Explore
What medications are used for Torsades de Pointes? Depending on your situation, your provider may give you: Magnesium and/or potassium. Isoproterenol. Beta blockers like Nadolol (Corgard®). What treatments are used for Torsades de Pointes? Your provider may use one of the following medical devices: Temporary or permanent cardiac pacemaker.
What are torsades de pointes and how are they treated?
Jan 15, 2018 · If torsades de pointes is found to have an underlying medical cause, this will be treated first. If a medication is causing the condition, a doctor may recommend an alternative treatment. For...
Which medications are used in the treatment of pulmonary torsades de pointes?
Treatment of torsade de pointes includes: isoproterenol infusion, cardiac pacing, and intravenous atropine. Intravenous magnesium sulfate, a relatively new mode of therapy for torsade de pointes, was proven to be extremely effective and is now regarded as the treatment of choice for this arrhythmia.
Is intravenous magnesium sulfate effective for torsade de pointes?
Aug 11, 2021 · Intravenous magnesium is the first-line pharmacologic therapy in Torsades de Pointes. Magnesium has been shown to stabilize the cardiac membrane, though the exact mechanism is unknown. The recommended initial dose of magnesium is a slow 2 g IV push. An infusion of 1 gm to 4 gm/hr should be started to keep the magnesium levels greater than 2 …
What are the treatment options for torsades?
Treatment If you are diagnosed with TdP, your doctor will check your potassium, magnesium, and calcium levels. If they are low, you will be given supplements …
How do you manage torsades de pointes?
The first step in managing Torsades de Pointes is preventing its onset by targeting modifiable risk factors. This includes discontinuing any QT prolonging drugs and optimizing a patient's electrolyte profile. Correcting hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia can all help to prevent the onset of torsades.Aug 11, 2021
What is the treatment for torsades?
The torsades rhythm is treated with magnesium sulfate 2 g IV over 1 to 2 minutes, correction of hypokalemia, pacing or isoproterenol to increase heart rate, and correction of the cause.
Do you shock torsades?
Occasional patients will have recurrent episodes of torsade (“Torsade storm”). Each individual episode may be treated with magnesium or defibrillation, if needed (Treatment step #1 above). However, additional therapies are required to stop recurrence and end the storm.Nov 22, 2021
What antiarrhythmic is used for torsades de pointes?
Antiarrhythmic drugs associated with torsade include the following: Class IA - Quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide. Class III - Sotalol, amiodarone (rare), ibutilide, dofetilide, almokalant.
Which drug is associated with torsades de pointes?
Antiarrhythmic drugs associated with torsade include the following: Class IA - Quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide. Class III - Sotalol, amiodarone (rare), ibutilide, dofetilide, almokalant.Jan 31, 2017
What is the most common cause of torsades de pointes?
Common causes for torsades de pointes include drug-induced QT prolongation and less often diarrhea, low serum magnesium, and low serum potassium or congenital long QT syndrome. It can be seen in malnourished individuals and chronic alcoholics, due to a deficiency in potassium and/or magnesium.
Can amiodarone treat torsades?
Torsades de pointes is caused by a prolonged QT. Almost all of the antiarrhythmics that we normally use to treat ventricular tachycardia, such as amiodarone and procainamide, will prolong the QT further, and therefore can make your patient worse. Do not give amiodarone or procainamide.Jan 9, 2017
Do you do CPR for torsades?
If torsades de pointes is present, then give magnesium 1-2 g diluted in 10 mL D5W IV/IO push, typically over 5-20 minutes (Class IIa for torsades). Continue CPR followed by 1 shock and additional CPR/medications for 5 cycles or 2 minutes.Jan 16, 2007
Does a pacemaker prevent torsades?
The pacemaker component of such devices should in theory help prevent torsades by preventing bradycardia. However, the rate of most pacemakers is not likely to provide protection from torsades.May 28, 2020
How is torsades de pointes diagnosis?
