What is the maximum amount of tPA given?
The benefit of tPA depends a lot on time. The sooner the patient receives tPA; the better are the outcomes. Maximum recommended dose is 90mg Patients less than or equal to 100 kg load with 0.09 mg/kg (10% of 0.9 mg/kg dose) as an IV bolus over 1 minute, followed by 0.81 mg/kg (90% of 0.9 mg/kg dose) as a continuous infusion over 60 minutes.
How much TPA should be taken after a stroke?
100 mg over 2 hours; may be administered as a 10 mg bolus followed by 90 mg over 2 hours Ischemic Stroke:The only blood test that is necessary before tPA usage is the blood glucose level. If the patient is on anticoagulation like coumadin, then only we should do PT, PTT, and INR, etc. The benefit of tPA depends a lot on time.
What is tPA therapy?
TPA is a naturally occurring protein found on endothelial cells, the cells that line blood vessels. It activates the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, an enzyme responsible for the breakdown of clots, 2 helping restore blood flow to the brain. It is a powerful medication that must be administered by an experienced medical team.
What are the risks of tPA treatment?
While tPA has been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of stroke, there is a risk associated with tPA treatment, even for people who have been medically cleared for tPA. It is a powerful blood thinner, and serious side effects may occur, including the following: 5

How long should you give CPR for fibrinolysis?
Some studies suggest allowing 15 minutes of CPR for drug to work.
What anticoagulants are used in fibrinolytic studies?
Anticoagulants, such as heparin, were used in most studies along with the fibrinolytic.
How long does it take to administer a 0.9 mg IV?
0.9 mg/kg IV; not to exceed 90 mg total dose; administer 10% of the total dose as an initial IV bolus over 1 minute and the remainder infused over 60 minutes
How much AMI should I take?
Recommended total dose for AMI is based on patient weight, not to exceed 100 mg, regardless of the selected administration regimen (accelerated or 3 hr)
How long after stroke can you take alteplase?
Patients who present within 3 hr of stroke symptom onset, should be treated with alteplase unless contraindications exist; longer time window (3-4.5 hr after symptom onset) shown to be safe and efficacious for select individuals; treatment of patients with minor neurological symptoms not recommended.
When to inspect parenteral drug products?
Inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit
Is thrombocytopenia a hazard?
Exercise caution with patients who have thrombocytopenia, other hemostatic defects (including those secondary to severe hepatic or renal disease), or any condition for which bleeding constitutes a significant hazard or would be particularly difficult to manage because of its location, or who are at high risk for embolic complications (e.g., venous thrombosis in the region of the catheter)
How long does tPA last?
Treatment with tPA has been effective for people with an ischemic stroke as long as it is received intravenously within up to 4.5 hours of the onset of symptoms. 3 Endovascular treatment to remove the clot or deliver tPA at the site of the clot is considered for up to 24 hours after a stroke.
What to do if you have a stroke and received tPA?
Eliminating illegal drug usage. Lowering cholesterol and fat levels. Managing diabetes if you have it. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure. If you or a loved one has had a stroke or has received tPA for treatment of a stroke, expect a recovery that may take time. Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation.
What is the FDA approved treatment for ischemic stroke?
on February 19, 2021. Tissue plasminogen activator, or tPA, is the only FDA-approved treatment for ischemic or thrombotic stroke, which is stroke caused by a blood clot interrupting blood flow to a region of the brain. 1 . Chris Ryan / Getty Images.
What conditions would make you ineligible to receive treatment with tPA?
Conditions that would make you ineligible to receive treatment with tPA include: 3 . Hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding in the brain) Brain aneurysm or AVM. Recent surgical procedure. Head injuries. Bleeding or blood clotting disorders. Bleeding ulcers. Pregnancy. Blood-thinning medication.
How to maximize your chances of getting a stroke?
The best way to maximize your chances of receiving the most effective treatment for a stroke is to get to the emergency room as soon as possible. A person who is having a stroke may not notice when they are experiencing symptoms.
What are the side effects of a blood thinner?
It is a powerful blood thinner, and serious side effects may occur, including the following: 5. Hemorrhage (bleeding) affecting the brain: Causes headaches, weakness, confusion, loss of consciousness, seizures. Hemorrhage of the digestive system: Causes blood in the stool or stomach pain.
Is TPA used for stroke?
Chris Ryan / Getty Images. It has also been used in treatment for pulmonary embolism and myocardial infarction. TPA is a blood thinner, and therefore it is not used for hemorrhagic strokes or head trauma.
How much ml is needed for a stroke?
Stroke: The dose for treating acute ischemic stroke is 0.9 mg/kg infused over one hour not to exceed 90 mg. Clogged catheters are cleared by injecting 2 mg/2 ml solution into the clogged catheter.
How long does Alteplase take to work?
