Liraglutide is the only GLP-1 receptor agonist indicated for use in children (≥10 years of age) with type 2 diabetes (10). Lixisenatide is available as a fixed-ratio combination with insulin glargine 100 units/mL (22); liraglutide 3.6 mg/mL plus insulin degludec 100 units/mL can also be given as a single injection (23).
Can GLP-1 based Polypharmacology be used to treat obesity and diabetes?
Abstract. Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are a new class of hypoglycemic drugs, including exenatide, liraglutide, albiglutide, lixisenatide, and taspoglutide. Insulin glargine is a standard agent used to supplement basal insulin in …
Does GLP-1 lower blood glucose?
The GLP-1 receptor agonist–basal insulin combination led to significantly improved glycemic control and reduced body weight without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia when compared to basal-bolus insulin alone. These features have sparked interest in using GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with severe insulin resistance (23,24).
What is the role of GLP-1 and GIP in insulin secretion?
Oct 21, 2017 · Similarly, another systematic review and meta-analysis compared the combination treatment of type 2 diabetes with a GLP-1 receptor agonist and basal insulin. The researchers found that, compared with other diabetic treatments, GLP-1 agonist and basal insulin combination had an improved mean reduction in HbA1c of -0.44%.
Should you add GLP-1 receptor agonists to your basal insulin regimen?
Jan 16, 2018 · GLP-1 therapy targets the GLP-1 receptors on the surface of beta cells, stimulating insulin secretion and restoring the incretin effect. These hormones make effective targets when treating type 2 diabetes because they help regulate insulin, glucose, and gastric emptying.

Can you use GLP-1 with insulin?
Basal insulin can be added to a GLP-1 receptor agonist with a slow titration to target goal fasting plasma glucose. In patients starting a GLP-1 receptor agonist, the dose of basal insulin should be decreased by 20 % in patients with an HbA1c ≤8 %.
What is the difference between GLP-1 and insulin?
Compared to insulin, GLP-1 RAs reduced HbA1c more effectively. Basal insulin was more effective in reducing fasting plasma glucose. GLP-1 RAs reduced body weight more effectively. The proportion of patients experiencing hypoglycemic episodes was 34% lower with GLP-1 RAs, with a similar trend for severe hypoglycemia.Oct 22, 2016
What is role of GLP-1 in insulin release?
Stimulation of insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells by glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists is known to be glucose-dependent. GLP-1R agonists potentiate glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and have little or no activity on insulin secretion in the absence of elevated blood glucose concentrations.
Can GLP-1 and metformin be used together?
In combination with GLP-1, metformin significantly lowers plasma glucose concentrations in type 2 diabetes mellitus subjects compared with GLP-1 alone, whereas insulin responses were similar.
What is GLP-1 medication?
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are a group of drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes. GLP-1 RAs are very effective at lowering blood sugar levels.Mar 23, 2020
Can GLP-1 cause hypoglycemia?
GLP-1 receptor agonists do not generally cause hypoglycemia, but it is recommendable to decrease the dose of concomitant sulphonylurea or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemic episodes.
What happens to GLP-1 in diabetes?
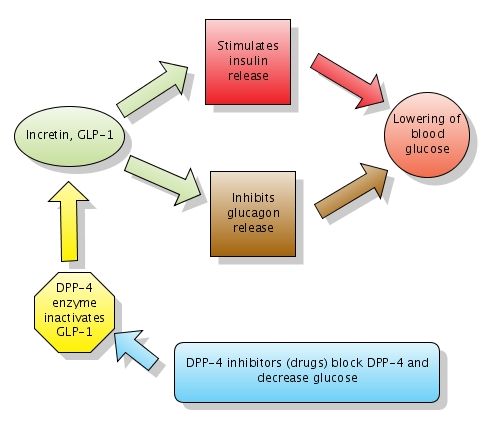
The main actions of GLP-1 are to stimulate insulin secretion (i.e., to act as an incretin hormone) and to inhibit glucagon secretion, thereby contributing to limit postprandial glucose excursions.
Are all GLP-1 injectable?
The downside to GLP-1 drugs is that all but one has to be taken by injection. And, like any medication, there is a risk of side effects, some serious.
How can I increase my GLP-1 naturally?
Tips for keeping GLP-1 levels in checkEat plenty of protein. High protein foods such as whey protein and yogurt have been shown to increase GLP-1 levels ( 71 , 72 ).Consider taking probiotics. Preliminary research suggests that probiotics may increase GLP-1 levels, though more human research is needed.
Which GLP-1 is best for weight loss?
Among once-weekly injectable glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, semaglutide (Ozempic) is more effective than exenatide (Byetta) and dulaglutide (Trulicity) for glycemic control and weight loss; it also prevents some adverse cardiovascular (CV) events in patients with established CV disease.Jul 11, 2019
What is a GLP-1 in diabetes?
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a hormone of the incretin system responsible for a variety of glucoregulatory effects, including glucose-dependent secretion of insulin and inhibition of glucagon release, the effects of which are impaired in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Fda Panel Backs Novo Nordisk Insulinglp-1 Combination Ideglira
FDA Panel Backs Novo Nordisk InsulinGLP-1 Combination IDegLira SILVER SPRING, MD A US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advisory committee has given its blessing to a new injectable that combines fixed doses of a long-acting basal insulin with a glucagonlike peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist for diabetes.
