What should you do if you get an uti during pregnancy?
You can help prevent UTIs during your pregnancy by: emptying your bladder frequently, especially before and after sex. wearing only cotton underwear. nixing underwear at night. avoiding douches, perfumes, or sprays. drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated.
How to cure UTI naturally during pregnancy?
You can help prevent UTIs during your pregnancy by:
- emptying your bladder frequently, especially before and after sex
- wearing only cotton underwear
- nixing underwear at night
- avoiding douches, perfumes, or sprays
- drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated
- avoiding any harsh soaps or body wash in the genital area
How do you treat an uti during pregnancy?
- Recognize that some symptoms of a UTI can seem common to a regular pregnancy, like urinating frequently and having a backache. ...
- Sometimes you might not have any symptoms from a UTI, so be sure to see your doctor regularly during pregnancy so you can be screened.
- Consider keeping a diary of how you’re feeling during your pregnancy. ...
Can UTI be harmful during pregnancy?
Well, it is completely fine to experience UTIs when pregnant, but it can make bad impact on your baby if left untreated. Well, only a UTI during pregnancy cannot cause miscarriage, but it can do this misfortune if anyhow it updates itself to full body infections called sepsis.
What is the best treatment for urinary tract infections during pregnancy?
What is UTI during pregnancy?
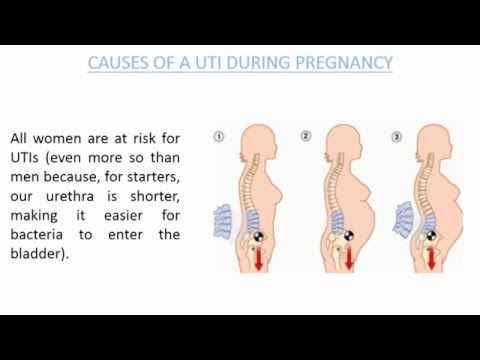
Why are women more susceptible to UTIs?
Does drinking water help with UTIs?
What antibiotics for UTI are safe during pregnancy?
Amoxicillin and cephalexin (Keflex) are usually the first-choice antibiotics for a UTI during pregnancy. Other antibiotics might be used as second-choice options, but only at certain times during pregnancy. Some antibiotics aren't safe at any point during pregnancy.
What is first line treatment for UTI in pregnancy?
Table IIAsymptomatic bacteriuriaFirst line treatmentAmoxicillin 500 mg every 8–12 h – for 3–7 daysCephalexin 500 mg every 12/6 h – for 3–7 daysFDA cat. BAmoxicillin/clavulanic acid 500 mg every 12 h – for 3–7 daysNitrofurantoin 100 mg every 12 h – for 5–7 days*4 more rows
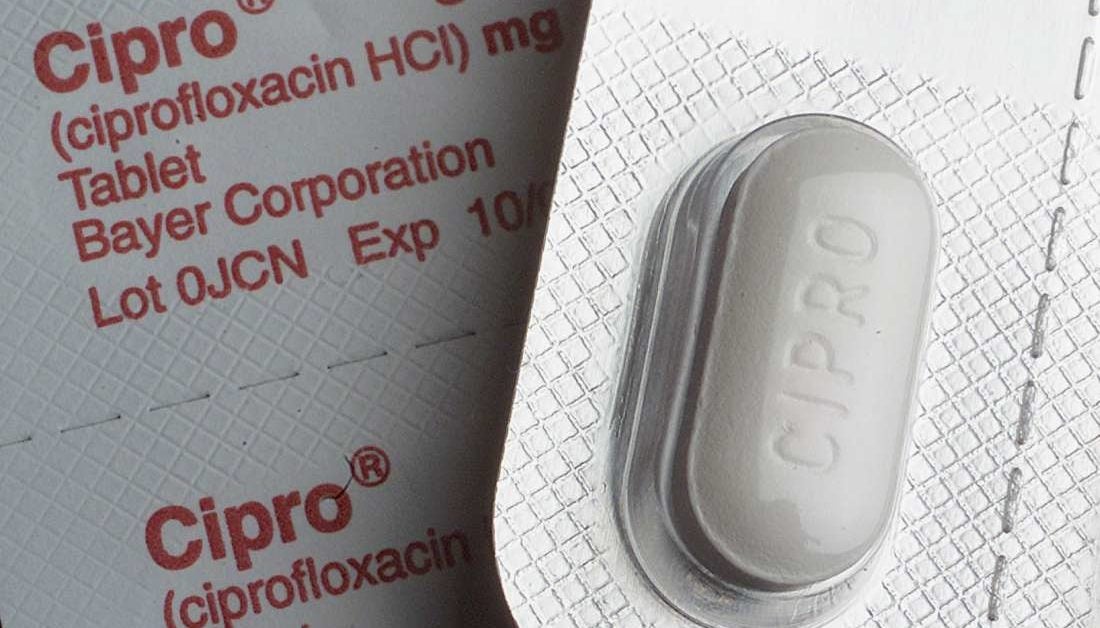
Is ciprofloxacin safe in pregnancy?