Heart attack: For heart attacks the recommended dose is a 15 mg injection followed by 50 mg or 0.75 mg/kg (up to 50 mg) infused over 30 minutes then 35 mg or 0.5 mg/kg (up to 35 mg) over 60 minutes. The total dose is 100 mg.
When was Alteplase first approved?
When was alteplase (TPA, Activase, Cathflo Activase) approved by the FDA? Alteplase was first approved for heart attacks in 1987. In 1996, it was approved for strokes.
What are the side effects of alteplase?
The most common and serious side effect of alteplase is bleeding. Minor bleeding is more common, but significant bleeding such as into the brain (intracranial hemorrhage) or fatal bleeding also occurs. Other important side effects include: Nausea. Vomiting.
How long does it take to give alteplase?
Initially, it was thought alteplase had to be administered within three hours of stroke onset.
What is the best medication for ischemic stroke?
Tissue plasminogen activator, or tPA, is a powerful clot-busting medication that can stop an ischemic stroke in its tracks. After suffering an ischemic stroke, and only a short time after symptoms began, tPA may be used. When a blood clot is stopping blood flow to the brain, a powerful clot-busting medication called tPA is used to dissolve ...
Is TPA effective for stroke?
Emergency Medical Treatment for Stroke. The use of tPA is so effective in treating acute ischemic stroke that it is used in emergency departments throughout the country. Unfortunately, only about five percent of patients who qualify for the treatment receive it.
Can thrombolytic therapy cause bleeding?
A danger of thrombolytic therapy is the possibility of unwanted bleeding. Clot-busting drugs cannot tell the difference between a “bad” clot that prevents blood flow to the brain cells and a “good” clot that has been formed to stop blood flow from a ruptured intracranial artery. If the drug breaks down a good clot, a hemorrhagic stroke can occur. Despite careful dosing, intracranial hemorrhage occurs in some patients who receive alteplase. Nevertheless, in appropriately selected patients, the benefits far outweigh this potential complication.
Can tPA be used for stroke?
While several tPA drugs can be used to break up heart attack -causing blood clots in the coronary arteries, only one is approved for the treatment of ischemic stroke: alteplase (Activase). It is given by intravenous infusion.
How long does it take to use TPA?
Clinical guidelines for the early treatment of stroke published jointly by the American Heart Association and American Stroke Association strongly recommend the use of TPA for eligible patients within three hours of symptom onset. Some of the eligibility criteria involved in the decision to use TPA include ...
How long after stroke can you get TPA?
Intravenous TPA has to be administered within the first few hours after a stroke begins. The start of a stroke is counted from the time that you first notice stroke symptoms. After this very short window of a few hours after a stroke starts, you cannot receive TPA because it might cause more harm than good at that point.
What is tissue plasminogen activator?
Tissue plasminogen activator is a powerful agent that dissolves blood clots. It is injected by intravenous administration (IV) for emergency stroke treatment. A stroke is caused by an interruption in blood flow either due to a blood clot ( ischemic stroke) or a bleed ( hemorrhagic stroke) in the brain. TPA is only used for strokes caused by blood ...
What is TPA in 2021?
Huma Sheikh, MD. on April 21, 2021. Tissue plasminogen activator, most commonly known as TPA, is a powerful blood thinner used for emergency stroke treatment. Approved 20 years ago for the treatment of stroke, it was initially viewed as both revolutionary and risky. Now, twenty years later, stroke treatment has advanced a lot, ...
How does TPA work?
When TPA is injected into a vein, it quickly travels through the blood to reach the clogged blood vessel, where it works by trying to dissolve the blood clot and to restore blood flow to the brain.
Is TPA a blood thinner?
Because TPA is a powerful blood thinner, the main side effect is bleeding. Bleeding is a serious complication that can result in a hemorrhagic stroke, which is often more serious than an ischemic stroke.
Do patients ask for TPA?
Most of the time, patients do not ask for TPA. But emergency medical workers are trained to recognize a stroke and emergency rooms are equipped with the staff and provisions to administer TPA when it is necessary.
Administration
- IV: Activase:ST-elevation MI or acute ischemic stroke: Administer bolus dose (prepared by one of three methods) over 1 minute followed by an infusion.Infusion: Remaining dose for STEMI or AIS may be administered as follows: Any quantity of drug not to be administered to the patient must be removed from vial(s) prior to administration of remaining dose.50 mg vial: Either PVC bag or glass vial and infusion set100 mg vial: Insert spike end of the infus…
- The protocol required that no anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents be given for 24 hours after treatment and that blood pressure be maintained within prespecified values. The medical monitor reviewed each patient's compliance with the protocol throughout the trial.