How is Torsades de Pointes diagnosed? Your provider can see a distinct pattern that looks like twisting points or peaks (which it means in French) on an electrocardiogram (EKG).Aug 13, 2021
How is polymorphic VT treated?
Unstable polymorphic VT is treated with immediate defibrillation. The defibrillator may have difficulty recognizing the varying QRS complexes; therefore, synchronization of shocks may not occur.Dec 5, 2017
How is torsades de pointes diagnosed?
Torsades de pointes can sometimes be diagnosed by assessing a person's calcium, magnesium, and potassium levels. However, a diagnosis is usually made using an electrocardiogram or EKG.Jan 15, 2018
What is the name of the heart that beats faster than the atria?
Torsades de pointes is French for “twisting of points” and refers to when the heart’s two lower chambers or ventricles, beat faster than the upper chambers, which are known as the atria. Most cases of torsades de pointes resolve on their own without treatment.
What is a torsades de pointes?
Torsades de pointes is a form of tachycardia that shows up as a ribbon-like EKG pattern. Problems that occur with the heart’s rhythm are known as arrhythmias. When the heart beats faster than usual, as in a case of torsades de pointes, it is called tachycardia. Torsades de pointes is French for “twisting of points” and refers to when ...
What causes sudden and uncontrollable changes in a person's heart rate in response to stress or exercise?
LQTS causes sudden and uncontrollable changes or arrhythmias in a person’s heart rate in response to stress or exercise. These arrhythmias can be very dangerous. There is also a range of conditions and medications that cause or influence the development of torsades de pointes. These include:
What medications cause torsades de pointes?
There is also a range of conditions and medications that cause or influence the development of torsades de pointes. These include: 1 antiarrhythmic drugs, including quinidine, procainamide, and disopyramide 2 antipsychotics or tricyclic antidepressants 3 methadone, erythromycin, and ketoconazole 4 intracranial bleeding, or bleeding inside the skull 5 electrolyte disturbances, such as hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia 6 acute myocardial infarction, or a blockage in a coronary artery 7 kidney injury 8 liver failure 9 toxins from heavy metals or insecticides 10 anorexia 11 malnutrition
What is the shape of a wavy line on an EKG?
In cases of torsades de pointes, these lines will form a distinctive shape, much like a party ribbon that has been twisted.
What is an EKG?
Image credit: CardioNetworks, (2010, April 10) An EKG measures the electrical activity of the heart. Electrical signals control the heart, starting at the top in the atria, and working their way down into the ventricles. This process makes the heart pump blood around the body.
What is the treatment for LQTS?
For people with a congenital form of LQTS, treatment includes: beta-adrenergic antagonists, such as propranolol. beta-blockers. pacemakers. implantable cardioverter defibrillator in rare cases. For people with acquired torsades de pointes, specific treatment is not usually needed.
What is Torsade de Pointes?
Torsade de pointes is an uncommon and unique type of ventricular tachycardia. It differs from other forms of ventricular tachycardia by its morphological features, underlying mechanism, and modes of therapy. Recognizing torsade de pointes is of major clinical importance, as standard antiarrhythmic regimens might not only be ineffective in ...
What are the factors that increase the likelihood of developing torsade de pointes?
Predisposing factors known to increase the likelihood of developing torsade de pointes are: electrolyte imbalance (hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or both) and slow heart rate induced either by sinus bradycardia or heart block.
