
Medication
Understanding the numbers
- These numbers apply only to the stage of the cancer when it is first diagnosed. ...
- These numbers don’t take everything into account. ...
- People now being diagnosed with thyroid cancer may have a better outlook than these numbers show. ...
Procedures
To cure hypothyroidism permanently, we start with diagnostic tests and assessments that point us to the root causes that apply to each individual patient. By addressing the underlying causes of Hashimoto’s disease (which accounts for 90% of hypothyroidism cases), we are almost always able to reverse these thyroid issues.
Self-care
- Severe and constant fatigue
- Changes in the menstrual cycle
- Constipation
- Depression
- Dry, coarse hair
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
- Disturbed sleep cycle, such as wanting to sleep all the time
- Intolerance to cold
- Decreased heart rate
Nutrition
Thyroid cancer
- Diagnosis. During needle biopsy, a long, thin needle is inserted through the skin and into the suspicious area.
- Treatment. Your thyroid cancer treatment options depend on the type and stage of your thyroid cancer, your overall health, and your preferences.
- Clinical trials. ...
- Coping and support. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. ...
See more
What are the chances of surviving thyroid cancer?
How to cure thyroid permanently?
How to tell if you have thyroid cancer?
What is the cure for thyroid cancer?

How serious is a tumor on thyroid?
Papillary thyroid cancer is highly curable and rarely fatal. Follicular: Follicular thyroid cancer accounts for up to 15% of thyroid cancer diagnoses. This cancer is more likely to spread to bones and organs, like the lungs. Metastatic cancer (cancer that spreads) can be more challenging to treat.
Is thyroid tumor curable?
Most thyroid cancers are very curable. In fact, the most common types of thyroid cancer — papillary and follicular cancers — have a more than 98% cure rate if they're caught and treated at an early stage.
What is the most common treatment for thyroid cancer?
Most cancers are treated with removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy), although small tumors that have not spread outside the thyroid gland may be treated by just removing the side of the thyroid containing the tumor (lobectomy).
Do you need chemo for thyroid cancer?
Chemotherapy is seldom helpful for most types of thyroid cancer, but fortunately it is not needed in most cases. It is often combined with external beam radiation therapy for anaplastic thyroid cancer and is sometimes used for other advanced cancers that no longer respond to other treatments.
What if thyroid biopsy is positive?
A positive marker indicates the need for a total thyroidectomy instead of a lobectomy, and negative markers may support a decision to forgo surgery for a follicular lesion of undetermined significance. Further studies are needed to determine the utility of these tests for indeterminate nodules.
Can you live without a thyroid?
Thyroid disease is common, and in some cases may require removal of your thyroid (thyroidectomy). Fortunately, you can live without your thyroid. You will need long-term thyroid hormone replacement therapy to give you the hormone your thyroid normally produces.
Do you need chemo or radiation for thyroid cancer?
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill cancer cells. There are many different chemotherapy drugs that can be used alone or in combination. Some come in pill form, but most are given through a vein. Chemotherapy may help control fast-growing thyroid cancers, such as anaplastic thyroid cancer.
What are the warning signs of thyroid cancer?
Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid CancerA lump in the neck, sometimes growing quickly.Swelling in the neck.Pain in the front of the neck, sometimes going up to the ears.Hoarseness or other voice changes that do not go away.Trouble swallowing.Trouble breathing.A constant cough that is not due to a cold.
How urgent is thyroid cancer surgery?
With thyroid cancer, you're not in a race to remove the tumor as soon as possible. Except for the most aggressive thyroid cancers (such as anaplastic thyroid cancer), these cancers are typically slow-growing. Even when the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, there's generally not an urgent need for surgery.
What is the life expectancy of someone with thyroid cancer?
Follicular thyroid cancers Around 85 out of every 100 men (around 85%) will survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed. Almost 90 out of every 100 women (almost 90%) will survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed.
What is the first stage of thyroid cancer?
Stage I: This stage describes a small tumor (T1) with no spread to lymph nodes (N0) and no distant metastasis (M0). Stage II: This stage describes a larger localized tumor (T2 or T3) with no spread to lymph nodes (N0) and no metastasis (M0).
What's the survival rate of thyroid cancer?
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time (usually 5 years) after they were diagnosed....Follicular thyroid cancer.SEER Stage5-Year Relative Survival RateRegional98%Distant63%All SEER stages combined98%1 more row•Mar 1, 2022
What factors should be considered when choosing a treatment plan for thyroid cancer?
