
There are a variety of treatment options for abnormal EF, including: Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), or beta-blockers. These medications can reduce the amount of hormones that weaken your heart muscle.
What are the different ways to increase ejection fraction?
Jun 18, 2014 · Brief Answer: defibrillator and pacemaker are best treatment. Detailed Answer: Hello and thank you for asking HCM, I understand your concern. Ejection fraction shows us how good your heart pumps. By patients with ejection fraction lower than 35, which is your case, an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) may be recommended.
What problems are there with ejection fraction?
“However, once the ejection fraction is < or =20%, ejection fraction is no longer a predictor of mortality,” says the paper. “These results suggest that it is unlikely that small increases in ejection fraction will be associated with a survival benefit in this group,” continues the paper, “and treatments aimed at increasing peak VO2 may be more appropriate.”
What is an ejection fraction, and what does it mean to you?
May 22, 2020 · Which substance classes form the basis of treatment for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction? ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers. Digoxin and ACE inhibitors. Angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors and digitoxin. I f channel blockers and beta-blockers
Does Entresto improve ejection fraction?
Apr 29, 2018 · If you have been prescribed medications for heart failure, diabetes, high blood pressure or another underlying cause, taking your prescribed medication may also improve your ejection fraction. Over time, as the medications are working, your heart may be able to recover, strengthen and perform better. 3. Get the right amount of physical activity.
How serious is an ejection fraction of 20?
An EF of 20% is about one-third of the normal ejection fraction. This means 80% of the blood stays in the ventricle. The heart is not pumping all the oxygen-rich blood the body needs. The blood that is not ejected from the ventricle can back up into the lungs and cause shortness of breath.
Can you live with an ejection fraction of 20?
Conclusion: Three year survival is low when ejection fraction is very low. However, once the ejection fraction is < or =20% ejection fraction is no longer a predictor of mortality.
How do you treat low ejection fraction?
Low ejection fraction treatmentLifestyle changes, such as getting exercise, losing weight, quitting smoking or reducing salt.Medication, such as beta blockers or diuretics, to help improve your heart function or get rid of excess fluids.More items...
What medication is used for low ejection fraction?
Digoxin. If you have reduced ejection fraction heart failure, your NYU Langone doctor may prescribe digoxin to improve the heart's ability to pump blood. It does so by strengthening contractions and reducing heart rate.
What is the lowest EF you can live with?
If you have an EF of less than 35%, you have a greater risk of life-threatening irregular heartbeats that can cause sudden cardiac arrest/death. If your EF is below 35%, your doctor may talk to you about treatment with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) or cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).Apr 29, 2019
How do you know when heart failure is near the end?
In the final stages of heart failure, people feel breathless both during activity and at rest. Persistent coughing or wheezing. This may produce white or pink mucus. The cough may be worse at night or when lying down.
Can you live a long life with a low ejection fraction?
"Patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction certainly are living longer, and I think are also living better," McMurray said.Jul 6, 2017
Can low EF be reversed?
Treatment with some combination of ACE inhibitor or ARB, beta blocker, BiDil (nitrate and hydralazine), or aldosterone inhibitor is generally effective in slowing or reversing the ventricular remodeling that accounts for the low EF.Jun 20, 2017
Does a pacemaker increase ejection fraction?
The lead in the left ventricle is guided through the coronary sinus. When the heart rate drops below the rate set with the pacemaker, it senses the drop and transmits electrical impulses to the left as well as the right ventricle to contract simultaneously, improving the ejection fraction and the cardiac function.
What is the first drug of choice for heart failure?
Digoxin has been the traditional first drug of choice for CHF, but with protracted controversy about its efficacy and safety. It is hope that new agents as vesnarione, and ibopamine may improve contractility without having adverse consequences.
What medications improve survival in heart failure?
In combination, the direct-acting vasodilators isosorbide dinitrate (Isordil) and hydralazine (Apresoline) were the first medications shown to improve survival in heart failure.Sep 15, 2001
How long does it take for Entresto to improve ejection fraction?
In this study, significant improvements were seen in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). At 12 months, the LVEF increased from a median of 28.2% to 37.8% (difference, 9.4% [95% CI, 8.8 to 9.9%]). A significant 5.2% increase in LVEF was also seen as early as 6 months (5.2%, 95% CI, 4.8% to 5.6%).Apr 23, 2020
What is the ejection fraction of blood?