Rival Sanofi, Novo Nordisk Insulin Combinations Gain Fda Approval
The FDA late Monday approved Soliqua and Xultophy, the competing combinations of insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists that analysts predict could await a market of up to $1 billion to treat type 2 diabetes (T2D). Sanofi announced the approval in a press release late Monday.
Effects Of Insulin Plus Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (glp-1ras) In Treating Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review And Meta-analysis
Abstract Combination therapy with insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) has already been proven an efficient treatment option for type 2 diabetes. This combination can effectively improve glycated hemoglobin levels, cause weight loss and reduce the dosage of insulin.
The Future Of Combination Therapies Of Insulin With A Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists In Type 2 Diabetes Is It Advantageous?
The Future of Combination Therapies of Insulin with a Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Is it Advantageous? European Endocrinology, 2014;10 (2):989 DOI: Safe and effective therapies for type 2 diabetes are needed to reduce the burden of late complications and costs associated with thischronic disease.
Basal Insulin Use With Glp-1 Receptor Agonists
IN BRIEF The combination of basal insulin and a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist is becoming increasingly common and offers several potential benefits to patients with type 2 diabetes.
Fixed-ratio Combination Of Basal Insulin And Glp-1 Receptor Agonist
Dhiren K. Patel, PharmD, CDE, BC-ADM, BCACP; and Jennifer D. Goldman, PharmD, CDE, BC-ADM, FCCP Ninety percent of diabetes cases are type 2, which is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Because it is a progressive multi-organ disease, effective therapies are critical.
Combining Incretin-based Therapies With Insulin
What is the rationale for adding incretin-based therapies to insulin? The combination of the incretin-based therapies, i.e., the dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), with basal insulin has, in theory, logical appeal.
Literature Search Methods
The PubMed database was searched using the terms: 1) GLP-1 AND (switch OR switching OR switched); and 2) GLP-1 AND (once-daily OR “once daily”) AND (once-weekly OR “once weekly”). These searches yielded 161 and 97 results, respectively.
Characteristics of Available Injectable GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Although they belong to a single medication class, the approved GLP-1 receptor agonists differ in many ways, including in structure, molecular size, pharmacology, efficacy, and safety ( Table 1) ( 7 – 13 ).
Why Switch Between GLP-1 Receptor Agonists?
In clinical practice, unique factors often drive therapeutic decisions that are made by patients, HCPs, or both. The following are potential reasons for switching between GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Practical Advice on Switching Between GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
The recommendations discussed here are largely based on the clinical experience of the authors and are summarized in Figure 2.
Future Perspectives and Conclusion
Until recently, GLP-1 receptor agonists have only been available as subcutaneous injections. However, oral semaglutide once daily provided similar glycemic control, produced greater weight loss, and had similar tolerability to liraglutide once daily ( 64) ( Table 2 ).
Article Information
The authors thank Stephen Purver (Spirit Medical Communications Group Ltd.) for assistance with medical writing and editorial support. Alisa Schiffman of Novo Nordisk was also provided with the opportunity to perform a medical accuracy review.
What are GIP and GLP-1?
Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) are the two primary incretin hormones secreted from the intestine on ingestion of glucose or nutrients to stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells . GIP and GLP-1 exert their effects by binding ...
Does GLP-1 inhibit bone absorption?
In adipose tissues, GIP but not GLP-1 facilitates fat deposition. In bone, GIP promotes bone formation while GLP-1 inhibits bone absorption. In the brain, both GIP and GLP-1 are thought to be involved in memory formation as well as the control of appetite.
What is a GLP-1 receptor agonist?
The GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of agents that allow the body to use its own insulin maximally. GLP-1 receptor agonists work by slowing gastric emptying. They are a glucose-dependent initiator of the body's own insulin release. Importantly, they are associated with a low incidence of hypoglycemia, which is an Achilles heel ...
What are the side effects of GLP-1?
One of the side effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonists is increased gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms—some nausea and GI discomfort. This diminishes after a couple of months of use, although a significant but small number of patients do not tolerate GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Why are GLP-1 receptor agonists so attractive?
GLP-1 receptor agonists become a very attractive option for patients, particularly because of the lower incidence of hypoglycemia. And let's face it: Our patients are concerned about weight because we have been telling them for years to try to lose weight. They would rather have a medicine that helps them do that.
Does GLP-1 cause weight gain?
With the combination of GLP-1 receptor agonist and basal insulin, there is less weight gain, equal A1c efficacy, and no more hypoglycemia than with insulin alone. In addition, when the combination of a GLP-1 receptor agonist and basal insulin is compared with a GLP-1 receptor agonist alone, there are fewer GI side effects ...
Can basal insulin be used alone?
The other interesting thing is that when patients are on basal insulin alone, more than half are not controlled to goal. Combination therapy with a GLP-1 receptor agonist and a basal insulin (two of which have been approved by the FDA ), can achieve higher efficacy than with either agent alone.
Can GLP-1 receptor antagonists be combined with insulin?
Combining GLP-1 Receptor Agonists With Insulin. Dr Skolnik: Patients have diabetes for years, and as they move through the diabetes continuum, their pancreatic beta cells have increasingly less insulin-secreting ability. Eventually, these patients reach the point where they need to use external insulin.
Is GLP-1 a good agonist?
Dr Shubrook: It sounds like GLP-1 receptor agonists are a good alternative and/or complement to insulin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes . These new combination products provide the opportunity to simplify medicine use. We will have to see what they cost. Pay attention. These GLP-1 receptor agonists are around to stay.
