Medication
There are 2 stages of treatment for V-fib. The first tries to stops your V-fib immediately to restore a blood pressure and pulse. The second stage focuses on reducing your chances of developing V-fib in the future. Treatment includes: CPR. The first response to V-fib may be cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). This will keep your blood moving.
Procedures
Nov 26, 2019 · If the patient remains in ventricular fibrillation, pharmacological treatment should begin. Epinephrine is the first drug given and may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes. If epinephrine is not effective, the next medication in the algorithm is amiodarone 300 mg.
Nutrition
Feb 23, 2020 · How do you fix ventricular fibrillation? Treatment options can include: Medications. Doctors use various anti-arrhythmic drugs for emergency or long-term treatment of ventricular fibrillation. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). Coronary angioplasty and stent placement. Coronary bypass surgery. 22 Related Question Answers Found
How do you treat ventricular fibrillation?
If you get medical care right away, here’s what may happen: Step 1: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation ( CPR) to keep your blood moving Step 2: Defibrillation to fix your heart rhythm Step 3: Medication to make the rhythm stable again
How do you stop ventricular fibrillation?
Apr 15, 2022 · Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) is a dangerous type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat. It affects your heart’s ventricles. Your heart is a muscle system that contains 4 chambers; the 2 bottom chambers are the ventricles. In a healthy heart, your blood pumps evenly in and out of these chambers. Contents hide.
How is pulseless V fib treated?
During the resuscitation of a patient with ventricular fibrillation, administer intravenous epinephrine (Adrenalin) or vasopressin (Pitressin) to enhance the effectiveness of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Procainamide (Pronestyl) or sotalol (Betapace) may be prescribed for a patient with stable ventricular tachycardia.
What is the prognosis of ventricular fibrillation (VF)?
May 15, 2020 · Treatment of torsade de pointes includes: isoproterenol infusion, cardiac pacing, and intravenous atropine. Intravenous magnesium sulfate, a relatively new mode of therapy for torsade de pointes, was proven to be extremely effective and is now regarded as the treatment of choice for this arrhythmia. How do you treat torsade de pointes?

What is the first treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
Epinephrine is the first drug given and may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes. If epinephrine is not effective, the next medication in the algorithm is amiodarone 300 mg. Defibrillation and medication are given in an alternating fashion between cycles of 2 minutes of high-quality CPR.Nov 26, 2019
What is the best treatment for terminating ventricular fibrillation?
External electrical defibrillation remains the most successful treatment for ventricular fibrillation (VF). A shock is delivered to the heart to uniformly and simultaneously depolarize a critical mass of the excitable myocardium.Jun 6, 2018
What medication is used for ventricular fibrillation?
In acute ventricular fibrillation (VF), drugs (eg, vasopressin, epinephrine, amiodarone) are used after three defibrillation attempts are performed to restore normal rhythm.Jun 6, 2018
What does ventricular fibrillation mean and how is it treated?
Ventricular fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat, that affects your heart's ventricles. Ventricular fibrillation is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. CPR and defibrillation can restore your heart to its normal rhythm and may be life saving.
Does a pacemaker help ventricular fibrillation?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the first of a new type of pacemaker that paces both ventricles of the heart to coordinate their contractions and improve their pumping ability.
Why is amiodarone used in ventricular fibrillation?
Article Sections. Amiodarone is a potent antiarrhythmic agent that is used to treat ventricular arrhythmias and atrial fibrillation. The drug prevents the recurrence of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias and produces a modest reduction of sudden deaths in high-risk patients.Dec 1, 2003
How do you detect ventricular fibrillation?
Ventricular Fibrillation DiagnosisElectrocardiogram The electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the heart's electrical activity. ... Holter Monitor A holter monitor is a small, portable machine that you wear for 24 hours.More items...
Can ventricular fibrillation correct itself?
Ventricular fibrillation seldom terminates spontaneously, since several re-entrant wavefronts, independent from each other, coexist, and the simultaneous extinction of all the circuits is unlikely.
How serious is ventricular fibrillation?
Ventricular fibrillation is more serious than atrial fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation frequently results in loss of consciousness and death, because ventricular arrhythmias are more likely to interrupt the pumping of blood, or undermine the heart's ability to supply the body with oxygen-rich blood.
