
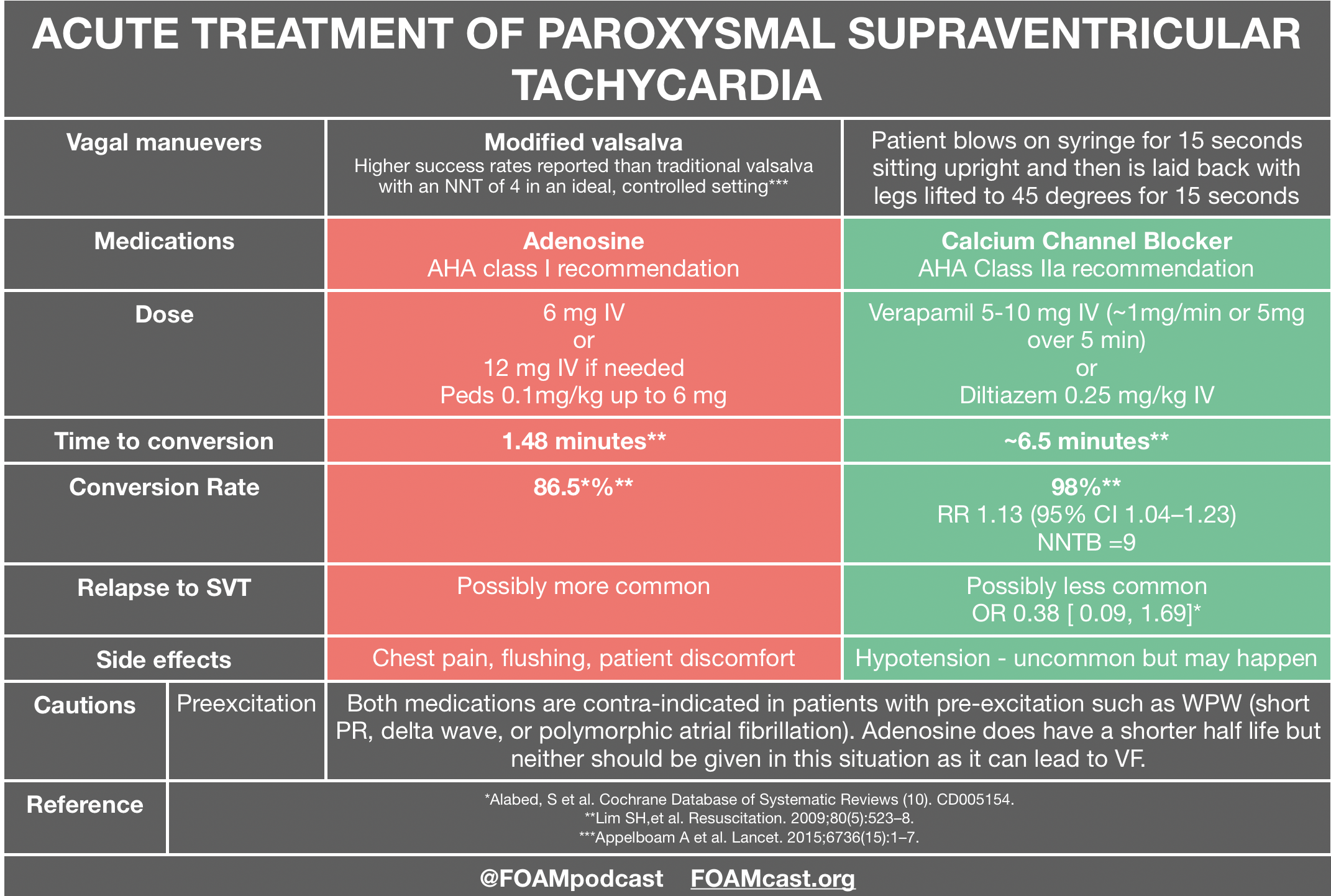
Medication
The patients, a 32-year-old man with paroxysmal AF and a 60-year-old man with persistent AF underwent successful pulmonary vein and posterior wall isolation using a dedicated PFCA catheter powered by the proprietary Adagio iCLAS™ cryoablation and pulsed field ablation (PFA) consoles.
Procedures
- Get on your hands and knees on the floor.
- Hold your back straight in a "tabletop" position.
- Slowly move your hips back and extend your arms, keeping your hands planted.
- Tuck your tailbone to sit your butt on your heels. You may need to spread your knees farther apart to sink back enough.
