Are TKI chemotherapy?
Any drug used to treat cancer (including tyrosine kinase inhibitors or TKIs) can be considered chemo, but here chemo is used to mean treatment with conventional cytotoxic (cell-killing) drugs that mainly kill cells that are growing and dividing rapidly. Chemo was once one of the main treatments for CML.Jun 19, 2018
What are the TKI drugs?
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) are effective in the targeted treatment of various malignancies. Imatinib was the first to be introduced into clinical oncology, and it was followed by drugs such as gefitinib, erlotinib, sorafenib, sunitinib, and dasatinib.
How long does TKI therapy last?
The NCCN recommends prompt resumption of TKI within 4 weeks of a loss of MMR, monthly molecular monitoring until MMR is re-established, then every 3 months thereafter, indefinitely.
Are TKI immunotherapy?
A number of recent studies have indicated that antiangiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) target multiple components of the tumor microenvironment and are an ideal class of agents for synergizing with cancer immunotherapy.
Is TKI an immunosuppressant?
Sunitinib has been shown to exert immunomodulatory effects in clinical studies, similar to that described in preclinical models, including observable reductions in the numbers of circulating immunosuppressive cells in patients after 4 weeks of treatment, thus making this TKI an attractive candidate for combination with ...Mar 16, 2015
How do TK inhibitors work?
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) block chemical messengers (enzymes) called tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases help to send growth signals in cells, so blocking them stops the cell growing and dividing. Cancer growth blockers can block one type of tyrosine kinase or more than one type.
How do TKI work?
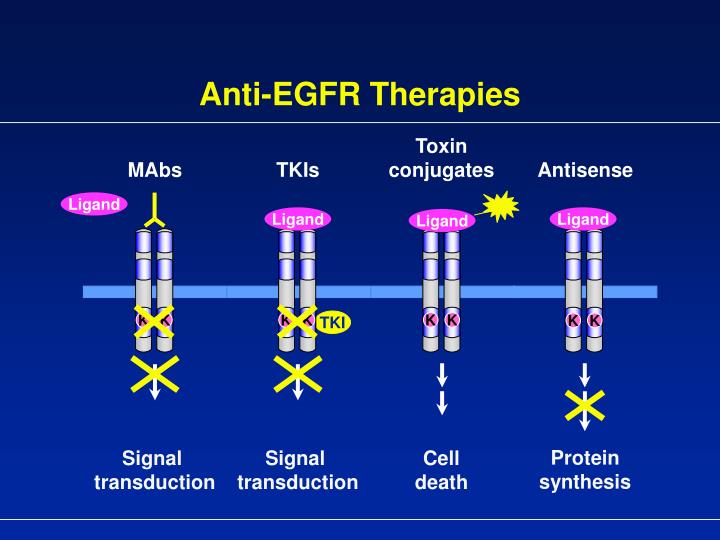
TKIs are a type of targeted therapy. They work by switching off (inhibiting) the tyrosine kinase made by the BCR-ABL1 gene in leukaemia cells. This slows or stops the bone marrow from making abnormal white blood cells. It also allows the leukaemia cells to mature and die.
Can TKI cure CML?
Although a bone marrow transplant is the only treatment that can cure CML, it is used less often now. This is because bone marrow transplants have a lot of side effects, while TKIs are very effective for CML and have fewer side effects.
Can CML patients live normal life?
While patients with CML are fortunate to have excellent therapies available to control their disease, most do not lead normal lives due to the diminished health-related quality of life that is associated with long term treatment.
What is the difference between immunotherapy and targeted therapy?
Targeted approaches aim to inhibit molecular pathways that are critical to tumor growth and maintenance, whereas immunotherapy endeavors to stimulate a host response that effectuates long-lived tumor destruction.
Is Keytruda a TKI?
A clinical trial compared patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma who received KEYTRUDA, an immunotherapy, in combination with axitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), to those who received sunitinib, another TKI, alone.
Is Gleevec a TKI?
Drugs known as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) that target BCR-ABL are the standard treatment for CML. These include: Imatinib (Gleevec)Nov 24, 2021
How often should I go to the TKI clinic?