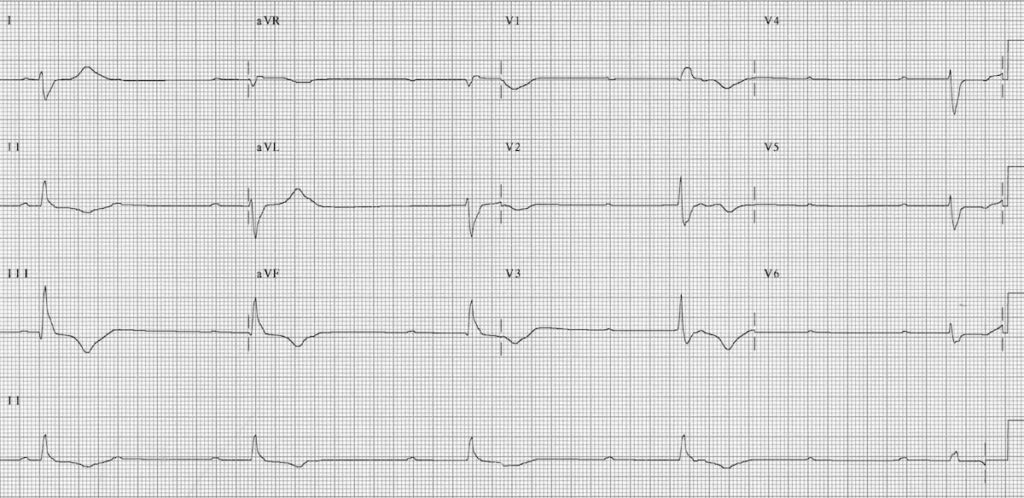
What does ventricular fibrillation look like on an ECG?
0:002:06Ventricular Fibrillation ECG - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipVentricular fibrillation PFF is a chaotic rhythm without any discernible pattern the rhythm consistsMoreVentricular fibrillation PFF is a chaotic rhythm without any discernible pattern the rhythm consists of completely disorganized electrical activity with undulations of varying shape and amplitude.
What is a V-fib?
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) is a dangerous type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat. It affects your heart’s ventricles. Your heart is a muscle system that contains 4 chambers; the 2 bottom chambers are the ventricles. In a healthy heart, your blood pumps evenly in and out of these chambers. This keeps blood flowing throughout your body.
What is an implantable cardiac defibrillator?
Implantable cardiac defibrillators are devices that are implanted within the body that can shock the heart back to normal rhythm within seconds if V-fib is present. Although this device does not necessarily prevent V-fib, it can rapidly and automatically diagnose and treat this potentially fatal heart rhythm.
Is ventricular fibrillation life threatening?
Ventricular fibrillation is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. CPR and defibrillation can restore your heart to its normal rhythm and may be life saving. Medications and cardiac procedures after an episode of ventricular fibrillation can prevent or reduce the chances of another episode.
What is VF in cardiac arrest?
Ventricular fibrillation (VF or V-fib) is the most common initial heart rhythm in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), and the most salvageable one . 5 In VF, the etiology of arrest is often attributed to either acute ischemia or non-ischemic arrhythmia. 8
What are the causes of VF?
The easiest way to remember the most common causes of VF are to review the reversible “Hs and Ts” in cardiac arrest. The Hs include hypoxia, hypovolemia, hypothermia, hyper/hypokalemia, and hydrogen ions (acidosis). The Ts are tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, toxins, and thrombosis (pulmonary or coronary).
How long does ventricular fibrillation last?
If nonsustained, meaning that the rhythm abnormality lasts less than 30 seconds, symptoms may not arise.
What causes ventricular fibrillation?
Causes of ventricular fibrillation include: 1 Injury to the heart, including electrocution accidents, or physical trauma to the area directly over the heart, resulting in sudden cardiac death ( commotio cordis) 2 Angina or chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart 3 A history of heart surgery 4 Certain medications 5 The use of illegal drugs, like cocaine or methamphetamine 6 Significant electrolyte abnormalities, such as abnormal potassium or magnesium levels
What is the cause of sudden cardiac arrest?
Ventricular fibrillation , the No. 1 cause of sudden cardiac arrest, impacts the flow of blood to the body and may result in severe consequences to one’s health. Within seconds, a person experiencing ventricular fibrillation can have no sign of a pulse and become unresponsive.
How many people die from ventricular fibrillation?
In the U.S., about 300,000 people die suddenly from ventricular fibrillation annually. 2 Ventricular fibrillation is sometimes triggered by a heart attack and can further cause blood pressure to fall, resulting in a shortage of blood supply and oxygen to vital organs, including the brain.
What is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death?
