
Explore
8 Treating Panic Disorder Establish treatment goals. • Reduce the frequency and intensity of panic attacks, anticipa-tory anxiety, and agoraphobic avoidance, optimally with full remission of symptoms and return to a premorbid level of func-tioning. • Treat co-occurring psychiatric disorders when they are present.
What is panic disorder and how is it treated?
In addition to exposure techniques, various physiologically based approaches (e.g., breathing retraining) and cognitively based approaches have been studied. These approaches target not only the avoidance behavior of agoraphobia, but also the panic attacks themselves.
What is the most effective treatment for panic disorders?
Feb 15, 2021 · Psychotherapy, also called talk therapy, is often recommended as a first-line treatment for panic disorder. While cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is the best known and most researched therapy ...
How do you cure panic disorder?
Jan 08, 2019 · In this review, the authors shed light on the staging model of panic disorder with stagespecific biological markers. In general, panic disorder can be effectively treated with pharmacological and psychological treatments such as cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness interventions . Although pharmacological treatments have proven to be potent in …
What are 3 treatments for panic disorder?
- Antidepressants.
- Anti-Anxiety Medications.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy.
- Panic-Focused Psychodynamic Psychotherapy.
Can panic disorder be cured?
What are two primary treatment for panic disorder?
Is panic disorder for life?
Is panic disorder a mental illness?
What is the strongest treatment for panic disorder?
Generally safe with a low risk of serious side effects, SSRI antidepressants are typically recommended as the first choice of medications to treat panic attacks.May 4, 2018
What is the first line treatment for panic disorder?
Which medicine is best for panic attacks?
- citalopram (Celexa)
- escitalopram (Lexapro)
- fluvoxamine (Luvox)
- paroxetine (Paxil)
- fluoxetine (Prozac)
- sertraline (Zoloft)
What is a quick reference guide for panic disorder?
Treating Panic Disorder: A Quick Reference Guide is a synopsis ofthe American Psychiatric Association’s Practice Guideline for theTreatment of Patients With Panic Disorder, Second Edition, whichwas originally published in the American Journal of Psychiatry inJanuary 2009 and is available through American Psychiatric Pub-lishing, Inc. The psychiatrist using this Quick Reference Guide(QRG) should be familiar with the full-text practice guideline onwhich it is based. The QRG is not designed to stand on its own andshould be used in conjunction with the full-text practice guideline.For clarification of a recommendation or for a review of the evidencesupporting a particular strategy, the psychiatrist will find it helpful toreturn to the full-text practice guideline.
What is avoidance in panic disorder?
Avoidance that is a manifestation of panic disorderLogistical barriers (e.g., economic factors, transportation, child care)Cultural or language barriersProblems in the therapeutic relationshipShort-term intensification of anxiety associated with treatment (e.g., due to medication side effects or exposure to fear cues)
When was the second edition of Panic Disorder published?
Based on Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With PanicDisorder, Second Edition, originally published in January 2009. A guide-line watch, summarizing significant developments in the scientificliterature since publication of this guideline, may be available at http://www.psychiatryonline.com/pracGuide/pracGuideTopic_9.aspx.
What is the best treatment for panic disorder?
Antidepressant medications successfully reduce the severity of panic symptoms and eliminate panic attacks. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants are equally effective in the treatment of panic disorder.
How often does panic disorder occur?
They can occur one to several times per week, usually unpredictably, and may interfere with the patient’s normal activities and work. 2 Although panic disorder often is chronic, the frequency of attacks and associated symptoms (e.g., depression, avoidant behavior) may wax and wane.
How effective are antidepressants?
Antidepressant medications have been shown to reduce panic severity, eliminate attacks, and improve overall quality-of-life measures in patients with panic disorder. 3 Two recent meta-analyses 9, 10 found that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are equally effective in reducing panic severity and the number of attacks. In these studies, 61 percent of patients were panic-free after six to 12 weeks of treatment, compared with 41 percent of control patients. These studies differ on whether SSRIs are better tolerated than TCAs. An earlier meta-analysis 11 found SSRIs to be superior to TCAs. However, the benefits of SSRIs may have been overstated in the latter study because of its failure to account for publication bias (i.e., the greater likelihood that small studies finding no difference between treatments will not be published).