- Keep breathing as you feel the stretch through your arms and back.
Nutrition
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation are treated with unsynchronized shocks, also referred to as defibrillation. If a patient develops ventricular fibrillation during synchronized cardioversion with a monophasic defibrillator, pulselessness should be verified.
How do you treat ventricular fibrillation?
Your blood pressure drops suddenly and significantly. The longer the body lacks blood, the greater the risk of damage to your brain and other organs. Ventricular fibrillation is the most frequent cause of sudden cardiac death. The risk of other long-term complications depends on how fast you receive treatment.
How do you stop ventricular fibrillation?
How is pulseless V fib treated?
What is the prognosis of ventricular fibrillation (VF)?

What is the first treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
Epinephrine is the first drug given and may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes. If epinephrine is not effective, the next medication in the algorithm is amiodarone 300 mg. Defibrillation and medication are given in an alternating fashion between cycles of 2 minutes of high-quality CPR.
What is the only treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
External electrical defibrillation remains the most successful treatment for ventricular fibrillation (VF). A shock is delivered to the heart to uniformly and simultaneously depolarize a critical mass of the excitable myocardium.
What is the first line treatment for ventricular tachycardia?
Anti-arrhythmic medications are the first-line therapy in emergency departments and CCUs, as discussed earlier. Amiodarone is most commonly used, along with lidocaine, and in some cases procainamide.
What is used to treat ventricular arrhythmias?
Amiodarone and sotalol are the principal agents used in the chronic treatment of VT. In addition, dronedarone and dofetilide, agents approved for the treatment of atrial fibrillation, and ranolazine, an antianginal agent, have been demonstrated to be protective against ventricular arrhythmia in small clinical studies.
What drugs can cause ventricular fibrillation?
The following drug classes may cause monomorphic ventricular tachycardia: anesthetics, antiarrhythmics, anticancer drugs, anticonvulsants, antidepressants, anti-manic medications, antiplatelet, antipsychotic, beta agonists, ergot derivatives, herbs, cocaine, inotropes, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, sympathomimetics, ...
Does a pacemaker help ventricular fibrillation?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the first of a new type of pacemaker that paces both ventricles of the heart to coordinate their contractions and improve their pumping ability.
Do beta blockers prevent ventricular tachycardia?
Beta-blockers are the first-line treatment for long-term symptomatic rate control in patients with a range of cardiac arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.
Does VT always require cardioversion?
Individuals suffering from pulseless VT or unstable VT are hemodynamically compromised and require immediate electric cardioversion to shock them out of the VT rhythm.
Which drug is an antiarrhythmic?
The most common medications in this class are: amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone) flecainide (Tambocor) ibutilide (Corvert), which can only be given through IV.
Which drug is used to treat atrial and ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation?
The class III drugs are used to treat primarily atrial fibrillation, however amiodarone is FDA approved only for the treatment of ventricular tachycardia. Amiodarone is very effective however amiodarone toxicity is a concern.
What is the drug of choice for atrial and ventricular tachycardia?
Amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone, Nexterone) Amiodarone is the drug of choice for the treatment of hemodynamically unstable VT that is refractory to other antiarrhythmic agents. Prehospital studies currently suggest that amiodarone is safe and efficacious for use in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
What causes ventricular fibrillation?
The heart during ventricular fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation is caused by either a problem in the heart's electrical properties or by a disruption of the normal blood supply to the heart muscle. Sometimes, the cause of ventricular fibrillation is unknown.
What is ventricular fibrillation?
Key points about ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat, that affects your heart’s ventricles. Ventricular fibrillation is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. CPR and defibrillation can restore your heart to its normal rhythm and may be life saving.
What is the procedure to eliminate electrical triggers of V-FIB?
Catheter ablation. This procedure uses energy to destroy small areas of your heart affected by the irregular heartbeat. This rarely used procedure for V-fib looks to eliminate electrical triggers of V-fib.
What is it called when your heart beats in and out of the heart?
This keeps blood flowing throughout your body. An arrhythmia that starts in your ventricle is called ventricular fibrillation. This occurs when the electrical signals that tell your heart muscle to pump cause your ventricles to quiver (fibrillate) instead.
What is an implantable cardiac defibrillator?
Implantable cardiac defibrillators are devices that are implanted within the body that can shock the heart back to normal rhythm within seconds if V-fib is present. Although this device does not necessarily prevent V-fib, it can rapidly and automatically diagnose and treat this potentially fatal heart rhythm.
