... Medication.
What triggers achalasia?
What causes achalasia? In most cases, it's caused by loss of the nerve cells that control the swallowing muscles in the esophagus. Healthcare providers don't yet know why these nerve cells are lost. In rare cases, achalasia is caused by a tumor.
What foods to avoid if you have achalasia?
Achalasia is a disorder of the esophagus, or food pipe, which causes the cells and muscles to lose function....Foods to avoid include:citrus fruits.alcohol.caffeine.chocolate.ketchup.
What is the life expectancy of achalasia?
Type 2 achalasia has the best response to treatment, with studies suggesting over 90% response to conventional treatments. Patients with treated achalasia generally do well, with a life expectancy no different than the general population.
Can you live a normal life with achalasia?
The prognosis in achalasia patients is excellent. Most patients who are appropriately treated have a normal life expectancy but the disease does recur and the patient may need intermittent treatment.
How long is surgery for achalasia?
The procedure can take up to three hours to complete. Most people remain in the hospital for one day. The most common potential side effect of the procedure is GERD. If necessary, a fundoplication may be performed later.
How successful is achalasia surgery?
Success rate — Surgery relieves symptoms in 70 to 90 percent of people. Symptom relief is sustained in about 85 percent of people 10 years after surgery and in about 65 percent of people 20 years after the surgery.
What are the three types of achalasia?
Achalasia is a heterogeneous disease categorized into 3 distinct types based on manometric patterns: type I (classic) with minimal contractility in the esophageal body, type II with intermittent periods of panesophageal pressurization, and type III (spastic) with premature or spastic distal esophageal contractions ( ...
How quickly does achalasia progress?
Clinical picture, stages of achalasia The main symptom of achalasia is dysphagia, which develops slowly over several weeks to years and increases as the disease progresses (6). As a rule, dysphagia manifests initially with solid food and later also with liquid food (7).
What are the complications of achalasia?
These complications include: Pneumonia. Lung infections (pulmonary infections). Other complications include:
How long does achalasia last?
Achalasia symptoms develop slowly, with symptoms lasting for months or years. Symptoms include: Trouble swallowing ( dysphagia ). This is the most common early symptom. Regurgitation of undigested food. Chest pain that comes and goes; pain can be severe. Heartburn. Cough at night.
How effective is Heller myotomy?
Minimally invasive surgery/laparoscopic Heller myotomy is effective in 76% to 100% of people with achalasia. Keep in mind that up to 15% of people experience gastroesophageal reflux symptoms after surgery. Botox injection successfully relaxes spastic esophageal sphincter muscles in up to 35% of people with achalasia.
What is the condition where the esophagus is unable to move food and liquids down into the?
What is achalasia? Achalasia is a rare disorder in which your esophagus is unable to move food and liquids down into your stomach. Your esophagus is the muscular tube that transports food from your mouth to your stomach. At the area where your esophagus meets your stomach is a ring of muscle called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES).
What is the name of the disorder in which the esophagus is damaged?
Achalasia: A Disorder of the Esophagus. Achalasia is a rare disorder in which damaged nerves in your esophagus prevent it from working as it should. Muscles at the lower end of your esophagus fail to allow food to enter your stomach. Symptoms include trouble swallowing, heartburn and chest pain. Treatment includes both nonsurgical (Botox ...
How does balloon dilation help with achalasia?
Balloon dilation improves symptoms in 50% to 93% of people with achalasia. Keep in mind that the procedure may need to be repeated to maintain symptom improvement. Repeated dilations increase the risk of causing a hole (perforation) in your esophagus.
How many people have achalasia?
Achalasia develops in about 1 in every 100,000 people in the U.S. each year. It is typically diagnosed in adults between the ages of 25 and 60, but can occur in children as well (less than 5% of cases are in children under age 16).
What is achalasia treatment?
Abstract. Background: Achalasia is an infrequent primary motility disorder of the esophagus. Because of uncertain etiology, treatment is only palliative and is directed at decreasing lower esophageal sphincter pressure, improving esophageal emptying and relieving the symptoms of achalasia.
What is the best diagnostic test for achalasia?