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and levofloxacin are also types of antibiotics. These drugs could cause problems with the baby's muscle and skeletal growth as well as joint pain and potential nerve damage in the mother.
What is best antibiotic for urinary tract infection?
Drugs commonly recommended for simple UTIs include:Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra, others)Fosfomycin (Monurol)Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin, Macrobid)Cephalexin (Keflex)Ceftriaxone.
Can I take Cefalexin when pregnant?
Pregnancy and breastfeeding It's usually safe to take cefalexin during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
Why is nitrofurantoin first line for UTI?
Since there is a lower chance of antibiotic resistance with nitrofurantoin and fosfomycin as compared to other classes of antibiotics, they are often used as first-line antibiotics for the treatment of UTI.
Is nitrofurantoin safe in 1st trimester?
While medical literature generally defines nitrofurantoin as an antibiotic that is safe for use during the first trimester of pregnancy, new concerns about a possible association between congenital malformations following exposure to nitrofurantoin during the first trimester of pregnancy have recently surfaced.
Is nitrofurantoin safe in pregnancy?
Nitrofurantoin is commonly prescribed in pregnancy with no known adverse effects on the developing baby. However, it is always a good idea to let your doctor know that you are pregnant if you have taken any medicines in case you need any additional monitoring or treatment.
Why Are Utis Common During pregnancy?
UTIs are common during pregnancy. That’s because the growing fetus can put pressure on the bladder and urinary tract. This traps bacteria or causes...
Is A Uti Dangerous During pregnancy?
Any infection during pregnancy can be extremely dangerous for you and your baby. That’s because infections increase the risk of premature labor.I f...
What Are The Treatment Options?
You can help prevent UTIs during your pregnancy by: 1. emptying your bladder frequently, especially before and after sex 2. wearing only cotton und...
How many pregnant women have UTI?
In this study, about 1 in 10 pregnant women had a diagnosis of a UTI just before or during pregnancy.
Can ACOG prescribe antibiotics to pregnant women?
Healthcare providers of various specialties should be familiar with ACOG’s recommendations about prescribing specific antibiotics to pregnant women and consider the possibility of early pregnancy when treating women of reproductive age.
Can you take antibiotics while pregnant?
Some antibiotic treatments for urinary tract infections (UTIs), such as nitrofurantoin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, have been linked to birth defects. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends avoiding these antibiotic treatments in early pregnancy if possible. A study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that about 4 in 10 women with UTIs during early pregnancy filled a prescription for nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Healthcare providers of various specialties should be familiar with ACOG’s recommendations about prescribing specific antibiotics to pregnant women and consider the possibility of early pregnancy when treating women of reproductive age. To help determine treatment options, women should inform all of their healthcare providers if they are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant.
Why do pregnant women have UTIs?
UTIs are common during pregnancy. That’s because the growing fetus can put pressure on the bladder and urinary tract. This traps bacteria or causes urine to leak.
What is the cause of a UTI?
A UTI occurs when bacteria from somewhere outside of a woman’s body gets inside her urethra (basically the urinary tract) and causes an infection. Women are more likely to get UTIs than men.
Why does urine get more concentrated during pregnancy?