Ejection fraction is the percentage of blood, relative to how much the heart chamber is filled with, that gets pumped out with each beat. Blood is pumped through the aorta, which branches out with vessels that further branch out so that the entire body receives oxygenated blood.
Is ejection fraction a predictor of mortality?
“However, once the ejection fraction is < or =20%, ejection fraction is no longer a predictor of mortality,” says the paper.
What is evidence based treatment?
Evidence-based treatments. Evidence-based treatments are available only for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). The basic principle here—besides treating the underlying cause (for example, by means of revascularization or heart valve surgery)—is neurohumoral inhibition by means of ACE inhibitors, ...
What is pharmacotherapy based on?
Pharmacotherapy is based on neurohumoral inhibition of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and the adrenergic system. The prognosis of patients with this condition has been further improved recently through the introduction of combined angiotensin receptor antagonists and neprilysin inhibitors.
What is less is more?
Less is more: heart rate monitoring. As a result of the reduced cardiac output due to the reduced ejection fraction, the heart rate increases as a reflex. In heart failure patients, an elevated heart rate leads to less economical ventricular function and has been repeatedly associated with a poorer prognosis (e9).
Does digitalis help with heart failure?
A meta-analysis on the studies available to date on digitalis in heart failure revealed that treatment with digitalis reduces hospitalizations and improves the symptoms of heart failure (16). In older, multimorbid patients with reduced renal function, digoxin poses the risk of accumulation and possible toxicity.
What does ejection fraction mean?
A heart at rest holds a certain amount of blood. Ejection fraction refers to the percentage of that blood your heart pumps out with each beat. “Assuming a normal heart size and rate, when ejection fraction is normal, the heart is pumping a normal amount of blood,” Dr. Finet explains. “We can assume the blood is moving at a normal speed around ...
How to take care of ticker?
Here are some ways to do that: Advertising Policy. 1. Partner up with a doctor. Whether it’s a cardiologist or your primary care physician, talk to a doctor about your symptoms.
What are the two main chambers of the heart?
The heart has two main muscular chambers: the left and the right ventricle. Each chamber has MVP status in the body, working together to perform jobs you literally couldn’t live without: 1 Right ventricle: Pumps blood to the lungs to get oxygenated. 2 Left ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood throughout your body.
What happens if you consume too much salt?
Consuming too much sodium, or salt, can have a domino effect: Diseased heart muscle, or cardiomyopathy, provides less blood to the kidneys. The kidneys retain sodium and fluid to compensate for the low blood flow. Sodium traps water, which abnormally accumulates on the heart and blood vessels.
Does losing weight improve ejection fraction?
“Losing weight won’t necessarily improve ejection fraction, but it can make you feel better,” Dr. Finet says. Tracking your weight will also help you and your doctor determine whether fluid is being built up due to the abnormal heart function.
How to reduce heart failure symptoms?
Although the correlations between heart failure and stress are unclear, being stressed can increase heart rate and blood pressure, two things that can worsen heart failure symptoms. Practice stress-reducing habits.
What to do if you have heart failure?
If your heart failure is stable, and you have your doctor’s okay, do what moves you. Here are some exercise tips to keep in mind. Consider a cardiac rehab program. It offers some unique benefits, and you may even be able to join a supervised home-based exercise program.
What are the risk factors for heart failure?
Several risk factors are associated with heart failure like high blood pressure, or hypertension, diabetes and metabolic syndrome. By managing those conditions, you may be able to help your heart failure and your ejection fraction improve. Know your plan and follow it carefully. If you have been prescribed medications for heart failure, diabetes, ...
How to get rid of lightheadedness and dizziness?
A brief warm up and cool down can help your body transition smoothly in and out of your exercise zone and reduce symptoms of dizziness and/or lightheadedness. 4. Pay attention to your weight. Your weight is important. Tracking your weight can give you important clues about how well your heart is managing its load.
Does alcohol cause heart failure?
Alcohol can increase the risk of heart failure and worsen symptoms. By eliminating alcohol, the signs and symptoms of heart failure often improve. Quit smoking. Smoking cigarettes is especially hazardous to people with heart failure. Discover the resources that can help you quit for good.
How to improve your walking?
It’s easy to do, and it may help you learn to pace yourself. Your provider may do a 6-minute walk test to help measure your improvements over time. You simply start by seeing how far you can walk in one six minute session.
Why is tracking your weight important?