Ventricular fibrillation is reported as the most frequent cause of sudden cardiac death. 1 . This form of abnormal heart rhythm (called an arrhythmia) is life-threatening and is considered a medical emergency that requires immediate attention and emergency treatment.
What is congenital heart disease?
Congenital (present at birth) heart disease. A history of heart attack. Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy) that causes weakened, stretched, or thickened heart muscle. Prolonged, untreated ventricular tachycardia. Issues with the aorta, the largest artery leaving the heart. Very high or very low potassium levels in the blood.
What is CPR training?
Getting CPR training can help you learn the basics on how to respond during a situation where someone around you may be experiencing ventricular fibrillation, which may possibly help to save their life . In this training, you will learn the proper method of delivering compression and breaths and how to use an AED.
What are the symptoms of ventricular fibrillation?
These warning signs may include: Chest pain. Very fast heartbeat (tachycardia) Dizziness. Nausea.
What causes the ventricles to contract?
In a normal heart rhythm, electrical signals travel from the heart's upper chambers (atria) to the heart's lower chambers (ventricles), causing the ventricles to contract and pump blood. In ventricular fibrillation, rapid, irregular electrical signals cause the ventricles to quiver uselessly instead of pumping blood.
How to help someone who is unconscious?
If you see someone collapse, seek emergency medical help immediately. Follow these steps: 1 Call 911 or your local emergency number. 2 If the person is unconscious, check for a pulse. 3 If no pulse, begin CPR to help keep blood flowing through the body until an automated external defibrillator (AED) is available. The American Heart Association recommends hands-only CPR. Push hard and fast on the person's chest — about 100 to 120 times a minute. It's not necessary to check the person's airway or deliver rescue breaths. Continue until emergency medical help arrives. 4 Use an AED as soon as it's available. Deliver a shock following the prompts on the device.
What causes sudden cardiac death?
The longer the body lacks blood, the greater the risk of damage to your brain and other organs. Ventricular fibrillation is the most frequent cause of sudden cardiac death. The risk of other long-term complications depends on how fast you receive treatment.
How many times a minute should you do CPR?
The American Heart Association recommends hands-only CPR. Push hard and fast on the person's chest — about 100 to 120 times a minute. It's not necessary to check the person's airway or deliver rescue breaths. Continue until emergency medical help arrives.
What is heart muscle disease?
Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy) Injuries that cause damage to the heart muscle, such as being struck by lightning. Drug misuse, especially with cocaine or methamphetamine. A severe imbalance of potassium or magnesium.
How many chambers does the heart have?
Your heart is made up of four chambers — two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles). The heart's rhythm is normally controlled by a natural pacemaker (the sinus node) in the right upper chamber (atrium). The sinus node sends electrical signals that normally start each heartbeat.
How long can you live with ventricular fibrillation?
Sometimes VT can last less than 30 seconds (nonsustained) and may not cause symptoms. But VT may be a sign of more-serious heart problems. If VT lasts more than 30 seconds, it will usually lead to palpitations, dizziness or fainting.
Can stress cause ventricular fibrillation?
Stress can cause a heart attack, sudden cardiac death, heart failure, or arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) in persons who may not even know they have heart disease. Lower threshold for abnormal heart rhythms including ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and atrial fibrillation.
Can ventricular fibrillation stop on its own?
Ventricular fibrillation seldom terminates spontaneously, since several re-entrant wavefronts, independent from each other, coexist, and the simultaneous extinction of all the circuits is unlikely.
Can you be conscious in V fib?
Defibrillators don't treat cardiac arrest. Instead, they treat ventricular fibrillation, one form of cardiac arrest. That's why they're called de-fibrillators. There's absolutely no way a patient with ventricular fibrillation could be awake; no blood flowing through the brain makes the patient unconscious.
How does amiodarone stop ventricular fibrillation?
Amiodarone is a potent antiarrhythmic agent that is used to treat ventricular arrhythmias and atrial fibrillation. The drug prevents the recurrence of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias and produces a modest reduction of sudden deaths in high-risk patients.
Does a pacemaker help ventricular fibrillation?
Use of electrical pacemakers in the treatment of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. Overdrive pacing may prevent certain cases of ventricular arrhythmias, and antitachycardia devices may be useful in terminating paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia.
Which of the following is the treatment of choice for torsades de pointes?
Treatment of torsade de pointes includes: isoproterenol infusion, cardiac pacing, and intravenous atropine. Intravenous magnesium sulfate, a relatively new mode of therapy for torsade de pointes, was proven to be extremely effective and is now regarded as the treatment of choice for this arrhythmia.