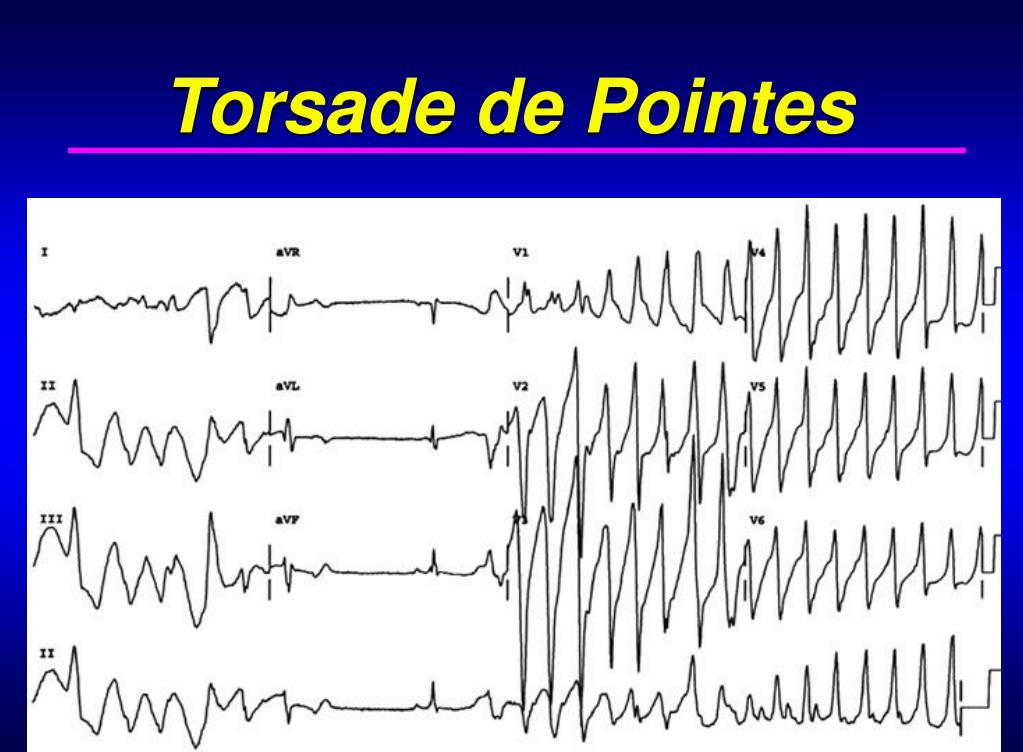
What is Torsades de Pointes?
Torsades de Pointes is a type of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia characterized by a gradual change in amplitude and twisting of the QRS complexes around an isoelectric line on the electrocardiogram.
Does isoproterenol help with TDP?
Isoproterenol has been shown to help prevent Torsades de Pointes in patients with prolonged QT that is refractory to magnesium. It is a non-selective beta agonist, which increases the heart rate and shortens the QT interval. This lowers the likelihood of an R-on-T phenomenon that can lead to TdP.
Is torsade de pointes hypotensive?
Today one needs to be aware that drug-induced long QT syndrome is common and hence, a thorough medication history must be obtained. Patients with torsade may be hypotensive, have a rapid pulse and have loss of consciousness. Evaluation. An electrocardiogram is paramount in the diagnosis of Torsades de Pointes.
Is Torsades de Pointes asymptomatic?
Around 50% of patients with Torsades de Pointes are asymptomatic. The most common symptoms reported are syncope, palpitations, and dizziness. However, cardiac death is the presenting symptom in up to 10% of patients. Patients with Jervell and Lange Nielsen syndrome may have a history of deafness.
Can you use overdrive pacing for torsades de pointes?
There are limited studies on the success of pacing for treatment of Torsades de Pointes; however, there are numerous case reports that show it is a viable option. Overdrive pacing can be used in the setting of both frequent runs of torsades and Torsades de Pointes that is refractory to magnesium.
What is TDP in cardiac?
TdP is an unusual type of tachycardia that sometimes resolves on its own, but can also worsen into a serious heart condition called ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation can lead to cardiac arrest, an event in which the heart suddenly stops. Cardiac arrest is usually fatal.
What medications cause TDP?
Tricyclic antidepressants may also put you at greater risk of TdP. Certain antiarrhythmia drugs, which are designed to restore a healthy heart rhythm for people with arrhythmias, are also associated with TdP. Some of the antiarrhythmic drugs of concern are: 1 quinidine 2 procainamide 3 disopyramide
What is an ICD in a pacemaker?