What is a V-fib?
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) is a dangerous type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat. It affects your heart’s ventricles. Your heart is a muscle system that contains 4 chambers; the 2 bottom chambers are the ventricles. In a healthy heart, your blood pumps evenly in and out of these chambers. This keeps blood flowing throughout your body.
What does it mean when your heart is quivering?
The quivering means that your heart is not pumping blood out to your body. In some people, V-fib may happen several times a day. This is called an “electrical storm.”. Because sustained V-fib can lead to cardiac arrest and death, it requires immediate medical attention.
What causes V-FIB in the heart?
Other causes include electrolyte abnormalities such as low potassium, certain medicines, and certain genetic diseases that affect the heart's ion channels or electrical conduction.
What is VF in cardiac arrest?
Ventricular fibrillation (VF or V-fib) is the most common initial heart rhythm in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), and the most salvageable one . 5 In VF, the etiology of arrest is often attributed to either acute ischemia or non-ischemic arrhythmia. 8
How many joules should a defibrillator be?
If the defibrillator is biphasic, the manufacturer recommended joules should be selected (usually 120 to 200 joules). If the amount is unknown, use the maximum available and subsequent doses should be equivalent, and possibly higher. 1.
What is the most important intervention for cardiac arrest?
Irrespective of the cause of cardiac arrest, the most important interventions are early recognition and calling for help—including appropriate management of the deteriorating patient—early defibrillation, high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) with minimal interruption of chest compressions, and treatment of reversible causes. 6
What are the causes of VF?
The easiest way to remember the most common causes of VF are to review the reversible “Hs and Ts” in cardiac arrest. The Hs include hypoxia, hypovolemia, hypothermia, hyper/hypokalemia, and hydrogen ions (acidosis). The Ts are tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, toxins, and thrombosis (pulmonary or coronary).
What are the symptoms of ventricular fibrillation?
These warning signs may include: Chest pain. Very fast heartbeat (tachycardia) Dizziness. Nausea.
What to do if you have a fast heartbeat?
If you see someone collapse, seek emergency medical help immediately. Follow these steps: Call 911 or your local emergency number . If the person is unconscious, check for a pulse.
What causes the ventricles to quiver uselessly instead of pumping blood?
In ventricular fibrillation, rapid, irregular electrical signals cause the ventricles to quiver uselessly instead of pumping blood. To understand how ventricular fibrillation occurs, it may be helpful to know how the heart normally beats.
What causes the ventricles to contract?
In a normal heart rhythm, electrical signals travel from the heart's upper chambers (atria) to the heart's lower chambers (ventricles), causing the ventricles to contract and pump blood. In ventricular fibrillation, rapid, irregular electrical signals cause the ventricles to quiver uselessly instead of pumping blood.
How to do CPR with no pulse?
If no pulse, begin CPR to help keep blood flowing through the body until an automated external defibrillator (AED) is available . The American Heart Association recommends hands-only CPR. Push hard and fast on the person's chest — about 100 to 120 times a minute.
What causes sudden cardiac death?
The longer the body lacks blood, the greater the risk of damage to your brain and other organs. Ventricular fibrillation is the most frequent cause of sudden cardiac death. The risk of other long-term complications depends on how fast you receive treatment.
What is the best medication for ventricular fibrillation?
Arrhythmia medications may be prescribed to help control general disturbances in heart rhythms. Anti-arrhythmic drugs may be used for emergency or long-term treatment of ventricular fibrillation. Those at risk of ventricular fibrillation, or sudden cardiac arrest, are commonly prescribed drugs called beta blockers. 1
Why do cardiologist do ventricular fibrillation?
While this procedure is typically used for the treatment of severe coronary artery disease, if ventricular fibrillation occurs due to a heart attack , a cardiologist may recommend this procedure in order to reduce the risk of future episodes.
How long does ventricular fibrillation last?
If nonsustained, meaning that the rhythm abnormality lasts less than 30 seconds, symptoms may not arise.
What causes ventricular tachycardia?
A variety of health conditions can also lead to ventricular tachycardia. Some of these include: 1 Congenital (present at birth) heart disease 2 A history of heart attack 3 Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy) that causes weakened, stretched, or thickened heart muscle 4 Prolonged, untreated ventricular tachycardia 5 Issues with the aorta, the largest artery leaving the heart 6 Very high or very low potassium levels in the blood 7 Sepsis (severe body infection) 3
How many people die from ventricular fibrillation?
