
The treatment is any independent variable manipulated by the experimenters, and its exact form depends on the type of research being performed. In a medical trial, it might be a new drug or therapy. In public policy studies, it could be a new social policy that some receive and not others.
What is a typical application of the scientific method?
In a typical application of the scientific method, a researcher develops a hypothesis, tests it through various means, and then modifies the hypothesis on the basis of the outcome of the tests and experiments.
How do scientists use the scientific method to solve problems?
When following the scientific method, scientists must ask questions, gather and look at the evidence and determine whether the answers to their questions can be found through that evidence. Scientists also use the method to determine whether all information presented and found can combine to create a logical answer.
What are the final steps of the scientific method?
These can be tested by collecting data using the appropriate methodology. The final steps of the scientific method include data analysis and validation of the hypothesis. Altogether, the conclusions drawn from the scientific method will lead to new questions.
When did the scientific method begin?
The term "scientific method" emerged in the 19th century, when a significant institutional development of science was taking place and terminologies establishing clear boundaries between science and non-science, such as "scientist" and "pseudoscience", appeared.

What is a treatment level in an experiment?
the specific condition to which a group or participant is exposed in a study or experiment. For example, in a design employing four groups, each of which is exposed to a different dosage of a particular drug, each dosage amount represents a level of the treatment factor.
How do you find treatments in an experiment?
Treatments are administered to experimental units by 'level', where level implies amount or magnitude. For example, if the experimental units were given 5mg, 10mg, 15mg of a medication, those amounts would be three levels of the treatment.
What are the 7 steps of the scientific method?
The seven steps of the scientific methodAsk a question. The first step in the scientific method is asking a question that you want to answer. ... Perform research. ... Establish your hypothesis. ... Test your hypothesis by conducting an experiment. ... Make an observation. ... Analyze the results and draw a conclusion. ... Present the findings.
What are the methods of the scientific method?
The six steps of the scientific method include: 1) asking a question about something you observe, 2) doing background research to learn what is already known about the topic, 3) constructing a hypothesis, 4) experimenting to test the hypothesis, 5) analyzing the data from the experiment and drawing conclusions, and 6) ...
What is the treatment variable?
the independent variable, whose effect on a dependent variable is studied in a research project.
What is treatment in biology?
Biological or biologic therapy is treatment designed to stimulate or restore the ability of the body's immune (natural internal defense) system to fight infection and disease.
What are the 6 basic steps of scientific method?
The scientific methodMake an observation.Ask a question.Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation.Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.Test the prediction.Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions.
What are the 6 scientific methods in order?
The Six StepsPurpose/Question. Ask a question.Research. Conduct background research. ... Hypothesis. Propose a hypothesis. ... Experiment. Design and perform an experiment to test your hypothesis. ... Data/Analysis. Record observations and analyze the meaning of the data. ... Conclusion.
What is scientific method order?
The correct order of the steps in the scientific method are: (1) Ask a question. (2) Make a hypothesis. (3) Test the hypothesis. (4) Analyze the results.
What are the 5 steps in scientific method?
Here are the five steps.Define a Question to Investigate. As scientists conduct their research, they make observations and collect data. ... Make Predictions. Based on their research and observations, scientists will often come up with a hypothesis. ... Gather Data. ... Analyze the Data. ... Draw Conclusions.
What are the 4 steps to the scientific method?
The scientific method has four steps:Observation and description of a phenomenon (a concept),Formulation of a hypothesis to explain the phenomenon,Test the hypothesis. ... Establish a theory based on repeated verification of the results.
What are the 3 scientific methods?
Observation. The first step of the scientific method involves making an observation about something that interests you. ... Hypothesis. The hypothesis is a key component of the scientific process. ... Experiment. Once you've developed a hypothesis, you must design and conduct an experiment that will test it. ... Results.
What is scientific method?
More specifically, it is the technique used in the construction and testing of a scientific hypothesis. Flow chart depicting the scientific method.
Why is the scientific method important?
The scientific method is critical to the development of scientific theories, which explain empirical (experiential) laws in a scientifically rational manner. In a typical application of the scientific method, a researcher develops a hypothesis, tests it through various means, and then modifies the hypothesis on the basis of the outcome ...
What is the variable that is deliberately changed in an experiment?
The variable deliberately changed in an experiment is known as the independent variable. The dependent variable is the variable that may change as a result of changes in the independent variable. In most experiments, one variable is independent, one is dependent, and all others are controlled. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
What are empirical tools?
