
Medication
12 rows · With advances in myasthenia gravis treatment, most patients have very good outcomes. The ...
Procedures
· How is myasthenia gravis treated? Treatment is directed first toward improving symptoms. The drug most commonly used is pyridostigmine. Pyridostigmine prolongs the time that Ach stays in the neuromuscular junction, thus giving it more of a chance to bind to the reduced number of AchR receptors.
Nutrition
Abstract With specialized care, patients with myasthenia gravis can have very good outcomes. The mainstays of treatment are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, and immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory therapies. There is good evidence thymectomy is beneficial in thymomatous and nonthymomatous disease.
How to treat myasthenia gravis naturally?
· In 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the use of eculizumab for the treatment of generalized myasthenia gravis in adults who test positive for the antiacetylcholine receptor (AchR) antibody. Anticholinesterase medications.
What to do if you have myasthenia gravis?
How can I alleviate myasthenia gravis symptoms? If you have MG, these steps can ease fatigue and boost muscle strength: Avoid going outside in the middle of a hot day. Apply cold compresses to your neck and forehead when you feel overheated. (Heat can make MG symptoms worse.)
What tests can help diagnose myasthenia gravis?
· Treatment options for generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) include medication, surgery, or a combination of therapies. Most people with gMG lead full, active lives with an effective treatment. You...
What symptoms would you expect with myasthenia gravis?
· The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today approved Vyvgart (efgartigimod) for the treatment of generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) in adults who test positive for the anti-acetylcholine receptor...
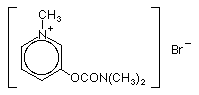
What is the standard treatment for myasthenia gravis?
The first medicine used for myasthenia gravis is usually a tablet called pyridostigmine, which helps electrical signals travel between the nerves and muscles. It can reduce muscle weakness, but the effect only lasts a few hours so you'll need to take it several times a day.
Is myasthenia gravis completely curable?
There's no cure for myasthenia gravis, but treatment can help relieve signs and symptoms, such as weakness of arm or leg muscles, double vision, drooping eyelids, and difficulties with speech, chewing, swallowing and breathing.
How long does it take to recover from myasthenia gravis?
Generally, it resolves in 2 to 3 months.
What triggers myasthenia gravis?
Cause of myasthenia gravis Myasthenia gravis is caused by a problem with the signals sent between the nerves and the muscles. It's an autoimmune condition, which means it's the result of the immune system (the body's natural defence against infection) mistakenly attacking a healthy part of the body.
Is myasthenia gravis a terminal?
Currently, there's no cure for myasthenia gravis. However, available treatments usually can control symptoms, allowing those diagnosed with the condition to lead relatively normal lives. In addition, most people with myasthenia gravis have a normal life expectancy.
What is the life expectancy of a person with myasthenia gravis?
There is no cure for MG, but most people with the condition have a normal life span. Only 3 to 4 out of every 100 people with MG die because of MG. Years ago, early death occurred in over a third of people with MG. Today, if someone dies of MG, death is usually due to a myasthenic crisis or a thymoma.
What happens if myasthenia gravis is left untreated?
This causes muscle weakness that can become severe enough to interfere with breathing and swallowing saliva or food, resulting in food or saliva going into your airway. Serious complications like these can result in injury or even death if left untreated.
What foods should I avoid with myasthenia gravis?
If your MG medication causes diarrhea or stomach upset, avoid foods that are fatty, spicy or high in fiber. Avoid dairy foods, except for yogurt which can sooth digestive problems. Good choices include mild foods like bananas, white rice, eggs and chicken. Diarrhea can lower potassium levels.
