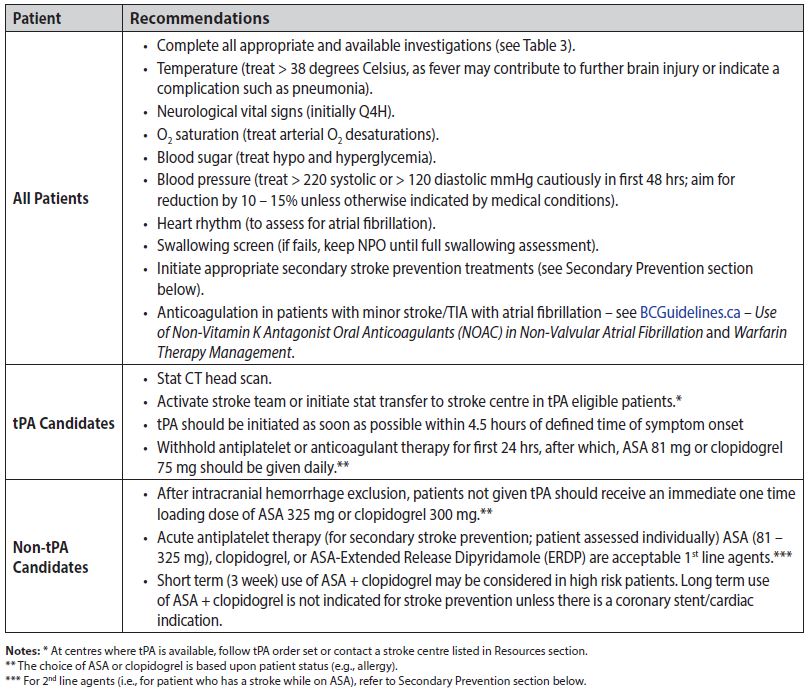
Medication
Types of Stroke
- Ischemic Stroke. Most strokes (87%) are ischemic strokes. ...
- Hemorrhagic Stroke. ...
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) For Blanche Teal-Cruise, a smoker for 40 years who also had high blood pressure, the transient ischemic attack (sometimes called a mini-stroke) she had on the ...
- More Information. ...
Procedures
The following are some things you can do to reduce your risk of dementia:
- Be physically active. ...
- Eat healthily by consuming at least 5 portions of fruits and vegetables a day and protein at least twice a week. ...
- Don’t smoke. ...
- Drink less alcohol. ...
Self-care
What is the prognosis for transient ischemic attack (TIA)? The signs and symptoms of a transient ischemic attack (TIA) go away within 24 hours and there are no remaining deficits or impairments in mental or physical functioning. However, a TIA should be an alarm to start treatment to prevent a stroke, which can lead to long-term deficits or death.
Nutrition
TIAs are sometimes called mini-strokes, because their symptoms last only for a few minutes up to 24 hours before disappearing. But warning stroke is a better label, because a TIA often foreshadows a full-blown stroke and needs to be taken seriously. TIAs are caused by a clot or blockage in the brain . The blockage is short term.
See more
How is a transient ischemic attack different from a stroke?
How to prevent Tia naturally?
What is the prognosis of transient ischemic attack (TIA)?
Why is transient ischaemic attack (TIA) called "mini stroke"?
See more

What is a transient ischemic attack and what is a treatment option for it?
Although the symptoms of a transient ischaemic attack (TIA) resolve in a few minutes or hours without any specific treatment, you'll need treatment to help prevent another TIA or a full stroke from happening in the future. A TIA is a warning sign that you're at increased risk of having a full stroke in the near future.
What medication is first line therapy for TIA?
Antiplatelet agents, rather than oral anticoagulants, are recommended as initial therapy. Aspirin 50–325 mg/day, a combination of aspirin and extended-release dipyridamole, and clopidogrel are all reasonable first-line options (class I recommendation).
Is a transient ischemic attack serious?
TIAs look like strokes in terms of signs and symptoms, but they are temporary. In other words, they leave no lasting brain damage or residual symptoms. However, they serve as a warning sign that a person is at higher risk of a major stroke and should seek immediate medical attention.