In choosing a treatment plan, factors to consider include the type and stage of the cancer and your general health. Often, more than one type of treatment is needed. Treatment of Thyroid Cancer, by Type and Stage.
What is the goal of cancer treatment?
If the cancer can’t be cured, the goal of treatment may be to remove or destroy as much of the cancer as possible and to keep it from growing, spreading, or returning for as long as possible. Sometimes treatment is aimed at palliating (relieving) symptoms such as pain or problems with breathing and swallowing.
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
Who is on the cancer treatment team?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team may include: Many other specialists may be involved in your care as well, including nurse practitioners, nurses, psychologists, social workers, rehabilitation specialists, and other health professionals.
Who are the specialists involved in cancer care?
Many other specialists may be involved in your care as well, including nurse practitioners, nurses, psychologists, social workers, rehabilitation specialists, and other health professionals. Health Professionals Associated with Cancer Care.
What is the procedure to remove thyroid cancer?
Operations used to treat thyroid cancer include: Removing all or most of the thyroid (thyroidectomy). An operation to remove the thyroid gland might involve removing all of the thyroid tissue (total thyroidectomy) or most of the thyroid tissue (near-total thyroidectomy).
What is targeted drug therapy for thyroid cancer?
Targeted drug therapy for thyroid cancer targets the signals that tell cancer cells to grow and divide.
How to remove thyroid tissue?
Removing a sample of thyroid tissue. During a fine-needle aspiration biopsy, your doctor inserts a long, thin needle through your skin and into the thyroid nodule. Ultrasound imaging is typically used to precisely guide the needle into the nodule. Your doctor uses the needle to remove samples of suspicious thyroid tissue.
What tests can be done to check thyroid nodules?
Physical exam. Your doctor will examine your neck to feel for physical changes in your thyroid, such as thyroid nodules. He or she may also ask about your risk factors, such as past exposure to radiation and a family history of thyroid tumors. Blood tests.
What tests can be done to determine if thyroid cancer is spreading?
Imaging tests may include CT, MRI and nuclear imaging tests that use a radioactive form of iodine.
Which glands are close to the thyroid?
Close. Parathyroid glands. Parathyroid glands. The parathyroid glands, which lie behind the thyroid, manufacture the parathyroid hormone, which plays a role in regulating your body's levels of the minerals calcium and phosphorus. Most people with thyroid cancer undergo surgery to remove the thyroid.
What is external radiation therapy?
External radiation therapy. Radiation therapy can also be given externally using a machine that aims high-energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, at precise points on your body (external beam radiation therapy). During treatment, you lie still on a table while a machine moves around you.
Why is thyroid cancer treated?
In the treatment of thyroid cancer, drugs may be given to prevent the body from making thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), a hormone that can increase the chance that thyroid cancer will grow or recur. Also, because thyroid cancer treatment kills thyroid cells, the thyroid is not able to make enough thyroid hormone.
What are the symptoms of thyroid cancer?
Medullary thyroid cancer is sometimes caused by a change in a gene that is passed from parent to child. Signs of thyroid cancer include a swelling or lump in the neck. Tests that examine the thyroid, neck, ...
What is a thyroid nodule?
A thyroid nodule is an abnormal growth of thyroid cells in the thyroid. Nodules may be solid or fluid-filled. When a thyroid nodule is found, an ultrasound of the thyroid and a fine-needle aspiration biopsy are often done to check for signs of cancer.
How does chemo work?
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body (systemic chemotherapy). When chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas (regional chemotherapy).
What is the role of iodine in thyroid?
Thyroid hormones do the following: Control heart rate, body temperature, and how quickly food is changed into energy (metabolism). Control the amount of calcium in the blood.
Why do we do clinical trials?
Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment. Many of today's standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials.
How do you know if you have thyroid cancer?
Signs of thyroid cancer include a swelling or lump in the neck. Tests that examine the thyroid, neck, and blood are used to detect (find) and diagnose thyroid cancer. Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
What is the treatment for medullary thyroid cancer?
Treatment for medullary thyroid cancer may include: Surgery: This is done to remove the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) and sometimes nearby lymph nodes. Radiation therapy.
What is the procedure to remove the thyroid gland?
Surgery: This is done to remove part or all of the thyroid (called a thyroidectomy) and sometimes nearby lymph nodes. Thyroid hormone therapy: This is done to suppress the pituitary gland from secreting more thyroid-stimulating hormone, which may stimulate a recurrence of papillary cancer.