What is cognitive behavior therapy?
Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) includes many techniques , such as applied relaxation, exposure in vivo, exposure through imagery, panic management, breathing retraining, and cognitive restructuring. Meta-analyses 13 – 15 support the efficacy of CBT in improving panic symptoms and overall disability. Most of the RCTs included in these meta-analyses included eight to 15 sessions of CBT, although a few studies have reported similar efficacy with only four sessions. 13 Meta-analyses have found that specialized cognitive therapy, behavior therapy, and combined CBTs are superior to general emotionally supportive psychotherapy in patients with panic disorder. 16
How do panic symptoms develop?
How do panic symptoms develop? A phobia of internal sensations is thought to drive the patient’s avoidance behavior. In addition to neurochemical and genetic models for the disorder, some researchers have proposed a cognitive model, in which patients learn to misinterpret thoughts and emotions as physical symptoms. For example, a woman who is afraid of being left alone when her husband leaves for work may experience that fear physiologically (e.g., shortness of breath, sweating), which in turn makes her feel more anxious (“What is wrong with me?”), deepening the spiral and leading to more symptoms. Another theory is that patients escalate otherwise benign body sensations into panic attacks (the behavioral model). For example, a man whose heart rate accelerates when he becomes angry may escalate that sensation and the resulting anxiety into the chest pain of a “heart attack.” Both examples demonstrate the patient’s phobia of internal sensations.
What percentage of people have panic disorder?
Panic disorder, as defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed. (DSM-IV), affects 1 to 3 percent of the general population at some point in their lives. 3 These patients, however, use health care resources to a disproportionately high extent. Psychiatric case-finding studies 4, 5 of patients presenting to emergency departments with chest pain found that 17 to 25 percent of these patients also met the criteria for panic disorder. In a large multi-center study 6 of primary care practices, the prevalence of panic disorder ranged from 1 to 6 percent across study sites.
How often do panic attacks occur?
Attacks occur suddenly and typically last more than 10 minutes (although the length of attacks is variable). They can occur one to several times per week, usually unpredictably, and may interfere with the patient’s normal activities and work. 2 Although panic disorder often is chronic, the frequency of attacks and associated symptoms (e.g., depression, avoidant behavior) may wax and wane.
What is the best treatment for panic disorder?
Psychotherapy, also called talk therapy, is often recommended as a first-line treatment for panic disorder. While cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is the best known and most researched therapy for panic disorder, other psychotherapy methods are available too.
How to reduce anxiety in panic disorder?
Research has found that engaging in aerobic exercise can decrease symptoms of anxiety in people with panic disorder. Build an exercise routine slowly. You can start with 20-minute sessions of whatever aerobic exercises you enjoy, like dancing, cycling, or walking. Other types of exercise may also be beneficial.
How many sessions of CBT are needed for panic disorder?
CBT typically consists of 12 sessions at 60 minutes each week.
What is the third phase of panic disorder?
In the third phase, you explore any conflicts or fears around ending therapy . Other treatments for panic disorder include acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR). Although more research is needed for MBSR and ACT, the results so far are promising.
How many people have panic attacks?
That’s about 1 in 20 people.
How many phases are there in anxiety?
It’s divided into three phases. The content of these phases varies by person. In the first phase, you explore the origins of your anxiety and discover the meaning of your symptoms. Having a deeper understanding of your anxiety, and knowing the source, can reduce anxiety and panic attacks.
Does yoga help with panic attacks?
For example, one small 2014 study found that yoga — on its own or in combination with CBT — helped reduce symptoms of panic disorder .
How to treat panic disorder?