Many empirical sciences, especially the social sciences, use mathematical tools borrowed from probability theory and statistics, together with outgrowths of these, such as decision theory, game theory, utility theory, and operations research.
What is the purpose of hypotheses?
In this way, hypotheses serve as tools by which scientists gather data. From that data and the many different scientific investigations undertaken to explore hypotheses, scientists are able to develop broad general explanations, or scientific theories. scientific method; examples of independent and dependent variables.
Is the scientific method unique to any field of science?
The process of observing, asking questions, and seeking answers through tests and experiments is not unique to any one field of science. In fact, the scientific method is applied broadly in science, across many different fields.
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a process used when conducting experiments and exploring observations. Some areas of science rely more heavily on this method to answer questions, as they are more easily tested than other areas. The goal of this method is to discover the relationships between cause and effect in various situations and applications.
Why do scientists use the scientific method?
Scientists also use the method to determine whether all information presented and found can combine to create a logical answer. The scientific method provides a way to apply logical and rational problem-solving methods to scientific questions.
What happens if you don't do the experiment?
If it did not happen, you can create a new hypothesis and return to step four, and conduct a new experiment to prove your new theory. If what you hypothesized happened during the experimentation phase, the final step is putting together your findings and presenting them to others.
What is hypothesis in science?
A hypothesis is an educated guess that seeks to answer a question that can be systematically tested. Your hypothesis should also include your predictions that you can measure through experimentation and research.
How many steps are there in the scientific method?
The seven steps of the scientific method. Based on the type of question being asked, the type of science being applied and the laws that apply to that particular branch of science, you may need to modify the method and alter or remove one or several of the steps. Here are the seven steps of the scientific method illustrated by an example scientific ...
How to make sure the results of an experiment are accurate?
If you change any factors in your experiment, keep all others the same to maintain fairness. After you complete the experiment, repeat it a few more times to make sure the results are accurate.
What is a science career?
A career in science involves the use of various processes and methods to reach conclusions. If you plan to pursue a scientific career path, it is helpful to understand some key methods that you might use and encounter in your daily tasks.
What happens if an experiment is analyzed and a hypothesis is disproved?
If your hypothesis is disproved, then you can go back with the new information gained and create a new hypothesis to start the scientific process over again.
Why do you want to be a savvy scientist?
Rather than starting from scratch in putting together a plan for answering your question, you want to be a savvy scientist using library and Internet research to help you find the best way to do things and ensure that you don't repeat mistakes from the past.
Why do scientists go back and construct a new hypothesis?
Scientists often find that their predictions were not accurate and their hypothesis was not supported , and in such cases they will communicate the results of their experiment and then go back and construct a new hypothesis and prediction based on the information they learned during their experiment.
What is hypothesis in science?
A hypothesis is an educated guess about how things work. It is an attempt to answer your question with an explanation that can be tested. A good hypothesis allows you to then make a prediction:#N#"If _____ [I do this] _____, then _____ [this] _____ will happen."
What is iterative process?
A process like the scientific method that involves such backing up and repeating is called an iterative process. Whether you are doing a science fair project, a classroom science activity, independent research, or any other hands-on science inquiry understanding the steps of the scientific method will help you focus your scientific question ...
How to find evidence for an answer?
If you want to find evidence for an answer or an answer itself then you construct a hypothesis and test that hypothesis in an experiment. If the experiment works and the data is analyzed you can either prove or disprove your hypothesis.
What is the scientific method?
Updated August 21, 2019. The scientific method is a series of steps followed by scientific investigators to answer specific questions about the natural world. It involves making observations, formulating a hypothesis, and conducting scientific experiments. Scientific inquiry starts with an observation followed by the formulation ...
What is the first step in the scientific method?
The first step of the scientific method involves making an observation about something that interests you. This is very important if you are doing a science project because you want your project to be focused on something that will hold your attention.
What is the scientific process of a hypothesis?
Hypothesis. The hypothesis is a key component of the scientific process. A hypothesis is an idea that is suggested as an explanation for a natural event, a particular experience, or a specific condition that can be tested through definable experimentation.
What should you do once you have developed a hypothesis?
Once you've developed a hypothesis, you must design and conduct an experiment that will test it. You should develop a procedure that states very clearly how you plan to conduct your experiment. It is important that you include and identify a controlled variable or dependent variable in your procedure.
What are some examples of hypothesis?
An example of a good hypothesis is: If there is a relation between listening to music and heart rate, then listening to music will cause a person's resting heart rate to either increase or decrease.