What is a thyroid adenomas?
Thyroid adenomas are small growths (nodules) that start in the cell layer that lines the inner surface of the thyroid gland. The adenoma itself may secrete thyroid hormone. If the adenoma secretes enough thyroid hormone, it may cause hyperthyroidism. Thyroid adenomas may be treated if they cause hyperthyroidism.
How to tell if thyroid nodule is cancerous?
Some signs that a nodule may be cancerous include: Presence of a single nodule rather than multiple nodules. Thyroid scan reveals the nodule is not functioning. Nodule is solid instead of filled with fluid (cyst) Nodule is hard. Nodule grows fast.
What is the most common form of thyroid cancer?
Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common form of thyroid cancer, accounting for about 80 percent of all cases. This form of thyroid cancer affects more women than men. Treatment for papillary cancer may include:
How do you know if you have thyroid cancer?
Symptoms. The first sign of a cancerous nodule in the thyroid gland is usually a painless lump in the neck. Other symptoms of thyroid cancer may include: Hoarseness or loss of voice as the cancer presses on the nerves to the voice box. Difficulty swallowing as the cancer presses on the throat. Throat or neck pain that does not go away.
How does thyroid cancer spread?
Medullary thyroid cancer accounts for about four percent of thyroid cancers. It tends to spread through the lymphatic system (which consist s of a system of vessels that connect lymph nodes throughout the body) and the bloodstream to other parts of the body.
What is the best treatment for thyroid cancer?
Surgery is the most widely used method to get rid of thyroid cancer. If the entire thyroid gland is removed, It’s called a thyroidectomy. If part of your thyroid gland is removed, the procedure is called a lobectomy.
How do thyroid pills help cancer?
The pills also help stop leftover cancer cells from growing and returning. They do this by lowering the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH is made by your pituitary gland. It tells your thyroid gland to make thyroid hormones. But it also encourages growth of the cancer.
How long does radiation therapy last for thyroid cancer?
It is very carefully delivered to protect the rest of your body as much as possible. You’ll get radiation therapy over several weeks.
Where does iodine go in a thyroid scan?
The iodine goes to the thyroid tissue and the radiation destroys it. It may also be used for cancer that spreads to nearby lymph nodes, spreads to other parts of the body, or returns.The level of radiation in this treatment is far higher than what is used in a radioiodine scan.
Is there a side effect to chemotherapy?
Usually, there are fewer side effects than with chemotherapy. Deciding on Treatment. If you get a diagnosis of thyroid cancer, your doctor will help you figure out the best treatment. They’ll explain the benefits and tell you about the risks. Pagination.
Can you get chemo with pills?
You may get pills, shots, or intravenous (IV) chemo. It has side effects, but your doctor will help you to manage them. Targeted therapy is a newer treatment that targets only certain parts of cancer cells, to slow or stop growth. This is normally taken in pill form.
What is the treatment for thyroid lesions?
Surgery is the therapy of choice for all primary lesions. Surgical options include total thyroidectomy or lobectomy. The choice of procedure is influenced mainly by the age of the patient and the size of the nodule. Survival results with the two procedures are similar for early-stage disease, with differences in the rates of surgical complications and local recurrences. [ 2 - 8]
What is the most advanced stage of thyroid cancer?
Stage II is the most advanced stage possible in a patient younger than 55 years. Stage III papillary or follicular thyroid cancer is only possible in patients aged 55 years or older. The thyroid tumor demonstrates extension into surrounding soft tissues, larynx, trachea, esophagus, or recurrent laryngeal nerve.
How old is a stage 1 thyroid cancer patient?
Stage I papillary or follicular thyroid cancer is localized to the thyroid gland in patients aged 55 years or older. In those younger than 55 years, the cancer may have spread to nearby tissues and lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body. In as many as 50% of the cases, papillary thyroid cancer is multifocal.
How many people will die from thyroid cancer in 2021?
Estimated new cases and deaths from thyroid cancer in the United States in 2021: [ 2] New cases: 44,280. Deaths: 2,200. Thyroid cancer affects women more often than men and usually occurs in people aged 25 to 65 years. The incidence of this malignancy has been increasing over the last decade.
What are the two types of cells in the thyroid?
