
What is the treatment for a trabeculated bladder?
Treatment is aimed at addressing the cause of the trabeculated bladder. A trabeculated bladder is usually a symptom of a blockage. The blockage must be removed to prevent the condition from worsening, and to allow the muscles walls to regain their elasticity. Although, once the elasticity of the bladder wall muscles is lost,...
What is the treatment for a blockage in the bladder?
BOO is treated in line with the cause of the problem. A thin, flexible tube (catheter) is inserted through the urethra into the bladder, in most cases. The placement of the catheter can relieve the blockage. In some cases, a tube is placed into the bladder through the belly area.
How do you treat a thicker bladder wall?
Treating a thickened bladder wall means treating the underlying condition that caused the change in the wall. For example, UTI treatment usually involves a course of antibiotic therapy. To prevent UTIs, practice good hygiene. Wipe front to back to reduce the risk of germs from the rectum reaching the urethra.
Can bladder outlet obstruction be treated?
Most cases of bladder outlet obstruction can be treated successfully if caught early. If treatment is delayed, however, the bladder or kidneys can be seriously damaged.
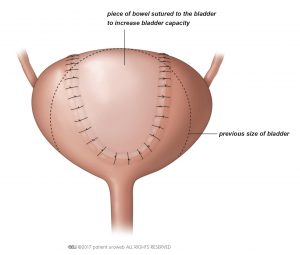
Can bladder Trabeculation be reversed?
Conclusion: Bladder hypertrophy was completely reversible after the surgical treatment of the obstruction in the majority of patients with BPH.
What does it mean if your bladder is Trabeculated?
Bladder trabeculation happens when the walls of the bladder thicken, making them harder to contract. When that happens, it's harder for people to completely empty their bladder when they urinate. Bladder trabeculation can occur in both men and women. The leading cause is an obstruction to the urethra.
What is the treatment for thickening of the bladder wall?
Increased intravesical pressure results from smooth muscle hypertrophy and thus the bladder wall thickens. Alpha-blocker therapy is the most preferred medical treatment in patients with LUTS. Bladder wall hypertrophy is caused by a thickening of the detrusor.
Is bladder wall thickening curable?
A thickening of the bladder wall can be a sign of several medical conditions. It's usually accompanied by other symptoms, too. Many of these conditions are easily treatable with an early diagnosis.
What does Trabeculated mean in medical terms?
(tră-bek'yū-lā'shŭn), 1. The occurrence of trabeculae in the walls of an organ or part. 2. The process of forming trabeculae, as in spongy bone.
Is bladder wall thickening painful?
Thickening of the bladder wall can be caused by an infection or a tumor, which can cause discomfort, painful urination, hematuria, hematuria, and even endanger the patient's life.
How painful is a cystoscopy?
People often worry that a cystoscopy will be painful, but it does not usually hurt. Tell your doctor or nurse if you feel any pain during it. It can be a bit uncomfortable and you may feel like you need to pee during the procedure, but this will only last a few minutes.
Can your bladder repair itself?
The bladder is a master at self-repair. When damaged by infection or injury, the organ can mend itself quickly, calling upon specialized cells in its lining to repair tissue and restore a barrier against harmful materials concentrated in urine.
How common is bladder wall thickening?
Results: Twenty-two patients (0.7% of cystoscopies) underwent cystoscopy for incidentally identified bladder wall thickening including 11 (50%) with focal bladder wall thickening, 8 (36.4%) with diffuse bladder wall thickening, and 3 (13.6%) with focal bladder mass lesions.
How long does it take to heal from cystoscopy?
You may feel the need to urinate more often, and your urine may be pink. These symptoms should get better in 1 or 2 days. You will probably be able to go back to work or most of your usual activities in 1 or 2 days. This care sheet gives you a general idea about how long it will take for you to recover.
Can you live without a bladder?
It can affect your body image, and you may worry about its impact on your relationships and sex life. With enough time, you should be able to do almost everything you did before. Even if you now use a urostomy bag (to collect your urine), you can go back to work, exercise, and swim.
How long does a cystoscopy take?
A simple outpatient cystoscopy can take five to 15 minutes. When done in a hospital with sedation or general anesthesia, cystoscopy takes about 15 to 30 minutes. Your cystoscopy procedure might follow this process: You'll be asked to empty your bladder.
How many millimeters is a trabeculated bladder?
A bladder that measures more than three millimeters when swollen and greater than five millimeters when normal is considered trabeculated. Treating a trabeculated bladder typically involves treating the cause of the obstruction. For men who have BPH, that starts with getting a diagnosis from a doctor.
How does the bladder work?
Your bladder walls typically expand to store urine, then contract to push urine out through your urethra and expel it from your body. When something blocks the urethra, like a kidney stone, it can slow down or stop urine from getting out. Your bladder walls must work harder as your bladder tries to force out urine.
Why does my bladder get thicker?
Your bladder walls must work harder as your bladder tries to force out urine. This causes the bladder walls to thicken. That thickening of the bladder walls is called trabeculation. When your bladder walls get too thick, they lose the ability to expand and contract, making it hard for your body to expel urine.
