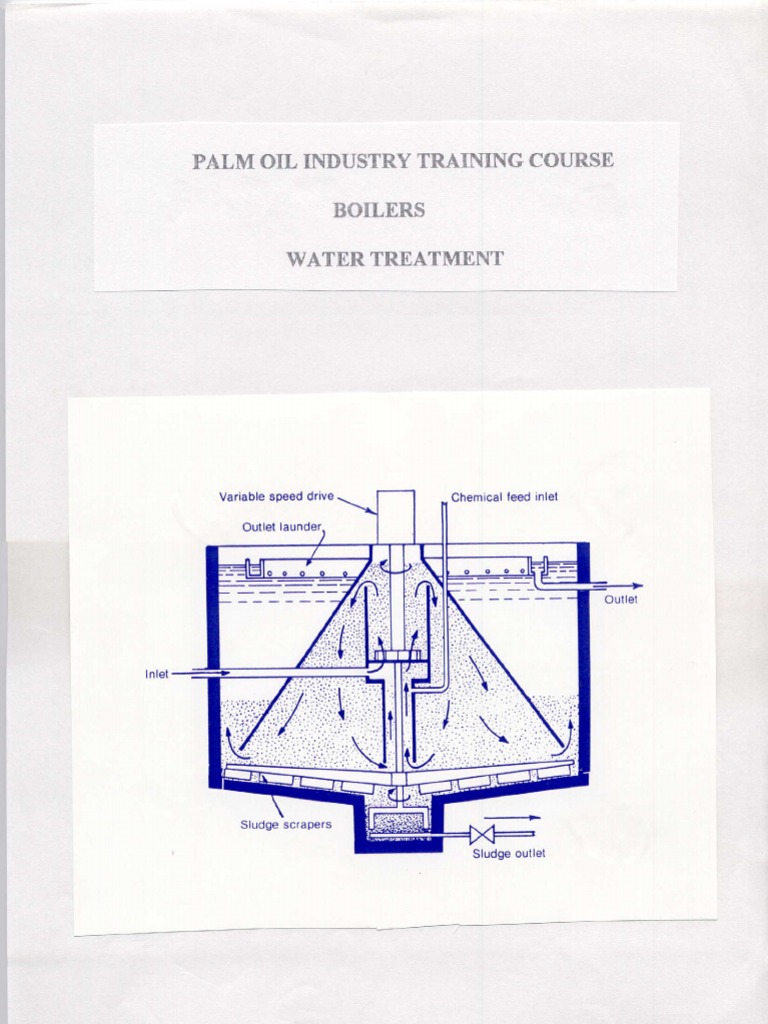
What are THMs in water?
THMs are a group of chemicals that are formed in the water along with other disinfection by-products. The chemicals included are chloroform, dibromochloromethane, bromodichloromethane, and bromoform. It is formed when chlorine and other disinfectants people use in the water react naturally with the inorganic and organic matter in the water.
What are trihalomethanes (THMs)?
Trihalomethanes (THMs) are a byproduct of the water treatment process. They are formed when natural organic material, such as the decaying vegetation commonly found in lakes and reservoirs, reacts with chlorine used to treat the water. This reaction produces “disinfection byproducts,” the most common...
How to control ThM in wastewater treatment plants?
According to the EPA, the best available technology for controlling the THM at the treatment plants is by removing the precursors by enhanced coagulation. Enhanced coagulation is the process of optimizing the process of filtration to maximize the elimination of the precursors.
What is the best treatment for thm's?
THM's are not only ingested by the water that we drink but also by inhaling them in the shower. The recommended treatment for THMs is activated carbon filtration or Reverse Osmosis . We can't find products matching the selection.
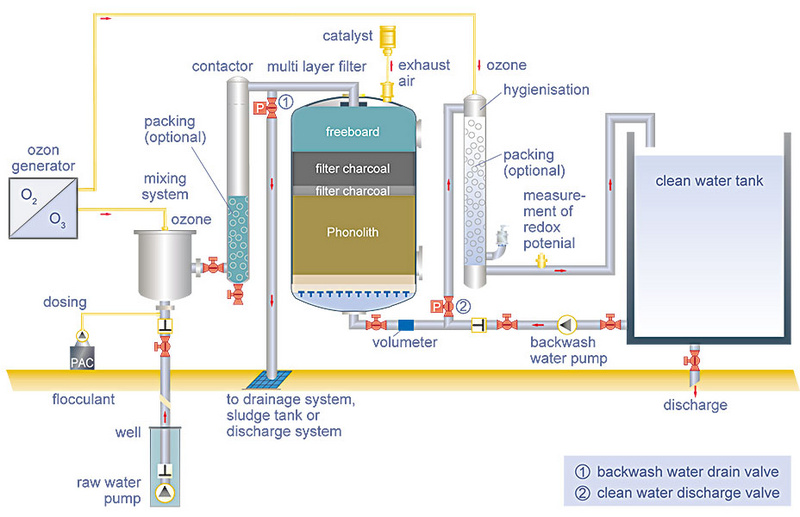
What causes high THM in water?