Another device that is sometimes part of a pacemaker, called an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), may also be helpful. An ICD monitors your heart rate. When an abnormal rhythm is detected, the device sends a small electrical charge to the heart with the goal of jolting it back into a normal rhythm.
What is torsades de pointes?
Torsades de pointes (French for “twisting of the points”) is one of several types of life-threatening heart rhythm disturbances. In the case of torsades de pointes (TdP), the heart’s two lower chambers, called the ventricles, beat faster than and out of sync with the upper chambers, called the atria.
What is the QT interval?
The electrical activity in the heart that occurs between the Q and T waves is called the QT interval. A QT interval is measured from the start of the Q wave through the end of the T wave. If this interval is abnormally long, you are at a higher risk for ventricular tachycardia and TdP. In a 2013 study.
What antiarrhythmics are associated with TDP?
Some of the antiarrhythmic drugs of concern are: quinidine. procainamide.
What to do if you have TDP?
If you are diagnosed with TdP, your doctor will check your potassium, magnesium, and calcium levels. If they are low, you will be given supplements to get your levels up into the healthy range. You will also undergo EKG monitoring until your heart returns to a normal rhythm .
What causes Torsades de Pointes?
There are several known Torsades de pointes causes. TdP can develop as a complication of QT syndrome, an uncommon condition where the gap between the Q and T wave in the heart is abnormally long. Your heartbeat operates by a series of electrical impulses. The Q and T waves are two of five electrical waves in the heart tracked by an ...
What is it called when your heart beats faster than normal?
Irregularities in the heart rhythm are called arrhythmias. A sudden increase in heart rate above the usual levels is called tachycardia. Torsades de pointes (TdP) is a rare form of tachycardia arrhythmia where the heart’s two lower chambers beat faster than, and out of sync with, the two upper chambers.
How to treat Torsades?
Other Torsades treatments include: 1 Addressing any underlying medical conditions that may be causing TdP. If you have acquired TdP, you may not receive treatment specific to it, as the condition typically dissipates naturally once the underlying condition is resolved. 2 If medication is causing the TdP, your doctor may prescribe alternative medications. 3 For a congenital form of TdP, your doctor may prescribe beta blockers, along with inserting a pacemaker or (in rare cases) an implantable cardioverter defibrillator. 4 If you do not experience syncope, ventricular tachycardia, or have a family history of the condition, you may be monitored by your doctor without any specific additional treatment.
What is an EKG?
An EKG measures the electrical currents in the heart and displays them as waves (wavy lines) on a screen. Doctors examine the waves for irregularities. These irregularities often take on distinctive shapes, as is the case for Torsades de pointes, which appears on the EKG screen as twisted ribbon. While arrhythmias are common, they can also be ...
What causes TDP in the heart?
TdP can also be triggered by certain medications, including antidepressants and anti-arrhythmia drugs. Additional risk factors for Torsades de pointes: Low potassium in the body. Low magnesium in the body.
What is the best treatment for TDP?
For a congenital form of TdP, your doctor may prescribe beta blockers, along with inserting a pacemaker or (in rare cases) an implantable cardioverter defibrillator.
Can Torsades de Pointes be fatal?
TdP can also be “sustained,” which means the TdP interrupts the normal functioning of the heart. Sustained symptoms require urgent medical attention as Torsades de pointes can escalate into serious and sometimes fatal heart complications.
What medications cause TDP?
