What are the treatment options for boggy uterus during pregnancy?
Simultaneous oxytocin infusion is helpful, although it is reasonable to defer it to after delivery of the placenta. If boggy uterus or uterine atony occurs, healthcare providers should be ready for initial medical management which is directed to the use of medications to improve uterine tone and induce uterine contractions.
What are the treatment options for an enlarged uterus?
Other conditions causing an enlarged uterus could need medical intervention. Fibroids that are large enough to stretch the uterus will probably need some kind of medical treatment. Your doctor may prescribe birth control drugs, such as birth control pills that contain estrogen and progesterone or a progesterone-only device like an IUD.
What are the treatments for uterine atony?
These may include close observation of blood pressure, pulse, red blood cell count, and more. Uterine atony can usually be managed by manual massage of the uterus, along with medications to promote uterine contractions (called uterotonic drugs). These drugs help enhance contractions of the uterus and control bleeding, they include: 3
What is bulky uterus and how to treat it?
The bulky uterus is a condition in which the uterus is bigger in size than it is supposed to be. This condition is not common, but it can be serious if not treated in time and can affect fertility in women. What Is Bulky Uterus? WHAT IS BULKY UTERUS? A bulky uterus is the generalised swelling of the uterine wall.
See more

What is the danger of a boggy uterus?
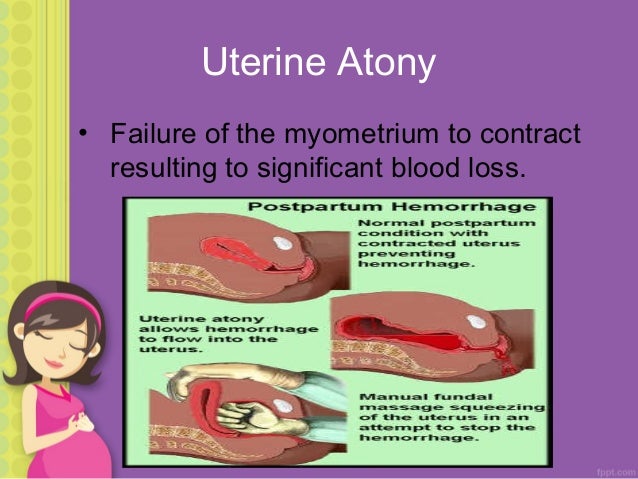
Atony of the uterus, also called uterine atony, is a serious condition that can occur after childbirth. It occurs when the uterus fails to contract after the delivery of the baby, and it can lead to a potentially life-threatening condition known as postpartum hemorrhage.
What does it mean when uterus is boggy?
Boggy uterus also known as uterine atony or hypotonic uterus, is when the uterus doesn't contract (tighten) as strongly as it should after the placenta is delivered after your baby is born. Normally, uterine contractions help stop the bleeding after the placenta separates from the uterus.
What should the nurse do if the fundus is boggy?
(b) Massage the fundus, if boggy, until firm (do not over massage, this fatigues the muscle).
What medications are used for uterine atony?
Initial Medical TreatmentOxytocin (Pitocin) can be given IV 10 to 40 units per 1000 ml or 10 units intramuscularly (IM). ... Methylergonovine (Methergine) given IM 0.2 mg. ... 15-methyl-PGF2-alpha (Hemabate) given IM 0.25 mg. ... Misoprostol (Cytotec): 800 to 1000 mg placed rectally.More items...•
What does boggy feel like?
A bog is described as a wet ground too soft to support a heavy body. Now, in medical terms, 'boggy' refers to abnormal texture of tissues characterized by sponginess, usually because of high fluid content.
How do you massage a boggy fundus?
0:020:44Uterine Massage Technique - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHands the uterine fundus is then massage gently in a rotating fashion with the upper hand while theMoreHands the uterine fundus is then massage gently in a rotating fashion with the upper hand while the lower uterine segment of the uterus is supported by the lower.
Can a full bladder cause a boggy uterus?
A full bladder can also prevent the uterus from contracting (see Figure 17-1). Figure 17-1 A distended bladder pushes the uterus upward and usually to one side of the abdomen. The fundus may be boggy or firm.
Can urine retention cause uterine atony?
Postpartum urinary retention can damage detrusor muscles and parasympathetic nerves of the bladder wall and change detrusor function, as well. Also, increased levels of progesterone during pregnancy and the early puerperium period might cause bladder atony and facilitate detrusor damage (12, 18, 19).