Levels of TTHM generally increase in the summer months due to the warmer temperatures, but can also be affected by seasonal changes in source water quality or by changing amounts of disinfection added. Water systems often can experience temporary increases in TTHM due to short-term increases in chlorine disinfection.
Does a Brita filter remove trihalomethanes?
For example, Brita water filters and PUR water filters do not remove THMs from water. Both Aquasana and Amway water filters are proven to be effective at removing more than 99% of THMs from water. Kenmore and Culligan water filters also filter out large percentages of these substances.
What are the side effects of trihalomethanes?
Exposure and Risk When people consume trihalomethanes at high levels over many years, they increase their risk of developing bladder cancer. Other health effects that may be associated with trihalomethanes include rectal and colon cancer, and adverse developmental and reproductive effects during pregnancy.
What does THM and HAA stand for?
Trihalomethanes (THM) and haloacetic acids (HAA) are disinfection by-products (DBPs) that form when disinfectants, such as chlorine, react with organic matter during the drinking water disinfection process.
Do Water softeners remove trihalomethanes?
Water Softeners The water softener systems are additional treatment solutions with great effectiveness in removing THMs in drinking water.
How do I get rid of total trihalomethanes?
For trihalomethane removal, aeration - either by diffused-air or with towers - and adsorption - either by powdered activated carbon or granular activated carbon - is effective. The major disadvantage of this approach is that trihalomethane precursors are not removed by aeration.
Does boiling water remove Tthm?
Trihalomethane concentrations were reduced in both chloraminated (74-98%) and chlorinated (64-98%) water upon boiling. Boiling chloraminated water for 1 min reduced chloroform concentration by 75%.
How do you remove trihalomethane from drinking water?
The easiest way to reduce or eliminate THMs in drinking water is to use a water pitcher with a carbon filter, install a tap-mounted carbon filter, or to use bottled water. When using a filter, check to verify that it is certified to remove THMs and follow replacement instructions recommended by the manufacturer.
Does bottled water contain trihalomethanes?
Various trihalomethanes were detected in four brands of bottled water, including Sam's Choice and Acadia, at two to three times greater levels than the bottled water industry's voluntary standard of 10 ppb (IBWA 2008).
What are THM levels?
Trihalomethanes (THMs) are the result of a reaction between the chlorine used for disinfecting tap water and natural organic matter in the water. At elevated levels, THMs have been associated with negative health effects such as cancer and adverse reproductive outcomes.
Are trihalomethanes carcinogenic?
IARC classified trichloromethane and bromodichloromethane as possible human carcinogens, and NTP determined that these chemicals are reasonably anticipated to be human carcinogens.
What are trihalomethanes and haloacetic acids?
Trihalomethanes (THMs) and haloacetic acids (HAAs) are the most common types of disinfection by-products found in chlorinated drinking water. Why is chlorine added to drinking water? Chlorine has been added to drinking water to get rid of harmful micro-organisms since the early 1900s.
Why is drinking water considered a treatment?
Drinking water treatment is a balance between ensuring the proper disinfection of water to control the presence of pathogens that can cause severe acute illness and potentially death, while minimizing the formation of disinfection by-products that are associated with cancer risks over long-term exposures.
What is the chemical that is found in water?
Trihalomethanes in Drinking Water. Trihalomethanes (THMs) are a group of compounds that can sometimes be found in chlorinated water that is drawn from a source with high levels of organic materials. THMs are by-products of the process of disinfecting water (i.e. the addition of chlorine to water systems). THMs are produced when chlorine reacts ...
Why is chlorinated water important?
Chlorine helps to prevent serious illness from organisms in water that can produce disease. Methods for treating drinking water must be designed and operated to remove or inactivate pathogens as a first priority; minimizing the formation of disinfection by-products is ...
Why is chlorine used in water disinfection?
Chlorine is routinely used for drinking water disinfection because it is a very effective way to reduce bacteria, viruses and parasites. Chlorine also helps to reduce bacterial growth, biofilm formation and recontamination of water as it travels from the treatment plant to your home.
What is a THM in water?