In general, panic disorder can be effectively treated with pharmacological and psychological treatments such as cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness interventions [9]. Although pharmacological treatments have proven to be potent in panic disorder therapy, their potential side effects can be obstacles for adherence to treatment and the long-term maintenance of achieved treatment outcomes. Thus, it is important to provide effective psychological interventions for panic disorder either as adjunctive or stand-alone treatment. However, despite evidence-based psychological therapy programs, the availability of treatment places is limited in conventional face-to-face mental health care. In this special issue, Apolinario-Hagen [10] has explored recent evidence based on the efficacy and acceptability of different internet-delivered treatments for adult patients with panic disorder. This review illustrates different effective and well accepted evidence-based internetdelivered psychological treatments for panic disorder. Of note, self-guided transdiagnostic internet cognitive behavioral therapy approaches appear to be efficient options for large scale dissemination in routine care. However, the discrepancy between high acceptability and slow uptake of internetdelivered treatments, as well as the unclear role of patients’ preferences, require further investigation.
What is the most common anxiety disorder?
Panic disorder is one of the most common anxiety disorders, with lifetime prevalence rates in the general population reported between 2.1–4.7% [1,2]. Panic disorder is typically associated with a chronic progression, which results in economic burden and a loss of quality of life, therefore, proper prevention and treatment of panic disorder is important. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) was revised to accommodate a paradigm shift from a categorical to a dimensional approach in psychiatric nosology and taxonomy. However, the categorical concept of panic disorder still remains in the DSM-5. An overview of the changes to diagnostic criteria for panic disorder from the DSM-IV to DSM-5 are as follows: 1) distinction of agoraphobia from panic disorder and 2) defining panic attacks as a specifier. In the DSM-5, a panic disorder diagnosis is operationally defined as the fulfillment of both recurrent unexpected panic attacks (Criterion A) and the existence of one or more of the following persistent panic attack related conditions for at least one month: concern, worry, and behavioral change (Criterion B). Panic disorder has been modeled in terms of the negative valence systems domain in the Research Domain Criteria initiative [3]. A panic attack (Criteria A) can be conceptualized as a prototypical expression of a fear response to an acute internal threat stimulus, while concerns and worries about the consequences of panic attacks (Criteria B) can be conceptualized as responses to potential harm within the negative valence system.
Is panic disorder a polygenic disorder?
Panic disorder is a complex heterogeneous multifactorial and polygenic disorder [7]. This heterogeneity not only complicates panic disorder diagnosis but also the treatment outcomes and prognosis. To date, no valid, specific, or sensitive biomarkers have been identified for panic disorder, or for the treatment response in panic disorder. In this special issue, Cosci and Mansueto [8] have reviewed the biological and clinical markers of panic disorder. Until now, potential candidate biomarkers of panic disorders have been proposed, including neuroimaging, respiratory patterns, heart rate variability, peripheral blood markers, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation; however, the clinical utility, sensitivity, specificity, and the predictive value of the biomarkers for panic disorder remain questionable. As a solution to the problem of low sensitivity and specificity of a single biomarker, it has been suggested that a wider and multivariable approach could be applied, including a combination of neuroimaging, genetic, epigenetic, proteomic, and metabolomics approaches to include the majority of multiple biological abnormalities of panic disorder. Alternatively, a staging model for panic disorder could also be a valid approach to include the susceptibility, diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive markers of panic disorder. Biomarkers would be more specific if they could be related to specific stages of panic disorder. In this review, the authors [8] shed light on the staging model of panic disorder with stagespecific biological markers.
What is the best treatment for panic disorder?
Talk with your doctor about the best treatment for you. Psychotherapy. A type of psychotherapy called cognitive behavioral therapy ( CBT) is especially useful as a first-line treatment for panic disorder. CBT teaches you different ways of thinking, behaving, and reacting to the feelings that come on with a panic attack.
How to help someone with panic disorder?
Both psychotherapy and medication can take some time to work. A healthy lifestyle can also help combat panic disorder. Make sure to get enough sleep and exercise, eat a healthy diet, and turn to family and friends who you trust for support.
What is it called when you have a panic attack?
People with panic disorder have sudden and repeated attacks of fear that last for several minutes or longer. These are called panic attacks . Panic attacks are characterized by a fear of disaster or of losing control even when there is no real danger. A person may also have a strong physical reaction during a panic attack .