Results: Esophageal manometry is the standard diagnostic evaluation for achalasia. Accurate diagnosis can also be made based on clinical findings and barium esophagogram. Medical treatment with nitrates or calcium channel blockers has variable results in alleviating the symptoms of achalasia but long-term results are disappointing because of tolerance and side effects. Intrasphincteric injection of botulinum toxin, pneumatic dilatation and surgical myotomy are variably effective at controlling the symptoms of achalasia but each modality has specific strength and weaknesses which make their choice suitable in a particular group of patients. While pneumatic dilatation is superior to botulinum toxin injection surgical myotomy provides the best long-term control of symptoms in patients with achalasia.
What database was used to search for achalasia?
Method: A Medline, PubMed and Cochrane database search was conducted using reference manager 11. Original articles and reviews published in the English literature on the management of achalasia were reviewed. Emphasis was placed on articles published in the last ten years on randomized controlled trials comparing the various forms of treatment.
Is pneumatic dilatation more effective than surgical myotomy?
Pneumatic dilatation is the most cost-effective alternative but its long-term efficacy is less than that of surgical myotomy. Endoscopic botulinum toxin injection can be considered when other forms of treatment are contraindicated.
What is the best treatment for achalasia?
oral medications, dilation or stretching of the esophagus, surgery (open and laparoscopic), endoscopic surgery, and. injection of muscle- relaxing medicines (botulinum toxin) directly into the esophagus. There is no specific diet to treat achalasia.
How to diagnose achalasia?
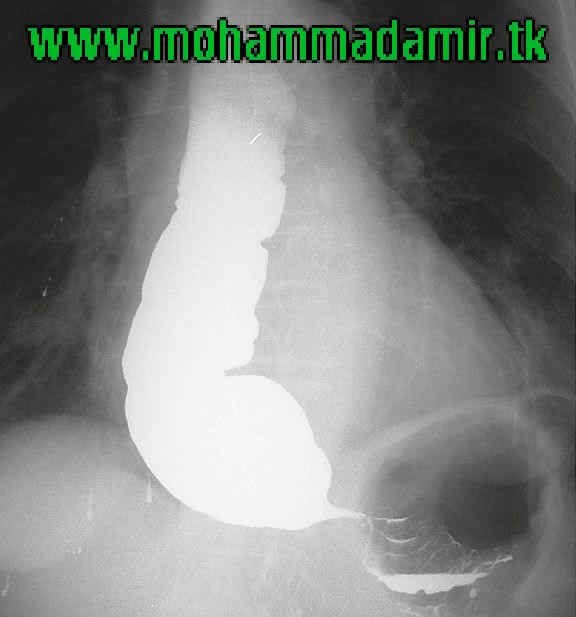
The diagnosis of achalasia usually is made by an X-ray study called a video-esophagram in which video X-rays of the esophagus are taken after barium is swallowed. The barium fills the esophagus, and the emptying of the barium into the stomach can be observed. In achalasia, the video-esophagram shows that the esophagus is dilated (enlarged or widened), with a characteristic tapered narrowing of the lower end, sometimes likened to a "bird's beak." In addition, the barium stays in the esophagus longer than normal before passing into the stomach.
What is achalasia?
Achalasia is a rare disease of the muscle of the esophagus (swallowing tube). The term achalasia means "failure to relax" and refers to the inability of the lower esophageal sphincter (a ring of muscle situated between the lower esophagus and the stomach) to open and let food pass into the stomach. As a result, people with achalasia have difficulty swallowing food. In addition to the failure to relax, achalasia is associated with abnormalities of esophageal peristalsis (usually complete absence of peristalsis), the coordinated muscular activity of the body of the esophagus (which comprises 90% of the esophagus) that transports food from the throat to the stomach.
What causes achalasia?
The cause of achalasia is unknown. Theories on causation invoke infection, heredity or an abnormality of the immune system that causes the body itself to damage the esophagus (autoimmune disease).
What is the name of the abnormality that causes achalasia?
