Medication
Jan 06, 2022 · Medications Medications to treat XLA include: Gammaglobulin. This is a type of protein found in blood that contains antibodies against infections. It's given by infusion into a vein every two to four weeks or by weekly injection. Reactions to gammaglobulin can include headache, chills, backache and nausea.
Therapy
There is no cure for XLA, but the condition can be successfully treated. Immunoglobulin replacement therapy is a life-long and life-saving treatment that restores some of the missing antibodies. In addition, some people benefit from a daily course of oral antibiotics to prevent or treat infections.
Self-care
Introduction: X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is the most common primary immunodeficiency in man, and is caused by a single genetic defect. Inactivating mutations in the Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) gene are invariably the cause of XLA,. XLA is characterized by a differentiation arrest at the pre-B cell stage, the absence of immunoglobulins ...
Nutrition
Recurrent infections can lead to organ damage. People with XLA can develop severe, life-threatening bacterial infections; however, affected individuals are not particularly vulnerable to infections caused by viruses. With treatment to replace antibodies, infections can usually be prevented, improving the quality of life for people with XLA.
Is there a cure for XLA?
Mar 26, 2021 · Treatment for XLA is IVIG. [ 33] Typical doses are 400-600 mg/kg/mo given every 3-4 weeks. Doses and intervals can be adjusted based on individual clinical responses. Therapy should begin at age...
What is immunoglobulin replacement therapy for XLA?
Mar 26, 2022 · Until gene therapy becomes developed, [ 48] the mainstay therapy for Bruton agammaglobulinemia, formally termed X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA), and other primary antibody deficiencies is to...
What causes XLA?
Jul 26, 2021 · There is currently no cure for XLA; however, early management with immunoglobulin replacement therapy and antibiotics to prevent and treat infections. Although this lifelong avenue is costly, it has been the mainstay of treatment for the past fifty years.
How often should I see my doctor if I have XLA?

What causes XLA?
XLA is an inherited immune disorder caused by an inability to produce B cells or the immunoglobulins (antibodies) that the B cells make. XLA is also called Bruton type agammaglobulinemia, X-linked infantile agammaglobulinemia, and congenital agammaglobulinemia.
How is agammaglobulinemia treated?
The administration of intravenous gammaglobulin replacement therapy is a standard treatment for agammaglobulinemia. Intravenous gammaglobulin or subcutaneou. is used to treat agammaglobulinemias and common variable immunodeficiency.
How can XLA be prevented?
Preventing bacterial infections is very important for people with XLA. Gammaglobulin (a type of protein in the blood that contains antibodies to prevent or fight infections) is the main treatment for people with XLA. In the past, most people received this by intravenous (IV) infusion every two to four weeks.
How is XLA diagnosed?
The diagnosis of XLA can be confirmed by demonstrating the absence of BTK protein in monocytes or platelets or by the detection of a mutation in BTK in DNA. Almost every family has a different mutation in BTK; however, members of the same family usually have the same mutation.
How common is XLA?
XLA is deemed to have a relatively low incidence of disease, with an occurrence rate of approximately 1 in 200,000 live births and a frequency of about 1 in 100,000 male newborns. It has no ethnic predisposition. XLA is treated by infusion of human antibody.
What causes agammaglobulinemia?
It is caused by a gene defect that blocks the growth of normal, mature immune cells called B lymphocytes. As a result, the body makes very little (if any) immunoglobulins. Immunoglobulins play a major role in the immune response, which protects against illness and infection.Feb 2, 2020
Is XLA curable?
There's no cure for XLA . The goal of treatment is to boost the immune system, preventing infections and aggressively treating infections that occur.Jan 6, 2022
Can females have XLA?
XLA affects males almost exclusively, although females can be genetic carriers of the condition. Most people with XLA are diagnosed in infancy or early childhood, after they've had repeated infections.Jan 6, 2022
What is immunoglobulin replacement?