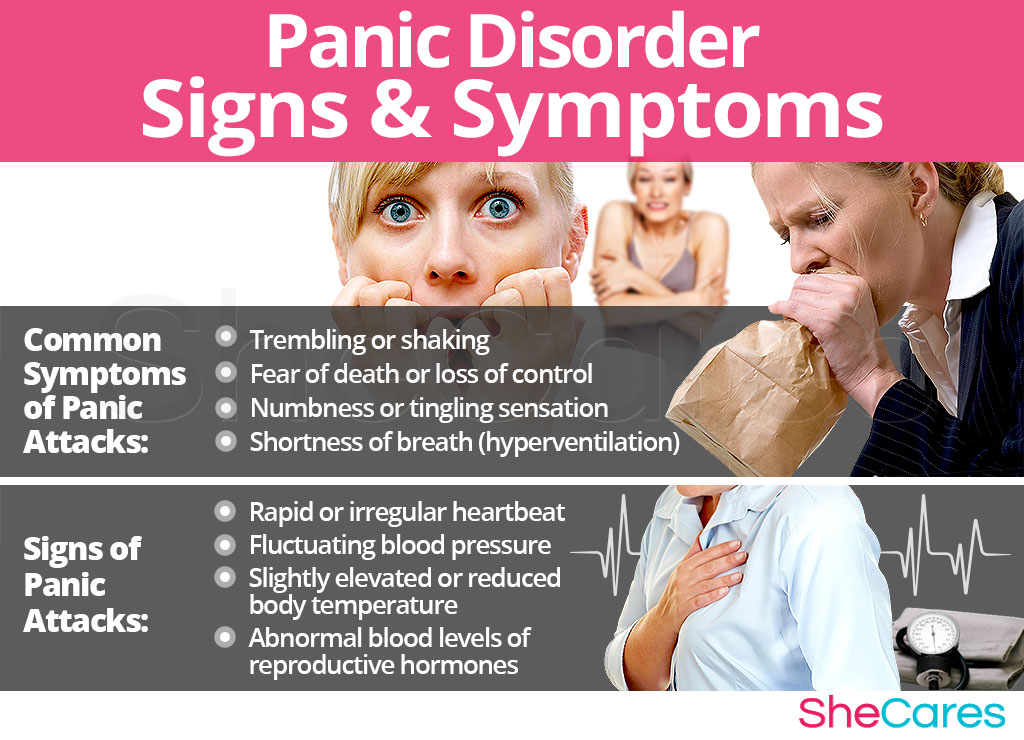
What are the symptoms of panic disorder?
Physical symptoms during a panic attack, such as a pounding or racing heart, sweating, chills, trembling, breathing problems, weakness or dizziness, ...
Why do some people have panic disorder?
Some researchers think that people with panic disorder misinterpret harmless bodily sensations as threats. By learning more about how the brain and body functions in people with panic disorder, scientists may be able to create better treatments. Researchers are also looking for ways in which stress and environmental factors may play a role.
What is the best medicine for panic attacks?
Another type of medication called beta-blockers can help control some of the physical symptoms of panic disorder, such as rapid heart rate. Although doctors do not commonly prescribe beta-blockers for panic disorder, they may be helpful in certain situations that precede a panic attack.
How does CBT help with panic attacks?
CBT teaches you different ways of thinking , behaving, and reacting to the feelings that come on with a panic attack. The attacks can begin to disappear once you learn to react differently to the physical sensations of anxiety and fear that occur during panic attacks. For more information on psychotherapy, see ...
What is panic disorder?
Definition. Panic Disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by unexpected and repeated episodes of intense fear accompanied by physical symptoms that may include chest pain, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, or abdominal distress. These episodes occur “out of the blue,” not in conjunction with a known fear or stressor.
Is the DSM-5 a post traumatic stress disorder?
The NCS-R was led by Harvard University. Unlike the DSM-IV criteria used in the NCS-R and NCS-A, the current D SM-5 no longer places post-traumatic stress disorder or obsessive compulsive disorder in the anxiety disorder category. They are listed in new DSM5 categories. Survey Non-response:
Is anxiety disorder a DSM?
Unlike the DSM-IV criteria used in the NCS-R and NCS-A, the current DSM-5 no longer places post-traumatic stress disorder or obsessive compulsive disorder in the anxiety disorder category. They are listed in new DSM5 categories.