What is the bladder?
The bladder is a hollow, triangle-shaped organ in your lower abdomen. Other organs and ligaments attached to the bones in your pelvis hold it in place. Your bladder walls typically expand to store urine, then contract to push urine out through your urethra and expel it from your body.
Why is it important to diagnose a blockage in the urinary tract?
Diagnosing the cause of a urinary tract blockage as soon as possible is important to prevent other complications besides bladder trabeculation. Your doctor may perform a bladder catheterization or other imaging tests to figure out why you have trouble urinating.
Can BPH cause trabeculation?
Bladder trabeculation in men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men can block the flow of urine. That can eventually cause trabeculation in the bladder. The condition typically affects men over 50 years old.
Can laser treatment cause a trabeculation?
Men can also develop bladder trabeculation after having laser treatment for an enlarged prostate. This procedure can cause blood clots to form within the bladder. Bladder trabeculation in women. Women can experience a severe form of pelvic organ prolapse, which can cause lower urinary tract issues.
How to treat diverticulum in bladder?
Diverticula caused by a block in the bladder are treated by taking out the block and maybe the diverticulum, as well. The surgery can be done by open surgery or through small tubes fed inside the bladder. A robot may be used to help with the surgery. Sometimes surgery on the outside of the bladder will also be needed. This surgery may be hard if the diverticulum has been infected and is swollen. For patients who can't have open surgery, the opening of the diverticulum into the bladder can be made larger. Samples of any tumors found in a diverticulum are tested for cancer.
What is the test to check for bladder tumors?
This is to check for bladder tumors in the diverticulum. A pressure test called "urodynamics" may also be done to see how well the bladder works and check for blocks. Your health care provider may use ultrasound, which takes pictures of your organs by bouncing sound waves off them, to see how any blocks affect your kidneys.
Why does my bladder leak after surgery?
damage to the intestines or ureters (the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys) urine leaking from the bladder after surgery. infection. Some patients will need to have the diverticulum removed with open surgery later. If your bladder doesn't work well, you may need to help drain it with a catheter.
What is the name of the pouch in the bladder wall that a person may either be born with or get later?
Bladder Diverticulum. A bladder diverticulum is a pouch in the bladder wall that a person may either be born with ("congenital") or get later ("acquired"). A congenital bladder diverticulum forms when some of the bladder lining pokes through a weak part in the bladder wall.
Why is my bladder not working?
Acquired bladder diverticula (more than 1 diverticulum) are most often caused by a block in the bladder outlet (such as from a swollen prostate or scars in the urethra), the bladder not working well because of nerve injury or, rarely, from prior bladder surgery. With acquired diverticula, many pouches often form.
What happens when your bladder is not full?
When it isn't full, the bladder is relaxed. Muscles in the bladder wall allow it to expand as it fills with urine. Nerve signals in your brain let you know that your bladder is getting full. Then you feel the need to go to the bathroom. The brain tells the bladder muscles to squeeze (or "contract").
Can you check a diverticulum with a cystoscope?
In some cases, after the cause of the diverticulum (such as a block in the bladder) is fixed, you won’t need to be treated further. Your health care provider may want to check the diverticulum with a cystoscope through the urethra once in a while.
What is the tube that drains the bladder called?
In some cases, a tube is placed into the bladder through the belly area. This tube, called a suprapubic catheter, will drain the bladder.
What is a bladder obstruction?
What is bladder outlet obstruction (BOO)? Bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) occurs when there is a blockage at the base or neck of the bladder. Such a blockage reduces or stops the flow of urine into the urethra, which carries urine from the body. BOO is most common in older men and often is linked to prostate problems.
What causes a bladder outlet to be blocked?
The causes of bladder outlet obstruction include: Scar tissue in the urethra. Bladder stones. An enlarged prostate gland. Prostate cancer. Tumors in the rectum, uterus or cervix.
Can you have surgery for boo?
In some cases, however, the long-term treatment of BOO requires surgery. The timely treatment of the disease can reduce problems.
Can a woman with a cystocele have a BOO?
Also, men with an enlarged prostate gland or women with cystocele (prolapsed bladder) can be diagnosed with BOO. Tests may include: Blood tests to check for kidney damage. Urine cultures to test for infection. Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder to find where the urine blockage is occurring.
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Surgery or medication to treat bladder or other pelvic cancers. Recovery after treatment relies on what is causing the bladder obstruction. For example, bladder stone removal can be a relatively simple procedure, while treatments for cancer can be ongoing with longer recovery periods.
What causes a blockage in the bladder?
Treatment for bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) —a blockage at the base of the bladder that stops or slows the flow of urine—depends upon the underlying cause, of which there are several, including: 1 Enlarged prostate ( benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH) 2 Bladder cancer or other pelvic cancers 3 Bladder stones 4 Injury or surgery that caused scarring of the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder).
How long does it take for kidneys to work after a bladder blockage?
If the kidneys were damaged as a result of the obstruction, they will start working properly again within 3 weeks to 5 months. Again, this depends upon the severity of the damage done.