What happens after a transient ischemic attack?
During a transient ischemic attack, a blood clot restricts or prevents blood from reaching certain subsections of the brain. These parts of the brain may go without needed resources such as sugar and oxygen for minutes to hours. After the TIA resolves, the brain doesn't fully return to normal.
Should I see a neurologist after a TIA?
Always treat a TIA as seriously as you would a stroke. "Even though the symptoms resolve, there might be damage to the brain, so you need to see a neurologist," Dr. Rost advises.
Does aspirin help with a TIA?
Aspirin is recommended for secondary prevention after transient ischaemic attack (TIA) or ischaemic stroke on the basis of trials showing a 13% reduction in long-term risk of recurrent stroke.
Should you go to hospital for TIA?
Nevertheless, if you suffer a TIA, even if symptoms disappear, you should go immediately to an emergency room or call 911. While a TIA is not a full-blown stroke, it is a warning that a full-blown stroke may be right around the corner. In a nutshell, a TIA needs immediate medical attention.
How long does it take to recover from a transient ischemic attack?
This can cause sudden symptoms similar to a stroke, such as speech and visual disturbance, and numbness or weakness in the face, arms and legs. But a TIA does not last as long as a stroke. The effects last a few minutes to a few hours and fully resolve within 24 hours.
What can trigger a TIA?
The blockage in the blood vessels responsible for most TIAs is usually caused by a blood clot that's formed elsewhere in your body and travelled to the blood vessels supplying the brain. It can also be caused by pieces of fatty material or air bubbles.
Should I take aspirin after TIA?
Aspirin is already given to people who have had a stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA – often called a 'mini-stroke') to prevent further strokes after they have been assessed in hospital and in the longer-term, reducing the subsequent stroke risk by about 15%.
Will an MRI show if you had a TIA?
Tests will be done to rule out a stroke or other disorders that may cause the symptoms: You will likely have a head CT scan or brain MRI. A stroke may show changes on these tests, but TIAs will not. You may have an angiogram, CT angiogram, or MR angiogram to see which blood vessel is blocked or bleeding.
What are the warning signs of a TIA?
The signs and symptoms of a TIA resemble those found early in a stroke and may include sudden onset of:Weakness, numbness or paralysis in the face, arm or leg, typically on one side of the body.Slurred or garbled speech or difficulty understanding others.Blindness in one or both eyes or double vision.More items...•
Do you give heparin for TIA?
Intravenous heparin therapy is often used in patients presenting with transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke as either bridging therapy for anticoagulation with warfarin, or as primary therapy in suspected intracranial arterial dissection, crescendo TIAs, or suspected hypercoagulable states.
What is the best medication for stroke?
Emergency IV medication. An IV injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) — also called alteplase (Activase) or tenecteplase (TNKase) — is the gold standard treatment for ischemic stroke. An injection of TPA is usually given through a vein in the arm within the first three hours.
How long should you take clopidogrel after a TIA?
Recent minor non-cardioembolic ischemic stroke or high-risk TIA, DAPT with aspirin plus clopidogrel should be initiated early (ideally within 12–24 hours of symptom onset and at least within 7 days of onset) and continued for 21–90 days.
Should I take aspirin after TIA?
Aspirin is already given to people who have had a stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA – often called a 'mini-stroke') to prevent further strokes after they have been assessed in hospital and in the longer-term, reducing the subsequent stroke risk by about 15%.
How long does it take for a transient ischaemic attack to resolve?
Although the symptoms of a transient ischaemic attack (TIA) resolve in a few minutes or hours without any specific treatment, you'll need treatment to help prevent another TIA or a full stroke from happening in the future.
How to reduce the chance of stroke after TIA?
These include: eating a healthy, balanced diet – a low-fat, reduced-salt, high-fibre diet is usually recommended, including plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables.
What is the procedure to remove the lining of the carotid arteries?
A carotid endarterectomy involves removing part of the lining of the carotid arteries – the main blood vessels that supply the head and neck – plus any blockage inside the carotid arteries.
Why do you take antihypertensive if you have high blood pressure?