The larger urinary tract, along with increased bladder volume and decreased bladder tone, all cause the urine to become more still in the urethra. This allows bacteria to grow. To make matters worse, a pregnant woman’s urine gets more concentrated. It also has certain types of hormones and sugar.
What are the symptoms of a UTI?
pelvic or lower back pain. frequent urination. feeling that you have to urinate frequently. fever. nausea or vomiting. Between 2 and 10 percent. Trusted Source. of pregnant women experience a UTI. Even more worrisome, UTIs tend to reoccur frequently during pregnancy.
Do women get UTIs during pregnancy?
Women who’ve had UTIs before are more prone to get them during pregnancy. The same goes for women who’ve had several children.
What is a UTI in pregnancy?
A UTI is an infection in any part of the urinary system, including the bladder and kidneys. Research suggests it is common for pregnant women to get UTIs.
How to reduce the chances of getting a UTI?
The following tips may help to reduce a person’s likelihood of getting a UTI: drink plenty of water. drink unsweetened cranberry juice or take cranberry pills. wash carefully around the genitals and anus.
How to get rid of a swollen lining in the urinary tract?
Drinking plenty of water: Water dilutes urine and helps flush bacteria out of the urinary tract. Drinking cranberry juice: According to a 2012 review. Trusted Source. , cranberries contain compounds that may help to stop bacteria from attaching to the lining of the urinary tract.
Why is urine acidic during pregnancy?
The urine is also less acidic and contains more proteins, sugars, and hormones during pregnancy. This combination of factors increases the risk of a UTI occurring. Women are also susceptible to UTIs during and after giving birth. During labor, there is an increased risk of bacteria entering the urinary tract.
How often should I urinate after sex?
pass urine whenever the urge arises, and at least every 2–3 hours. urinate before and after having sex. Pregnant women will usually attend a screening to check for UTIs in their early pregnancy. These checks are an important step in helping to prevent UTI infections or detecting them early.
Can a pregnant woman have a UTI?
UTIs are common, and some women may experience them during pregnancy. Women who have symptoms of a UTI during pregnancy should see their doctor immediately. Without treatment, UTIs can cause serious complications for a pregnant woman and the developing fetus. Prompt intervention can help to prevent these complications.
Can a baby with a UTI have low birth weight?
A baby born to a woman with an untreated UTI may also have a low birth weight at delivery.
How to prevent urinary tract infection during pregnancy?
You may do everything right and still experience a urinary tract infection during pregnancy, but you can reduce the likelihood by doing the following: Drink 6-8 glasses of water each day and unsweetened cranberry juice regularly. Eliminate refined foods, fruit juices, caffeine, alcohol, and sugar. Take Vitamin C (250 to 500 mg), Beta-carotene ...
Why do pregnant women get UTIs?
Pregnant women are at increased risk for UTIs starting in week 6 through week 24 because of changes in the urinary tract. The uterus sits directly on top of the bladder. As the uterus grows, its increased weight can block the drainage of urine from the bladder, causing a urinary tract infection during pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of a urinary infection?
If you have a urinary tract infection, you may experience one or more of the following symptoms: When bacteria spreads to the kidneys you may experience back pain, chills, fever, nausea, and vomiting.
How long does it take for a baby to urinate after taking antibiotics?
Doctors usually prescribe a 3-7 day course of antibiotics that is safe for you and the baby. Call your doctor if you have fever, chills, lower stomach pains, nausea, vomiting, contractions, or if after taking medicine for three days, you still have a burning feeling when you urinate.
How to get rid of a swollen bladder?
Eliminate refined foods, fruit juices, caffeine, alcohol, and sugar. Take Vitamin C (250 to 500 mg), Beta-carotene (25,000 to 50,000 IU per day) and Zinc (30-50 mg per day) to help fight infection. Develop a habit of urinating as soon as the need is felt and empty your bladder completely when you urinate.
How to clean a genital area after urinating?
After urinating, blot dry (do not rub), and keep your genital area clean. Make sure you wipe from the front toward the back.
Can a urine culture detect a urinary tract infection?
A urinalysis and a urine culture can detect a urinary tract infection throughout pregnancy.
How to treat urinary tract infection during pregnancy?