Can bladder outlet obstruction cause kidney damage?
Left untreated, bladder outlet obstruction can harm the bladder or kidneys as the pressure of the urine builds up in the upper urinary tract. In order to minimize this type of damage, the most important first step during treatment is to relieve the pressure caused by the blockage.
What is the best treatment for urinary incontinence?
tricyclic antidepressants. A doctor may use botulinum toxin A, or Botox. NIH external link. , to treat urinary incontinence when other medicines or self-care treatments don’t work. Injecting Botox into the bladder relaxes it, which makes more room for urine and lowers the chances of developing UI.
What is bladder training?
Bladder training is when you urinate on a schedule to help reduce leaking. Based on a bladder diary (PDF, 487.59 KB) , your doctor may suggest using the bathroom on a regular schedule, called timed voiding. Gradually lengthening the time between trips to the bathroom can help stretch your bladder so it can hold more urine. Record your daily bathroom habits so you and your doctor can review your diary.
What is a pessary catheter?
For women. A pessary is a soft plastic ring used for stress incontinence that you or your doctor insert into your vagina.
How to treat stress incontinence?
During a short office visit, a doctor can inject a bulking gel or paste near your urinary sphincter to treat stress incontinence. The injected material “bulks” or helps thicken the area around the urethra and helps close your bladder opening so you have less leaking.
How to make your pelvic floor stronger?
Strong pelvic floor muscles hold in urine better than weak muscles. You can make your pelvic floor muscles stronger by doing Kegel exercises. These exercises involve tightening and relaxing the muscles that control urine flow.
How to stop urinate?
You may be able to suppress, or control, the strong urge to urinate, called urge or urgency suppression. With this type of bladder training, you can worry less about finding a bathroom in a hurry. Some people distract themselves to take their mind off needing to urinate. Other people find that long, relaxing breaths or holding still can help. Doing pelvic floor exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor also can help control the urge to urinate. Quick, strong squeezes of the pelvic floor muscles can help suppress urgency when it occurs, which may help you get to the toilet before you leak.
How to treat UI?
to treat UI, but they can cause constipation. Stop smoking. If you smoke, get help to stop smoking. External link. . Quitting smoking at any age is good for your bladder health and overall health. Smoking raises your chances of developing stress incontinence, because smoking causes chronic, or long-lasting, coughing.
Why is it important to treat bladder obstruction?
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of bladder outlet obstruction is important to prevent serious problems caused by urine backing up into your system. If you can't pass urine, emergency treatment includes insertion of a tube (catheter) through the tip of your penis and into your bladder. This tube helps urine drain from your bladder.
What causes a man's bladder to be blocked?
Enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) — this is the most common cause of bladder outlet obstruction in men. Scarring of the urinary channel (urethra) or bladder neck, as a result of injury or surgery. Use of certain medications, including antihistamines, decongestants or drugs to treat overactive bladder.
Why does my bladder back up?
Bladder outlet obstruction can cause urine to back up in your system, leading to difficulty urinating and other uncomfortable urinary symptoms. Possible causes of bladder outlet obstruction might include: Enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) — this is the most common cause of bladder outlet obstruction in men.
How to treat thickened bladder wall?
For example, UTI treatment usually involves a course of antibiotic therapy. To prevent UTIs, practice good hygiene. Wipe front to back to reduce the risk of germs from the rectum reaching the urethra.
What causes a bleed in the bladder?
Sometimes irritation and inflammation of the bladder wall causes bleeding from the bladder lining. This is considered hemorrhagic cystitis. Causes may include: 1 radiation therapy 2 chemotherapy 3 an infection 4 exposure to certain chemicals, such as insecticides or dyes
What is the cause of urinary tract infection?
Inflammation due to urinary tract infection (UTI) A UTI is often the result of bacteria entering the urethra and then the bladder. These infections are more common among females than males. UTIs are often associated with sexual intercourse, but a woman who isn’t sexually active can also develop a bladder infection.
How do you know if your bladder is thickening?
You may urinate more frequently, or you may notice that it feels different when you relieve yourself. You may also notice changes in the urine itself.
Why does my bladder wall thicken?
Bladder wall thickening. The muscular wall of your bladder tends to grow thicker if it has to work harder to urinate. It can also thicken if it becomes irritated and inflamed. Scarring of the bladder wall may also cause it to thicken. Common causes of bladder wall thickening include:
What causes a UTI to thicken?
One of the major responses to a UTI is inflammation of the bladder wall, a condition known as cystitis. Prolonged inflammation can lead to thickening of the wall. Some other causes of cystitis include inflammation triggered by cancer treatments, like radiation and chemotherapy, or prolonged use of a catheter.
What causes bladder tumors to grow?
Noncancerous tissue growths. Abnormal tissue growth in the bladder wall causes tumors to grow and the wall to thicken. Noncancerous ( benign) tumors include papillomas. For some cases, viruses may be the cause of these growths. Other benign bladder tumors include leiomyomas, but these are rare.