This is because high blood pressure increases your risk of having a TIA or stroke.
How do anticoagulants help with TIA?
Anticoagulant medicines can help to prevent blood clots by changing the chemical composition of your blood in a way that stops clots from forming. They're usually offered to people who had a TIA that was caused by a blood clot in their heart.
What are some examples of anticoagulants?
Warfarin, apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban and rivaroxaban are examples of anticoagulants that may be offered to some people who have had a TIA. A side effect of all anticoagulants is the risk of bleeding, because these medicines reduce the blood's ability to clot.
How to reduce risk of stroke?
Plus, strength exercises on 2 days every week. stopping smoking – if you smoke, stopping may significantly reduce your risk of having a stroke in the future. cutting down on alcohol – men and women are advised to limit alcohol intake to 14 units per week.
Make an Appointment
Our team of dedicated access representatives is here to help you make an appointment with the specialists that you need.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a TIA depend on the size and location of the blockage. Symptoms may include:
Diagnosis
There is no single test that can diagnose a TIA. A doctor will take as much information as possible from the patient and his or her family, or anyone who witnessed the TIA. The doctor will perform a thorough physical and neurological exam, looking for weakness, numbness, lack of coordination or trouble speaking or understanding.
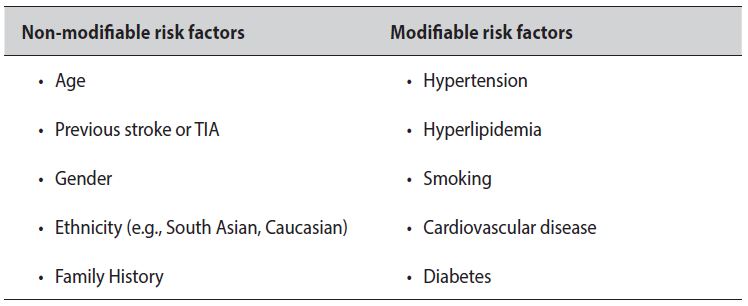
Risk Factors
Two types of arteries supply blood to the brain, and a blockage in either type can result in a TIA. A blockage in one of the cerebral arteries prevents blood from reaching the portion of the brain ordinarily sustained by that artery. A blockage in one of the carotid arteries causes blood flow problems for the entire brain–not just a single section.
Treatments
The goal of treatment is to prevent a stroke. The foundation of stroke prevention is usually a combination of medication and lifestyle changes.
How to avoid stroke?
Make sure to limit saturated fats and sugar and avoid trans fats. Get a good night's sleep. Regular shut-eye can lower your risk of a stroke. Create a routine to relax at night and get to bed at a reasonable time. Limit alcohol. If you drink, keep it to one drink a day if you're a woman or two if you're a man.
What drugs can cause a TIA?
Drugs like amphetamines, cocaine, and heroin can raise your chances of a TIA or stroke. In addition to other lifestyle changes, if you're a woman, you should take a few more steps to avoid a TIA or stroke. For instance, if you're over age 75, ask your doctor to check you for atrial fibrillation.
What is the procedure called to open the carotid artery?
Another choice is a procedure called carotid angioplasty and stenting. Your doctor makes a small opening in your groin. They'll use a balloon-like device to widen your carotid artery, then put in a small wire tube, called a stent, to keep it open. They then remove the balloon.
What to do if your neck is blocked?
Surgery. If one of the carotid arteries in your neck is narrowed or blocked, you may need surgery to help clear it out and restore normal blood flow. One option is an operation called carotid endarterectomy, where your doctor opens up the carotid artery, scrapes out the plaque, and closes it back up.
How to control high blood pressure?
If you drink, keep it to one drink a day if you're a woman or two if you're a man. Manage your other health conditions. The more you control issues like high blood pressure, diabetes, and atrial fibrillation, the better. Stick to an exercise routine.
What is the name of the drug that helps blood clots?
Anticoagulants change those proteins to make it harder for them to form clots. If you only need an anticoagulant for the short term, you might get one called heparin . For longer-term use, you might get one of these drugs:
Why do you need regular tests after a stroke?