In the U.S., about 300,000 people die suddenly from ventricular fibrillation annually. 2 Ventricular fibrillation is sometimes triggered by a heart attack and can further cause blood pressure to fall, resulting in a shortage of blood supply and oxygen to vital organs, including the brain.
What causes a thickened heart muscle?
Some of these include: Congenital (present at birth) heart disease. A history of heart attack. Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy) that causes weakened, stretched, or thickened heart muscle. Prolonged, untreated ventricular tachycardia. Issues with the aorta, the largest artery leaving the heart.
What to do if there is no pulse?
If there is no pulse, immediately begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to maintain as much blood flow to the organs as possible until a portable automated external defibrillator (AED) can be applied and used to deliver an electrical shock (defibrillation) to the heart.
Diagnosis and Tests
Ventricular fibrillation is usually confirmed by an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), especially after a person has been resuscitated from cardiac arrest. This is also useful to determine the heart’s ability to function going forward.
Management and Treatment
The condition is a life-threatening medical emergency and every minute counts. The following actions can help save the life of someone who has gone into sudden cardiac arrest because of ventricular fibrillation:
Frequently Asked Questions
Atrial fibrillation is similar to ventricular fibrillation, but it’s happening in the upper chambers of the heart, called the atria. When the atria fibrillate, they beat very fast (sometimes several hundred times per minute). This can cause blood to collect in the atria and over time, this can cause the atria to stretch and enlarge.
What to do if you have a V-fib?
Step 2: Defibrillation to fix your heart rhythm. Step 3: Medication to make the rhythm stable again. Defibrillators for V-fib.
What are the symptoms of ventricular fibrillation?
The main symptom is fainting. You may also have symptoms of ventricular tachycardia (VT). This is when the lower chambers of your heart beat too fast. It can lead to V-fib. Signs and symptoms of VT include: Chest pain. Pounding or fast heartbeat.
What are the complications of V-FIB?
V-fib can lead to serious complications including: Injuries from CPR. Skin burns from defibrillation. Brain injury from a lack of oxygen. Injury to your heart muscle. Death. Ventricular Fibrillation Prevention. You can’t completely prevent an episode of ventricular fibrillation.
What tests are used to check for heart damage?
Tests of how well your heart works, such as an EKG. Blood tests to look for heart damage. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI exams, and echocardiograms. Ventricular Fibrillation Treatment. V-fib comes on quickly and needs treatment just as fast.
Why do doctors not know what causes ventricular fibrillation?
For instance, it happens most often during or right after a heart attack. That may be because the heart’s electrical signals can become unstable when there isn’t enough blood flow.
What is the heart muscle called that keeps your heart from pumping blood the way it should?
Ventricular fibrillation, or V-fib, is a dangerous problem with your heart rhythm (called an arrhythmia) that keeps your heart from pumping blood the way it should. It is a medical emergency. Your heart muscle has four main sections, called chambers. The bottom two chambers are the ventricles.
What happens if you have a V-FIB?
Shortness of breath. Passing out. Sudden cardiac arrest is the worst thing that can happen with V-fib. The two main signs are not responding to someone touching or speaking to you, and having severe problems breathing (gasping for air or not breathing at all).
Drugs used to treat Ventricular Fibrillation
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
What Is Ventricular Fibrillation?
- Ventricular fibrillation is always diagnosed in an emergency situation. A pulse check will reveal no pulse if sudden cardiac death occurred. Tests to diagnose and determine the cause of ventricular fibrillation include: 1. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick and painless test measures th…
Symptoms
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Causes
- Lifestyle changes that help keep your heart as healthy as possible include the following: 1. Eat a healthy diet.Heart-healthy foods include fruits, vegetables and whole grains, as well as lean protein sources such as soy, beans, nuts, fish, skinless poultry and low-fat dairy products. Avoid added salt (sodium), added sugars and saturated fats. 2. Exercise regularly.Get at least 150 min…
Diagnosis
- Some abnormal heart rhythms can be triggered by emotional stress. Taking steps to ease stress and anxiety can help keep your heart healthy. Some types of complementary and alternative therapies may help reduce stress, such as: 1. Yoga 2. Meditation 3. Relaxation or mindfulness techniques Getting support from your loved ones also is key to managing stress.
Treatment