Left untreated, an infection can spread to the kidneys and cause early labor and low birth weight. The most common treatment for UTIs is a course of antibiotics, most of which are safe for pregnancy and highly effective.
How many pregnant women get UTIs?
As many as 13 percent of pregnant women get UTIs, typically between their sixth and 24th week of pregnancy. While an infection can develop in any part of the urinary system, most develop in the lower tract, often because bacteria has entered the system via the urethra and has begun to multiply in the bladder.
Why does urine become more concentrated during pregnancy?
Increase in blood volume — Blood volume increases during pregnancy, something that increases blood flow to the kidneys , which end up making much more concentrated urine. Because highly-concentrated urine isn't as effective at removing bacteria from the urethra or bladder, any bacteria in the urinary tract can multiply over time.
What is a UTI?
Tweet. A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that can occur anywhere along the urinary tract. Women are already more prone to urinary tract infections (UTIs) than men, and their risk of developing them only increases during pregnancy. As many as 13 percent of pregnant women get UTIs, typically between their sixth and 24th week ...
Why do pregnant women have to have a urine test?
Pregnant women usually undergo this test at all (or nearly all) of their prenatal visits to ensure an infection has not developed. If the test is positive, the urine may be sent to a lab for further analysis to determine which bacteria are causing the infection and which drugs they are most susceptible to.
What is the name of the UTI?
The name of the UTI varies depending on the infection location: Urethritis: infection of the urethra (the tube that transports urine outside the body from the bladder) Cystitis: infection of the bladder. Pyelonephritis: infection of the kidney.
When does uterus dilate?
Ureteral dilation — Beginning at six weeks of pregnancy, the tubes that connect each kidney to the bladder (the ureters) widen. As the uterus grows it places increased pressure on the ureters, causing them to further dilate. Wider ureters allow bacteria to more easily enter the urinary system.
Why do women get infections during pregnancy?
Hormones are one reason. In pregnancy, they cause changes in the urinary tract, and that makes women more likely to get infections. Changes in hormones can also lead to vesicoureteral reflux, a condition in which your pee flows back up from your bladder to your kidneys. This can cause UTIs.
Why is it so hard to let out urine while pregnant?
These changes also put you at higher risk for a UTI. Because you’re pregnant, your growing uterus presses on your bladder. That makes it hard for you to let out all the urine in your bladder. Leftover urine can be a source of infection.
How do you know if you have a UTI?
If you have a UTI, you may have: An urgent need to pee, or peeing more often. Trouble with peeing. A burning sensation or cramps in your lower back or lower belly. A burning feeling when you pee. Urine that looks cloudy or has an odor. Blood in your pee, which can turn it red, bright pink, or cola-colored.
How long does it take for a UTI to go away?
UTI Treatment During Pregnancy. You’ll take antibiotics for 3 to 7 days or as your doctor recommends. If your infection makes you feel uncomfortable, your doctor will probably start your treatment before you get your urine test results. Your symptoms should go away in 3 days.
What is the tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
Ureters (tubes that carries urine from your kidneys to your bladder) Bladder. Urethra (a short tube that carries urine from your bladder to outside your body) Bacteria cause most UTIs. Anyone can get one, but they're most common in women, and they can be extra concerning if you're pregnant.
How to get rid of a sex itch?
Drink at least eight glasses of water a day. Wipe yourself from front to back when you go to the bathroom. Empty your bladder shortly before and after sex. If you need a lubricant when you have sex, choose a water-based one. Don't douche. Avoid strong feminine deodorants or soaps that cause irritation.
Can you get a UTI while pregnant?
Anyone can get one, but they're most common in women, and they can be extra concerning if you're pregnant. If you think you might have a UTI, tell your doctor.
What is a UTI in a clinic?
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common complaint encountered in outpatient setting, whether primary care or specialist clinic. It is imperative for the clinician to have a comprehensive grasp on the epidemiology, physiology, pathophysiology, and treatment strategies of UTIs. Another frequently encountered entity, especially in the specialty clinics, is resistant bacteria causing UTI and recurrent UTIs. This challenging entity is further complicated with the increasing rates of bacterial resistance and the increasing fear of extended spectrum beta-lactamase and multidrug resistant organisms. The authors reviewed UTI in females with emphasis on antimicrobial and non-antimicrobial treatment strategies.