What is MG in neuromuscular transmission?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is the most common acquired disorder of neuromuscular transmission. It occurs due to the production of pathogenic autoantibodies that bind to components of the neuromuscular junction, the most common being the acetylcholinesterase receptor (AChR). The incidence is estimated at 0.3 to 2.8 per 100,000 and the worldwide prevalence at 700,000.1In 1934, cholinesterase inhibition was demonstrated as the first effective treatment for MG.2Until the last 20 years, most MG treatment was investigated through retrospective clinical studies. More recently, there have been a number of randomized controlled clinical trials (Box 1). The decades that various MG treatments were introduced is shown in Box 2. This development has been associated with dramatic improvements in survival and prognosis in MG.3The primary reasons for reduced mortality rates are the improvement in intensive respiratory care and the introduction of immunosuppressive treatments. Although the mortality rate was previously quite high, resulting in the name MG, the current mortality rate in MG is reported as 0.06 to 0.89 per million person-years.4The various treatments for MG and the approximate time lag to onset of action are outlined in Table 1.
Do MG patients respond to acetylcholinesterase inhibitors?
Patients with muscle-specific kinase (MuSK) autoantibody-positive disease have lower response rates than patients with the AChR autoantibody.12,13Juvenile patients with MG may have a particularly robust acetylcholinesterase inhibitor response.14Patients with ocular MG, and particularly those with diplopia, frequently seem to not fully respond to acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, although ptosis seems to be more responsive than ocular paresis.15,16The apparent limited response in patients with diplopia may be because, unless the ocular motility is completely restored, some degree of diplopia will persist.
Does immunotherapy reduce MG?
Several retrospective studies have provided evidence that immunotherapy ( including treatment with corticosteroids) may reduce the risk of developing generalized MG in patients with ocular MG.27,28In the largest of these studies, after 2 years of follow-up, 36% of patients not treated on prednisone progressed to generalized MG versus only 7% of patients treated with prednisone.27In another retrospective study, pyridostigmine was used without prednisone in 59 of 97 patients with ocular MG with 12 developing generalized MG, whereas none of the 38 prednisone-treated cases developed generalized MG.16
Can you take prednisone for myasthenic crisis?
Daily prednisone use is also the rule for patients in myasthenic crisis and for those with worsening symptoms but who are not yet in crisis. A switch to alternate day prednisone can be made months later, when the patient has begun to improve significantly. A daily long-term steroid regimen may be indicated in patients with diabetes and hypertension to avoid wide swings in serum glucose and blood pressure, respectively.
Why is myasthenia gravis worse?
Because myasthenia gravis is marked by use-related weakness in particular muscle groups, repeated activity of affected muscle makes weakness worse. The weakness improves with rest, only to recur as activity resumes. Which muscle groups are affected may vary from person to person. Often, the muscles around the eyes are affected.
What is the site of myasthenia gravis?
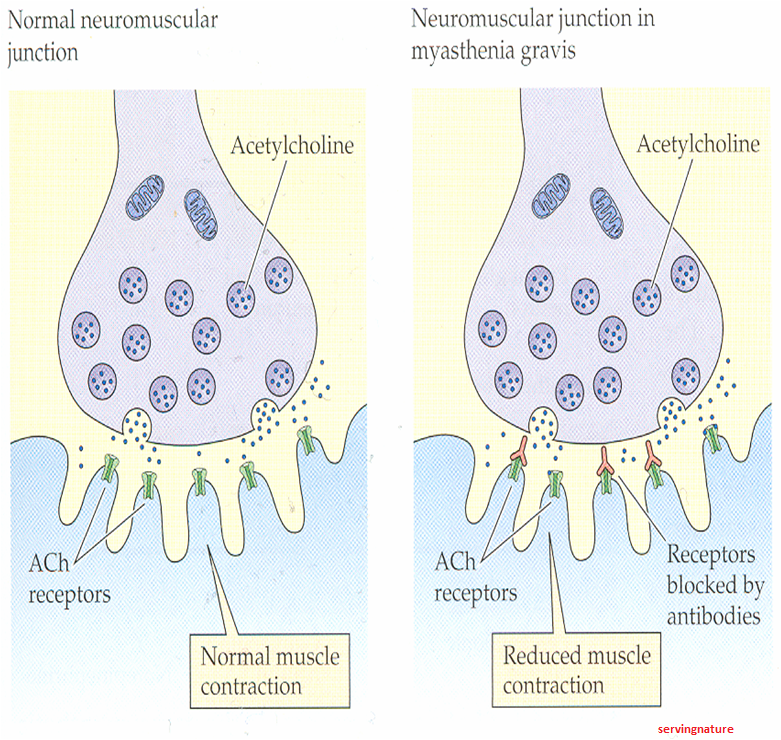
Myasthenia gravis impairs the transmission of signals from nerves to muscles at a site called the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), where nerves make contact with muscle. This causes temporary weakness of muscles in use. When the affected muscle or muscle group is rested, it recovers strength.