Immunoglobulin replacement therapy is a treatment given to boost the IgG antibody levels when they are low. This treatment can strengthen the immune system and help immune deficient patients fight off infections. When someone donates blood, the red cells and plasma are separated.
What is XLA immunodeficiency?
X-Linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is an inherited immunodeficiency in which the body is unable to produce the antibodies needed to defend against bacteria and viruses.
Why do XLA patients not have tonsils?
Doctors may find that people with XLA have very small tonsils and lymph nodes (glands of the neck). This is because tonsils and lymph nodes are made up of B lymphocytes. In people with XLA, the size of these tissues are reduced because of the absence of B lymphocytes.
What does XLA mean?
X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is a condition that affects the immune system and occurs almost exclusively in males. People with XLA have very few B cells, which are specialized white blood cells that help protect the body against infection.
What is XLA in medicine?
Listen. Managing X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) mainly consists of preventing infections and treating infections aggressively when they do occur. Sudden infections in individuals with XLA are usually treated with antibiotics that are taken for at least twice as long as taken in healthy individuals. Preventing bacterial infections is very ...
What is X-linked agammaglobulinema?
X-linked agammaglobulinema is a primary immunodeficiency characterized by very low levels of immunoglobulins ( proteins made by the immune system to help fight infections). People affected by this condition generally begin developing frequent and recurrent bacterial infections from about 6 months of age. Commonly diagnosed infections include lung infections (pneumonia and bronchitis), middle ear infections, conjunctivitis, sinus infections, various skin infections, and infections that are associated with chronic diarrhea. [1] [2] [3] X-linked agammaglobulinemia is caused by changes ( mutations) in the BTK gene and is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. [2] [3] Treatment aims to boost the immune system, which may be accomplished by administering immunoglobulins through a vein (IVIG) or subcutaneously (SCIG). Frequent infections are generally treated with antibiotics. [1] [2]
What is MedlinePlus?
MedlinePlus was designed by the National Library of Medicine to help you research your health questions, and it provides more information about this topic. Genetics Home Reference (GHR) contains information on X-linked agammaglobulinemia. This website is maintained by the National Library of Medicine.
What is support and advocacy?
Support and advocacy groups can help you connect with other patients and families, and they can provide valuable services. Many develop patient-centered information and are the driving force behind research for better treatments and possible cures. They can direct you to research, resources, and services.
What do doctors look for in a diagnosis?
Healthcare professionals typically look at a person’s medical history, symptoms, physical exam, and laboratory test results in order to make a diagnosis.
Can XLA be given live?
Furthermore, children with XLA should not be given live viral vaccines. For example, they should be given inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) rather than the oral polio vaccine.
What is XLA in medical terms?
X-Linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is an inherited immunodeficiency in which the body is unable to produce the antibodies needed to defend against bacteria and viruses .
What are the B cells in XLA?
B cells are responsible for producing the antibodies that the immune system relies on to fight off infection. The most common bacteria causing infection in XLA are Streptococcus, Staphylococcus and Haemophilus. Keep pace with the latest information and connect with others. Join us on Facebook. Symptoms.
How long does an infant's IgG last?
This maternal IgG only lasts for several months, and then the infant needs to start producing antibodies on its own.
Can XLA be treated?
XLA can be detected through screening tests that measure immunoglobulin levels or the number of B cells in the blood. There is no cure for XLA, but the condition can be successfully treated.
What is XLA in biology?
Description. X-linked agammaglobulinemia ( XLA) is a condition that affects the immune system and occurs almost exclusively in males. People with XLA have very few B cells, which are specialized white blood cells that help protect the body against infection. B cells can mature into the cells that produce special proteins called antibodies ...
Where is the Expand Section gene located?
Expand Section. This condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. The gene associated with this condition is located on the X chromosome, which is one of the two sex chromosomes. In males (who have only one X chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition.
Why is the BTK gene important?
