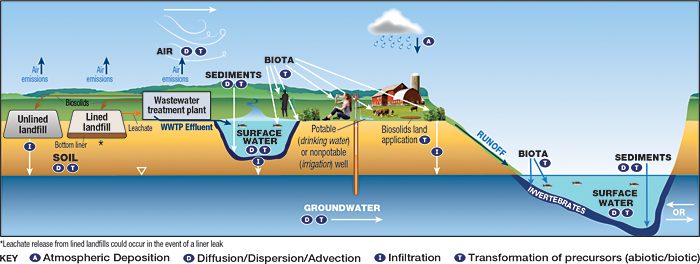
What do you mean by total residual chlorine?
Total chlorine residual is the total amount of free and combined chlorine existing in water. The difference between the amount of chlorine added to water and the amount of free, combined, or total residual that remains after a specific contact time is called the chlorine demand of a system.
What is the minimum chlorine residual drinking water?
0.2 mg/LThe minimum recommended WHO value for free chlorine residual in treated drinking water is 0.2 mg/L. CDC recommends not exceeding 2.0 mg/L due to taste concerns, and chlorine residual decays over time in stored water.
Is total chlorine the same as total residual chlorine?
Total Residual Chlorine is the result of a Total Chlorine test that is performed after disinfection has occurred. Any Total Chlorine test can be considered a Total Residual Chlorine test based on when the test is performed.
How do you test for residual chlorine?
You simply fill a tube with water, add 1-5 drops of the solution, and look for the color change. These kits are sold in many stores as a way to test the concentration of total chlorine in swimming pool water.
What is difference between free chlorine and residual chlorine?
These hypochlorite ions are called as free chlorine. This free chlorine is responsible for the chlorination of the microbes in water. All the free chlorine is not consumed in the chlorination. This remaining chlorine is called residual chlorine.Jan 9, 2017
Why is residual chlorine important?
Residual chlorine is the low level amount of chlorine remaining in the water after a certain period or contact time after its initial application. It constitutes an important safeguard against the risk of subsequent microbial contamination after treatment—a unique and significant benefit for public health.
Is residual chlorine free or total?
Total Chlorine Residual: The total amount of chlorine present in a sample. This is the sum of the free chlorine residual and the combined available chlorine residual. Chlorination may produce adverse effects.
Why is total chlorine higher than free chlorine?
If total chlorine is higher than free chlorine, there are contaminants in the pool. Subtract the free chlorine measurement from the total chlorine measurement to calculate the amount of combined chlorine (total – free = combined). If combined chlorine is higher than 0.5 ppm you should shock the pool.Mar 9, 2022
What happens if combined chlorine is high?
If your total chlorine level is high, you will use a non-chlorine shock; if it is low, you will use a chlorinated shock. As a rule, you will need to raise free chlorine to 10 times your combined chlorine to hit what is known as “break point.” Therefore, it is good to deal with combined chlorine while it is still small.
How much chlorine do I need for 1000 Litres?
To dose water in a tank with 5 mg/L chlorine use: 40 millilitres of liquid pool chlorine or 170 millilitres of bleach, for every 1000 litres in the tank.
What is the toxicity test used by the EPA?
EPA or the State may use the results of the toxicity tests and chemical analyses conductedpursuant to these permits , as well as national water quality criteria developed pursuant to Section 304(a)(1) of theClean Water Act (CWA), state water quality criteria, and any other appropriate information or data, to developnumerical effluent limitations for any pollutants, including but not limited to those pollutants listed in Appendix D of
What is a major discharger?
“Major” dischargers are facilities with design flows equal to orgreater than one million gallons per day and any other facilities designated by EPA, in itsdiscretion, as “major facilities.” See 40 CFR §§ 122.2, 124.2. All other facilities are “Minor”dischargers. General permit coverage is available only to Minor dischargers in Massachusetts andto Major and Minor dischargers in New Hampshire that meet the requirements of this part. Existing facilities that appear to be eligible for coverage under this general permit are listed, andtheir status as "major" or "minor" facilities identified, in Attachment A to the Response toComments document. EPA and the relevant state agency will make a final eligibilitydetermination for each facility upon review of the facility's NOI submission.
