Medication
Sep 02, 2021 · Prevent future episodes of ventricular tachycardia. Emergency treatment. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR): Emergency procedure of chest compression that is often given in combination with artificial ventilation and must be followed by defibrillation in most cases; Electrical defibrillation: Done by using an automated external defibrillator (AED)
Procedures
Treatment for ventricular tachycardia, when it isn’t life threatening, usually involves medications and addressing the underlying cause. However, patients with prior heart attacks, moderately reduced heart function, or symptomatic congestive heart failure can benefit from an ICD, a small electronic device that can prevent sudden death.
Self-care
Treatment for ventricular tachycardia involves managing any disease that causes the condition. These treatments may improve or prevent the abnormal heart rhythm from returning. In emergency situations, CPR, electrical defibrillation and …
Nutrition
Feb 02, 2022 · Sometimes ventricular tachycardia can cause the heart to stop (sudden cardiac arrest). Treatment for ventricular tachycardia may include medication, a shock to the heart (cardioversion), catheter procedures or surgery to slow the …
How do you treat V tach with a pulse?
Ventricular tachycardia (VT or V-tach) is a type of abnormal heart rhythm, or arrhythmia. It occurs when the lower chamber of the heart beats too fast to pump well and the body doesn't receive enough oxygenated blood. A normal heartbeat begins with an electrical impulse from the sinus node, a small area in the heart's right atrium (right upper ...
How to fix Vtach?
Jul 28, 2021 · Seeking treatment for VT can improve a person’s outlook. Antiarrhythmic drugs Healthcare professionals may treat VT with a range of antiarrhythmic drugs. A person can take these drugs orally during...
How to treat tachycardia with home remedies?
If a medication or caffeine is causing the VT, you might need to stop taking it. Other treatments include: Cardioversion. Your doctor uses an electric shock to return your heart to its regular...
Does ventricular tachycardia go away?
Medicine treatment may include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or other antiarrhythmic medicines. In people who have frequent episodes, treatment with medicines can decrease how often these occur. But these medicines may have side effects. Many people with SVT have a procedure called catheter ablation.

What is the first line treatment for ventricular tachycardia?
What is the drug of choice for ventricular tachycardia?
Can ventricular tachycardia be cured?
How serious is ventricular tachycardia?
Does a pacemaker help ventricular tachycardia?
Does metoprolol help ventricular tachycardia?
Can you live a normal life with ventricular tachycardia?
What triggers ventricular tachycardia?
What is the most common cause of ventricular tachycardia?
Does tachycardia damage the heart?
Do beta blockers prevent ventricular tachycardia?
What is the survival rate for ventricular tachycardia?
What causes ventricular tachycardia?
Your heart rate is regulated by electrical signals sent to your heart muscle. Certain conditions can interfere with normal electrical signals and cause ventricular tachycardia:
What are the signs and symptoms of ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia goes away on its own in 30 seconds. However, sustained ventricular tachycardia can last more than 30 seconds and requires emergency treatment.
How is ventricular tachycardia diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and take a complete medical history. They may order tests that include:
What can you do to prevent ventricular tachycardia?
Following your doctor’s treatment recommendations can help you prevent or manage episodes of the disease. In some cases, the causative factor (cardiovascular disorder, tumor, drugs, electrolyte imbalance, etc.) may need to be addressed and treated. It is also advised to adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes:
What Is Ventricular Tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia is characterized by a fast, steady heart rhythm coming from one of the bottom chambers (ventricles) of the heart. Sometimes only a few of these fast beats occur and then the heart returns to a normal rhythm. However, when the abnormal rhythm lasts more than 30 seconds, it is called sustained ventricular tachycardia.
Contact Us
If you believe you should have an evaluation and would like to schedule an appointment with one of our cardiac surgery experts, call 1-800-294-9999 to speak to one of our knowledgeable coordinators who can help to connect you to the doctor that best meets your needs, or fill out an online appointment request form.
What is the heart rate of ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia starts in the heart’s lower chambers. Most patients who have ventricular tachycardia have a heart rate that is 170 beats per minute or more. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
What causes tachycardia in the heart?
When something goes wrong and signals are sent too quickly, it can cause tachycardia. Most patients with ventricular tachycardia have another heart problem, such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, an enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy) or heart valve disease.
What is the normal heart rate for tachycardia?
The ventricles are the heart’s two lower chambers. Blood flows from the top chambers of the heart (atria) into the ventricles, then it moves to the lungs and through the aorta to be circulated throughout the body. Tachycardia is a heart rate higher than 100 beats per minute. A normal resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute.
What happens if your heart rate is too high?
When the heart rate is extremely high or the ventricular tachycardia persists for more than a few seconds, it can cause fainting, unconsciousness or cardiac arrest and death. If you experience unexplained fainting, dizziness, lightheadedness, shortness of breath or palpitations, you should be evaluated for possible ventricular tachycardia.