You'll need regular tests to make sure you get just the right dose to prevent a stroke and limit side effects. Medicines for other conditions. When your doctor runs tests after a TIA, you might learn that you have another health problem that raises your stroke risk.
What is a transient ischemic attack?
A transient ischemic attack has the same origins as that of an ischemic stroke, the most common type of stroke. In an ischemic stroke, a clot blocks the blood supply to part of your brain. In a transient ischemic attack, unlike a stroke, the blockage is brief, and there is no permanent damage. The underlying cause of a TIA often is a buildup ...
How many people have a stroke after a transient ischemic attack?
About 1 in 3 people who has a transient ischemic attack will eventually have a stroke, with about half occurring within a year after the transient ischemic attack. A transient ischemic attack can serve as both a warning of a future stroke and an opportunity to prevent it.
What is a TIA?
Overview. A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary period of symptoms similar to those of a stroke. A TIA usually lasts only a few minutes and doesn't cause permanent damage. Often called a ministroke, a transient ischemic attack may be a warning. About 1 in 3 people who has a transient ischemic attack will eventually have a stroke, ...
How long do TIA symptoms last?
Symptoms. Transient ischemic attacks usually last a few minutes. Most signs and symptoms disappear within an hour, though rarely symptoms may last up to 24 hours. The signs and symptoms of a TIA resemble those found early in a stroke and may include sudden onset of:
How to reduce TIA?
Stopping smoking reduces your risk of a TIA or a stroke. Limit cholesterol and fat. Cutting back on cholesterol and fat, especially saturated fat and trans fat, in your diet may reduce buildup of plaques in your arteries. Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
What causes TIA in the brain?
The underlying cause of a TIA often is a buildup of cholesterol-containing fatty deposits called plaques (atherosclerosis) in an artery or one of its branches that supplies oxygen and nutrients to your brain. Plaques can decrease the blood flow through an artery or lead to the development of a clot.
When to see a doctor for TIA?
When to see a doctor. Since TIAs most often occur hours or days before a stroke, seeking medical attention emergently following a possible TIA is essential. Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect you've had a transient ischemic attack.
What are the symptoms of a transient ischemic attack?
Symptoms generally come on suddenly and can include: Difficulty seeing from one or both eyes. Numbness or weakness in the face, arms, or legs, especially on one side. Severe headache.
How to reduce risk of TIA?
To reduce the risk of a future TIAs or strokes, follow these tips: If you smoke, stop. Monitor your blood pressure and follow your doctor’s treatment plan if your blood pressure is high. The target blood pressure is less than 140/90 mm Hg for all adults who have a history of TIA or stroke.
What is a TIA?
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) or Mini Stroke. TIA symptoms are similar to stroke symptoms but do not last as long and result in no permanent brain injury. TIAs should be considered a warning of the likelihood of a coming stroke. Appointments 866.588.2264. Appointments & Locations.
How long does a TIA last?
A transient ischemic attack (TIA), also sometimes referred to as a “mini-stroke,” starts like a stroke but only lasts from several minutes up to 24 hours. Unlike a stroke, a TIA does not kill the brain cells, so there is no lasting damage to the brain. However, when a TIA begins, there is no way to tell if a person is having a stroke or a TIA.
What happens when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted?
A stroke happens when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted. This can happen when a blood vessel in the brain bursts (hemorrhagic stroke), or when there is some type of blockage that cuts off blood supply (ischemic stroke ). When brain cells are deprived of oxygen, they die.
What are the risks of TIA?
Risks of TIA and stroke include: Older age. The risk of stroke doubles with each decade after age 55 in both men and women. Family history of stroke. Male sex. Men have a higher risk of TIA; women have a higher lifetime risk of stroke. Race or ethnicity.
How to take statins?
Statin drugs are the drugs of choice if drug therapy is recommended. Eat a Mediterranean-style diet (a diet high in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fish, legumes, poultry, olive oil, nuts, and low-fat dairy products). Limit your intake of red meat and sweets. Reduce your salt (sodium) intake to less than 2.4 g/day.
Drugs used to treat Transient Ischemic Attack
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.