In thyroid cancer, cell type is an important determinant of prognosis and treatment. The thyroid has two cell types: follicular cells and parafollicular C cells. The management of thyroid cancer depends on the cell of origin and how well the integrity of the cell type is maintained.
What are the risks of radiation therapy?
Patients with a history of radiation therapy administered in infancy or childhood for benign conditions of the head and neck (such as enlarged thymus, tonsils, or adenoids; or acne) have an increased risk of cancer and other abnormalities of the thyroid gland.
What is the tissue that surrounds the thyroid gland?
Thyroid gland tissue envelops the upper trachea just below the thyroid and cricoid cartilages that make up the larynx. The gland has an isthmus and often asymmetric right and left lobes; usually four parathyroid glands lie posteriorly. When swallowing, the thyroid may be felt to rise with the larynx—most commonly in the presence of a disease process.
How to treat a benign thyroid nodule?
If a biopsy shows that you have a noncancerous thyroid nodule, your doctor may suggest simply watching your condition. This usually means having a physical exam and thyroid function tests at regular intervals.
What is the best way to see thyroid nodules?
This imaging technique uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of your thyroid gland. A thyroid ultrasound provides the best information about the shape and structure of nodules. Doctors may use it to distinguish cysts from solid nodules or to determine if multiple nodules are present.
How long does it take for thyroid nodules to shrink?
This causes the nodules to shrink and signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism to subside, usually within two to three months. Anti-thyroid medications.
How to treat cancerous nodules?
A common treatment for cancerous nodules is surgical removal. In the past, it was standard to remove a majority of thyroid tissue — a procedure called near-total thyroidectomy. However, today more limited surgery to remove only half of the thyroid may be appropriate for some cancerous nodules.
What test can tell if you have hyperthyroidism?
Thyroid function tests. Tests that measure blood levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and hormones produced by your thyroid gland can indicate whether you have hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Ultrasound. This imaging technique uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of your thyroid gland.
What are the risks of thyroid surgery?
Risks of thyroid surgery include damage to the nerve that controls your vocal cords and damage to your parathyroid glands — four tiny glands located on the back of your thyroid that help control your body's levels of minerals, such as calcium.
How long does it take to biopsy a nodule?
The procedure is usually done in your doctor's office, takes about 20 minutes and has few risks.
What is the most common first treatment for thyroid cancer?
In fact, papillary thyroid cancer surgery is ...
Why is thyroid hormone suppressive therapy given to papillary thyroid cancer patients?
Giving thyroid hormone to papillary thyroid cancer patients is called thyroid hormone suppressive therapy when the goal is to decrease the pituitary production of TSH.
What is papillary thyroid cancer?
Papillary thyroid cancer evidence of invasion (or extension) outside of the thyroid gland capsule (called soft tissue extension) Papillary thyroid cancer that has spread to at least two lymph nodes in the neck (in any area of the neck) The papillary thyroid cancer team desire to destroy any additional thyroid tissue.
How long does it take to get a thyroid scan for RAI?
Following either of the above approaches to treat a papillary thyroid cancer with RAI, a scan is obtained following the therapeutic dose in 48 to 72 hours to determine the location and percent uptake of the radioactive iodine. The strength of radioactive iodine is described in millicuries.
What is RAI treatment?
RAI treatment is a type of internal radiation therapy. RAI treatment was the first true "targeted therapy" developed in the treatment of cancer. The papillary thyroid cancer patient swallows a radioactive iodine form of iodine called iodine 131 (I-131) in a liquid or pill (capsule) form.
How long does thyroid cancer last?
Papillary thyroid cancer patients must be taken off of levothyroxine thyroid hormone (T4 hormone) for a minimum of four weeks, taken off of liothyrionine thyroid hormone (T3 hormone) for a minimum of two weeks, or receive a medication which is TSH (which is a pharmaceutical production of the Thyroid Stimulating Hormone [TSH] produced as a recombinant protein which is identical to the TSH normally produced by the pituitary gland). Additionally, papillary thyroid cancer patients must be on a low iodine diet for a minimum of four weeks to starve their body of iodine. Those patients which have undergone CAT scans with intravenous contrast must wait until their blood iodine levels have been adequately decreased (usually at least two months). Note, a desire to treat with radioactive iodine should never prevent the use of necessary CAT scans for the evaluation of a papillary thyroid cancer patient.
What is the term for the removal of half of the thyroid gland?
