Explore
Treatment for other disorders may include drug therapy, such as immunosuppressives, physical therapy, bracing to support weakened muscles, and surgery. The myopathies are neuromuscular disorders in which the primary symptom is muscle weakness due to dysfunction of muscle fiber.
What is myopathy and how is it cured?
No, there is not a cure for myopathy itself. However, it can be treated to improve symptoms. If myopathy is related to an illness, like a virus or electrolyte imbalance, the muscle symptoms will improve when the underlying condition resolves. Immunosuppressants can help relieve symptoms of certain types of myopathy.
Is there a cure for myopathy?
- people of female sex
- low body mass index (BMI)
- advanced age, particularly age 80 and older
- having untreated hypothyroidism, high blood pressure, liver disease, and kidney disease
- heavy alcohol consumption
- vigorous exercise
- having type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- excessive cranberry or grapefruit juice intake
What type of Doctor treats myopathy?
These include:
- Muscle weakness
- Motor delay
- Respiratory impairment
- Bulbar muscle dysfunction (malfunction of the muscles responsible for swallowing and speech)
What are the treatment options for myopathies?

What is the best treatment for myopathy?
Supportive and symptomatic treatment may be the only treatment available or necessary for some disorders. Treatment for other disorders may include drug therapy, such as immunosuppressives, physical therapy, bracing to support weakened muscles, and surgery. The prognosis for individuals with a myopathy varies.
Is there a cure for muscle myopathy?
No, there is not a cure for myopathy itself. However, it can be treated to improve symptoms. If myopathy is related to an illness, like a virus or electrolyte imbalance, the muscle symptoms will improve when the underlying condition resolves. Immunosuppressants can help relieve symptoms of certain types of myopathy.
How long does it take to recover from myopathy?
Prognosis. Corticosteroid-induced myopathy is reversible, with improvement in myopathy within 3 to 4 weeks of tapering corticosteroids, although recovery can take months to a year. Complications of corticosteroid-induced myopathy include the morbidity and subsequent mortality associated with chronic muscle weakness.
What kind of doctor treats myopathy?
Patients with dermatomyositis, polymyositis, or necrotizing myopathy are usually treated by rheumatologists. Those with dermatomyositis may also work with a dermatologist. Those with IBM are often treated by neurologists.
How long can you live with myopathy?
Cumulative survival from diagnosis has been estimated at 74.9% at 5 years and 62.5% at 10 years. Pulmonary involvement represented the main cause of death. Although myopathy is not a rare symptom associated with SSc, it has not attracted sufficient attention.
How do I know if I have myopathy?
The common symptoms of myopathy are muscle weakness, impaired function in activities of daily life, and, rarely, muscle pain and tenderness. Significant muscle pain and tenderness without weakness should prompt consideration of other causes.
How do you test for myopathy?
Doctors use a blood test to look for elevated levels of a substance called creatine kinase, which is released into the bloodstream when muscle fibers deteriorate. Elevated levels may mean you have an inflammatory myopathy.
Does myopathy come go?
The following are some symptoms of polymyositis. These symptoms may come and go: Muscle weakness: This is the most common symptom. The muscles involved usually are those closest to the trunk of the body, and the onset of weakness is usually gradual, occurring over 3 to 6 months or rarely the symptoms come on rapidly.
Who gets myopathy?
Who gets Myopathy? Anyone can get a myopathy. Some develop at an early age, while other types develop later in life.
What causes myopathy?
Myopathy can develop as the result of inherited disorders, such as muscular dystrophies, or acquired conditions of the muscles, such as the common muscle cramp. Other causes of myopathy include immune disorders that cause inflammation and pain. Numerous inherited myopathies exist.
What causes myopathy in the legs?
There are many medical conditions that can lead to myopathy. These conditions can affect the muscles directly or they may interfere with how the muscles function. Some common medical conditions that cause myopathy include: diabetes, thyroid disease, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Does myopathy affect the brain?
Inclusion body myopathy with early-onset Paget disease and frontotemporal dementia (IBMPFD) is a condition that can affect the muscles, bones, and brain. The first symptom of IBMPFD is often muscle weakness (myopathy), which typically appears in mid-adulthood.
What is myopathy in a muscle?