What is the protein that attacks the junction of myasthenia gravis?
If you have autoimmune MG, your immune system produces antibodies that inappropriately attack certain proteins at the junction. One such protein is the acetylcholine receptor (AchR), located on the muscle membrane at the junction.
What is the best treatment for achy spondyloma?
Treatment is directed first toward improving symptoms. The drug most commonly used is pyridostigmine. Pyridostigmine prolongs the time that Ach stays in the neuromuscular junction, thus giving it more of a chance to bind to the reduced number of AchR receptors.
How many people have myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) — a medical term that translates as “serious muscle weakness” — is a rare neuromuscular disease. An estimated 30,000 to 60,000 people in the United States have this disorder, which affects people of all ages, sexes, and ethnicities. Recently updated consensus guidelines have added to our knowledge of different forms ...
How often is eculizumab given?
Eculizumab is given through an injection into a vein once a week for five weeks, then every two weeks after this initial period.
What to discuss with a neurologist about treatment?
As new information about treatment becomes available, discuss possible treatment changes with your neurologist, who can help ensure that the treatment choices you make align with your goals for improvement, as well as your personal values and preferences.
What is the treatment for myasthenia gravis?
The mainstays of treatment are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, and immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory therapies.
Is thymectomy good for myasthenia gravis?
The mainstays of treatment are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, and immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory therapies. There is good evidence thy mectomy is beneficial in thymomatous and nonthymomatous disease.
Is thymectomy an off label treatment?
The mainstays of treatment are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, and immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory therapies. There is good evidence thymectomy is beneficial in thymomatous and nonthymomatous disease. Nearly all of the drugs used for MG are considered "off-label.". The 2 exceptions are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors ...
What are the symptoms of myasthenia gravis?
During a physical exam for myasthenia gravis, your health care provider may observe signs such as a droopy eyelid, difficulty holding your arms out at shoulder length for a reasonable length of time, or a weak grasp. Blood tests may reveal the presence of acetylcholine-receptor or muscle-specific tyrosine kinase-seropositive (MuSK) antibodies. Specialized tests use electricity to stimulate muscles, and at the same time, measure the strength of muscle contraction.
What is a myasthenic crisis?
Myasthenic crisis is a sudden worsening of symptoms, often with difficulty breathing and/or swallowing. It is life-threatening and requires treatment in the intensive care unit with temporary placement on a respirator. Myasthenic crisis can occur during a severe infection, so you'll probably need to be treated with antibiotics, as well.
What is the immunotherapy agent for pyridostigmine?
These include azathioprine ( Imuran ), cyclosporine ( Neoral ), eculizumab (Solaris) mycophenolate (CellCept), and prednisone to suppress the immune system.
Can myasthenia gravis be treated with antibiotics?
Myasthenic crisis can occur during a severe infection, so you'll probably need to be treated with antibiotics, as well. Some women notice that their symptoms worsen around the time of their menstrual period. Pregnancy's effect on myasthenia gravis is unpredictable.
Is there a cure for myasthenia gravis?
There is no cure for myasthenia gravis, but it is treated with medications and sometimes surgery. You may be put on a drug called pyridostigmine ( Mestinon ), that increases the amount of acetylcholine available to stimulate the receptors.