How long do you have to wear a Holter monitor?
Your doctor may also want to track your heart rhythm at home. If so, you will wear a Holter monitor at home for 24 to 48 hours. Normal Heart Rhythm recorded on EKG. Ventricular Tachycardia recorded on EKG. Your doctor may refer you to a specialist to electrophysiology testing.
What is an ICD device?
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator. An ICD is a device that is implanted under the skin. It monitors and controls the heart’s rhythm. If it detects an episode of ventricular tachycardia, it acts quickly to get your heart back to a normal rhythm.
What is an ICD?
An ICD consists of a pulse generator, which is about the size of a pager, and one or more lead wires that connect the pulse generator to the heart. The leads are inserted through the veins and positioned in the heart.
What are the symptoms of tachycardia?
Unstable patients have signs or symptoms of insufficient oxygen delivery to vital organs as a result of the tachycardia. Such manifestations may include the following: 1 Dyspnea 2 Hypotension 3 Altered level of consciousness
Can antiarrhythmics be used for VT?
Combinations of these therapies are often used when structural heart disease is present. Antiarrhythmic drugs have traditionally been the mainstays of treatment for clinically stable patients with VT. However, some patients experience unacceptable side effects or frequent recurrence of VT with drug therapy.
Can tachycardia cause cardiomyopathy?
Prolonged exposure to this (or any other) tachycardia may cause a tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy, which typically improves with medical or ablative treatment of the VT. [ 19] Pulseless VT. Pulseless VT, in contrast to other unstable VT rhythms, is treated with immediate defibrillation.
Can VT cause hemodynamic collapse?
Sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) may lead to hemodynamic collapse. Consequently, these patients require urgent conversion to sinus rhythm. The strategy for conversion depends on whether the patient is hemodynamically stable or unstable.
What is catheter ablation?
Catheter ablation may also be used in patients with cardiomyopathy. The goal in these cases is to reduce the arrhythmia burden and thereby minimize the number of ICD shocks. Ablation is also used in patients with bundle-branch reentrant VT. [ 40] .
What causes ventricular tachycardia?
Causes. Ventricular tachycardia is caused by a disruption in the normal electrical impulses that control the rate of your heart's pumping action. Many things can cause or contribute to problems with the heart's electrical system.
What is VT in heart?
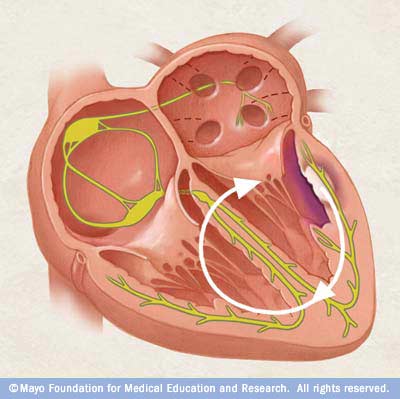
The problem may involve either a small cluster of cells or a large area of scar tissue. Ventricular tachycardia is a heart rhythm disorder (arrhythmia) caused by abnormal electrical signals in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). This condition may also be called V-tach or VT.
What causes a heart to beat faster?
In ventricular tachycardia, an abnormal electrical impulse originating in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) causes the heart to beat faster. The problem may involve either a small cluster of cells or a large area of scar tissue.
What is VT in medical terms?
Ventricular tachycardia is a heart rhythm disorder (arrhythmia) caused by abnormal electrical signals in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). This condition may also be called V-tach or VT. A healthy heart normally beats about 60 to 100 times a minute at rest.
How many times does the heart beat in a minute?
A healthy heart normally beats about 60 to 100 times a minute at rest. In ventricular tachycardia, the heart beats faster than normal, usually 100 or more beats a minute. The chaotic heartbeats prevent the heart chambers from properly filling with blood. As a result, your heart may not be able to pump enough blood to your body and lungs.
What causes scarring in the heart?
Abnormalities of the heart that result in scarring of heart tissue (sometimes called "structural heart disease"), the most common cause is a prior heart attack. Poor blood flow to the heart muscle due to coronary artery disease. Congenital heart conditions, including long QT syndrome.
What is the heart rhythm?
Normal heartbeat. In a normal heart rhythm, a cluster of cells at the sinus node sends out an electrical signal. The signal then travels through the atria to the atrioventricular (AV) node and then passes into the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump out blood.
What are the symptoms of ventricular tachycardia?
When ventricular tachycardia lasts a short time, there may be no symptoms except palpitations — a fluttering in the chest. But ventricular tachycardia lasting more than 30 seconds may cause more severe symptoms: 1 Chest pain 2 Dizziness 3 Fainting ( syncope) 4 Shortness of breath 5 Cardiac arrest
Can ventricular tachycardia cause syncope?
When it lasts only a few seconds, ventricular tachycardia may cause no problems. But when sustained, vent ricular tachycardia can lower the blood pressure, resulting in syncope (fainting) or lightheadedness. Ventricular tachycardia can also lead to ventricular ...