This gene provides instructions for making the BTK protein, which is important for the development of B cells and normal functioning of the immune system . Most mutations in the BTK gene prevent the production of any BTK protein. The absence of functional BTK protein blocks B cell development and leads to a lack of antibodies.
What are the proteins that B cells produce?
B cells can mature into the cells that produce special proteins called antibodies or immunoglobulins. Antibodies attach to specific foreign particles and germs, marking them for destruction. Individuals with XLA are more susceptible to infections because their body makes very few antibodies.
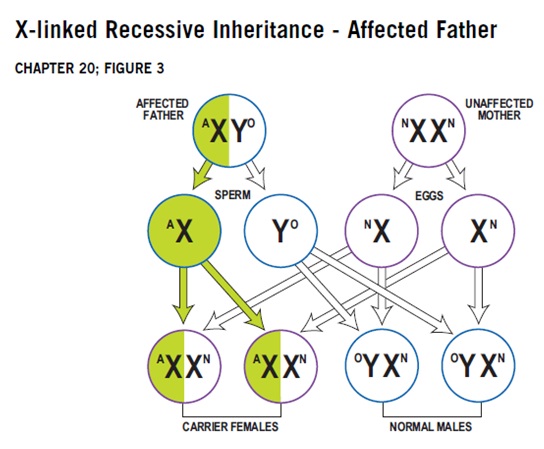
Why are males affected by X-linked recessive disorders more frequently than females?
Because it is unlikely that females will have two altered copies of this gene, males are affected by X-linked recessive disorders much more frequently than females. A characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons.
Can XLA cause diarrhea?
Infections that cause chronic diarrhea are also common. Recurrent infections can lead to organ damage. People with XLA can develop severe, life-threatening bacterial infections; however, affected individuals are not particularly vulnerable to infections caused by viruses.
Can XLA cause a sinus infection?
In children with XLA, infections generally take longer to get better and then they come back again, even with antibiotic medications. The most common bacterial infections that occur in people with XLA are lung infections (pneumonia and bronchitis), ear infections (otitis), pink eye (conjunctivitis), and sinus infections (sinusitis).
Is multivitamin used in XLA?
Nutritional intervention or supplementation and the use of multivitamin and mineral preparations are usually unnecessary in XLA, although some patients with autoimmune colitis occasionally require such therapy. Determining the etiology of the diarrhea (often infectious) is more important.
Is trimethoprim a first line antibiotic?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the first-line drug for both. Recently released antibiotics such as linezolid for penicillin-resistant pneumococci are presumably effective, although results in primary immunodeficiency diseases are not yet published. Many infections require interventions in addition to antibiotics.
Can antibiotics be used for bronchiectasis?
Some clinicians advocate rotating the use of antibiotics in select patients with bronchiectasis and frequent exacerbations.
Is ceftriaxone used for pneumonia?
Intravenous ceftriaxone may be required for chronic pulmonary infection, acute severe pneumonia, or sepsis. As with other patient populations, the risk for penicillin-resistance among S pneumoniae is an increasing concern; ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, and vancomycin are used to treat penicillin-resistant organisms.
Can SCIG be given at home?
[ 51] . A major advantage is that SCIG can be administered at home.
What is XLA in pediatrics?
X-linked agammaglobulinemia or XLA is one of the most common pediatric primary immunodeficiencies that prevent affected individuals from making antibodies and requires lifelong immunoglobulin replacement therapy for survival.
How long does it take for XLA to show up?
XLA patients commonly present with a history of recurrent upper respiratory tract infections, including sinusitis and otitis media, beginning after 6 to 9 months when most of the maternal antibodies have been exhausted.
Is there a cure for XLA?
There is currently no cure for XLA; however, early management with immunoglobulin replacement therapy and antibiotics to prevent and treat infections. Although this lifelong avenue is costly, it has been the mainstay of treatment for the past fifty years.