In addition to the failure to relax, achalasia is associated with abnormalities of esophageal peristalsis (usually complete absence of peristalsis), the coordinated muscular activity of the body of the esophagus (which comprises 90% of the esophagus) that transports food from the throat to the stomach.
What is the lack of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax and the presence of?
Achalasia can be defined as the lack of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax and the presence of abnormal motility in the remainder of the esophagus.
Why is endoscopy important in achalasia?
Endoscopy also is helpful in the diagnosis of achalasia although it can be normal early in achalasia. Endoscopy is a procedure in which a flexible fiberoptic tube with a light and camera on the end is swallowed. The camera provides direct visualization of the inside of the esophagus. One of the earliest endoscopic findings in achalasia is resistance as the endoscope is passed from the esophagus and into the stomach due to the high pressure in the lower esophageal sphincter. Later, endoscopy may reveal a dilated esophagus and a lack of peristaltic waves. Endoscopy also is important because it excludes the presence of esophageal cancer and other causes of dysphagia.
What is the best treatment for achalasia?
Medication: Two commonly used medications to treat achalasia are calcium channel blockers and long-acting nitrates. These medicines are used if surgery is not a choice and symptoms continue after Botox® injections.
How to treat a swollen esophagus?
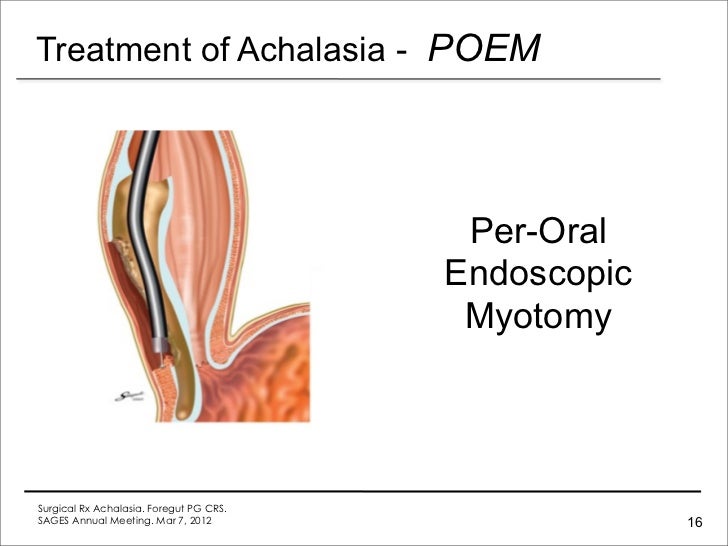
The exact treatment your physician recommends depends on the severity of your symptoms. Treatments include: 1 Botox® injection: Botox®, a commercial name for botulinum toxin, can be injected into the muscles that control your esophageal sphincter to relax the opening. The results may last anywhere from three months to a year. 2 Medication: Two commonly used medications to treat achalasia are calcium channel blockers and long-acting nitrates. These medicines are used if surgery is not a choice and symptoms continue after Botox® injections. 3 Pneumatic (balloon) dilation: Using an endoscope, a special balloon is passed through the mouth and into the esophagus, where it is inflated to stretch the restrictive muscles. 4 Heller myotomy: During this surgical procedure, the muscles of the esophageal sphincter are cut. 5 Per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM): Using an endoscope inserted in the mouth and through the esophagus, surgeons can access and cut abnormal muscle fibers that prevent the valve at the base of the esophagus from opening. 6 Fundoplication: Used sometimes in conjunction with POEM, a part of the upper stomach is wrapped around the lower esophagus, preventing stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus after the muscles have been cut.
What is Achalasia?
Achalasia is an uncommon disorder of the esophagus. The disorder makes it difficult for food to pass from the esophagus into the stomach.
What test can show if you have achalasia?
Diagnosis. Tests will be done to diagnose achalasia. These tests will also look for other conditions that could be causing the symptoms. Esophagography (barium swallow). You will swallow a thick liquid (barium) that can be seen on an X-ray. The test can show whether the esophagus is enlarged or dilated.
How long does it take for achalasia to show?
The symptoms of achalasia come on gradually. They may take years to progress.
What is the best non surgical treatment for a swollen stomach?
