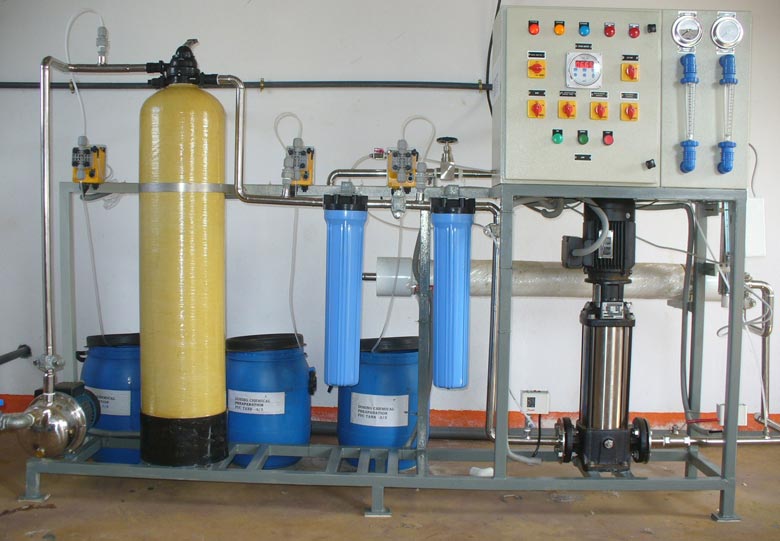

What are the basic elements of a water treatment plant?
The basic elements of a typical large water treatment plant have four objectives: pretreatment, prefiltration, filtration, chemical treatment, and disinfection. Although treatment is necessary to improve the quality of drinking water, the process also creates its own pollution problems.
What are the dimensions of a water treatment plant?
A water treatment plant is designed for 30 million gallons per day (mgd). The flocculator dimensions are length = 100 ft, width = 50 ft, depth = 16 ft. Revolving paddles attached to four horizontal shafts rotate at 1.7 rpm. Each shaft supports four paddles that are 6 in. wide and 48 in. long. Paddles are centered 6 ft from the shaft.
What are centralized water treatment plants?
Centralized water treatment plants are based on coagulation, flocculation and disinfection processes and found to be most cost-effective in treating large quantities of water. However, they entail large infrastructure costs which is difficult to raise in rural regions of developing countries and are generally installed using government funding.
What is a wastewater treatment plant?
A wastewater treatment plant is a place where wastewater from homes and other buildings is collected and processed. WWTP is an abbreviation for Waste-Water Treatment Plant. A wastewater treatment plant is also referred to as a sewage treatment plant.

Is the first structure in a water treatment plant?
The first step in this water treatment plant is that the wastewater drains to the plant with the help of gravity through the main sewer system. A mechanical stage then begins called the preliminary treatment or pre-treatment.
What is flocculation in water treatment?
Flocculation is a water treatment process where solids form larger clusters, or flocs, to be removed from water. This process can happen spontaneously, or with the help of chemical agents. It is a common method of stormwater treatment, wastewater treatment, and in the purification of drinking water.
What are the components of water treatment plant?
Components Of Water Treatment PlantRaw water source, for example, and impounding reservoir, lake, or river canal.Intake well.Water pumping system.Cascade aerator.Alum mixer.Clarifier.Filter bed washing system.Sand filters.More items...•
What are the 3 parts of the water treatment process?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.
What is flocculation process?
Flocculation is a process by which a chemical coagulant added to the water acts to facilitate bonding between particles, creating larger aggregates which are easier to separate. The method is widely used in water treatment plants and can also be applied to sample processing for monitoring applications.
What is flocculant made of?
The aluminum-based flocculants include aluminum sulfate, aluminum chloride, sodium aluminate, aluminum chlorohydrate, and polyaluminum chloride. The iron-based flocculants include ferric chloride, ferric sulfate, ferrous sulfate, and ferric chloride sulfate [15, 69].
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
Public water systems often use a series of water treatment steps that include coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection.
What are the 4 steps of water treatment?
They typically consist of several steps in the treatment process. These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution.
What is the function of water treatment plant?
A water treatment plant is a destination where wastewater (water which is no longer fit for its current purpose) moves to once it leaves homes and businesses through sewage pipes. The sewage system contains miles of pipes below ground where wastewater flows to the treatment plant for processing.
What are the 7 methods of water treatment?
Top 7 Methods of Water TreatmentCoagulation / Flocculation. Coagulation is adding liquid aluminum sulfate or alum and/or polymer to raw or untreated water. ... Sedimentation. When water and flocs undergo the treatment process, they go into sedimentation basins. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Sludge Drying. ... Fluoridation. ... pH Correction.