When did the scientific method start?
The term "scientific method" emerged in the 19th century, when a significant institutional development of science was taking place and terminologies establishing clear boundaries between science and non-science, such as "scientist" and "pseudoscience", appeared.
What happens when you apply the scientific method to research?
When applying the scientific method to research, determining a good question can be very difficult and it will affect the outcome of the investigation.
What is peer review in science?
The process of peer review involves evaluation of the experiment by experts, who typically give their opinions anonymously. Some journals request that the experimenter provide lists of possible peer reviewers, especially if the field is highly specialized. Peer review does not certify the correctness of the results, only that, in the opinion of the reviewer, the experiments themselves were sound (based on the description supplied by the experimenter). If the work passes peer review, which occasionally may require new experiments requested by the reviewers, it will be published in a peer-reviewed scientific journal. The specific journal that publishes the results indicates the perceived quality of the work.
How are measurements accompanied by uncertainty?
The uncertainty is often estimated by making repeated measurements of the desired quantity. Uncertainties may also be calculated by consideration of the uncertainties of the individual underlying quantities used. Counts of things, such as the number of people in a nation at a particular time, may also have an uncertainty due to data collection limitations. Or counts may represent a sample of desired quantities, with an uncertainty that depends upon the sampling method used and the number of samples taken.
What is the ubiquitous element of the scientific method?
This model can be seen to underlie the scientific revolution. The ubiquitous element in the scientific method is empiricism.
How do scientists test hypotheses?
This is an investigation of whether the real world behaves as predicted by the hypothesis. Scientists (and other people) test hypotheses by conducting experiments. The purpose of an experiment is to determine whether observations of the real world agree with or conflict with the predictions derived from a hypothesis. If they agree, confidence in the hypothesis increases; otherwise, it decreases. The agreement does not assure that the hypothesis is true; future experiments may reveal problems. Karl Popper advised scientists to try to falsify hypotheses, i.e., to search for and test those experiments that seem most doubtful. Large numbers of successful confirmations are not convincing if they arise from experiments that avoid risk. Experiments should be designed to minimize possible errors, especially through the use of appropriate scientific controls. For example, tests of medical treatments are commonly run as double-blind tests. Test personnel, who might unwittingly reveal to test subjects which samples are the desired test drugs and which are placebos, are kept ignorant of which are which. Such hints can bias the responses of the test subjects. Furthermore, failure of an experiment does not necessarily mean the hypothesis is false. Experiments always depend on several hypotheses, e.g., that the test equipment is working properly, and a failure may be a failure of one of the auxiliary hypotheses. (See the Duhem–Quine thesis .) Experiments can be conducted in a college lab, on a kitchen table, at CERN's Large Hadron Collider, at the bottom of an ocean, on Mars (using one of the working rovers ), and so on. Astronomers do experiments, searching for planets around distant stars. Finally, most individual experiments address highly specific topics for reasons of practicality. As a result, evidence about broader topics is usually accumulated gradually.
What is the process of making a hypothesis?
The process in the scientific method involves making conjectures (hypotheses), deriving predictions from them as logical consequences, and then carrying out experiments or empirical observations based on those predictions. A hypothesis is a conjecture, based on knowledge obtained while seeking answers to the question.
Why is the scientific method important?
The scientific method can help these kids to develop critical thinking and to give them the tools required to solve complex problems.
What are the two methods of scientific research?
Question 2: To be able to draw valid conclusions, a scientist must use a methodology that… 1 Generate reproducible data 2 Can appropriately test the hypothesis 3 Is precise enough to distinguish between conditions 4 Is performed in a controlled environment
Why are experiments important?
Obviously, experiments are an important part of the scientific method. Every rigorous scientific experiment needs to be performed using the appropriate methodology. For instance, the instrument used to test the hypothesis must be accurate and efficient. In order to be valid, the experiment must be performed along with appropriate control groups and in controlled conditions to assess the effect of a single parameter at a time. Furthermore, the scientist must take into account all the factors that can introduce a bias during data collection. The experiment also needs to be reproduced a few times to make sure that the results are reproducible and are not obtained randomly. Finally, different methodologies can be used to test the same hypothesis, therefore strengthening the validity of the scientific findings.
What happens when a scientist performs a scientific experiment?
Once the different scientific experiments are performed, the scientist will be able to re-examine the initial hypothesis. If the methodology was appropriate and that the influence of external factors was reduced to a minimum, the scientist will then be able to use his data and analysis to validate or invalidate his initial hypothesis.
What is a vivo experiment?
In Vivo Experiments. To assess the biological properties of the newly identified molecule, the scientist will next use animals to analyze how the molecule can affect a complex organism such as rats. This is a complex experiment that needs to be designed properly in order to draw the right conclusions.
Why is literature search important in scientific research?
The idea is to see if anything relevant to the question is already known. In addition, the literature search can be used to determine the appropriate methodology to address the question.
What makes the scientific method so strong?
However, what makes the strength of the scientific method is to share the knowledge gained from a scientific experiment that was performed. This way, the scientific community can benefit from the work of others before establishing their own hypotheses.
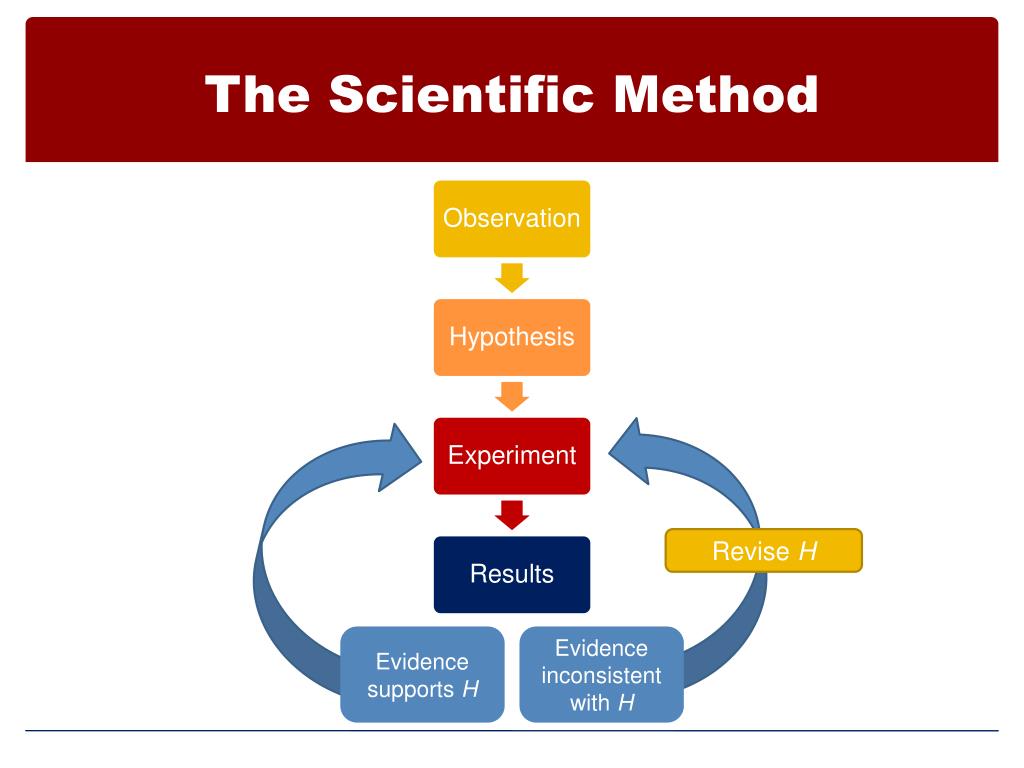
Observation
Question
- Once you've made your observation, you must formulate a question about what you have observed. Your question should tell what it is that you are trying to discover or accomplish in your experiment. When stating your question you should be as specific as possible. For example, if you are doing a project on plants, you may want to know how plants interact with microbes. Your qu…
Hypothesis
- The hypothesis is a key component of the scientific process. A hypothesis is an idea that is suggested as an explanation for a natural event, a particular experience, or a specific condition that can be tested through definable experimentation. It states the purpose of your experiment, the variables used, and the predicted outcome of your experiment. It is important to note that a …
Experiment
- Once you've developed a hypothesis, you must design and conduct an experiment that will test it. You should develop a procedure that states very clearly how you plan to conduct your experiment. It is important that you include and identify a controlled variable or dependent variable in your procedure. Controls allow us to test a single variable in an experiment because they are unchan…
Results
- The results are where you report what happened in the experiment. That includes detailing all observationsand data made during your experiment. Most people find it easier to visualize the data by charting or graphing the information.
Conclusion
- The final step of the scientific method is developing a conclusion. This is where all of the results from the experiment are analyzed and a determination is reached about the hypothesis. Did the experiment support or reject your hypothesis? If your hypothesis was supported, great. If not, repeat the experiment or think of ways to improve your procedure.