What is the permit number for Massachusetts?
MAG580000). This general permit for dischargers in theCommonwealth of Massachusetts authorizes discharges into all waters of the Commonwealth andIndian Country lands, except as provided in section III.K , below, unless otherwise restricted by theMassachusetts Surface Water Quality Standards, 314 CMR 4.00 (or as revised), including 314CMR 4.04(3) Protection of Outstanding Resource Waters.
Can a permittee discharge wastewater?
The permittee is authorized to discharge only in accordance with the terms and conditions of this General Permit. Discharges of wastewater from any other point sources, including sanitary sewer overflows (SSOs) or combinedsewer overflows (CSOs), are not authorized by this permit and shall be reported in accordance with Part IV,Standard Conditions, Section D.1.e., Reporting Requirements (Twenty-four hour oral reporting, five-day writtenreporting).
Continuous Monitoring
NPDES and some WQM permits require permittees to monitor their treated effluent for specific pollutants or parameters to confirm compliance with effluent limitations, collect information for future assessments, and/or verify operational performance of treatment facilities.
Discharge Monitoring Reports
Wastewater monitoring data required by permits are typically recorded on Discharge Monitoring Reports (DMRs) and DMR Supplemental Reports.
What is wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment is a process uses to remove contaminants from sewage or wastewater and convert it into effluent and that can be returned to the water table with minimum impact on the environment or can be directly reused.
What is sludge treatment?
Sludge treatment is the solid-liquid separation process where there is the least requirement of residual moisture in the solid phase and the very lowest solid particle residues are required in the separation of the liquid phase.
What is the chemical used to kill bacteria in water?
Chemicals are used for the treatment of water in this process. To kill bacteria chlorine is commonly used as an oxidizing chemical and decomposes water by adding contaminants into it. Ozone is also another one of the oxidizing agent used for purifying the wastewater. To bring the water to a pH of 7 neutralization is another process.
What is CETP in SSI?
CETP is set up in that location where there is a cluster of Small scale industries are located . In India ministry of environment and forest sponsored a scheme centrally namely CETP in order to curb pollution especially to treat the effluent discharging from many Small scale industries. So the main objective of CEPT is to reduce the treatment cost which is carried by the individual unit to the maximum while protecting the water environment to the maximum. Thus the design and technical specifications of making CEPT can be referred to in any book of wastewater management.
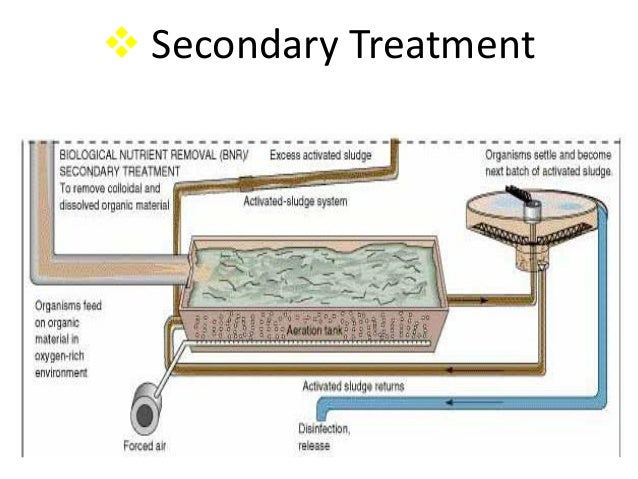
What is activated sludge?
Activated sludge plants processes that use dissolved oxygen to promote the growth of biological floe that removes organic material. in which process traps particulate and can, convert ammonia to nitrate and nitrate to nitrogen gas.
What is the purpose of a primary clarifier?
Sewage flows through the large tanks commonly knows as primary clarifiers or primary sedimentation tanks. Tanks are larger in shapes in which sludges settle down and floating material such as grease and oils can rise to the surface and skimmed off. The main purpose of the primary sedimentation stage is to get both liquids that are homogenous and can be biologically treated and can separately treat sludge.