Treatment
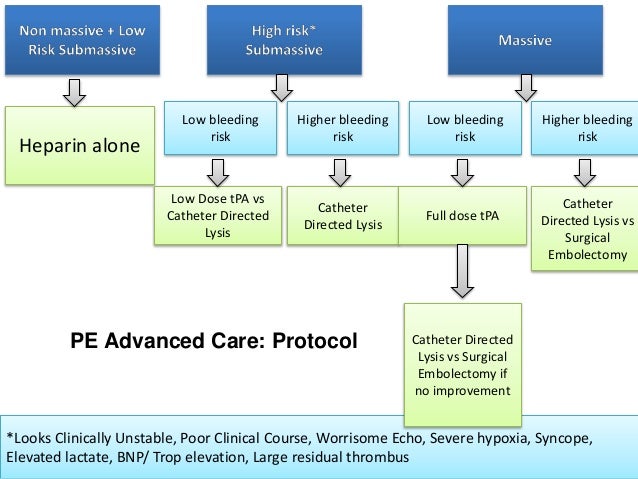
- Recommended criteria for treatment: Based on the 2015 American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (AHA/ASA) focused update of the 2013 guidelines for the early management of patients with AIS, endovascular therapy with stent retrievers is recommended over intra-arterial fibrinolysis. Initial treatment with intra-arterial fibrinolysis is beneficial for selected patients with major ischemic strokes (<6 hours' duration) caus…
Adverse Reactions
- >10%: Cardiovascular: Intracranial hemorrhage (CVA: Within 90 days: 15%, within 36 hours: 6%; AMI: <1%)1% to 10%:Cerebrovascular accident (new ischemic stroke in CVA: 6%)Dermatologic: Ecchymosis (AMI: 1%)Gastrointestinal: Gastrointestinal hemorrhage (AMI: 5%)Genitourinary: Genitourinary tract hemorrhage (AMI: 4%)Frequency not defined:Hematologic & oncologic: Arterial embolism, major hemorrhage, pulmonary embolism…
Benefits
- This study found a benefit of intravenous t-PA therapy for patients with ischemic stroke when treatment was initiated within three hours of the onset of symptoms. As compared with patients given placebo, patients treated with t-PA were at least 30 percent more likely to have minimal or no disability at three months, as measured by the outcome scales (absolute increase in favorable outcome, 11 to 13 percent). This benefit was not associated wit…
Results
- >50% present in plasma cleared ~5 minutes after infusion terminated, ~80% cleared within 10 minutes; fibrinolytic activity persists for up to 1 hour after infusion terminated (Semba 2000)
- For each primary hypothesis, MantelHaenszel tests were used to compare the proportion of patients with improvement in the NIHSS 24 hours after the onset of stroke. There was no adjustment for multiple comparisons, since the three hypotheses were prespecified. Patients who for some reason were not assessed with the NIHSS at 24 hours were considered to have had no improvement. The primary hypothesis was tested with a global statisti…
Research
- Data from an early study in patients with undifferentiated out of hospital cardiac arrest suggest that the use of alteplase as a bolus may improve rates of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) and survival to hospital admission in these patients [Bottiger 2001]. However, a similar randomized, controlled study reported no difference in these endpoints [Abu-Laban 2002]. Several retrospective studies evaluating cardiac arrest due to pr…
- Two previous small, randomized studies of intravenous t-PA for stroke found no conclusive evidence of efficacy.24,25 In a recently completed large, placebo-controlled European trial in which 1.1 mg of t-PA per kilogram was given intravenously within six hours of hemispheric ischemia, the investigators reported no benefit in the population analyzed according to the intention to treat.26 Two other large, randomized trials of intravenou…
Diagnosis
- STEMI (ACCF/AHA [OGara 2013]): Ischemic symptoms within 12 hours of treatment or evidence of ongoing ischemia 12 to 24 hours after symptom onset with a large area of myocardium at risk or hemodynamic instability.
- Intracranial hemorrhage, serious systemic bleeding, death, and new stroke were the primary adverse events monitored. To detect intracranial hemorrhage, CT scans were required at 24 hours and 7 to 10 days after the onset of stroke and when any clinical finding suggested hemorrhage. A hemorrhage was considered symptomatic if it was not seen on a previous CT scan and there had subsequently been either a suspicion of hemorrhage or a…
Pharmacology
- Initiates local fibrinolysis by binding to fibrin in a thrombus (clot) and converts entrapped plasminogen to plasmin...
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to alteplase or any component of the formulationTreatment of STEMI or PE: Active internal bleeding; history of recent stroke; recent (within 3 months [ACCF/AHA: Within 2 months]) intracranial or intraspinal surgery or serious head trauma; presence of intracranial conditions that may increase the risk of bleeding (eg, intracranial neoplasm, arteriovenous malformation, aneurysm); known bleeding diathesis; severe uncontrolled hy…
Monitoring Parameters
- Acute ischemic stroke (AIS): Baseline: Neurologic examination, head CT (without contrast), blood pressure, CBC, aPTT, PT/INR, glucose. During and after initiation: In addition to monitoring for bleeding complications, the 2013 AHA/ASA guidelines for the early management of AIS recommends the following: Perform neurological assessments every 15 minutes during infusion and every 30 minutes thereafter for the next 6 hours, then hourly …