Treatment consisted of aspiration of exudate from the retrobulbar area, systemic oxacillin at 50 mg/kg divided t.i.d., and temporary tarsorrhaphy (Rosenberg and Blouin, 1979).
Is MRSA coagulase negative?
aureus, and perhaps particularly MRSA, have been reported since 1970 2 (and a catalase-negative example was reported recently). However, they stated that the first tube- coagulase - negative MRSA was reported in 1993.
What is MRSA and how dangerous is it?
What is MRSA? MRSA is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a potentially dangerous type of staph bacteria that is resistant to certain antibiotics and may cause skin and other infections. As with all regular staph infections, recognizing the signs and receiving treatment for MRSA skin infections in the early stages reduces the
Is Shigella coagulase positive or negative?
Shigella species are facultative anaerobes, are non-motile, oxidase negative, urease negative, do not decarboxylate lysine, and all except S. dysenteriae type 1 are catalase positive1. The species may be differentiated by biochemical tests and serology of their lipopolysaccharides2. What does positive catalase test mean?
What antibiotics treat coagulase negative staph in urine?
If coag-negative staph is considered pathogenic, vancomycin is the preferred treatment. Second-line alternatives that are also active in the setting of methicillin resistance such as telavancin, linezolid, or daptomycin may be considered based on patient factors and the site of infection.

What is the best treatment for Staphylococcus?
The treatment of choice for S. aureus infection is penicillin. In most countries, S. aureus strains have developed a resistance to penicillin due to production of an enzyme by the bacteria called penicillinase....These include:methicillin.nafcillin.oxacillin.cloxacillin.dicloxacillin.flucloxacillin.
What does coagulase positive Staphylococcus mean?
Staphylococcus aureus and other coagulase-positive staphylococci (CoPS) are opportunistic pathogens associated with a large spectrum of diseases that range from skin and mucosal infections to life-threatening septicemias in humans and animals.
What causes coagulase positive Staphylococcus?
Coagulase positive staphylococci are known human pathogens. Transmission of these organisms occurs through direct contact with colonized or infected persons or through indirect contact with contaminated objects. S. aureus is the most common species in this group; additional species include S.
What antibiotic kills coagulase-negative staph?
Recently, several new antimicrobials with good activity against coagulase-negative staphylococci have been introduced into clinical practice: linezolid, tigecycline and daptomycin. Linezolid displays good activity against the coagulase-negative staphylococci, including glycopeptide resistant strains (4,18,40,75,150).
Which group of staphylococci usually causes the most serious infections?
Staphylococcus aureus is the most dangerous staphylococcal species. Most staphylococcal diseases involve direct tissue invasion and cause skin and soft-tissue infections, IV catheter infections, pneumonia, endocarditis, or osteomyelitis.
What are the two types of staphylococcal coagulase?
Coagulase is an enzyme-like protein and causes plasma to clot by converting fibrinogen to fibrin. Staphylococcus aureus produces two forms of coagulase: bound and free. Bound coagulase (clumping factor) is bound to the bacterial cell wall and reacts directly with fibrinogen.
Does Cipro cover coagulase negative Staphylococcus?
In contrast MR Staphylococcus epidermidis and other coagulase-negative strains showed a constant susceptibility to this agent (80%). Ciprofloxacin has limited usefulness against MR Staphylococcus aureus but can be still used to treat Staphylococcus epidermidis infections.
Which disease is caused by staphylococci?
It is the leading cause of skin and soft tissue infections such as abscesses (boils), furuncles, and cellulitis. Although most staph infections are not serious, S. aureus can cause serious infections such as bloodstream infections, pneumonia, or bone and joint infections.
Is Staphylococcus a toilet infection?
Doctors and other medical institutions, have warned that mere toilet infections, if not properly treated can cause staphylococcus, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which is one of the major culprit responsible for infertility.
Does ceftriaxone cover coagulase-negative staph?
Patients with deep-seated infections caused by methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) or coagulase-negative Staphylococcal species will be randomly assigned home IV treatment with ceftriaxone OR one of the three other antibiotics before leaving the hospital.
Which antibiotic is most effective against Staphylococcus aureus?
The antibiotics most effective against all S aureus cultures for outpatients were linezolid (100%), trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole (95%) and tetracyclines (94%). Linezolid (100%), trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole (100%) were most effective against MRSA isolates.
Can ciprofloxacin treat Staphylococcus aureus?
Ciprofloxacin appears to be safe and effective for a wide variety of clinical infections. In-vitro and animal studies point to high cure rates for both methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections.