One is removal of about half of the thyroid gland called a thyroid lobectomy . The other is removal of all of the thyroid gland and is called a total thyroidectomy. The third type of thyroidectomy is called a subtotal thyroidectomy where almost all of the thyroid gland is removed.
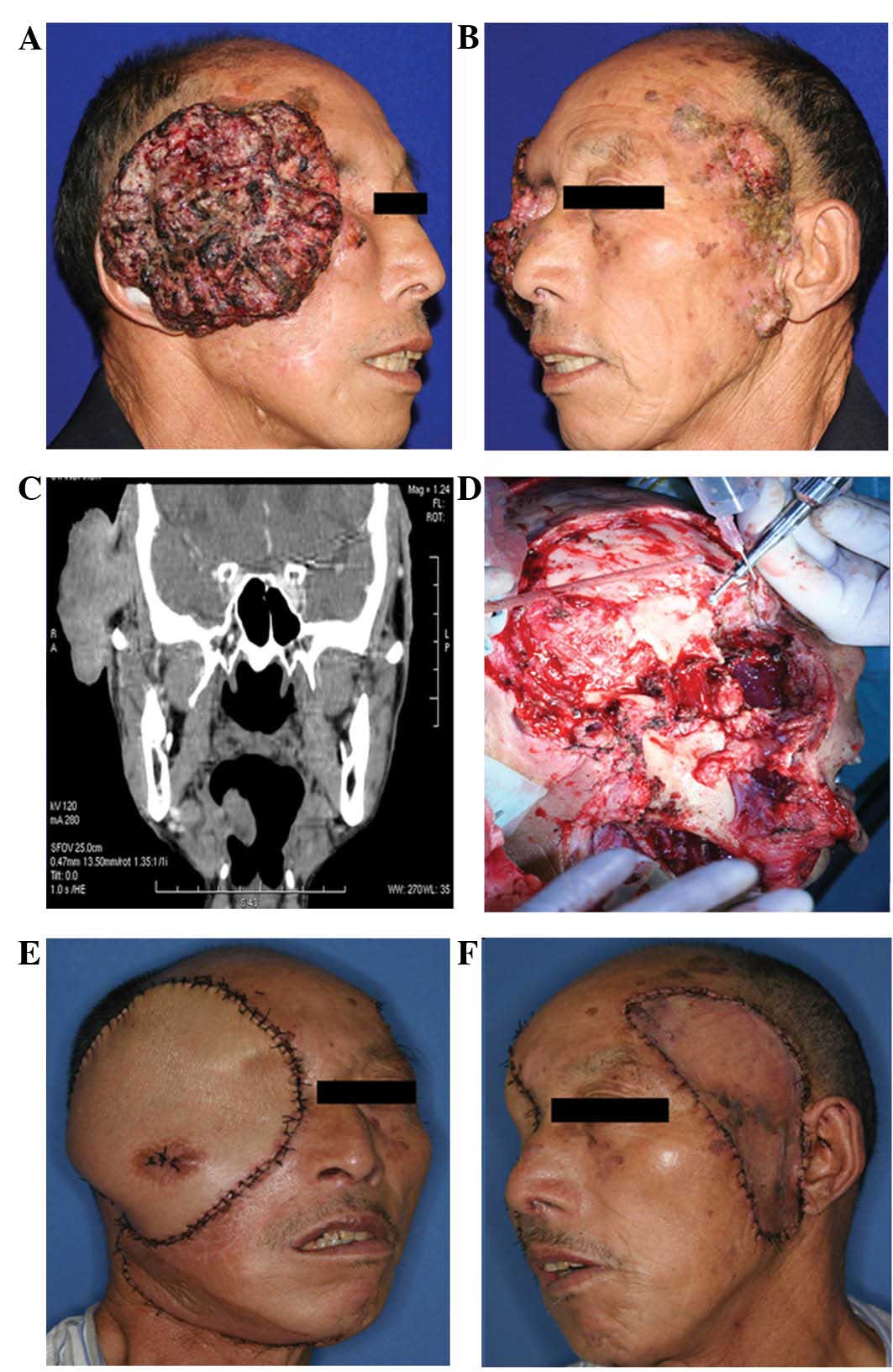
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Tests and procedures used to diagnose thyroid cancer include: 1. Physical exam.Your health care provider will examine your neck to feel for changes in your thyroid, such as a lump (nodule) in the thyroid. The provider may also ask about your risk factors, such as past exposure to radiation and a family history of thyroid cancers. 2. Thyroid functio...