How to treat panic disorder?
Anti-anxiety and antidepressant medications. Counseling, such as cognitive behavioral therapy. Treatment for panic disorders is usually quite effective. Treatment will help you learn to recognize that the symptoms are not life-threatening.
What are the symptoms of panic disorder?
Nausea or belly pain. Dizziness or lightheadedness. Feeling unreal or disconnected from oneself. Fear of losing control. Fear of " going crazy" or dying. Numbness. Chills or hot flashes. Chest pain and other symptoms that mimic a heart attack. Panic disorder can be upsetting and disabling.
What does it mean when you have a panic attack?
If you have repeated, and unexpected panic attacks, you may have panic disorder. Panic disorder causes bouts of overwhelming fear when there is no specific cause for the fear. In between panic attacks, you may worry greatly about when and where the next one may happen. It can even keep you from leaving your home.
How do you know if you have a panic attack?
Symptoms of a panic attack may include: Pounding heart. Sweating. Trembling or shaking. Shortness of breath. Sense of choking. Nausea or belly pain. Dizziness or lightheadedness.
When does panic disorder start?
Panic disorder is a common mental health problem. It often starts in the teens or early adulthood, but may also begin in childhood. Women are twice as likely as men to have it. There may be a genetic link. It tends to run in families.
Can panic attacks cause depression?
It is a common disorder and can often lead to depression. Panic disorders can be disabling because you become so afraid of when the next panic attack may happen that you can't cope with regular tasks. Treatment involves use of anti-anxiety medicines and antidepressants along with cognitive behavioral therapy.

Causes
Treatment
- Patients with panic disorder have several treatment options. Determining which treatment is best for a given patient is done through a shared decision-making process between the patient and physician. A suggested approach to treatment is outlined in Figure 1. Antidepressant medications have been shown to reduce panic severity, eliminate attacks, an...
Society and culture
- Table 212 lists dosing and cost information for the antidepressants that have been proved in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder. The choice of antidepressant should be based on side effect profiles and patient preferences. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors also are effective in the treatment of panic disorder, but their use is limited by …
Performance
- In the CBT trials, an average of 73 percent of treated patients were panic-free at three to four months, compared with 27 percent of control patients (number needed to treat, 2),13 and 46 percent of treated patients remained panic-free at two years.14 Although these statistics are impressive, they represent studies in selected populations that may not reflect typical general pr…
Components
- It is unclear which component of CBT is more important: cognitive therapy (e.g., identifying misinterpreted feelings, educating patients about panic attacks) or behavior therapy (e.g., breathing exercises, relaxation, exposure). However, the efficacy of exposure techniques alone, in which the patient repeatedly confronts the anxiety-provoking stimulus through imagery or in vivo…
Prevention
- If referral for formal CBT isnotanoption, self-directed CBT videotapes and books have been proved effective in controlled studies,18 although less so than standard CBT.19 At least minimal contact with a therapist is necessary to reduce panic symptoms.20 Clums21 Coping with Panic: A Drug-Free Approach to Dealing with Anxiety Attacks is a widely available self-help book that has been …
Prognosis
- Studies also are conflicting about how long to continue antidepressant therapy (with or without CBT). Studies have shown a relatively low relapse rate after six months of antidepressant therapy.27 Moreover, continued antidepressant therapy beyond six months does not decrease relapse rates.28 A recent study29 that controlled for post-treatment therapy after CBT found no …
Medical uses
- Benzodiazepines are as effective as anti-depressants in reducing panic symptoms and frequency of attacks, are well tolerated, and have a short onset of action.14,30 However, benzodiazepines may cause depression25 and are associated with adverse effects during use and after discontinuation of therapy.3 They also fare less well than anti-depressants in other outcome me…
Investigation
- The authors and a reference librarian familiar with medical literature searched the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, BMJs Clinical Evidence, the Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects, Evidence-Based Medicine Reviews, MEDLINE (1966 to 2003), Web of Science, and Psych-Lit for meta-analyses and RCTs, using the search terms panic disorder and panic attack. …
Resources
- 1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed., text revision. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association, 2000....