Overview. Myopathy refers to a disease of the muscles. In these cases, the muscles work less effectively than they should. That can occur when the muscles do not develop properly, when they have become damaged, or when they are lacking important components.
What are the most common myopathies?
Commonly acquired myopathies include: 1 Inflammatory/ autoimmune myopathy : This occurs when the body attacks itself, causing muscle degeneration or interfering with function. Myopathies characterized by inflammation in or near the muscle include polymyositis, dermatomyositis, sarcoidosis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis. 6 2 Toxic myopathy : This occurs when a toxin, a medication, or a drug impairs muscle structure or function. 7 3 Endocrine myopathy : This occurs when a disorder of the hormones interferes with muscle function. The most common causes include thyroid or adrenal gland problems. 8 4 Infectious myopathy : This may happen when an infection prevents the muscles from functioning properly. 9 5 Myopathy secondary to electrolyte imbalance : Electrolyte problems, such as excessively high or low potassium levels, can interfere with the function of the muscles. 9
What is congenital myopathy?
Types of Myopathy. Congenital myopathy means myopathy that a person is born with. Many of these conditions are believed to be hereditary and passed on from parents to children through genetics. While the symptoms of congenital myopathies often begin at a very young age, that is not always the case.
What is nemaline myopathy?
Nemaline myopathy : This is a group of disorders characterized by the presence of structures called "nemaline rods" in the muscles. Nemaline myopathy is often associated with respiratory muscle weakness. 3.
Why do myopaths have abnormal bones?
Myopathy is often associated with the abnormal shape of the bones, often because the muscles don't adequately support the bones.
What are the causes of metabolic myopathy?
1. Metabolic myopathy : This group of diseases is caused by metabolic problems that interfere with muscle function.
Why is respiratory support important in myopathy?
Often, respiratory support is the key component in advanced myopathy, so that your breathing can be safely maintained. 1 .
What causes myopathy in the body?
Causes of Myopathy. Inflammatory myopathies can occur when the body’s immune system causes inflammation in the muscle. This inflammation can stem from medications or environmental toxins. Infectious myopathies can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. Muscles can also be affected by systemic illnesses, including connective tissue diseases ...
How do you know if you have myopathy?
Symptoms of Myopathy. If you have a muscle disease, you may experience weakness, most likely in the thighs and upper arms. It can become difficult to climb stairs, rise from a chair, or lift your arms above your head. Cramping, stiffness, and soreness can also occur.
What causes muscle disorders?
Muscle disorders arise from abnormalities that affect the muscle’s structure or metabolism, and have a variety of causes. Some are inherited while others are acquired. Inherited myopathies have a genetic basis and typically appear in childhood, but first symptoms can also appear in adulthood.
What is the name of the disorder of the skeletal muscle?
Myopathy . Myopathy is a disorder of the skeletal muscles. Muscle disorders arise from abnormalities that affect the muscle’s structure or metabolism, and have a variety of causes. Some are inherited while others are acquired.
Can myopathies cause soreness?
Cramping, stiffness, and soreness can also occur. Some myopathies can affect muscles in the hands or feet, or facial and eye muscles. In some cases, the problem can affect the heart and breathing muscles.
What are the treatments for myopathy?
Genetic counseling. Medications, such as albuterol to reduce muscle weakness or azathioprine for inflammation. Nutritional and respiratory support. Orthopedic devices to help support limbs. Surgery. Physical or speech therapy. For toxic, electrolyte, endocrine, or infectious causes of myopathy, identifying the cause and eliminating, correcting, ...
What causes myopathies?