When you first start treatment with a TKI, you will need to go to the clinic every 1 to 2 weeks. This is so your doctors can closely monitor how well treatment is working, and to check for any side effects. As time goes on, you will not need to go as often. Eventually, you may only need a check-up every 3 to 6 months.
What is the most common TKI for CML?
If a TKI does not work, or stops working, you can usually be switched to a different one. The three main TKI drugs currently used for CML are: Imatinib is the most commonly used TKI for CML. It can be used in any phase. Nilotinib can be used as a first treatment in the chronic phase.
What is the treatment for chronic myeloid leukaemia?
Treating chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) with TKIs. The main treatment for chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) uses drugs called tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). TKIs are a type of targeted therapy. They work by switching off (inhibiting) the tyrosine kinase made by the BCR-ABL1 gene in leukaemia cells. This slows or stops the bone marrow ...
How long does it take for imatinib to work?
It takes longer to get a cytogenetic response than a haematological response. It sometimes takes many months. About 8 out of 10 people taking imatinib for CML in the chronic phase (80%) get a complete cytogenetic response. This means there are no Ph+ cells detected in the bone marrow sample.
Can you get pregnant with TKI?
Contraception and fertility with TKIs. Because TKIs are a newer type of drug, there is not a lot of information available yet about getting pregnant or making someone pregnant while taking TKIs. Taking a TKI during pregnancy increases the risk of harm to a developing baby.
What is ponatinib used for?
Ponatinib (Iclusig ®) Ponatinib may be used for people who have leukaemia cells with a particular gene change (mutation) called T3151. Only a few people with CML have this gene change in their leukaemia cells. You may be offered ponatinib if you have tried other TKI treatments but they have stopped working.
How many cells can a PCR test detect?
The PCR test can detect 1 leukaemia cell in 10,000 normal blood cells. It does this by measuring a substance made by the BCR-ABL1 gene in the leukaemia cells. When you are first diagnosed with CML, you will have blood taken for a PCR test. After diagnosis, you will have this done every three months.
What is a TKI drug?
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) is a group of pharmacologic agents that disrupt the signal transduction pathways of protein kinases by several modes of inhibition.
What is a TKI?
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) is a group of pharmacologic agents that disrupt the signal transduction pathways of protein kinases by several modes of inhibition. This activity will review the currently available drugs, their mechanism of action, routes of administration, indications, contraindications, ...
What is imatinib used for?
Imatinib is an oral chemotherapy medication designed to target the BCR-Abl hybrid protein, a tyrosine kinase signaling protein produced in patients with Philadelphia-chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia.
What is the Life After Stopping TKIs study?
The Life After Stopping TKIs (LAST) study enrolled 172 adults with CML from 14 university medical centers and cancer centers across the United States. Participants had CML that was well controlled with one of four TKIs used to treat the disease: imatinib, dasatinib (Sprycel), nilotinib, or bosutinib (Bosulif).
What is the test for CML?
Both tests rely on a technology known as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect the genetic alteration that causes CML, a fusion of two different genes known as BCR-ABL .
Does imatinib help with CML?
For many people with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), the drug imatinib (Gleevec) changed a once-fatal blood cancer into a manageable disease and allowed them to live a nearly normal lifespan. Until recently, imatinib and related drugs for CML, known as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), had to be taken every day for life, ...
How do TKIs work?
TKIs operate by four different mechanisms: they can compete with adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the phosphorylating entity, the substrate or both or can act in an allosteric fashion, namely bind to a site outside the active site, affecting its activity by a conformational change.
What is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor?
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor ( TKI) is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine kinases are enzymes responsible for the activation of many proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated by adding a phosphate group to the protein ( phosphorylation ), a step that TKIs inhibit.
What is the short name for tyrosine phosphorylation inhibitor?
They are also called tyrphostins, the short name for " tyrosine phosphorylation inhibitor ", originally coined in a 1988 publication, which was the first description of compounds inhibiting the catalytic activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).
Is Sunitinib a kinase inhibitor?
Sunitinib, an inhibitor of the receptors for FGF, PDGF and VEGF is also based on early studies on TKIs aiming at VEGF receptors. Adavosertib is a Wee1 kinase inhibitor that is undergoing numerous clinical trials in the treatment of refractory solid tumors.