What causes tachycardia in the heart?
Ventricular tachycardia most often occurs when the heart muscle has been damaged and scar tissue creates abnormal electrical pathways in the ventricles. Causes include: 1 Heart attack 2 Cardiomyopathy or heart failure 3 Myocarditis 4 Heart valve disease
Where does ventricular tachycardia start?
Ventricular tachycardia begins in the lower chambers (ventricles) and is quite fast. When it lasts only a few seconds, ventricular tachycardia may cause no problems.
What is a CPVT?
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is a genetic condition that can cause a fast abnormal heart beat from the ventricles. CPVT may cause a loss of consciousness or sudden death due to the lack of blood pumped to the body.
What is radiofrequency ablation?
Radiofrequency ablation: a minimally invasive procedure to destroy the cells that cause ventricular tachycardia; less effective when there is structural heart disease. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD): an implanted device that delivers an electrical pulse to the heart to reset a dangerously irregular heartbeat.
What is an ICD device?
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD): an implanted device that delivers an electrical pulse to the heart to reset a dangerously irregular heartbeat. Medication: A number of antiarrhythmic medications are used to prevent ventricular tachycardia. These include: Sotolol. Flecainide. Propafenone.
What is VT?
The human heart consists of four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria, and the two lower ones are the ventricles.
Types
There are two main types of VT: non-sustained VT (NSVT) and sustained VT (SVT).
Causes
There may be a link between VT and conditions that affect the heart’s electrical conduction system. However, it is not always clear what leads to VT.
When to contact a doctor
A person should contact a doctor immediately if they notice they have an abnormal heartbeat.
Outlook
VT typically requires treatment. The outlook for people with VT is usually good if they receive treatment quickly.
Summary
VT causes the heart to beat very quickly at a rate of over 100 beats per minute. It begins in the ventricles of the heart and can cause a variety of symptoms, including heart palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
Where does ventricular tachycardia start?
This method treats the ventricular tachycardia and can cure it. Ventricular tachycardia starts in the lower chambers of your heart , but the upper part might also be the source of the problem. Supraventricular tachycardia ( SVT) starts in your atria.
How fast does tachycardia beat?
Ventricular tachycardia can result in rates of 170 beats a minute or even more. When this happens, your heart’s upper chambers don’t have time to refill and send that blood to the ventricles. So your blood doesn’t get pumped throughout your body the way it should.
How does the heart work?
They work together to pump blood throughout your body. Every day, a healthy heart beats about 100,000 times. Your heartbeat is controlled by electrical signals. These signals follow a pattern. They start in the sinoatrial (SA) node. It’s in one of your atria and is often called your heart’s natural pacemaker.
How many times does a heart beat?
Every day, a healthy heart beats about 100,000 times . Your heartbeat is controlled by electrical signals. These signals follow a pattern. They start in the sinoatrial (SA) node. It’s in one of your atria and is often called your heart’s natural pacemaker.
Where does the heart beat start?
Your heartbeat is controlled by electrical signals. These signals follow a pattern. They start in the sinoatrial (SA) node. It’s in one of your atria and is often called your heart’s natural pacemaker. The signal causes your atria to contract so blood moves into your ventricles.
What are the symptoms of VT?
VT can cause: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy. Chest pain. Heart palpitations. Shortness of breath. Fainting. Tightness in your neck.
What medications slow your heart rate?
Medications to slow your heart rate such as amiodarone (Nexterone, Pacerone ), flecainide ( Tambocor ), lidocaine (Lidopen), propafenone (Rhythmol SR), or sotalol ( Betapace, Sotylize). These don’t work as well as cardioversion, and they can have side effects. Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
What is the treatment for SVT?
But these medicines may have side effects. Many people with SVT have a procedure called catheter ablation.
What are the symptoms of SVT?
SVT is usually treated if: You have symptoms such as dizziness, chest pain, or fainting that are caused by your fast heart rate. Your episodes of fast heart rate are occurring more often or do not return to normal on their own.
What is the goal of SVT?
The goals of treatment are to prevent episodes, relieve symptoms, and prevent problems. You and your doctor can decide what type of treatment is right for you. SVT is usually treated if: You have symptoms such as dizziness, chest pain, or fainting that are caused by your fast heart rate.
How to tell if you have SVT?
SVT is usually treated if: 1 You have symptoms such as dizziness, chest pain, or fainting that are caused by your fast heart rate. 2 Your episodes of fast heart rate are occurring more often or do not return to normal on their own.

Symptoms
Treatment
Medical uses
Prognosis
Specialist to consult
Management
Research
- Unstable patients with monomorphic VT should be immediately treated with synchronized direct current (DC) cardioversion, usually at a starting energy dose of 100 J (monophasic; comparable biphasic recommendations are not currently available). Unstable polymorphic VT is treated with immediate defibrillation. The defibrillator may have difficulty rec...