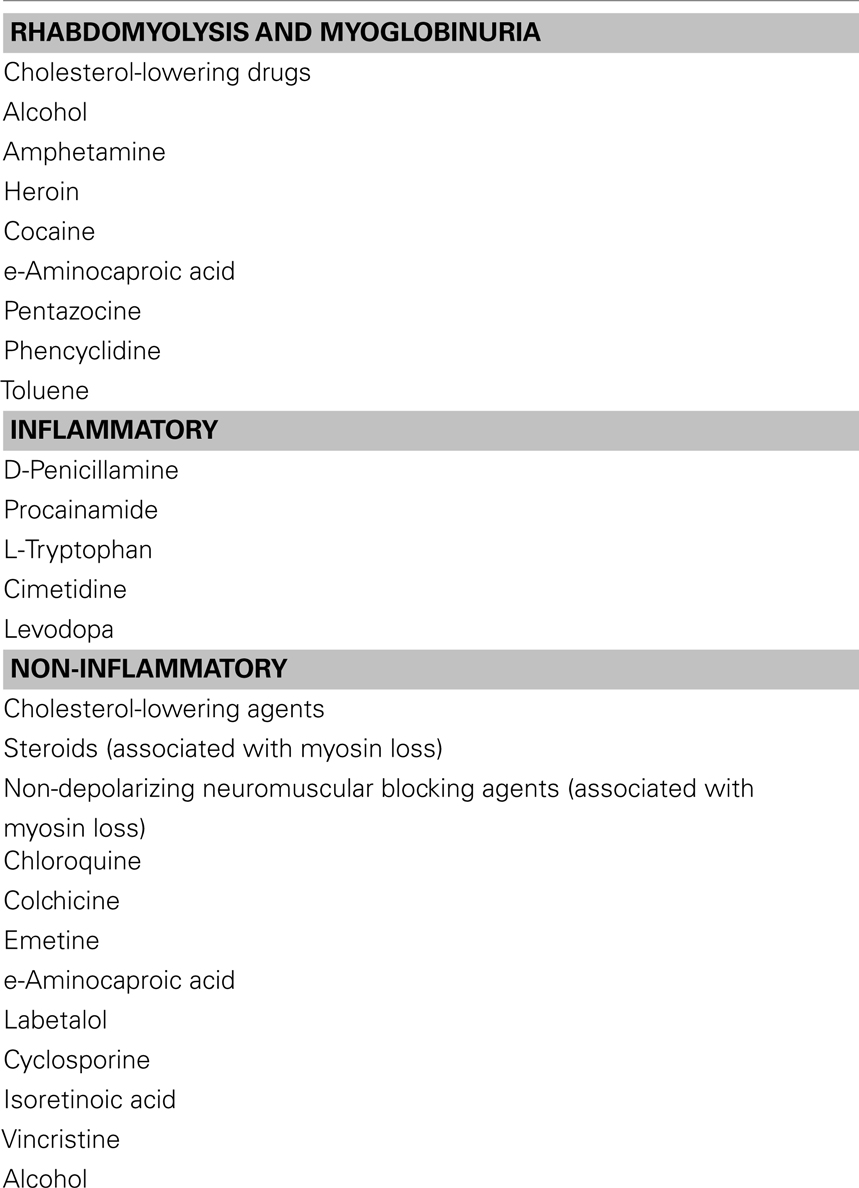
Examples of acquired causes of myopathies include: 1 Electrolyte imbalances, such as excessively high or low potassium levels 2 Infection such as tetanus or HIV 3 Inflammatory or autoimmune myopathies (eg, dermatomyositis and polymyositis) 4 Endocrine myopathies (hormonal imbalances, such as those caused by thyroid or adrenal gland problems) can interfere with muscle function 5 Toxins and medications (eg, colchicine for gout, statins for high cholesterol)
What causes muscle weakness?
Causes of myopathy are varied and include any condition that causes dysfunction of the muscle fibers leading to muscle weakness. Causes are usually grouped into those that are inherited, and those that are acquired.
How do you know if you have myopathy?
Symptoms of myopathy vary depending on the cause but may include: Muscle weakness. Muscle cramps or spasms. Muscle stiffness. Delayed motor skills. Difficulty or awkward walking. Difficulty brushing teeth or hair. Drooping eyelids. Facial weakness.
What are the symptoms of congenital myopathy?
Congenital myopathy: These are rare muscle diseases present at birth, symptoms include skeletal and facial abnormalities and developmental delays in muscle skills. Glycogen-storage disease of muscle: Caused by mutations in the genes that control enzymes that metabolize glycogen and glucose. Mitochondrial myopathies: Caused by genetic abnormalities ...
What is the name of the disorder where abnormal genes interfere with the production of proteins needed to form healthy muscle?
