Treatment can be chemotherapy, HER2-targeted therapy, immunotherapy or hormone therapy. Neoadjuvant therapy may also be called preoperative therapy. Some women with early breast cancer may have neoadjuvant therapy as a first treatment. Neoadjuvant therapy may shrink a tumor enough so lumpectomy becomes an option instead of mastectomy.
What is the best treatment for breast cancer?
This may include: 1 Chemotherapy. 2 Hormone therapy (tamoxifen, an aromatase inhibitor, or one followed by the other). 3 HER2 targeted drugs, such as trastuzumab (Herceptin) and pertuzumab (Perjeta). 4 Some combination of these.
What are the treatment options for Stage I to III breast cancer?
Treatment for stages I to III breast cancer usually includes surgery and radiation therapy, often along with chemo or other drug therapies either before or after surgery.
What is the best treatment for triple negative breast cancer?
Chemotherapy is usually the standard treatment. An immunotherapy drug, atezolizumab (Tecentriq), has been approved for use along with the chemotherapy drug, albumin-bound paclitaxel (Abraxane), for people with advanced triple negative breast cancer whose tumor makes the PD-L1 protein.
What is the treatment for HER2-positive breast cancer?
In some cases, additional chemo is given after surgery as well. After surgery, some women with HER2-positive cancers will be treated with trastuzumab (with or without pertuzumab) for up to a year.

Is 1.3 cm a large breast tumor?
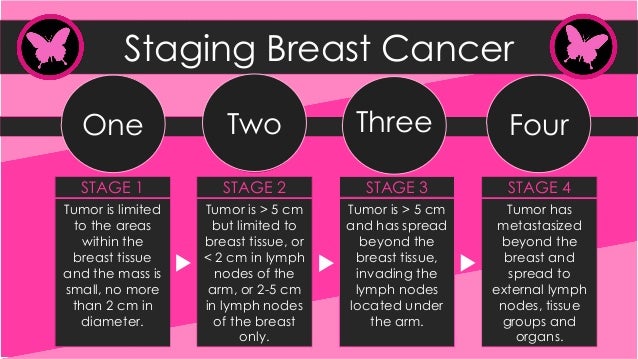
T1: The tumor is 2 cm (0.79 inches (in)) or less in diameter. T2: The tumor is more than 2 cm (0.79 in) but less than 5 cm (1.97 in) across. T3: The tumor is larger than 5 cm (1.97 in) in width. T4: The tumor can be of any size but is growing into the chest wall or skin.
Is a 1 cm tumor big?
The smallest lesion that can be felt by hand is typically 1.5 to 2 centimeters (about 1/2 to 3/4 inch) in diameter. Sometimes tumors that are 5 centimeters (about 2 inches) — or even larger — can be found in the breast.
Do you need chemo for Stage 1 breast cancer?
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is not usually offered for stage 1 breast tumours. It may be offered after surgery (called adjuvant therapy) for these tumours if there is a high risk that the cancer will come back (recur). Find out more about the risk of breast cancer recurrence and adjuvant therapy.
What is the most common treatment for Stage 1 breast cancer?
Surgery is the main treatment for stage I breast cancer. These cancers can be treated with either breast-conserving surgery (BCS; sometimes called lumpectomy or partial mastectomy) or mastectomy.
What stage is a 1cm breast tumor?
T1: Tumor is smaller than 2 cm across. T2: Tumor is 2 to 5 cm across. T3: Tumor is larger than 5 cm across. T4: Any size tumor is growing into chest walls or skin.
Can a 1cm breast tumor spread?
Many breast cancers do not spread to lymph nodes until the tumor is at least 2 cm to 3 cm in diameter. Some types may spread very early, even when a tumor is less than 1 cm in size.
Is mastectomy recommended for Stage 1 breast cancer?
If you receive a diagnosis of stage 1 breast cancer, your doctor may recommend local treatments such as surgery and radiation therapy to treat your breast cancer at the site. Both lumpectomy and mastectomy are options for stage 1 breast cancer.
How long is chemotherapy for stage 1 breast cancer?
Typically, if you have early-stage breast cancer, you'll undergo chemotherapy treatments for three to six months, but your doctor will adjust the timing to your circumstances. If you have advanced breast cancer, treatment may continue beyond six months.
Do you need radiation for Stage 1 breast cancer?
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors.
How soon after breast cancer diagnosis do you start treatment?
Waiting between 31 and 90 days to first treatment after diagnosis with breast cancer may be beneficial for doctors and patients who want a more extensive diagnostic plan and additional time to make decisions, according to the results of a new study.
What stage of breast cancer requires mastectomy?