Pneumatic (balloon) dilation. This is widely thought to be the best non-surgical treatment. Your doctor passes an endoscope into your stomach while you are sedated.
Is there a way to prevent achalasia?
Since the cause of achalasia is unknown, there is no way to prevent it.
Is there a cure for achalasia?
There is no known cure for achalasia. But several treatments can provide good to excellent relief from symptoms for a number of years. When treatment needs to be repeated, it can be as successful as initial treatment.
Does achalasia hurt?
The study is generally painless. Some people with achalasia experience discomfort, similar to what they feel when swallowing foods or liquids.
How do you know if you have achalasia?
Achalasia symptoms generally appear gradually and worsen over time. Signs and symptoms may include: Inability to swallow (dysphagia), which may feel like food or drink is stuck in your throat. Regurgitating food or saliva. Heartburn. Belching. Chest pain that comes and goes. Coughing at night.
Where does food come from in achalasia?
Food then collects in the esophagus, sometimes fermenting and washing back up into the mouth, which can taste bitter. Some people mistake this for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). However, in achalasia the food is coming from the esophagus, whereas in GERD the material comes from the stomach. There's no cure for achalasia.
Can achalasia be treated?
There's no cure for achalasia. Once the esophagus is paralyzed, the muscle cannot work properly again. But symptoms can usually be managed with endoscopy, minimally invasive therapy or surgery.
Is achalasia inherited?
There are theories about what causes this, but viral infection or autoimmune responses have been suspected. Very rarely, achalasia may be caused by an inherited genetic disorder or infection. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Achalasia care at Mayo Clinic.
How to manage achalasia?
This painful disorder can be managed by changing what you eat. If there is an emergency, get to a hospital immediately. If you suspect a loved one has this condition, nothing can be done without a proper diagnosis. Have them see a specialist immediately before it’s too late!. Achalasia is an extremely rare disease that affects the muscles in the body’s digestive tract.
What is the best medicine for achalasia?
The herb most commonly used in natural remedies for Achalasia and one of the most important herbs used to improve circulation is Ginkgo Biloba. Natural remedies for Achalasia can include herbs that help with the uptake of nutrients, minerals, and vitamins like calcium, magnesium, etc.
What Are The Symptoms Of Achalasia?
Searching for symptoms of Achalasia can be a bit confusing since there are many different conditions that can cause problems with the brain and nerves. Brain fog can arise from a number of problems, some serious and some not so serious. Sometimes Achalasia is the result of a disease or a medication and can be very disabling. In some cases, it can be caused by psychological factors such as stress or anxiety resulting in poor thinking ability. Here are some symptoms to look out for.
How to diagnose extraesophageal achalasia?
Extraesophageal Achalasia is diagnosed by the endoscopy examination. The endoscopy includes investigating the pharynx, the upper esophagus, and extra-abdominal regions with fluoroscopy. About 5ml of barium is distributed by a balloon catheter into the upper esophagus. This is observed as it goes downwards towards the stomach on fluoroscopy.
What is the cause of esophageal achalasia?
These muscles are responsible for peristalsis, the wavelike motion of food through your body. Esophageal Achalasia is triggered by a hiatus hernia, the muscle at the top of the esophagus does not relax properly. Symptoms include difficulty swallowing and heartburn, It could lead to food becoming trapped and respiratory complications.
What is the best remedy for esophagus spasms?
I found that if you cannot get a hold of regular licorice roots, you can use candied ginger. You can also try Slippery Elm in cases where the irritation is mild and the spasms do not last long. Capsule forms of Slippery Elm are fine but make sure you dissolve them in water before taking them.
What to eat to help with roughage?
Diet: A usual diet such as fruits, nuts, vegetables high in roughage can help. The patient must lose weight and stop smoking, medication, applying pressure to the neck gets air passage opened, surgical intervention
Surgical treatments
For people who are at low risk of surgical complications, treatments can include the following procedures:
Medications
In some cases, medications like muscle relaxers and isosorbide or nifedipine are used to relieve achalasia cardia symptoms. Diet changes to the thickness and textures of foods and liquids may also help.