The main methods of treatment:
- Conservative therapy. It is recommended to use medicines from the group of angioprotectors, glucocorticosteroids,...
- Panretinal photocoagulation (laser coagulation). The technique stimulates regression of newly formed capillaries.
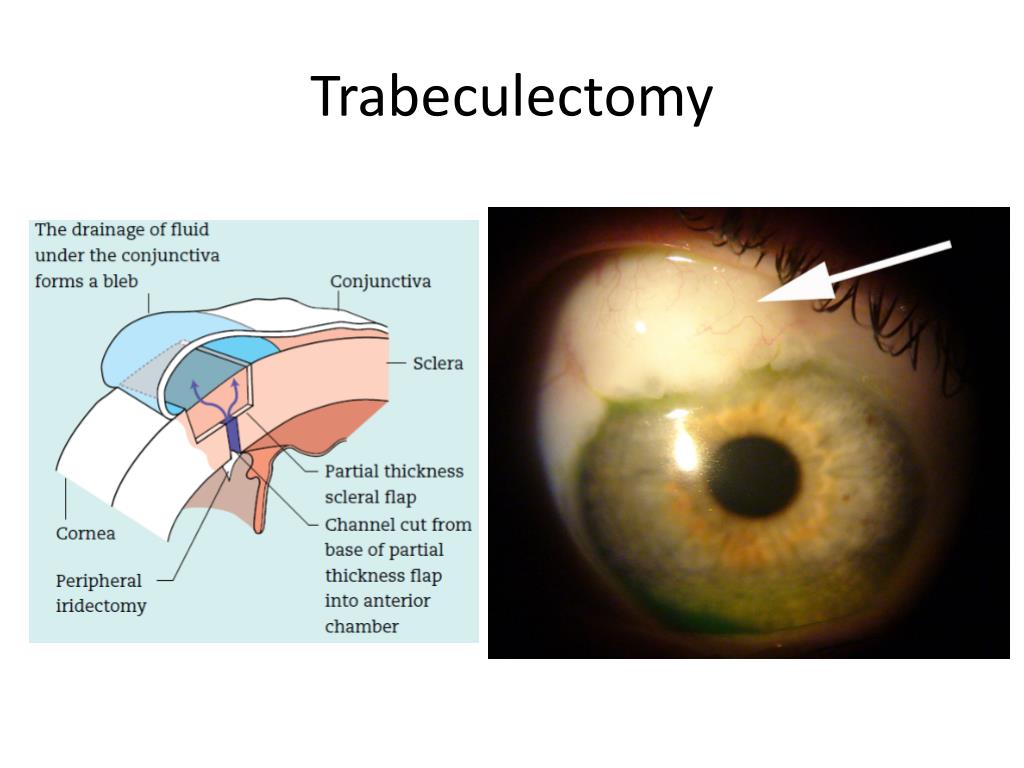
- Surgical treatment. Surgical intervention is indicated if rubeosis has arisen against the background of...
How is neovascularization treated in rubeosis iridis?
Treatment of Neovascularization Once rubeosis iridis has begun, the primary goal of treatment is to reduce the ischemic drive of neovascularization. This is best accomplished with panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) to destroy ischemic retina, minimize the eye's oxygen demand, and reduce the amount of VEGF being released.
What is rubeosis of the iris?
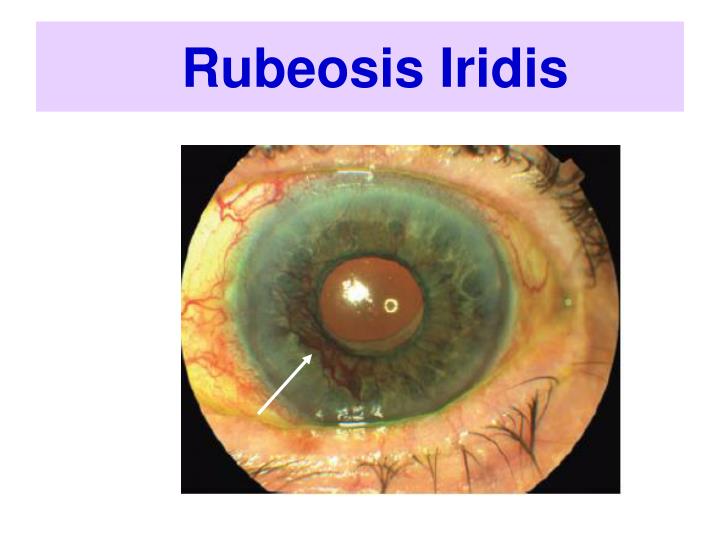
Rubeosis iridis. Rubeosis iridis, also called neovascularization of the iris ( NVI ), is a medical condition of the iris of the eye in which new abnormal blood vessels (formed by neovascularization) are found on the surface of the iris.
What are the signs and symptoms of rubeosis iridis?
Flare in the anterior chamber is usually present in most eyes with rubeosis iridis. An anterior chamber cellular response is seen in almost one fifth of eyes with the ocular ischemic syndrome, 5 but it rarely exceeds grade 2, as per the Schlaegel classification. 26 Keratic precipitates can be present, but are unusual.
Can anecortave acetate be used to treat rubeosis iridis?
To provide use of Anecortave Acetate Sterile Suspension of 15mg for a series of five patients with rubeosis iridis. Rubeosis iridis refers to neovascularization of the iris. It is caused by a number of conditions which include, but are not limited to severe diabetic retinopathy, central retinal vein occlusion, chronic inflammation, and infection.
Is rubeosis iridis painful?
As fibrotic membranes develop and contract, the iridocorneal angle closes, resulting in closed angle glaucoma. In untreated cases, NVG will cause blindness and pain, often ending in enucleation.