What nursing interventions are necessary when there is increased postpartum bleeding?
Nursing Interventions Save all perineal pads used during bleeding and weigh them to determine the amount of blood loss. Place the woman in a side lying position to make sure that no blood is pooling underneath her. Assess lochia frequently to determine if the amount discharged is still within the normal limits.
Which type of medication is used to decrease excessive bleeding and uterine atony?
Ergonovine (Ergotrate Maleate) Used to prevent and treat PPH due to uterine atony by producing firm contraction of the uterus within minutes.
What drug relaxes the uterus?
Doctors may try to stop or delay preterm labor by administering a medication called terbutaline (Brethine). Terbutaline is in a class of drugs called betamimetics. They help prevent and slow contractions of the uterus. It may help delay birth for several hours or days.
What medications are used for prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage?
Uterotonic agents include oxytocin, ergot alkaloids, and prostaglandins. Oxytocin is the most effective treatment for postpartum hemorrhage, even if already used for labor induction or augmentation or as part of AMTSL.
What is a boggy uterus?
Boggy uterus also known as uterine atony or hypotonic uterus, is when the uterus doesn’t contract (tighten) as strongly as it should after the placenta is delivered after your baby is born. Normally, uterine contractions help stop the bleeding after the placenta separates from the uterus. But when these contractions aren’t strong enough, hemorrhage can happen. Signs and symptoms of uterine atony or “boggy uterus” include heavy bleeding and not having contractions after giving birth. A boggy uterus after delivery complicates 1 in 40 births in the United States and is responsible for at least 75% of cases of postpartum hemorrhage 1). Postpartum hemorrhage is defined as ≥500 ml blood loss within 24 hour of vaginal delivery or 1000 ml loss within 24 hour of cesarean section 2). Postpartum hemorrhage is the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide. But prompt recognition of the problem, and effective management with uterine massage, uterotonic drugs, and/or other crucial interventions, can arrest post-delivery bleeding.
How many births are caused by a boggy uterus?
A boggy uterus after delivery complicates 1 in 40 births in the United States and is responsible for at least 75% of cases of postpartum hemorrhage 1). Postpartum hemorrhage is defined as ≥500 ml blood loss within 24 hour of vaginal delivery or 1000 ml loss within 24 hour of cesarean section 2).
What is adenomyosis gynecologic?
Adenomyosis is a gynecologic condition characterized by ectopic endometrial tissue within the uterine myometrium 9) . Adenomyosis occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus (endometrial tissue) grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. The displaced tissue continues to act normally — thickening, breaking down and bleeding — during each menstrual cycle. An enlarged uterus and painful, heavy periods can result. Historically, adenomyosis was a histologic diagnosis that required biopsy or more often hysterectomy. Presently, the diagnosis can be made non-invasively using ultrasound or MRI.
What is diffuse uterine atony?
Diagnosis of diffuse uterine atony or boggy uterus is prompted typically by finding of more than usual blood loss during examination demonstrating a flaccid and enlarged uterus, which may contain a significant amount of blood.
What is the mechanism of contraction of the myometrium?
Contraction of the myometrium that mechanically compresses the blood vessels supplying the placental bed provides the principal mechanism uterine hemostasis after delivery of the fetus, and the placenta is concluded. The process is complemented by local decidual hemostatic factors such as tissue factor type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor as well as by systemic coagulation factors such as platelets, circulating clotting factors.
What is the best medication for postpartum hemorrhage?
Other alternatives include 15-methyl-prostaglandin, also known as carboprost (Hemabate) (0.25 mg IM), and misoprostol (1 mg placed rectally), which is an inexpensive prostaglandin E1 analogue that has been used in several trials with good success in controlling postpartum hemorrhage in cases refractory to oxytocin.
Is a partial hysterectomy invasive?
Myomectomy and partial hysterectomy are more invasive options that aim to preserve fertility. These options allow for targeting of deeper foci; however, subsequent scarring may lead to disease recurrence as the endometrial-myometrial interface is disrupted, a risk factor for adenomyosis.
What does it mean when your uterus is boggy?
In boggy uterus, uterus looks loose or more flaccid than usually it should be. Boggy uterus may be associated with two main conditions named uterine atony and adenomyosis. Uterine atony is the condition in which uterus loses its natural shape or tone. The muscles become loose and the natural shape of uterus disturbs. While in adenomyosis, the endometrium extends outward. Endometrium is the lining which covers the uterus. The extended endometrium get into the outermost covering named myometrium.