A mastectomy may be a treatment option for many types of breast cancer, including: Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), or noninvasive breast cancer. Stages I and II (early-stage) breast cancer. Stage III (locally advanced) breast cancer — after chemotherapy.
What is the easiest breast cancer to treat?
Ductal carcinoma in situ or DCIS The cancer cells have not spread through the walls of the ducts into the nearby breast tissue. Nearly all women with DCIS can be cured.
What is the treatment for stage IV breast cancer?
Treatment for stage IV breast cancer is usually a systemic (drug) therapy.
What is the difference between stage 2 and stage 3 breast cancer?
Stage II: These breast cancers are larger than stage I cancers and/or have spread to a few nearby lymph nodes. Stage III: These tumors are larger or are growing into nearby tissues (the skin over the breast or the muscle underneath), or they have spread to many nearby lymph nodes. Treatment of Breast Cancer Stages I-III.
What is stage 0 breast cancer?
Stage 0 means that the cancer is limited to the inside of the milk duct and is non-invasive. Treatment for this non-invasive breast tumor is often different from the treatment of invasive breast cancer. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a stage 0 breast tumor. Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) used to be categorized as stage 0, ...
Is lobular carcinoma in situ a stage 0 tumor?
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a stage 0 breast tumor. Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) used to be categorized as stage 0, but this has been changed because it is not cancer. Still, it does indicate a higher risk of breast cancer. See Lobular Carcinoma in Situ (LCIS) for more information.
What kind of treatment is needed for breast cancer?
The further breast cancer progresses, the greater the combination of therapies a person needs.
How much does breast cancer cost?
The CDC adds that the total medical cost of breast cancer care in the United States is $16.5 billion, and this accounts for 13% of all cancer treatment costs. The cost an individual might pay for breast cancer depends on their health insurance coverage.
How many percent of breast cancer is triple negative?
Treatment for triple-negative breast cancer. Triple-negative breast cancer makes up 10–20% of breast cancers. This type of breast cancer does not respond to hormone therapy or therapies that treat cancer cells with HER2 proteins. Because of this, triple-negative breast cancer has fewer treatment options.
What is the difference between radiation and hormone therapy?
Internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance in needles, catheters, or wires that a healthcare professional places into, or near, the cancer. Hormone therapy: Some cancer cells use hormones to grow. Hormone therapy removes hormones or blocks their action. This stops the cancer cells from growing.
How big is a stage 3 breast tumor?
A person has stage 3 breast cancer when a tumor is larger than 5 cm in length and is growing in either the muscles over and under the breast. There may also be a considerable number of cancer cells in the lymph nodes.
What is the first step for breast cancer?
People with stage 1 breast cancer will usually undergo surgery first and then receive radiation therapy. If the cancer is at stage 2 or 3, a doctor will prescribe some drug therapies before surgery.
Where does cancer spread?
This means that the cancer has spread beyond the breast and lymph nodes and that secondary tumors are growing in other areas of the body. These areas usually include the bones, liver, lungs, and other organs that receive and process a lot of blood. At this stage, drugs are the main therapy options.
Why is tumor size important in breast cancer?
Tumor size is an important factor in breast cancer staging, and it can affect a person’s treatment options and outlook. Tumors are likely to be smaller when doctors detect them early, which can make them easier to treat. However, the size of the tumor is only one of the factors that doctors consider when staging a person’s breast cancer.
What is the survival rate for breast cancer?
The overall 5-year relative survival rate for breast cancer is 90% .
What are the factors that determine the stage of breast cancer?
However, doctors also take into account several other factors, including: lymph node involvement . the location of the cancer and whether it has spread. hormone receptor status.
What hormones are used to test for breast cancer?
The receptors are proteins that respond to the hormones estrogen and progesterone by telling the cancer cells to grow.
How do doctors determine if breast cancer has spread?
They do this by removing one or more of the lymph nodes in the armpit and examining them under a microscope.
What is the term for cancer that spreads from the breast to the brain?
Metastasis. Metastasis is when cancer spreads from its original location in the breast to distant parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs, brain, or bones. The symptoms of metastatic breast cancer depend on which organs the cancer has spread to, and they can vary greatly.
What is HER2 in cancer?
HER2 status refers to whether breast cancer cells are producing too much of a protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). Doctors test for HER2 status by taking a sample of the cancer and sending it to a laboratory for analysis.
What is the first step in treating breast cancer?
Surgery. Surgery is usually the first step in treating early breast cancer. You may have a mastectomy (the entire breast is removed) or a lumpectomy (only the tumor and some surrounding tissue are removed). With either type of surgery, some lymph nodes in the underarm area (axillary lymph nodes) may be removed to find out if they contain cancer.