What is a coagulase positive staphylococcus aureus?
Staphylococcus aureus) Coagulase-positive staphylococci bacteria are potential pathogens that are carried by 30–40 % of the healthy population. Baird–Parker agar is often used for enumeration, with incubation at 37 °C for 48 hours, but atypical colonies can cause confusion.
What is the etiological agent of staphylococcal food poisoning?
Abstract. Staphylococcal enterotoxins, produced by Staphylococcus aureus and few other species of coagulase positive staphylococci (CPS), are the etiological agents of the staphylococcal food poisoning (SFP), one of the most widespread foodborne intoxications.
What is the medium of Staph. aureus?
The medium contains a supplement of egg yolk and tellurite. Typical, coagulase-positive Staph. aureus produces colonies that are grey–black and shiny, with a narrow, white margin surrounded by a zone of clearing (often described as 'rabbit eye' colonies).
What antibiotics are used for deep infections?
Systemic antibiotics are rarely indicated but may be required in severe or deep infections. Potentiated sulfonamides are commonly used, but resistant organisms may require treatment with drugs such as penicillin, cephalosporins, enrofloxacin, erythromycin and gentamicin.
Can Staphylococcus aureus cause mastitis?
Staphylococcus aureus. Coagulase-positive Staphylococcus aureus can cause clinical and subclinical mastitis in lactating animals. In this way, they can contaminate raw milk during milking. Milk and dairy products can also be contaminated by strains of human origin.
Is prawn a coagulase positive food?
One food and one category of foods, i.e., desiccated coconut and cooked seawater or freshwater foods (such as prawns, shrimps, crayfish, lobsters, crab meat, oysters, mussels, clams), and fish, respectively, are specifically tested for coagulase-positive S. aureus and must be found negative-on-test when analyzed.
Can you detect coagulase positive S. aureus?
Therefore, detection of low numbers of coagulase-positive S. aureus during cheese ripening is possible while a high concentration of toxin could be present. To avoid this situation, the most suitable time to sample cheese for coagulase-positive S. aureus is immediately after manufacture.
Where are staphlococci found?
Staphylococci are ubiquitous bacteria found on the skin, nose and throat in warm-blood animals (mammals and birds) and especially in humans. They have also been isolated in the natural environment (soil, water, dust and air), at home (kitchen, fridge), in hospitals environment, in food processing plants and from foodstuffs.
What is a stylococcus aureus?
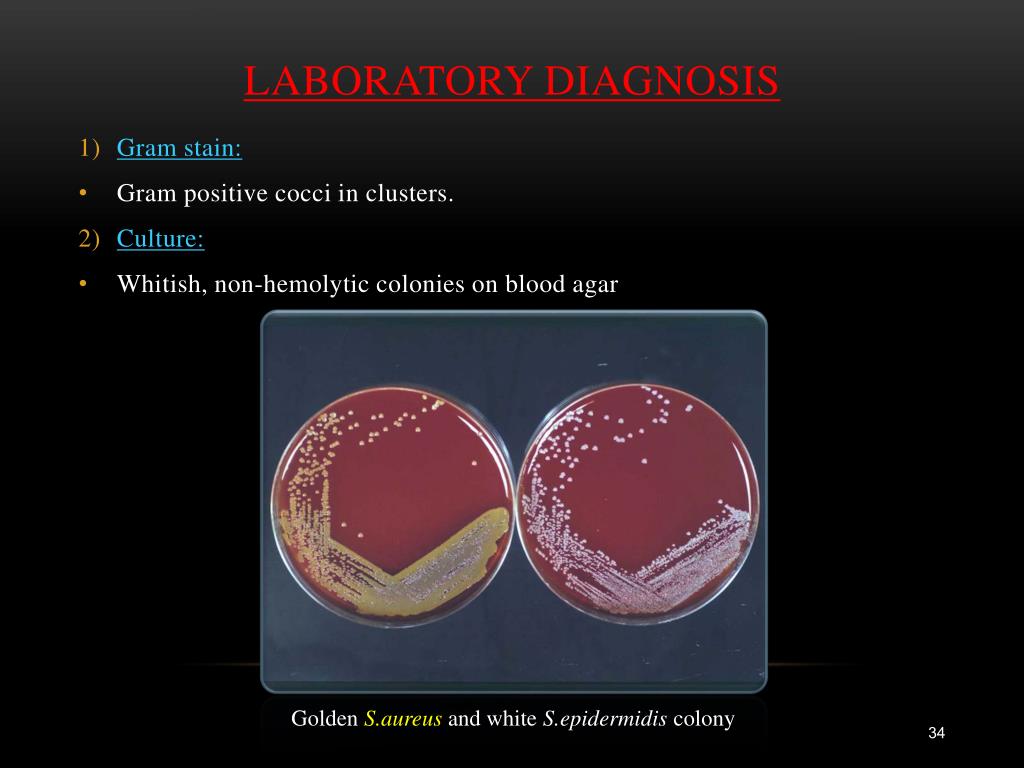
S. aureus , the type species of the Staphylococcus genus is a golden yellow colony-forming Staphylococcus. It produces numerous toxins including staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) responsible for staphylococcal food-poisoning outbreaks (SFPO). To date, 21 different serotypes (SEA to SEE, SEG to SEV) have been described, six of them have been involved in SFPO: SEA (the most commonly detected in SFPO) to SEE, SEH. Unlike the bacterium, SEs are stable to heat treatments generally applied during food processing.#N#Other species of coagulase-positive staphylococci (CPS) can also produce SEs, but their role in SFPO has still not been clarified.