What is Rubeosis in the eye?
Rubeosis is a term that describes abnormal blood vessel growth on the iris and the structures in the front of the eye. Normally there are no visible blood vessels in these areas.
What causes rubeosis iridis?
Clinical Course. The three most common clinical entities leading to rubeosis iridis are diabetes mellitus, CRVO, and carotid occlusive disease. Patients with these conditions or any other predisposing factors should undergo careful slit lamp examination to detect for early signs of neovascularization.
How does rubeosis iridis cause glaucoma?
Rubeosis iridis is defined as neovascularization of the iris characterized by numerous coarse and irregular vessels on the surface and stroma of the iris. These new blood vessels may cover the trabecular meshwork, cause peripheral anterior synechia and give rise to secondary glaucoma.
How common is central retinal vein occlusion?
After diabetic retinopathy, CRVO is the second most common retinal vascular disorder. CRVO usually occurs in people who are aged 50 and older. In most cases, it is not known what causes the condition.
Does neovascularization cause glaucoma?
Neovascular glaucoma (NVG) is a potentially blinding secondary glaucoma, characterized by the development of neovascularization of the iris, elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) and, in many instances, poor visual prognosis.
What is the treatment for neovascular glaucoma?
Medical therapy is indicated, with topical atropine and steroids being the most important agents. Antiglaucoma medications, topical beta-blockers, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are also recommended. The role of topical brimonidine and latanoprost in advanced disease is unclear.
What causes inflammatory glaucoma?
One type of inflammatory glaucoma is uveitic glaucoma. The patient will initially suffer from uveitis. There are many causes of uveitis, such as auto-immune disorders, Crohn's disease, infections such as Lyme's disease, Toxoplasmosis, Shingles, and lymphoma.
What is stage2 glaucoma?
Stage 2 Glaucoma – The second stage of glaucoma is when you or your loved one will start to notice symptoms. These may include patchy or blurry vision or mild to moderate eye pain. At this point, your doctor may recommend medication therapies, like topical beta-blockers or carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
What causes new blood vessels to grow in the eye?
What causes corneal neovascularization? The main underlying cause is lack of oxygen to the cornea. Long-term use of contact lenses is a main contributor, but toxic contamination from lenses or solution, trauma or infection, chemical burns, or lens deposit buildup can also be a cause.
How is glaucoma detected?
Glaucoma is usually picked up during a routine eye test, often before it causes any noticeable symptoms. Other tests are usually needed afterwards to diagnose and monitor the condition. It's important to have regular eye tests so problems such as glaucoma can be diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
Can glaucoma cause eye bleeds?
Optic disc hemorrhage is a common clinical feature of glaucoma, indicating active disease with likely progression and visual field loss. These small bleedings form notch-like lesions at the edge of the optic disc in the nerve fiber layer and often correlate with visual field loss.
What is the medical term for the iris of the eye?
Ophthalmology. Rubeosis iridis, is a medical condition of the iris of the eye in which new abnormal blood vessels (formed by neovascularization) are found on the surface of the iris.
How long does it take for a neovascularization to go away?
The injection blocks the direct effect of VEGF and acts more quickly but will wear off in about 6 weeks.

General Information
- Rubeosis iridis is a widespread pathological condition in ophthalmology. According to statistics, in 21% of cases, rubeosis develops against the background of thrombosis of the central retinal vein. Newly formed vessels in the iris are detected in 4-8% of patients with diabetes mellitus, ho…
Causes of Rubeosis Iridis
- The etiology of rubeosis iridis is not fully understood. Activation of the neovascularization process is provoked by a number of internal and external factors. The main causes of the development of rubeosis include: 1. Metabolic disorders. Rubeosis often occurs a second time against the background of diabetic retinopathy in patients with a decompensated form of diabetes mellitus. …
Pathogenesis
- Vascular proliferation is a compensatory reaction to hypoxia of surrounding tissues. Oxygen starvation potentiates the synthesis of nitric oxide, which belongs to the number of vasodilators. Increased angiogenesis is caused by ischemia of the membranes of the eye caused by insufficient blood supply or the presence of an organic barrier in the path of blood flow in the or…
Classification
- Rubeosis iridis is an acquired pathology. Signs of the congenital form are often associated with intrauterine fetal hypoxia, but they have no practical significance, because they are leveled independently in the neonatal period. From a clinical point of view , the following types of iris rubeosis are distinguished: 1. Pupillary. It is characterized by enhanced angiogenesis in the regi…
Symptoms
- Patients complain of discomfort in the orbit area with prolonged visual load. Symptoms of the disease are photophobia, the appearance of “fog” or “shroud” in front of the eyes. Visual acuity decreases slightly. Visual dysfunction is caused by a spasm of accommodation and is reversible. Narrowing of the visual fields leads to deterioration of peripheral vision, which is manifested by …
Complications
- In this pathology, the process of neovascularization extends to the angle of the anterior chamber (FCA) of the eye, which leads to the appearance of a network of newly formed vessels and a violation of the outflow of intraocular fluid. Therefore, the most severe complication of rubeosis is neovascular glaucoma, which is characterized by a severe course and resistance to drug therap…
Diagnostics
- Diagnosis requires an objective examination of the patient. At the beginning of the development of pathology, changes are not detected with the naked eye. With a prolonged course of the disease, pathological changes have the form of a lace pattern. A special complex of ophthalmological examination includes: 1. Biomicroscopy of the eye. The technique allows you t…
Prognosis and Prevention
- The prognosis for life and work capacity in the case of iris rubeosis is favorable. Timely treatment of the disease allows you to avoid the development of dangerous complications and restore visual functions. No specific preventive measures have been developed. Non-specific methods of prevention are reduced to the control of intraocular pressure and blood glucose levels. Patients …