Why is my uterus boggy?
Boggy uterus have two main leading causes 1st one is uterine atony and 2nd one is adenomyosis. In adenomyosis, glandular de arrangement of uterine muscles leads to boggy uterus. It is considered the common cause of all uterine problems after the age of 30 years. About 20 percent of women with adenomyosis have boggy uterus. The exact reason is still unknown but the abnormality in barrier separating endometrium and myometrium causes endometrium to get into myometrium causing adenomyosis and ultimately boggy uterus. In case of uterine atony, muscular abnormality leads to boggy uterus.
How to treat fibroids in the uterus?
Uterine artery embolization is another treatment method used to solve the problem of fibroids. The principle behind it is to inject small particles into the uterine arteries with the help of a thin tube. This cuts of the blood supply to fibroids and they thus shrink and eventually die.
What are the symptoms of a bulky uterus?
The common symptoms are as following: Abnormalities in the menstrual cycle. Heavy bleeding and cramping in the pelvic region. Swelling and cramping in the legs.
Why do women have a bulky uterus after menopause?
Most women see a decline in the symptoms after menopause because, at that point, the oestrogen level starts decreasing. One of the most commonly known reasons behind a bulky uterus is fibroids. Fibroids are non-cancerous tumours that are like little lumps or bulges that can weigh up to a few pounds.
How is a myomectomy done?
Myomectomy is done to remove the fibroids. Based on the size and position of the fibroids, myomectomy can be done using the traditional surgical method or through a laparoscopy. In more severe cases where fibroids cannot be removed by surgery, the uterus is completely removed from the body, which is called Hysterectomy.
How to tell if you have an enlarged uterus?
Still, it may go unnoticed for a long time as a diagnosis of the enlarged uterus is not expected most of the time. Routine check-ups by a gynaecologist can help to track down the problem in time.
What is the term for the thickening of the uterus?
Adenomyosis is the diffuse thickening of the uterus that happens when the endometrium, i.e. the tissue coating the uterus, moves into the external muscle mass of the uterus. It is a noncancerous condition that has similar symptoms as that of fibroids.
What is the purpose of the uterus?
The uterus is a small, muscular female reproductive organ which is responsible for keeping and nourishing the foetus until it is ready for birth. The bulky uterus is a condition in which the uterus is bigger in size than it is supposed to be. This condition is not common, but it can be serious if not treated in time and can affect fertility in ...
What are the symptoms of an enlarged uterus?
An enlarged uterus may cause a number of symptoms, such as weakness, cramping, constipation, pain during sex, and menstrual abnormalities. menstrual cycle abnormalities, such as heavy bleeding and cramping.
What causes a uterus to be enlarged?
Polycystic ovarian syndrome. A range of conditions may cause an enlarged uterus, including polycystic ovary syndrome. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) also causes an enlarged uterus. It is the result of hormonal imbalances in menstruation and the shedding of the endometrial lining of the uterus. It affects 1 in 10.
What is the term for a condition that mimics fibroids?
Adenomyosis is a noncancerous condition that mimics symptoms of fibroids. It results in the lining of the uterus becoming embedded directly in the muscle wall of the uterus. During the menstrual cycle, the cells of the muscle bleed, causing pain and swelling.
What happens to the endometrial lining during the menstrual cycle?
The accumulation of the endometrial lining causes inflammation and enlargement of the uterus.
What are the complications of uterine enlargement?
Complications may include: hysterectomy (removal of all or part of the uterus) loss of fertility. miscarriage and other pregnancy complications. infection due to uterine inflammation.
Can an enlarged uterus cause pain?
An enlarged uterus can cause pain and other health complications. A woman can be unaware that she has an enlarged uterus. Most often, women discover they have a problem during a pelvic exam. It is possible a woman may notice a bloated belly or that clothes seem too tight, but for most, a diagnosis of an enlarged uterus is unexpected.
Is an enlarged uterus a serious health condition?
Conclusion. An enlarged uterus is usually not an indication of a serious health condition. Doctors will use CT scans and ultrasounds to determine the exact cause of enlargement. Most of the time, no treatment is necessary and doctors will just monitor the cause of enlargement.
What is the term for a condition in which the uterine lining grows into the uterine wall?
The exact cause of the condition is unknown, but adenomyosis is tied to estrogen levels. Most women see a resolution of their symptoms after menopause.
How long does it take for a uterus to shrink?