How to treat V-FIB?
If you get medical care right away, here’s what may happen: Step 1: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation ( CPR) to keep your blood moving. Step 2: Defibrillation to fix your heart rhythm. Step 3: Medication to make the rhythm stable again. Defibrillators for V-fib.
What are the symptoms of ventricular fibrillation?
The main symptom is fainting. You may also have symptoms of ventricular tachycardia (VT). This is when the lower chambers of your heart beat too fast. It can lead to V-fib. Signs and symptoms of VT include: Chest pain. Pounding or fast heartbeat.
Why do doctors not know what causes ventricular fibrillation?
For instance, it happens most often during or right after a heart attack. That may be because the heart’s electrical signals can become unstable when there isn’t enough blood flow.
What is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death?
Ventricular fibrillation happens when the electrical signals in your heart go haywire. This causes a ventricle to quiver (fibrillate) instead of pumping blood through your body. Without medical treatment right away, V-fib can be deadly. In fact, it’s the most common cause of sudden cardiac death.
What is an AED?
This type is called an automated external defibrillator (AED). It can help save the life of someone who’s in cardiac arrest. Two other types of defibrillators can also help someone with a dangerous arrhythmia such as V-fib. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD).
What is an ICD device?
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (IC D). A surgeon places this device inside your chest or belly. When your heart is out of its regular rhythm, it gives high- or low-energy electrical shocks to get your heartbeat back to normal. (If your ventricles start to quiver, it will deliver a high-energy shock.)
What is the best treatment for acute heart failure?
Interventions for acute heart failure include administering a rapid-acting diuretic, such as furosemide (Lasix), to reduce preload. Interventions also typically include placing the patient in the high-Fowler position rather than the supine position.
What is the recommended energy level for a biphasic defibrillator?
If a biphasic defibrillator is used to manage a patient with stable, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, the recommended energy level is 100 joules. The recommended energy level for supraventricular tachycardia and atrial flutter is 50 to 100 joules. The level for atrial fibrillation is 120 to 200 joules.
What is premature atrial complex?
Premature atrial complexes are ectopic beats that are initiated by an irritable atrial focus. P waves are present, but because the ectopic focus originates the impulse outside the sinoatrial node, the premature P waves have a different configuration. Atrial flutter causes no P waves, but it causes flutter waves in a sawtoothed pattern.
How long does chest pain last?
A. Of these patients, the man, age 48, is most likely to present with crushing chest pain that lasts longer than 30 minutes. Up to 20 percent of patients with an acute myocardial infarction do not experience chest pain. Patients with diabetes mellitus are more prone to neuropathy and may not experience pain.
What causes a flutter in the heart?
Atrial flutter is usually initiated by a premature atrial complex and is the most common in patients with coronary artery disease, rheumatic heart disease, pulmonar y embolism, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Elevated intracranial pressure can initiate bradycardia.
What causes sudden cardiac arrest?
A common cause of sudden cardiac arrest in adults is ventricular tachycardia that, if untreated, deteriorates into ventricular fibrillation. Supraventricular tachycardia, sinus tachycardia, and junctional tachy cardia are not causes of sudden cardiac arrest.
What are the symptoms of myocardial infarction?
Women have more atypical symptoms, such as profound fatigue and shortness of breath . Among patients older than age 85, the classic symptom of acute myocardial infarction is shortness of breath. A man, age 64, presents to the emergency department with severe dyspnea and weakness.

Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
What Is Ventricular Fibrillation?
- Ventricular fibrillation requires emergency medical treatment to prevent sudden cardiac death. The goal of emergency treatment is to restore blood flow as quickly as possible to prevent organ and brain damage. Emergency treatment for ventricular fibrillation includes: 1. Cardiopulmonar…
Symptoms
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Causes
- Lifestyle changes that help keep your heart as healthy as possible include the following: 1. Eat a healthy diet.Heart-healthy foods include fruits, vegetables and whole grains, as well as lean protein sources such as soy, beans, nuts, fish, skinless poultry and low-fat dairy products. Avoid added salt (sodium), added sugars and saturated fats. 2. Exercise regularly.Get at least 150 min…
Diagnosis
- Some abnormal heart rhythms can be triggered by emotional stress. Taking steps to ease stress and anxiety can help keep your heart healthy. Some types of complementary and alternative therapies may help reduce stress, such as: 1. Yoga 2. Meditation 3. Relaxation or mindfulness techniques Getting support from your loved ones also is key to managing stress.
Treatment