Your weight is important. Tracking your weight can give you important clues about how well your heart is managing its load. Track and respond to weight fluctuations. You may notice patterns that help you respond appropriately to situations before they get worse. Maintain a healthy body weight.
What causes low ejection fraction?
Risk factors that could contribute to low ejection fraction include: Congenital or familial heart valve disease or cardiomyopathy: Some people are born with, or develop inherited forms of, malformed or dysfunctional heart valves or weakening of the heart muscle. Heart attack: A heart attack can damage the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively.
What does it mean when your EF is low?
A low ejection fraction (or low EF) is typically 45 or less and can be evidence of heart failure or cardiomyopathy (a disease of the heart muscle). The heart’s ejection fraction (EF) refers to the amount – or percentage – of blood pumped (or ejected) out of the heart’s left ventricle with each contraction. The EF is an important measurement that ...
How to prevent heart disease?
Practice good heart health: Watch what you eat, exercise (as advised by your physician), and avoid smoking, heavy alcohol use and drug abuse. Take your medications as prescribed: If you have high blood pressure, high cholesterol or diabetes, be certain to take your prescribed medications as directed.
What is the EF of a heart?
The EF is an important measurement that physicians use to determine how well your heart is pumping out blood and to diagnose or track heart failure. A normal range for heart ejection fraction may be between 50 and 70. Baptist Health is known for advanced, superior care for patients with heart problems and the diagnosis, ...
Can a heart transplant help with low EF?
Heart Transplant. Though rare, when medications, lifestyle changes or devices can’t help people with dangerously low ejection fractions and severe heart problems, a heart transplant might be an option. This is a serious surgery for treating low EF with numerous risks and a long recovery period.
What are the symptoms of a swollen leg?
Feeling bloated or full. Heart palpitations. Loss of appetite. Mental confusion. Nausea. Rapid, forceful or irregular heartbeat. Shortness of breath. Swelling, especially in the feet and lower legs.
What is a nuclear heart scan?
Nuclear heart scan: This safe scan reveals how efficiently blood is flowing through your heart. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein and flows to the heart. It releases energy that allows special cameras to capture pictures of the coronary arteries and heart function. Causes.
What does EF mean in heart failure?
An EF that is below normal can be a sign of heart failure. If you have heart failure and a lower-than-normal (reduced) EF (HF-rEF), your EF helps your doctor know how severe your condition is. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the measurement of how much blood is being pumped out of the left ventricle of the heart ...
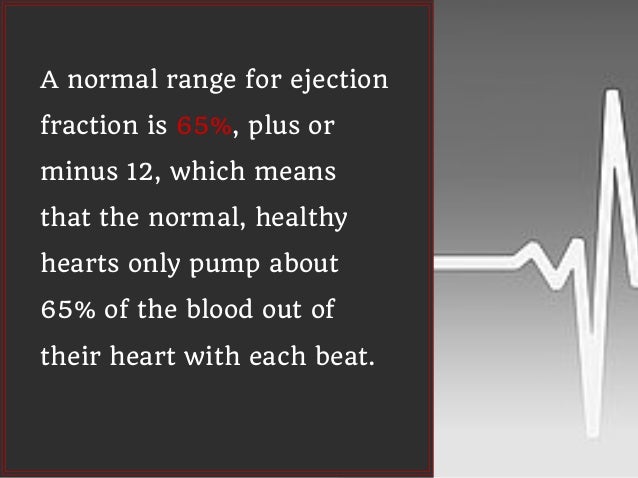
What is a 65% LVEF?
An LVEF of 65%, for example, means that 65% of the total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pumped out with each heartbeat. Your EF can go up and down, based on your heart condition and how well your treatment works. Ejection Fraction (EF) %: 55% to 70%. Pumping Ability of the Heart: Normal.
What is EF in heart?
Most times, EF refers to the amount of blood being pumped out of the left ventricle each time it contracts. The left ventricle is the heart's main pumping chamber.
How does the heart work?
How the Heart Works. A healthy heart beats about 60 to 80 times per minute to pump blood throughout the body. The right and left sides of the heart work together. Blood that is low in oxygen first enters the right upper chamber (right atrium) of the heart.
Where does blood flow in the heart?
The blood flows from the right atrium to the lower chamber (right ventricle) through the open tricuspid valve. Blood passes through a valve before leaving each chamber of the heart. There are four valves in your heart; valves make sure blood flows in only one direction through your heart.