How to treat breast cancer locally?
Treatment for locally advanced breast cancer usually begins with neoadjuvant therapy. Neoadjuvant therapy helps shrink the tumor (s) in the breast and lymph nodes so surgery can more easily remove all the cancer. Learn more about neoadjuvant therapy.
What is neoadjuvant therapy?
Neoadjuvant therapy is treatment given before surgery. Treatment can be chemotherapy, HER2-targeted therapy or hormone therapy. Neoadjuvant therapy may also be called preoperative therapy. Some women with early breast cancer may have neoadjuvant therapy as a first treatment. Neoadjuvant therapy may shrink a tumor enough so a lumpectomy becomes an ...
What is a locally advanced breast cancer?
Locally advanced breast cancer. Locally advanced breast cancer has spread beyond the breast to the chest wall or the skin of the breast. Or, it has spread to many axillary lymph nodes. Locally advanced breast cancer can also refer to a large tumor.
What is tumor profiling?
Tumor profiling may also be called genomic testing or molecular profiling . Learn more about factors that affect treatment options. For a summary of research studies on chemotherapy and early breast cancer, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section.
How long do women live with breast cancer?
Women diagnosed with breast cancer that had spread to nearby lymph nodes, but not to other parts of the body were 86 percent as likely to live 5 years beyond diagnosis as women in the general population. With recent improvements in treatment, survival for women diagnosed today may be even higher. However, prognosis for breast cancer depends on each ...
Where is breast cancer found?
Early breast cancer is contained in the breast. Or, it has only spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area (axillary lymph nodes). This term often describes stage I and stage II breast cancer.
What is the lymph node closest to breast cancer called?
When early-stage breast cancer is removed, the lymph node closest to the cancer – called the sentinel node – often is removed and sent to a pathologist for evaluation. Removing just this one node is called sentinel node biopsy ...
How many women were diagnosed with breast cancer in 2011?
The researchers looked at the records of more than 74,300 women who were diagnosed between 1998 and 2011 with early-stage breast cancer that was 5 cm or smaller in size (smaller than 2 inches), had negative margins, and had two or fewer positive sentinel nodes. All the women had lumpectomy plus whole-breast radiation therapy.
What does it mean when cancer cells are in the sentinel node?
If cancer cells are in the sentinel node, it means the cancer has spread beyond the breast. Until recently, doctors thought that more treatment was necessary to reduce the risk of the cancer coming back (recurrence), including removing other underarm lymph nodes (called axillary node surgery/dissection). But a practice-changing study, called the ...
How many women had mastectomy in 2011?
22% of women who had mastectomy in 2011 had only sentinel node surgery. more than 50% of women diagnosed with cancers larger than 5 cm who got no or partial-breast radiation therapy had only sentinel node surgery. The results of this study are both encouraging and concerning. It’s encouraging that most of the women eligible to have only sentinel ...
Do you need axillary node surgery for breast cancer?
Women diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer with one or two positive sentinel nodes who plan to have lumpectomy plus whole-breast radiation don’t need axillary node surgery. Women who have one or more positive sentinel nodes and plan to have mastectomy with no radiation should be offered axillary node surgery.
Can you have more than one lymph node removed?
Most Women Diagnosed With Early-Stage Disease Don’t Have More Than a Few Lymph Nodes Removed. Once you create an account at Breastcancer.org, you can enter information about your breast cancer diagnosis (e.g. breast cancer stage), plan your treatments, and track your progress through treatments.
Is black cancer triple negative?
there were two or more positive nodes. the cancer was grade 3. The researchers said it may be that some doctors aren’ t comfortable only doing a sentinel node biopsy on women diagnosed ...
Common Breast Cancers in Older Adults
The most common cancer diagnosed in this age group is invasive ductal carcinoma, or IDC , followed by invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) . These cancers arise in different tissues of the breast, but are treated in similar ways.
Individualized Breast Cancer Treatment for Older Adults
Tran says her group’s approach to dealing with breast cancer in patients of any age is highly individualized. “We recommend both the treatments and the order in which the patient will receive them, which is very important. For instance, radiation is not common before surgery, since it makes wound healing more difficult.”
Breast Cancer in Patients Age 70 and Older: Questions and Answers
In gauging which treatment might be best for an individual, Tran looks at the characteristics of the tumor. This can help identify tumors that are likely to respond to hormone-blocking therapy alone and those that may respond to other modes of treatment.
A Team Approach to Breast Cancer Treatment
Tran says older patients — or anyone diagnosed with breast cancer — can benefit from getting care at a comprehensive center, such as the one where she performs surgery: the Sullivan Breast Center at Sibley Memorial Hospital in Washington, D.C.