Muscular dystrophy: A group of muscle diseases where abnormal genes (mutations) interfere with the production of proteins needed to form healthy muscle. Myoglobinurias: Caused by disorders in the metabolism of myoglobin, a fuel necessary for muscle work (eg, McArdle syndrome, Tarui disease)
Can you get a muscle biopsy at 11 weeks?
Genetic testing may also be done and a muscle biopsy may be taken of your muscle for examination in a laboratory. You can consider minimally invasive prenatal testing (such as chorionic villus sampling at 11 weeks or amniocentesis at 15 weeks) if you are pregnant and have a known family history of inherited myopathies.
What is Alcoholic Myopathy?
Alcoholic myopathy is a condition involving muscle weakness and loss of muscle due to abnormal breakdown of muscle tissue. 2 This muscular degeneration leads to muscle dysfunction, which impacts various parts of the body and their functionality and can be either acute or chronic. 2,3
Symptoms of Alcoholic Myopathy
The symptoms of alcoholic myopathy can vary between people, and not everyone will experience all symptoms. 3 In addition, the symptoms of acute alcoholic myopathy are significantly different from chronic alcoholic myopathy. 1,3 Symptoms associated with acute alcoholic myopathy include: 1,2,3
Causes and Risk Factors
Alcohol-related myopathy happens as a direct result of alcohol consumption. 1,3 Alcohol affects the body, including the muscles, which leads to muscle weakness and wasting. Alcohol consumption and alcohol use disorders commonly lead to: 1,2,3
Alcoholic Myopathy Treatment & Outlook
Alcoholic myopathy can lead to major complications. When muscle fibers break down, they release proteins and electrolytes into the blood, which can cause other issues. 2,4 This can lead to high levels of potassium in the blood (hyperkalemia), which can make the heart beat abnormally and is potentially fatal.
Ways to Get in Contact With Us
If you believe you or someone you love may be struggling with addiction, let us hear your story and help you determine a path to treatment.
Is Alcoholic Myopathy Reversible?
In most cases, alcoholic myopathy is a reversible condition. Total abstinence from alcohol can often help reverse the symptoms. 1,2 For acute alcoholic myopathy, symptoms can typically be reversed within a few days to weeks, while chronic alcoholic myopathy can often take between 2 months to a year to be reversed.
How to treat myopathy?
Treatment options for myopathy include splinting, bracing, medications, physical therapy, and surgery. In rare cases, myopathy may be a sign of a serious neuromuscular disorder. Seek immediate medical care (call 911) for serious symptoms, including difficulty lifting the front part of your foot and toes, weakness in your legs, feet or ankles, ...
What is the best treatment for myopathies?
Both acquired and inherited chronic myopathies require supportive therapy, such as physical therapy, bracing, or surgery, to decrease inflammation if appropriate, reduce symptoms, and increase function.
What is myopathy in a muscle?
What is myopathy? Myopathy refers to any disease that affects muscle tissue. Diseases of the muscle result in weakness, inflammation, tetany (spasms), or paralysis. Myopathy can be the result of either inherited or acquired causes. Acute "acquired" myopathies, such as acute stiffness, spasm, or cramp, are common.
Why do I get myopathy?
Most commonly, people develop acquired myopathy from muscle fatigue, electrolyte imbalance, or dehydration, resulting in stiffness or cramping. Other causes of myopathy include immune disorders that cause inflammation and pain.
What are congenital myopathies?
Congenital myopathies, that are present at birth. Familial periodic paralysis. Glycogen storage disease of muscle (including Pompe’s disease) Mitochondrial myopathies (abnormalities of the cellular components known as mitochondria) Muscular dystrophy.
What are the complications of myopathy?
Complications of myopathy include: Chronic muscle pain (myalgia) Disability. Paralysis.
What are some examples of myopathy?
Examples include: Common muscle cramps. Dehydration (loss of body fluids and electrolytes, which can be life threatening when severe and untreated) Endocrine disorders. Infection. Myositis (muscle inflammation) Neuron disorders (typically neuromuscular diseases)

Overview
Clinical significance
Pathophysiology
Causes
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Prognosis
Prevention
Treatment
- There are not effective treatments that can regenerate or heal your muscles to cure myopathy. When there is an identifiable cause, such as an endocrine problem, correcting the cause can help improve the symptoms of myopathy, or may at least help prevent it from worsening.