What is the most important step in water treatment?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.
What is water treatment system?
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, including being safely returned to the environment.
Components Of Water Treatment Plant
Given the industrial process of treating water, a water treatment plant comprises of the following:
Final Words
As is evident from the above description, the packaged drinking water plant is a lengthy and conspicuous one. Several elements need to perform accurately to ensure the final product meets the daily requirements of humans.
How Are Buildings Typically Used at Water Treatment Facilities?
The process for treating water includes many steps to produce potable and safe water for drinking purposes. Water treatment plants typically involve the following steps.
The Benefits of Having Fabric Buildings for Water Treatment Plants
Fabric structures aren’t simply “tents” or makeshift enclosures. Specifically, fabric buildings from Alaska Structures ® offer so much more than just a quick-fix solution to replace or expand water treatment facilities. Engineered fabric structures:
A Modern Building Solution for an Aging Infrastructure Problem
Traditional construction materials such as wood, concrete, brick, and other prefabricated building solutions share the same negative attributes.
What is water treatment?
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, including being safely returned to the environment. Water treatment removes contaminants ...
Why use multiple barrier approach in surface water treatment plant?
In a surface water treatment plant units used are: A multiple barrier approach should be adopted for reliability reasons of safety in the water supply system. In the case of malefaction or maintenance of one unit, the system will be able to continue to operate with the rest of the units being in operation.
What is a water filtration unit?
A filtration unit is built-in into one of the last stages of the water treatment cycle. Filter units aim to remove the suspended solids that were not removed in the previous treatment process. The filters are made out of fine and coarse sand layers were by means of mechanical screening trapping of solid particles in between the grains of sand occur hence purifying and cleaning the water from impurities. Tests of filter performance can be done by assessing the turbidity of a sample of the water.
What is flocculation tank?
Flocculation is the slow mixing process by which fine particulates are caused to clump together into a floc. The floc may then float to the top of the liquid. The design criteria of the flocculation tank are based on previous studies assumed as common practice in the industry.
What is the process of adding chemicals to the water that promotes the clumping of fines found in the
1. COAGULATION. Coagulation is the rapid mixing process of adding compound chemicals to the water that promote the clumping of fines found in the lake (e.g. soil particles) into large flocs thus they can be easily separated. Adding of coagulants such as aluminium sulphate ( alum ), ferric sulphate or sodium aluminate will destabilise colloidal ...
How does sedimentation work?
Sedimentation is the process of removing solid particles by gravity. As per Britannica, a sedimentation tank allows suspended particles present in the water to settle out of the water as the flow rate through the tank is slow. This process allows a layer of sludge, which is a mass of solid particles coming together to form at the bottom of the tank where it can be removed. Assumptions are used to determine dimensions of the tank based on the retention time (RT) and surface overflow rate (SOR). The calculations are done as follow:
Why is water treatment important?
Water treatment removes contaminants and undesirable components or reduces their concentration so that the water becomes fit for its desired end-use. This treatment is crucial to human health and allows humans to benefit from both drinking and irrigation use.
3. Coagulation
Even if the water appears relatively clear and free from large pieces of organic material, looking at a drop under a microscope would probably reveal a world of floating particles and microorganisms. To remove the tiny floaters and swimmers, technicians add chemicals such as aluminum and iron compounds that make them coagulate into small clumps.
4. Flocculation
Flocculation is similar to coagulation but with more dramatic results. In this step, turbines or paddles stir the water for 20 to 30 minutes to increase the frequency with which the smaller pieces bump into each other. This slow agitation causes clumped particles to form larger pieces called flocs.
5. Sedimentation
The flocculated water then rests in a sedimentation basin for 2 to 4 hours. During this time, the flocs gradually sink to the bottom, leaving behind water free from particulate matter. To ensure the sedimentation process removed all impurities, the product flows through a deep layer of sand or anthracite on its way to the final step.
6. Disinfection
The deadliest pathogens in drinking water are invisible to the naked eye. For this reason, the final step is to kill any microorganisms remaining in the otherwise clean drinking water by the addition of disinfectant chemicals. Chlorine is a common substance many plants use, but some also use ozone, chlorine dioxide, or chloramines.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
Wastewater treatment plant is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater and converting it into effluent that can be recycled into the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent has an acceptable environmental impact or is reused for a variety of purposes. A wastewater treatment plant is where the treatment ...
How does a sewage treatment plant filter wastewater?