Does myasthenia gravis decrease muscle strength?
If you have myasthenia gravis, muscle strength will decrease predictably over the course of testing. You may be given certain medications -- edrophonium or neostigmine -- as part of a diagnostic exam.
Can myasthenia gravis be prevented?
There are no known ways to prevent myasthenia gravis. If you already have the condition, take these steps to avoid an exacerbation:
How to treat myasthenia gravis?
Treatments include: Medications: Cholinesterase inhibitors (anticholinesterase) boost signals between nerves and muscles to improve muscle strength.
How to stop MG from getting worse?
Avoid going outside in the middle of a hot day. Apply cold compresses to your neck and forehead when you feel overheated. (Heat can make MG symptoms worse.)
What is MG in medical terms?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own parts. MG affects the communication between nerves and muscles (the neuromuscular junction). People with MG lose the ability to control muscles voluntarily.
What is MG in the body?
MG is an autoimmune disease. For unknown reasons, the body’s immune system attacks itself. In someone with a healthy immune system, nerves and muscles communicate a bit like a tiny baseball game: Nerves (the pitcher) send signals to muscles (the catcher) across a synapse (connection) called the neuromuscular junction.
What is IV infusion?
Monoclonal antibodies: You receive intravenous (IV) infusions of biologically engineered proteins. These proteins suppress an overactive immune system. IV immunoglobulin (IVIG): You receive IV infusions of donor antibodies over a period of two to five days. IVIG can treat myasthenia crisis as well as generalized MG.
How many people have MG?
MG affects about 20 out of every 100,000 people. Experts estimate that 36,000 to 60,000 Americans have this neuromuscular disease. The actual number of people affected may be higher, as some people with mild cases may not know they have the disease.
How old is MG?
MG mostly affects women aged 20 to 40 and men aged 50 to 80. About one in 10 cases of MG occur in teenagers (juvenile MG). The illness can affect people of all ages but is rare in children. These factors increase risk: History of other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Infections.
What is the treatment for myasthenia gravis?
Treatment options for generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) include medication, surgery, or a combination of therapies.
What is the most common treatment for GMG?
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are a common gMG treatment used since the 1960s, according to a 2019 research review.
What is gMG in medical terms?
Generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) is a chronic autoimmune disease that interferes with signals between nerve cells and muscles. This can result in muscle weakness that worsens with activity.
How can a doctor help you find the right treatment for a symtom?
Your doctor can help you find the right treatment based on your overall health, age, and severity of symptoms.
What is the purpose of pyridostigmine?
This type of oral medication, which includes pyridostigmine (Mestinon), improves signaling between nerve cells and muscles.
What is the goal of treatment?
The goal of treatment is to manage symptoms such as:
Is there a cure for a syphilis?
While there’s no cure for the condition yet, a range of treatments can help you manage symptoms and lead a full, active life.
Thymectomy
Thymectomy is surgery to remove the thymus gland. It has been around for a long time, but only in 2016 did a thorough study confirm that it works for myasthenia gravis.
Monoclonal Antibodies
These newer medications target specific parts of the immune system. Eculizumab (Soliris) blocks the part of the immune system called the terminal complement cascade, which binds to antibodies and damages the junction between the nerve and muscle (neuromuscular junction). Sometimes the effects of this drug are dramatic.
New Drugs in the Pipeline
Another new drug called efgartigimod is in clinical trials. It leads to the rapid removal of antibodies, including the autoantibodies that cause myasthenia gravis. It has an effect similar to plasma exchange, but it's easier to use. In fact, I've called this drug "plasma exchange in a bottle."
Much Less Serious
We now have a large group of treatments for myasthenia gravis and more coming down the pipeline. Nearly everybody with this condition can now be well treated and managed.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Your doctor will review your symptoms and your medical history and conduct a physical examination. Your doctor might use several tests, including: