
How is a tetanus patient treated?
There's no cure for tetanus. A tetanus infection requires emergency and long-term supportive care while the disease runs its course. Treatment consists of wound care, medications to ease symptoms and supportive care, usually in an intensive care unit.Jun 15, 2021
What is the most effective treatment for tetanus?
Doctors may prescribe penicillin or metronidazole for tetanus treatment. These antibiotics prevent the bacterium from multiplying and producing the neurotoxin that causes muscle spasms and stiffness. Patients who are allergic to penicillin or metronidazole may be given tetracycline instead.
Can a person recover from tetanus?
The disease causes muscle contractions, particularly of your jaw and neck muscles. Tetanus is commonly known as lockjaw. Severe complications of tetanus can be life-threatening. There's no cure for tetanus.Jun 15, 2021
Can you survive tetanus with treatment?
Tetanus infection can be life-threatening without treatment. Approximately 10 to 20 percent of tetanus infections are fatal, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) . Tetanus is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment in a hospital.
What are the warning signs of tetanus?
Tetanus symptoms include:Jaw cramping.Sudden, involuntary muscle tightening (muscle spasms) – often in the stomach.Painful muscle stiffness all over the body.Trouble swallowing.Jerking or staring (seizures)Headache.Fever and sweating.Changes in blood pressure and fast heart rate.
Do antibiotics treat tetanus?
Antibiotics do not prevent or treat tetanus. However, antibiotics (such as penicillin, amoxicillin–clavulanate or metronidazole) can prevent other bacterial infections. All tetanus-prone wounds must be disinfected and, where appropriate, have surgical treatment.Jun 4, 2018
What is the survival rate of tetanus?
Current statistics indicate that mortality in mild and moderate tetanus is approximately 6%; for severe tetanus, it may be as high as 60%. Mortality in the United States resulting from generalized tetanus is 30% overall, 52% in patients older than 60 years, and 13% in patients younger than 60 years.Jan 18, 2019
Is tetanus permanent?
The toxin does no permanent damage, and patients who receive appropriate supportive care generally recover. Sometimes symptoms develop rapidly, and some people live in remote areas where they are not able to receive appropriate care and are at a higher risk of death from tetanus.
What is the drug of choice for tetanus?
These agents are used to eradicate clostridial organisms in the wound, which may produce tetanus toxin. They are administered to patients with clinical tetanus; however, their efficacy is questioned. Penicillin G was long considered the drug of choice, but metronidazole is now considered the antibiotic of choice.Jan 18, 2019
Who is at risk of developing tetanus?
Risk Groups Most reported cases occur in adults. From 2009–2017, more than 60% of the 264 reported cases were among people 20 through 64 years of age. In addition, a quarter of those reported cases were among people 65 years old or older. The risk of death from tetanus is highest among people 65 years old or older.
What happens if tetanus is left untreated?
If left untreated, a tetanus infection can progress from mild spasms to powerful whole-body contractions, suffocation, and heart attack.Mar 10, 2020
Does all rust have tetanus?
Rust doesn't cause tetanus, but stepping on a nail might if you're not immunized. In fact, any damage to the skin, even burns and blisters, allows tetanus-causing bacteria to enter the body. Tetanus is not as common as it once was....Protect with Tetanus-diphtheria (Td) Shots.ShotWhenBoostersEvery 10 years3 more rows•Apr 10, 1997
How to fight tetanus?
Vaccination with one of the standard tetanus vaccinations helps your immune system fight the toxins. Antibiotics, given either orally or by injection, may help fight tetanus bacteria. Other drugs. Other medications might be used to regulate involuntary muscle activity, such as your heartbeat and breathing.
How long does tetanus last?
The disease progresses for about two weeks, and recovery can last about a month.
What to do if you have a cut?
Lifestyle and home remedies. Proper wound care is important for any cut or wound. Seek medical care if you have a puncture wound, a deep cut, an animal bite, a foreign object in your wound, or a wound contaminated with dirt, soil, feces, rust or saliva. If you're unsure when you last had a tetanus vaccine, seek medical care.
What is the treatment for muscle spasms?
Antitoxin therapy is used to target toxins that have not yet attacked nerve tissues. This treatment, called passive immunization, is a human antibody to the toxin. Sedatives that slow the function of the nervous system can help control muscle spasms.
What to do if you are allergic to antibiotics?
Manage adverse reactions. If the antibiotic causes a rash, stop using it. If you're allergic to the adhesive used in most bandages, switch to adhesive-free dressings or sterile gauze and paper tape. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
How to stop bleeding from a wound?
After the bleeding stops, rinse the wound with a saline solution, bottled water or clear running water. Use antibiotics. Apply a thin layer of an antibiotic cream or oint ment to discourage bacterial growth and infection. Cover the wound. Bandages can keep the wound clean and keep harmful bacteria out.
How to prevent tetanus?
Prevention through Routine Vaccination. Since people cannot naturally acquire immunity to tetanus, the best way to prevent tetanus is to vaccinate your patients. CDC recommends tetanus vaccines for all infants and children, preteens and adolescents, and adults.
What are the symptoms of tetanus?
Tetanus is a clinical syndrome without confirmatory laboratory tests. Characteristic symptoms of tetanus are painful muscular contractions, primarily of the masseter and neck muscles and secondarily of trunk muscles. Trismus, or lockjaw, is a common sign of tetanus (see generalized tetanus under Clinical Features ). A common first sign suggestive of tetanus in older children and adults is abdominal rigidity, although rigidity is sometimes confined to the region of injury. Generalized spasms occur, frequently induced by sensory stimuli. History of an injury or apparent portal of entry may be lacking. Clinicians rarely recover the organism from the site of infection.
What is the most common form of tetanus?
Generalized tetanus is the most common form, accounting for more than 80% of cases. The most common initial sign is spasm of the muscles of the jaw or “lockjaw”. Other signs may follow “lockjaw.” These can include painful spasms in other muscle groups in the neck, trunk, and extremities and generalized, seizure-like activity or convulsions in severe cases. Nervous system abnormalities, as well as a variety of complications related to severe spasm and prolonged hospitalization, can accompany generalized tetanus. The clinical course of generalized tetanus is variable and depends on the
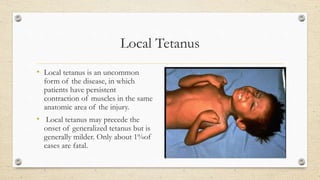
What is a localized tetanus?
Localized tetanus is an unusual form of the disease consisting of muscle spasms in a confined area close to the site of the injury. Although localized tetanus often occurs in people with partial immunity and is usually mild, progression to generalized tetanus can occur.
How many IU of tig for tetanus?
However, experts recommend 500 international units (IU), which appears to be as effective as higher doses ranging from 3,000 to 6,000 IU and causes less discomfort.
What is the sign of tetanus?
A common first sign suggestive of tetanus in older children and adults is abdominal rigidity, although rigidity is sometimes confined to the region of injury.
How long does it take for a tetanus to show up?
A shorter incubation period is associated with more severe disease, complications, and a higher chance of death. In neonatal tetanus, symptoms usually appear from 4 to 14 days after birth, averaging about 7 days.
What is the best medicine for tetanus?
There are some other drugs sometimes used to ease the symptoms of tetanus, such as magnesium sulfate (reduces muscle spasms), certain beta blockers (helps regulate heartbeat and breathing) and morphine (strong sedative and painkiller).
How long does tetanus treatment last?
You will be given IV antibiotics. Metronidazole 500 mg every six to eight hours is the preferred treatment for tetanus. Treatment will last seven to ten days.
How long does tetanus last?
In the U.S., virtually all infants get vaccinated with a series of DTaP shots, which contain protective antibodies against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis. However, protection generally lasts only about 10 years against tetanus infection, so booster shots are needed in early and later adulthood. [9]
How long does it take for tetanus to appear?
Tetanus symptoms can appear anytime from a few days to several weeks after the bacteria enter your body — often through a puncture wound of the foot, such as stepping on a contaminated nail. The doctor will rely on a physical exam, as well as a medical and immunization history, to diagnose tetanus.
What to do if you get a puncture wound?
If you get a deep injury (such as a puncture wound) from something sharp that appears contaminated with soil, rust, feces or other debris, then clean the wound and get a tetanus shot shot from your doctor or an urgent care clinic as a preventative strategy. Be prepared to take antibiotics.
What are the complications of tetanus?
In addition to airway obstruction and respiratory arrest (the most common reason people with tetanus die), other possible complications that can occur include: pneumonia, heart failure, brain damage and bone fractures (the ribs and spine are most common).
Is Mayo Clinic a cure?
X Trustworthy Source Mayo Clinic Educational website from one of the world's leading hospitals Go to source. This is not a cure, however, and can only neutralize "free" toxins that have not bonded to nerve tissue. Any toxins that have already bonded to nerve tissue will not be affected. As such, time is of the essence.
1. Get Medical Help Immediately
Go to a medical clinic or hospital emergency room for tetanus symptoms: rigid muscles and painful spasms, often starting in jaw and neck.
2. Follow Up
The person will immediately receive an injection of immune globulin and a tetanus shot.
What is the treatment for tetanus?
Additional treatments of tetanus include wound care, antibiotics, and medications to control muscle spasms. Mechanical ventilation and sedation may also be required. 5
Can antibiotics be used for tetanus?
While antibiotics are not recommended for use against tetanus, they can be used if a wound appears to be infected. 2 A person who has sustained a wound considered to be at high risk for tetanus should receive a single dose of human TIG administered by intramuscular injection as quickly as possible.
What is the cause of tetanus?
Causes. The bacterium that causes tetanus is called Clostridium tetani. The bacterium can survive in a dormant state in soil and animal feces. It's essentially shut down until it discovers a place to thrive. When the dormant bacteria enter a wound — a condition good for growth — the cells are "awakened.".
What are the risks of getting tetanus?
Other factors that increase the risk of tetanus infection are: Cuts or wounds exposed to soil or manure. A foreign body in a wound, such as a nail or splinter.
How long does it take for tetanus to show symptoms?
The average time from infection to appearance of signs and symptoms (incubation period) is 10 days. The incubation period can range from 3 to 21 days. The most common type of tetanus is called generalized tetanus. Signs and symptoms begin gradually and then progressively worsen over two weeks. They usually start at the jaw ...
How long does it take for tetanus to start?
Signs and symptoms begin gradually and then progressively worsen over two weeks. They usually start at the jaw and progress downward on the body. Signs and symptoms of generalized tetanus include: Painful muscle spasms and stiff, immovable muscles (muscle rigidity) in your jaw.
Why is tetanus rare?
Because of the widespread use of vaccines, cases of tetanus are rare in the United States and other parts of the developed world. The disease remains a threat to people who aren't up to date on their vaccinations. It's more common in developing countries.
What are the complications of tetanus?
Complications. Complications of tetanus infection may include: Breathing problems. Life-threatening breathing problems can occur from tightening of the vocal cords and muscle rigidity in the neck and abdomen, especially during a generalized spasm. Blockage of a lung artery (pulmonary embolism).
Is tetanus a contagious disease?
Diphtheria is a serious bacterial infection of the nose and throat. Acellular pertussis, also called whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory infection.
How to stop tetanus from breaking?
Wounds from objects outdoors or crush injuries are at higher risk for getting C. tetani spores into a wound. Apply a clean and dry cloth to stop or minimize bleeding.
What is the cause of tetanus?
Tetanus is an infectious disease caused by wounds contaminated with the bacteria Clostridium tetani that live in soil and animal feces. Tetanus is an infectious disease caused by contamination of wounds with the bacteria Clostridium tetani, and/or the spores they produce that live in the soil and animal feces.
How long does it take for tetanus to manifest?
Cephalic tetanus primarily affects one or several muscles in the face rapidly (in one to two days) after a head injury or ear infection. Trismus ("lockjaw") may occur.
What is the function of tetanolysin?
The function of tetanolysin is unclear, but tetanospasmin is responsible for the disease. Typically, a person gets tetanus after an acute injury or trauma that results in a break in the skin. Most cases result from a puncture wound, laceration (cut), or an abrasion (scrape).
How often does DTaP cause vomiting?
Fussiness occurs most frequently (one in three children), followed by tiredness and decreased appetite (one in 10), while vomiting is infrequent (about one in 50). Moderate or uncommon effects of DTaP are a seizure or high fever (105 F or higher); these occur in about one of 14,000 children vaccinated.
How is tetanus acquired?
Tetanus is acquired through contact with the environment ; it is not transmitted from person to person. Tetanus results in severe, uncontrollable muscle spasms. For example, the jaw is "locked" by muscle spasms, causing the disease to sometimes be called "lockjaw.".
How to tell if a neonate has tetanus?
In localized tetanus, pain, cramps, or muscle spasms occur at or near a recent skin injury. Neonates show signs of being generally irritable, muscle spasms, and poor ability to take in liquids (poor sucking response), usually seen in neonates about 7-10 days old. Laboratory tests are rarely used to diagnose tetanus.
Overview
- Tetanus is a serious disease caused by a bacterial toxin that affects your nervous system, leading to painful muscle contractions, particularly of your jaw and neck muscles. Tetanus can interfere with your ability to breathe and can threaten your life. Tetanus is commonly known as \"lockjaw.\"Thanks to the tetanus vaccine, cases of tetanus are rare in the United States and oth…
- Tetanus is an infectious disease caused by contamination of wounds with the bacteria Clostridium tetani, and/or the spores they produce that live in the soil and animal feces. Tetanus has been recognized for centuries. The term is derived from the ancient Greek words tetanos and teinein, meaning taut and stretched, which describe the condition of the muscles affected by th…
- Tetanus is a disease caused by a bacterial infection. The bacteria are usually found in soil, dust, and the bowel movements of some animals and humans. The bacteria often enter the body through a puncture wound or burn. The bacteria produce a toxin that damages nerves. This causes severe muscle spasms. Left untreated, tetanus can be life-threatening.
Treatment
- Medical treatment has two aims: limit growth and eventually kill the infecting C. tetani and thus eliminate toxin production; the second aim is to neutralize any toxin that is formed. If the toxin has already affected the patient, the two aims are still important, but supportive measures will be needed for the patient. These steps are outlined below:
- When you have a wound, as long as it breaks the skin, it is possible to develop tetanus. Most doctors recommend the following if you have received your primary (active) immunization in the past. If the wound is clean and you have not had a tetanus booster in the last 10 years, it is recommended that you receive one. If the wound is dirty or tetanus-prone, then your doctor woul…
- Your healthcare provider will examine your wound and ask about your symptoms. Tell him if the wound was not cleaned immediately or you saw dirt or other objects in the wound. No tests are available to check for tetanus. Your healthcare provider will look for certain signs or symptoms, such as lockjaw, to help diagnose tetanus. If the infection becomes generalized, you will need t…
Symptoms
- Signs and symptoms of tetanus appear anytime from a few days to several weeks after tetanus bacteria enter your body through a wound. The average incubation period is seven to 10 days.Common signs and symptoms of tetanus include: 1. Spasms and stiffness in your jaw muscles (trismus) 2. Stiffness of your neck muscles 3. Difficulty swallowing 4. Stiffness of your …
- You may have stiff and weak muscles only in the area of the wound. This is called localized tetanus. Symptoms may go away without treatment, or they may spread. Infection that spreads is called generalized. You may develop any of the following within days or weeks of the infection:
- The severity of the symptoms will often depend on the number of organisms that are able to enter the body and the quantity of toxins produced in the body, but this is generally considered a serious condition warranting immediate treatment. Symptoms can appear after spores have entered the wound and germinated. The muscles around the infected wound may become rigid first. The do…
- The toxin causes spasmodic, tonic contractions of the voluntary muscles by interfering with the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters from presynaptic nerve endings. If more toxin is released at the site of the infection than the surrounding nerves can take up, the excess is carried off by the lymph to the bloodstream and thus to the CNS, where it causes descending tetanus. Even minor …
Prevention
- The majority of all adult types of tetanus cases can be prevented by active immunization with tetanus toxoid (tetanospasmin toxin that is inactivated); neonatal cases are prevented by good hygiene and careful, sterile technique used to sever the umbilical cord and later (at 2 months old), beginning active immunizations. There are two main vaccines recommended by the U.S. Center…
- Because established tetanus is often fatal, even with expert treatment, prevention is of paramount importance. The two major means of preventing tetanus are immunization and wound care. If you have never received a primary immunization as a child and you have an open wound, the doctor will likely give you the first vaccine dose at the time of your wound care as well as a single dose …
- Active immunization can be accomplished with tetanus toxoid. If a dangerous wound occurs after immunization, another injection of toxoid to increase the circulating antibody should be given. If the animal has not been immunized previously, it should be treated with 1,5003,000 IU or more of tetanus antitoxin, which usually provides passive protection for as long as 2 wk. Toxoid should b…
- All travelers should be up-to-date with tetanus toxoid vaccine before departure. Ensure adequate immunity to tetanus by completing the childhood primary vaccine series with tetanus toxoid, a booster dose during adolescence, and at 10-year intervals thereafter during adulthood. An age-appropriate tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine may be needed as early as 5 years since the last …
Diagnosis
- If you are concerned about your child's condition, contact your doctor and describe any symptoms that appear to be present so that they can determine whether or not medical attention is necessary. Very young children receiving a tetanus shot may be kept for monitoring after the shot is given so that any necessary treatment can be administered right away.