If your uterus in enlarged because of pregnancy, it will naturally begin to shrink after you deliver. By one week postpartum, your uterus will be reduced to half its size. By four weeks, it’s pretty much back to its original dimensions. Other conditions causing an enlarged uterus could need medical intervention.
What is a tumor that grows inside and outside the uterus?
Fibroids. Fibroids are tumors that can grow inside and outside the uterus. Experts aren’t sure what causes them. Hormonal fluctuations or genetics may contribute to the development of these growths. According to the Office on Women’s Health at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Trusted Source.
How many times does the uterus grow?
The uterus normally fits into the pelvis. When you’re pregnant, your growing baby will cause your uterus to increase in size 1,000 times, from the size of a clenched fist to a watermelon or larger by the time you deliver.
How do you know if you have an enlarged uterus?
You may feel a heaviness in your lower abdomen or notice your abdomen protruding as your uterus enlarges. You may not have any noticeable symptoms, however. Read on to learn more about the causes and symptoms of an enlarged uterus, and how to treat this condition.
What are the symptoms of a tumor in the uterus?
Depending on the size of the tumors, your uterus can swell. Additional symptoms include: abnormal vaginal bleeding, such as bleeding not related to your menstrual cycle. pain with sex.
What can I take for adenomyosis?
Anti-inflammatory medications, like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and hormonal contraception such as the birth control pill can help relieve the pain and heavy bleeding associated with adenomyosis. These medications won’t help to decrease the size of an enlarged uterus, however. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend a hysterectomy.
What is a benign mass that grows in the uterus?
Uterine fibroids are benign masses that grow in the uterus for unclear reasons. Uterine fibroids are commonly called by the shorter name, "fibroids.". The medical term for a fibroid is leiomyoma, which refers to a proliferation or abnormal growth of smooth muscle tissue. Uterine fibroids arise from the tissue in the muscle layer of the wall ...
What is a uterine growth?
Uterine growths are tissue enlargements of the female womb (uterus). Uterine growths can be caused by either harmless or dangerous conditions. Growths are sometimes referred to medically as masses or tumors. An example of a harmless (benign or non-cancerous) growth, which does not pose a threat, is a polyp of the cervix.
What is a benign tumor of the uterus called?
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors of the uterus (the womb) and the single most common indication for hysterectomy. See a picture of Uterine Fibroids and learn more about the health topic.
What is a polyp in the uterus?
Polyps of the uterus are benign overgrowths, or bulges, of the normal tissue lining the uterus into the uterine cavity. Polyps may also be found in the uterine cervix. Polyps are usually attached to the underlying tissue by a base or stalk, and they vary in size. Polyps only rarely contain cancerous cells.
What is the name of the muscle that grows in the wrong layer of the uterus?
Adenomyosis is the growth of uterine tissue from one particular layer of the uterus (the endometrial glands from the lining tissue of the uterus) into the "wrong" layer (the muscle layer, called the myometrium).
What is a hysterectomy?
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure in which the uterus is removed. There are a variety of surgical techniques for performing hysterectomies, which include vaginal hysterectomy, total hysterectomy, laparoscopy-assisted vaginal hysterectomy (LAVH), supracervical hysterectomy, laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy, radical hysterectomy, and oophorectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy hysterectomies.
What is a laparoscopic hysterectomy?
Laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy (LAVH) is a surgical procedure using a laparoscope to guide the removal of the uterus and/or Fallopian tubes and ovaries through the vagina. During LAVH, the uterus is detached from the ligaments that attach it to other structures in the pelvis using laparoscopic tools.
Causes
There are several factors known to prevent the uterine muscles from contracting after labor, common factors include:
Symptoms
The primary symptom of uterine atony is a relaxed uterus, which is one that shows no signs of tightness or tension after birth. When palpated (manually felt) after delivery by a healthcare provider, the uterus may feel boggy (spongy) or enlarged.
Diagnosis
When there are signs of excessive bleeding, and the uterus feels boggy, soft, and relaxed, after a person gives birth, a diagnosis of uterine atony is often made.
Treatment
Uterine atony can usually be managed by manual massage of the uterus, along with medications to promote uterine contractions (called uterotonic drugs).
Frequently Asked Questions
Postpartum hemorrhage is strongly linked with uterine atony. This is because uterine contractions are instrumental in assisting with the blood clotting process and helping the uterus to stop bleeding after delivery (particularly after the placenta is delivered).