The wastewater that enters the sewage treatment plant is first filtered through bar screens, a process known as screening. The bar screen separates large trash objects from the wastewater, such as rags, sticks, cans, plastic bags, napkins, sanitary towels, and so on. As a result, screening removes large pieces of trash from the wastewater.
What is the solid component of sewage?
The majority of the solid organic matter (faeces, for example) settles as sludge on the sloping bottom of the sedimentation tank. As a result, the solid component of sewage is known as sludge .
Why is activated sludge returned to the aeration tank?
Some of the activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank to boost the population of aerobic bacteria and accelerate the cleaning of watery waste. The digester tank receives the remaining activated sludge. The water in the second sedimentation tank contains very little organic material and suspended matter.
What is WWTP in water treatment?
WWTP is an abbreviation for Waste-Water Treatment Plant. A wastewater treatment plant is also referred to as a sewage treatment plant. A modern wastewater treatment plant treats wastewater or sewage through a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes until it becomes fit to be discharged into the environment.
Where is sludge removed from sedimentation tanks?
The sludge is removed from the bottom of the first sedimentation tank and placed in a large, closed tank known as the digester tank. Many different types of anaerobic bacteria decompose the organic matter in sludge in the digester tank to produce biogas.
What is a WWTP?
A wastewater treatment plant is a facility that treats wastewater, making it considerably cleaner and safer to be released into water bodies. A wastewater treatment plant is a place where wastewater from homes and other buildings is collected and processed. WWTP is an abbreviation for Waste-Water Treatment Plant.
Where is Bhandup Water Treatment Plant?
Bhandup Water Treatment Plant, Mumbai, India; capacity of 739 million gallons per day. The plant occupies 365 acres at the edge of Sanjay Gandhi National Park, a 40-sq-mile expanse of wooded hills that is home to deer, porcupine, leopards, antelope, monkeys, crocodiles and many species of snakes and birds.
How is water drawn into the plant?
Water is drawn into the plant from two crib structures two miles offshore and transported through tunnels located almost 200 ft beneath the lake and ranging in diameter from 10 to 20 ft. Inside the plant, rotating screens catch fish and debris.
What is the capacity of the Eugene Sawyer water purification plant?
8. Eugene Sawyer Water Purification Plant, Chicago; capacity of 720 million gallons per day. The Chicago Bureau of Engineering designed the plant, which was originally known as the South Water Filtration Plant. Opened in 1947, it was renamed in 2016.
What is the last chemical added to Chicago water?
One of the very last chemicals added, polyphosphate, is used to coat the inside of Chicago's pipes, preventing the lead in old plumbing from leaching into the water supply. Then, the water is pumped into settling tanks, where the floc sinks to the bottom. This sedimentation phase eliminates roughly 90% of the particulate matter from the water.
How many lakes are there in the Mumbai water plant?
The park encompasses two lakes, Vihar Lake and Tulsi Lake, that serve as the plant's reservoirs. In 2016, a 15-kilometer-long, 5.5-meter-dia tunnel was completed in order to phase out aboveground pipelines bringing water to the plant from four reservoirs northeast of Mumbai.
How big is the Michigan plant?
Designed and built by Chicago’s Bureau of Engineering, the plant began operating in 1964. It stands on a man-made, 61-acre peninsula that extends into Lake Michigan. The original 1,100-ft-long, 180-ft-wide plant extended from 36 ft below lake level to 25 ft above.
Where does the Cantareira plant get its water from?
The plant began operating in 1973. It receives raw water from the Cantareira system, a complex of six reservoirs in the hills north of the city. The plant uses alum to coagulate and flocculate particles, which are removed by settling and filtration. It has six settling basins.
How Are Buildings Typically Used at Water Treatment Facilities?
The Benefits of Having Fabric Buildings For Water Treatment Plants
- Fabric structures aren’t simply “tents” or makeshift enclosures. Specifically, fabric buildings from Alaska Structures®offer so much more than just a quick-fix solution to replace or expand water treatment facilities. Engineered fabric structures: 1. Are custom-designedto meet the unique building requirements of your water treatment plant 2. Meet location-specific wind and snow loa…
A Modern Building Solution For An Aging Infrastructure Problem
- Traditional construction materialssuch as wood, concrete, brick, and other prefabricated building solutions share the same negative attributes.
Fabric Structures For Water Treatment Plants
- Fabric structures for water treatment plants are a modern building solution that offers many cost-saving advantages over typical construction methods, including: 1. Shorter construction schedules 2. Reduced labor costs 3. Minimal equipment and tools needed for assembly 4. Ability to install and safely anchor onto virtually any level surface 5. Relo...