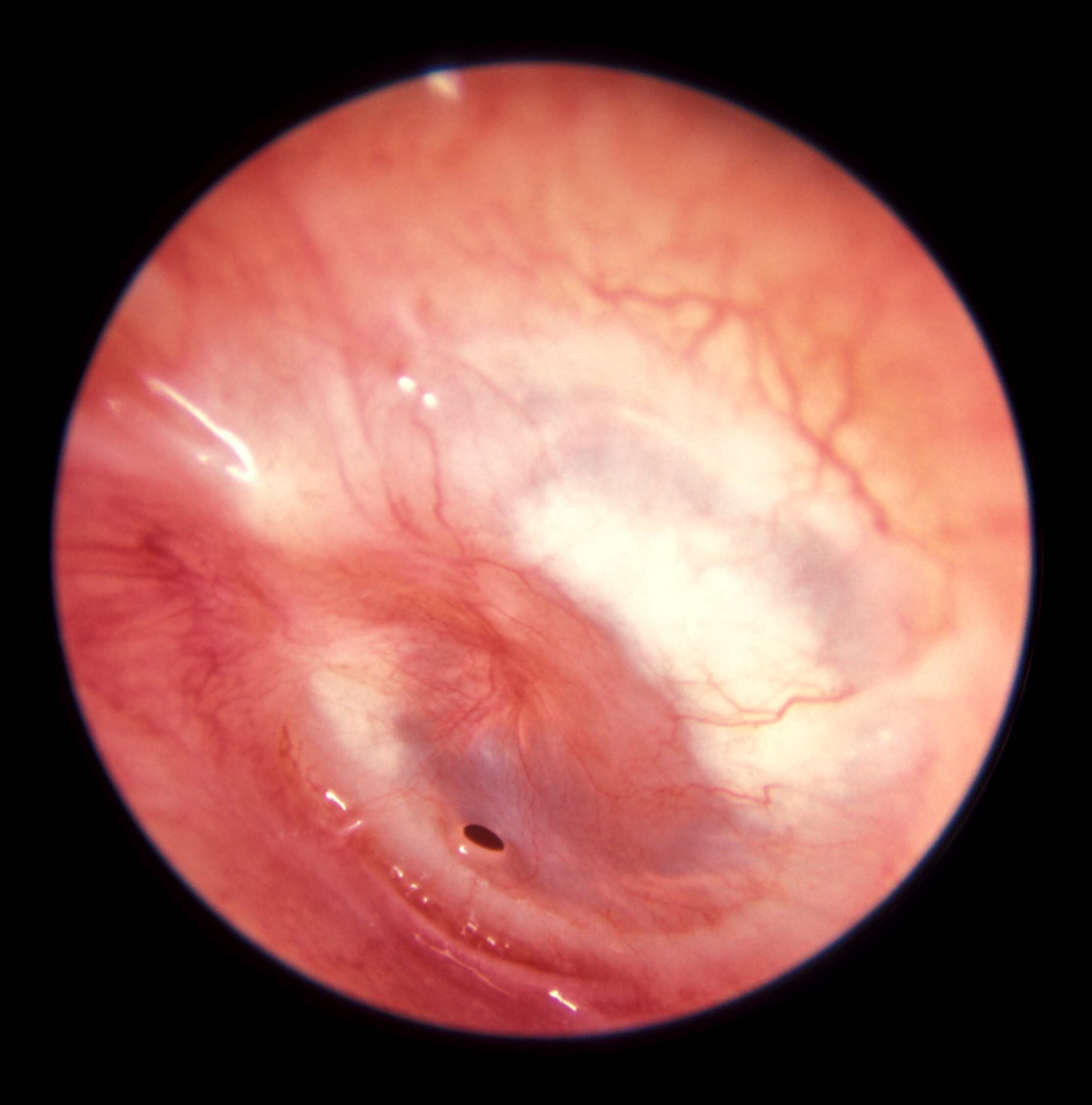
When should AOM be treated with antibiotics?