Trihalomethanes (THM) in drinking water. Trihalomethanes (THM) in drinking water. Impurities in Water. 0. Trihalomethanes (THM) are a group of four chemicals that are formed along with other disinfection by products when chlorine or other disinfectants used to control microbial contaminants in drinking water react with naturally occurring organic ...
What is the third phase of THM?
It must be emphasized that any changes made to water treatment practices must not compromise the effectiveness of disinfection.
Why is chlorine used in water?
The use of chlorine is, however, essential to maintain the required residual in the water distribution system in order to ensure microbiologically safe water.
When was the THMs guideline established?
The Federal-Provincial Subcommittee on Drinking Water established the current guideline for THMs in 1993. The guideline is based on the risk of cancer reported in animal studies of chloroform, the THM most often present and in greatest concentration in drinking water.
Where are THMs found?
Levels of THMs are generally highest in treated water from sources with high organic matter content, such as rivers and lakes. Lower levels of THMs are usually found when the source water is groundwater.
Is tap water safe?
You do not need to stop drinking tap water unless you are have been advised to do so by the provincial or municipal governments.
Is disinfection a part of drinking water?
Disinfection is an essential component of public drinking water treatment . The health risks from disinfection by-products, including THMs, are much less than the risks from consuming water that has not been appropriately disinfected. ^ Top of Page.
What Are Trihalomethanes?
Trihalomethanes or THMs are a group of four chemical compounds that can form when chlorine and other disinfectants are added to drinking water to control microbial contaminants. The chlorine reacts with organic matter that makes its way into our raw water supplies like surface water, and thus, THMs form.
Effects of Having Trihalomethanes in Drinking Water
Trihalomethanes in drinking water have created a lot of concerns from top resources like the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO). THMs are linked to heart, lung, kidney, liver issues, and central nervous system damage.
Can You Remove Trihalomethanes from Drinking Water?
The answer is yes, but there are challenges. Getting rid of trihalomethanes in drinking water may seem like an impossible task, but it can be done. The best way to keep THMs out of our water is to start at the municipal level, removing or reducing the amount of chlorine added to the water before filtering it.
The Science of Water
Some countless contaminants and toxins lurk within our water. Sometimes it’s hard to keep track! However, with help from the Science of Water, you no longer have to keep track. We know that keeping the water in your home safe and nourishing for you and your family is a top priority, and our team agrees.
Why are THMs in water?
Its formation is due to the chlorine-based disinfectants' reaction with the organic materials present in the untreated water supplies.
How to avoid THMs in water?
Another method to avoid the THMs in the water is through something other than the gas or the hypochlorites as the disinfectants. Some of the possible disinfectants are chlorine dioxide, chloramines, UV light, and ozone. However, they can also produce some harmful by-products after that.
What is reverse osmosis water filtration?
Reverse osmosis is when the dissolved inorganic solids, just like salts, are removed from the water.
What are the factors that affect the formation of THMs?
Some of the reactions that form THMs during the treatment, distribution, and storage within the drinking water systems are influenced by time, pH level, and temperature.
What chemicals are in water?
The chemicals included are chloroform, dibromochloromethane, bromodichloromethane, and bromoform. It is formed when chlorine and other disinfectants people use in the water react naturally with the inorganic and organic matter in the water.
Can you get THMs from drinking water?
Exposure of People from THMs in Drinking Water. People can be exposed to THMs whenever they drink water that is contaminated by such compounds. Apart from this, one can get exposed to THMs whenever they take a shower, bath, or other activities to expose their body to the contaminants.
Is THM in drinking water harmful?
Some of the main health concerns of THM exposure in drinking water are an injury to the kidneys, liver, increased risk of the bladder, and malfunction of the central nervous system. Thus, in this article, we will discuss how we can minimize THMs in drinking water. Also, we will tackle the standards and initiatives set forth by ...
Maximum Contaminant Level
The EPA’s Stage 2 Disinfectants/Disinfection Byproducts Rule sets the US maximum contaminant level for four THMS (chloroform, bromodichloromethane, dibromochloromethane and bromoform) and five HAAs (monochloro‐, monobromo‐, dichloro‐, dibromo‐, and trichloroacetic acids) at 80 μg/L and 60 μg/L, respectively, on the basis of a locational running annual average (as opposed to a system wide average)..
Public Health Concern
The formation of THMS as a result of water chlorination was first discovered in the 1970’s. THMS are considered carcinogenic and an environmental pollutant.
WETS Treatment
In THMS water treatment, it is crucial to identify the optimum approach – as to removal of the organic precursors, removal of the THMS after formation, or a combination of the two, along with optimization of chlorination. Each situation needs to be dealt with on a case-by-case basis, so a well-executed pilot study is essential.