How long does it take to recover from a syringe infection?
In the majority of cases, recovery occurs within 18 to 24 hours without specific treatment, while diarrhoea and general weakness can last 24 hours or longer. Death is rare, occurring in the most susceptible people to dehydration (infants and the elderly) and people affected by an underlying illness.
What is the genus of staph?
Bacteria and enterotoxins. Staphylococcus is the main genus of the Staphylococcacceae family in the order of Bacillales, the class of Bacilli and the phylum of Firmicutes. There are 3 coagulase-positive Staphylococcus (CPS) species: ► Staphylococcus aureus,
Which species is more pathogenic, Staphylococcus aureus or Staphylococcus au
Among those three species, S. aureus is the specie with the more pathogenic of the genus Staphylococcus. In the frame of the mandate, the hazard considered is food poisoning due to the enterotoxins of S. aureus.
Do you need a mask for S. aureus?
Regarding preventive measures carried out by at-risk food handlers, it is not necessary to screen S. aureus carrier before recruitment, nor to exclude a healthy carrier (nose or throat carriage), provided that these GHPs are applied.
Can sterilisation cause SFPO?
Destruction of SEs: no compatible treatment with food processes can guarantee complete inactivation. Depending on the amount of enterotoxins initially present, sterilisation (of milk for example, UH T-type treatment) can only partially destroy the SEs, leaving enough in the food to cause SFPO .
Why is staphylococcus a suspect?
Staphylococcal food poisoning is usually suspected because of case clustering (eg, within a family, attendees of a social gathering, or customers of a restaurant). Confirmation (typically by the health department) entails isolating staphylococci from suspect food and sometimes testing for enterotoxins.
Where are staphylococci carried?
Pathogenic staphylococci are ubiquitous. They are carried, usually transiently, in the anterior nares of about 30% of healthy adults and on the skin of about 20%; from these locations, staphylococci can cause infection in the host and others. Carriage rates are higher in hospital patients and personnel.
What is the most common form of staphylococcal disease?
Skin infections are the most common form of staphylococcal disease. Superficial infections may be diffuse, with vesicular pustules and crusting ( impetigo ) or sometimes cellulitis , or focal with nodular abscesses ( furuncles and carbuncles ). Deeper cutaneous abscesses are common.
How long does it take for a prosthetic joint to get infected?
Staphylococcal infection of a prosthetic joint in the months after implantation is usually acquired during surgery, whereas infections occurring more than 12 months after surgery are likely due to hematogenous spread.
Which pathogens are virulent?
The ability to clot blood by producing coagulase distinguishes the virulent pathogen, Staphylococcus aureus, from the less virulent coagulase-negative staphylococcal species. Coagulase-positive S. aureus is among the most ubiquitous and dangerous human pathogens, for both its virulence and its ability to develop antibiotic resistance. ...
What antibiotics are resistant to tedizolid?
Some strains are partially or totally resistant to all but the newest antibiotics, which include linezolid, tedizolid, quinupristin/dalfopristin, daptomycin, telavancin, dalbavancin, oritavancin, tigecycline, eravacycline, omadacycline, delafloxacin, ceftobiprole (not available in the US ), ceftaroline, and lefamulin.
Is PVL a staphylococcal disease?
aureus (CA-MRSA) and has been thought to mediate the ability to necrotize; however, this effect has not been verified. Toxin-mediated staphylococcal diseases include the following: Toxic shock syndrome.