Key Action Statement 3A: Severe AOM: The clinician should prescribe antibiotic therapy for AOM (bilateral or unilateral) in children 6 months and older with severe signs or symptoms (ie, moderate or severe otalgia or otalgia for at least 48 hours or temperature 39°C [102.2°F] or higher).Mar 1, 2013
How is serous otitis media treated?
Etiologic treatment of serous otitis rests on restoration of satisfactory nasal ventilation (education to improve nose-blowing, adenoidectomy), improvement of eustachian tube patency (corticosteroids), and modification of the characteristics of middle ear secretions (mucolytic agents and mucomodifying agents).
What is the basic course of treatment for otitis media?
High-dosage amoxicillin (80 to 90 mg per kg per day, divided into two daily doses for 10 days) is recommended as first-line antibiotic therapy in children with acute otitis media. 1,24 In children older than six years with mild to moderate disease, a five- to seven-day course is adequate.Dec 1, 2007
How long do you treat AOM?
APPROPRIATE DURATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL THERAPY FOR AOM (43–45) Ten days of oral antimicrobial treatment courses are appropriate for children <2 years of age, for children with recurrent AOM or otitis media associated with a perforated TM, and for cases where initial therapy failed.
What is an AOM?
Overview. Acute otitis media (AOM) is a painful type of ear infection. It occurs when the area behind the eardrum called the middle ear becomes inflamed and infected. The following behaviors in children often mean they have AOM: fits of fussiness and intense crying (in infants)
How do you treat serous otitis media in adults?
(Serous Otitis Media; Otitis Media with Effusion) Most cases resolve in 2 to 3 weeks. If there is no improvement in 1 to 3 months, some form of myringotomy is indicated, usually with insertion of a tympanostomy tube. Antibiotics and decongestants are not effective.
What type of antibiotics treat ear infections?
Here are some of the antibiotics doctors prescribe to treat an ear infection:Amoxil (amoxicillin)Augmentin (amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate)Cortisporin (neomycin/polymxcin b/hydrocortisone) solution or suspension.Cortisporin TC (colistin/neomycin/thonzonium/hydrocortisone) suspension.More items...•Nov 26, 2018
Can ciprofloxacin treat otitis media?
Ciprofloxacin appears to be an effective treatment of chronic otitis media, and superior to amoxycillin/clavulanic acid.
What antibiotics treat middle ear infection?
Antibiotics are often not needed for middle ear infections because the body's immune system can fight off the infection on its own. However, sometimes antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, are needed to treat severe cases right away or cases that last longer than 2–3 days.Jul 1, 2021
How is Otomycosis treated?
Medication. Your doctor will probably prescribe antifungal ear drops. They may contain clotrimazole, fluconazole, or miconazole. In a study of 214 people with otomycosis, researchers found that clotrimazole drops, miconazole cream, and fluconazole drops had the same effectiveness.Apr 20, 2021
What myringotomy means?
Myringotomy is a surgical procedure of the eardrum or tympanic membrane. The procedure is performed by making a small incision with a myringotomy knife through the layers of tympanic membrane (see the image below).Nov 9, 2021
What causes ear infections in adults?
Ear infections in adults are typically caused by germs, such as viruses, a fungus, or bacteria. The way a person becomes infected will often determine the kind of infection they get. People with weakened immune systems or inflammation in the structures of the ear may be more prone to ear infections than others.
What is AOM in 2021?
Last Update: March 16, 2021. Continuing Education Activity. Acute otitis media (AOM) is defined as an infection of the middle ear and is the second most common pediatric diagnosis in the emergency department following upper respiratory infections. Although acute otitis media can occur at any age, it is most commonly seen between the ages ...
What is acute otitis media?
Acute otitis media is defined as an infection of the middle ear space. It is a spectrum of diseases that include acute otitis media (AOM), chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM), and otitis media with effusion (OME).
How long does amoxicillin stay in your system?
When a bacterial etiology is suspected, the antibiotic of choice is high-dose amoxicillin for ten days in both children and adult patients who are not allergic to penicillin. Amoxicillin has good efficacy in the treatment of otitis media due to its high concentration in the middle ear.