What is a UTI?
A UTI is an inflammatory response at the level of the urothelium to fight a bacterial infection. A UTI is almost always associated with bacteriuria, the presence of bacteria in urine, and pyuria, the presence of white blood cells in the urine. Bacteriuria can be present without pyuria, which could be due to bacterial contamination or aseptic technique in the urine collection. On the contrary, pyuria can be present without bacteriuria indicating an inflammatory process of the urothelium such as a urinary stone or a malignancy.[8] The differentiation between complicated [Table 1] and uncomplicated UTI[9] has clinical importance for duration and type of treatment that will be tackled in the discussion part later on. In general, uncomplicated UTI is present in patients with no anatomical or functional abnormalities in their urinary tract system.
What is a recurrent UTI?
UTI can be characterized into either first, unresolved, or recurrent infections. A first UTI is one that occurs in a person with no previous or a remote infection. An unresolved UTI is a re-infection with the same bug and similar antibiogram to a previous UTI treated with appropriate antibiotics. A rUTI occurs after resolution of the previous infection.[8] Conflicting definitions for rUTIs exist; however, most specialists agree that to be considered recurrent, the patient needs to have suffered more than two episodes in the last 6 months or more than three episodes in the past year.[10,11]
Why is UTI important?
UTI is of paramount importance in pregnant women, given that bacteriuria in the presence of pregnancy could lead to complications and miscarriage. UTI is the second most common pathology affecting pregnant women after anemia and, at the same time, the most common infection in this subgroup of patients. Approximately 5%–10% of women will develop UTI during their pregnancy, and it is estimated that out of all admissions of pregnant women, 5% is attributed to UTIs. UTIs, if mismanaged, can significantly increase the risk for pyelonephritis secondary to pregnancy-related adaptive changes in the urinary tract, resulting in serious maternal and fetal complications such as preterm labor, low birth weight, or maternal systemic infection.[32]
How does a UTI affect mental health?
Urinary infections carry a big toll on an individual's health including his mental health and sense of well-being. More than half of patients with UTI suffer from clinical depression and 38.5% suffer from anxiety, with a significant improvement in the quality of life after proper treatment and prophylaxis.[7]
What is a catheter-associated UTI?
It is defined as the presence of signs or symptoms of UTI in a patient with indwelling urethral, suprapubic, or even intermittent catheterization with a significant presence of bacteriuria. CAUTI is a serious iatrogenic infection and associated with increased morbidity and mortality in hospitalized and nursing home care patients.[12] Elaborating on CAUTI is beyond the spectrum of the manuscript; however, the authors recognize that UTI from indwelling catheters is a serious complication and must be prohibited by decreasing unnecessary catheterization and abiding by a proper sterile technique while catheterizing patients.[13]
What are the factors that cause a urinary infection?
For a urinary infection to occur, there are many superimposing factors that interplay including host factors, inoculum size, and the virulence of the infecting bug. The first event that leads to a UTI is the inoculation. The most common theorem for inoculation is the ascending route. Enteric bacteria colonize the perineum and ascend into the urethra and bladder.[14]
What is the best treatment for urinary tract infections during pregnancy?
Treatments for urinary tract infections during pregnancy include antibiotic medications to battle the bacteria and increased hygiene for prevention.
What is UTI during pregnancy?
Treating UTIs During Pregnancy. Tweet. A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that can occur in any part of the urinary system, including the urethra, bladder, ureters or kidneys.
Why are women more susceptible to UTIs?
Because women have a shorter urethra and because their urethra is in close proximity to the anus, they are more susceptible to UTIs. During pregnancy, as hormone fluctuations and an expanding uterus cause changes to the urinary tract, their risk of developing a UTI is even higher.
Does drinking water help with UTIs?
Stagnant urine allows concentrated populations of bacteria to multiply and cause a urinary tract infection. Drinking plenty of water can not only prevent UTIs but can help treat them, as it increases urine volume and allows the body to flush out harmful bacteria.