- You will need to give a thorough history of your dog's health, including a background history of symptoms. Your veterinarian will also ask about any previous injuries or traumas that might have led to the infection. After taking a detailed history, your veterinarian will then conduct a complete physical examination on your dog. Routine laboratory tests will include a complete blood count (…
- The clinical signs and history of recent trauma are usually adequate for a clinical diagnosis of tetanus. It may be possible to confirm the diagnosis by demonstrating the presence of tetanus toxin in serum from the affected animal. In cases in which the wound is apparent, demonstration of the bacterium in gram-stained smears and by anaerobic culture may be attempted.
- Diagnosis is clinical; no confirmatory laboratory tests are available. Tetanus is a nationally notifiable disease.
Causes
- Tetanus is caused by a toxin made by spores of bacteria, Clostridium tetani, found in soil, dust and animal feces. When the spores enter a deep flesh wound, they grow into bacteria that can produce a powerful toxin, tetanospasmin. The toxin impairs the nerves that control your muscles (motor neurons). The toxin can cause muscle stiffness and spasms — the major signs and sym…
- Tetanus usually occurs when a wound becomes contaminated with Clostridium tetani bacterial spores. Infection follows when spores become activated and develop into gram-positive bacteria that multiply and produce a very powerful toxin (tetanospasmin) that affects the muscles. Tetanus spores are found throughout the environment, usually in soil, dust, and animal waste. T…
- Clostridia are anaerobic bacteria, meaning they thrive best in the absence of oxygen. They're commonly found in soil, but can also be found in the lower intestines of mammals. They can produce spores that can survive for years.Anyone who cuts himself or herself with a dirty object is at risk of getting Clostridium tetani in the wound. The bacteria are only really dangerous if they'r…
Epidemiology
- In the United States, because of widespread immunization and careful wound care, the total annual number of cases has averaged about 40-50 cases per year since 1995. In developing countries of Africa, Asia, and South America, tetanus is far more common. The annual worldwide incidence is between 500,000-1 million cases. The majority of new cases worldwide are in neon…
- Distributed worldwide. More common in rural and agricultural regions, areas where contact with soil or animal excreta is likely, and areas where immunization is inadequate. Tetanus can affect any age group.
Contraindications
- Contraindications to vaccination are few; a toxoid allergy that previously manifested itself in the patient causing a serious allergic reaction (anaphylaxis, coma, or seizures) is the major contraindication for the vaccine. Other reasons may be due to illnesses that have occurred in some patients usually less than six weeks after previous vaccination (for example, Guillain-Barr…
- Children who are receiving a tetanus shot should be watched carefully to ensure that they are not suffering from tetanus shot side effects.
Risks
- Tetanus-prone wounds are those that are deeper or are contaminated with dirt or soil. If you are unsure about when you received your last tetanus shot, it is better to be safe and receive another booster than sorry. You may experience increased redness and soreness at the injection site if it has been a shorter period of time since your last booster.
- Those suffering from a negative reaction to a tetanus shot will frequently experience confusion, irritability or excessive fatigue. If you begin to experience these symptoms or seizures fevers higher than 103 degrees Fahrenheit (39.4 Celsius), severe ongoing headaches, swelling and blistering at the injection site or in the glands near the armpit or severe vomiting should contact …
Pathophysiology
- The spores of C tetani are unable to grow in normal tissue or even in wounds if the tissue remains at the normal oxidation-reduction potential of the circulating blood. Suitable conditions for multiplication occur when a small amount of soil or a foreign object causes tissue necrosis. The bacteria remain localized in the necrotic tissue at the original site of infection and multiply. As b…