When does otitis media occur?
Although acute otitis media can occur at any age, it is most commonly seen between the ages of 6 to 24 months. Approximately 80% of all children will experience a case of otitis media during their lifetime, and between 80% and 90% of all children will have otitis media with an effusion before school age.
What is the most common bacterial infection in the middle ear?
Infection of the middle ear can be viral, bacterial, or coinfection. The most common bacterial organisms causing otitis media are Streptococcus pneumoniae, followed by non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae(NTHi), and Moraxella catarrhalis.
What is the name of the condition that affects the middle ear?
There are different types of ear infections. Middle ear infection (acute otitis media) is an infection in the middle ear. Another condition that affects the middle ear is called otitis media with effusion. It occurs when fluid builds up in the middle ear without being infected and without causing fever, ear pain, or pus build-up in the middle ear.
How long does a middle ear infection last?
Pus, discharge, or fluid coming from the ear. Worsening symptoms. Symptoms of a middle ear infection that last for more than 2–3 days. Hearing loss. This list is not all-inclusive. Please see a doctor for any symptom that is severe or concerning.
What causes a middle ear infection?
Causes. A middle ear infection may be caused by: Bacteria, like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae (nontypeable) —the two most common bacterial causes. Viruses, like those that cause colds or flu.
How long does it take for a child to feel better after antibiotics?
This gives the immune system time to fight off the infection. If your child doesn’t feel better after 2–3 days of rest, extra fluids, and pain relievers, the doctor may write a prescription for an antibiotic.
Can antibiotics be used for ear infections?
Antibiotics are often not needed for middle ear infections because the body’s immune system can fight off the infection on its own. However, sometimes antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, are needed to treat severe cases right away or cases that last longer than 2–3 days. For mild cases of middle ear infection, your doctor might recommend watchful ...
What is the best medicine for a fever?
Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen to relieve pain or fever. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about over-the-counter medicines that can help you feel better. Always use over-the-counter medicines as directed. Top of Page.
How to prevent ear infections?
You can help prevent ear infections by doing your best to stay healthy and keep others healthy, including: Receive recommended vaccines, such as flu vaccine and pneumococcal vaccine. Pneumococcal vaccine protects against a common cause of middle ear infections, Streptococcus pneumonia. Clean your hands.
What is the purpose of a pneumatic otoscope?
A pneumatic otoscope blows a puff of air into the ear to test eardrum movement. Tympanometry is a test that can be performed in most health care providers' offices to help determine how the middle ear is functioning.
What are the different types of otitis media?
Different types of otitis media include the following: Acute otitis media. This middle ear infection occurs abruptly causing swelling and redness. Fluid and mucus become trapped inside the ear, causing the child to have a fever and ear pain. Otitis media with effusion. Fluid (effusion) and mucus continue to accumulate in ...
What is the cause of ear infections?
Middle ear infections are usually a result of a malfunction of the eustachian tube, a canal that links the middle ear with the throat area. The eustachian tube helps to equalize the pressure between the outer ear and the middle ear.
Why is my eustachian tube not working?
The following are some of the reasons that the eustachian tube may not work properly: A cold or allergy which can lead to swelling and congestion of the lining of the nose, throat, and eustachian tube (this swelling prevents the normal drainage of fluids from the ear) A malformation of the eustachian tube.
What is the name of the inflammation in the middle of the ear?
Middle Ear Infection. Otitis media is inflammation or infection located in the middle ear. Otitis media can occur as a result of a cold, sore throat, or respiratory infection.
How do you know if you have otitis media?
Ear Infection Symptoms. The following are the most common symptoms of otitis media. However, each child may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include: Unusual irritability. Difficulty sleeping or staying asleep. Tugging or pulling at one or both ears. Fever, especially in infants and younger children.
How long does fluid stay in the ear?
If fluid remains in the ear (s) for longer than three months, and the infection continues to reoccur even with the use of antibiotics, your child's health care provider may suggest that small tubes be placed in the ear (s).