Knowledge that TdP may occur in patients taking certain prescription drugs has been both a major liability and reason for removal of 14 medications from the marketplace. Forty nine drugs known to cause TdP and another 170 that are known to prolong QTc remain on the market because the drugs provide medical benefit and the risk of TdP can be managed and mitigated by instructions in the drug label. Examples of compounds linked to clinical observations of TdP include amiodarone, most fluoroquinolones, methadone, lithium, chloroquine, erythromycin, azithromycin, pimozide, and phenothiazines. The anti-emetic agent ondansetron may also increase the risk of developing TdP. It has also been shown as a side effect of certain anti-arrhythmic medications, such as sotalol, procainamide, quinidine, ibutilide, and dofetilide In one example, the gastrokinetic drug cisapride (Propulsid) was withdrawn from the US market in 2000 after it was linked to deaths caused by long QT syndrome-induced torsades de pointes. This effect can be directly linked to QT prolongation mediated predominantly by inhibition of the hERG channel and, in some cases, augmentation of the late sodium channel.
What is a TDP?
Torsades de pointes, torsade de pointes or torsades des pointes ( TdP) ( / tɔːˌsɑːd də ˈpwæ̃t /, French: [tɔʁsad də pwɛ̃t̪], translated as "twisting of peaks") is a specific type of abnormal heart rhythm that can lead to sudden cardiac death. It is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia that exhibits distinct characteristics on ...
What drugs can cause torsades de pointes?
Certain drugs and combinations of drugs resulting in drug interactions are common contributors to torsades de pointes risk. QT-prolonging medications such as clarithromycin, levofloxacin, or haloperidol, when taken concurrently with cytochrome P450 inhibitors, such as fluoxetine, cimetidine, or particular foods including grapefruit, ...
Why do Torsades occur?
Torsades occurs as both an inherited (linked to at least 17 genes) and as an acquired form caused most often by drugs and/or electrolyte disorders that cause excessive lengthening of the QT interval.
How to prevent torsades?
Treatment to prevent recurrent torsades includes infusion of magnesium sulphate, correction of electrolyte imbalances such as low blood potassium levels ( hypokalaemia ), and withdrawal of any medications that prolong the QT interval.
What are some examples of TDP?
Examples of compounds linked to clinical observations of TdP include amiodarone, most fluoroquinolones, methadone, lithium, chloroquine, erythromycin, azithromycin, pimozide, and phenothiazines. The anti-emetic agent ondansetron may also increase the risk of developing TdP.
What happens if you prolong your QT?
Prolongation of the QT interval can increase a person's risk of developing this abnormal heart rhythm, occurring in between 1% and 10% of patients who receive QT-prolonging antiarrhythmic drugs.
What is a torsade de pointes?
Torsades de Pointes. Torsades is defined as the combination of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia plus a prolonged QT-interval. Torsades can be caused by either congenital long-QT syndrome or acquired long-QT syndrome (due to electrolyte abnormalities and/or medications). The vast majority of torsades results from acquired long-QT syndrome, ...
What is polymorphic ventricular tachycardia?
Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Defined as ventricular tachycardia with varying QRS amplitude. This is commonly referred to as torsades de pointes, but it's actually not the same thing. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia may be caused by several etiologies (e.g. congenital QT prolongation, acquired QT prolongation, ischemia, ...
What is recurrent torsade?
Recurrent torsades may reflects inadequate magnesium dosing (e.g. patient is bolused with 2-4 grams, without an infusion). The first step when managing recurrent torsades is therefore to ensure that the patient has truly received an adequate dose of magnesium.
What happens if you break torsades?
If the EKG shows a prolonged QT-interval, the patient is diagnosed with torsades. If you simply break torsades but do nothing else, it is likely to recur. The following therapies will prevent recurrence of ventricular tachycardia in this situation:
Can magnesium cause tachycardia?
giving two-four grams magnesium and walking away). This will often cause recurrence of ventricular tachycardia in a few hours after the serum magnesium levels fall. Leaving patients on QT-prolonging meds (make sure to scour the medication list for any problematic drugs).
What is the best antiarrhythmic for torsades?
lidocaine. Lidocaine is the preferred anti-arrhythmic drug for torsades, although there isn't a ton of evidence supporting its use. Do not use amiodarone, procainamide, beta-blockers, or most other antiarrhythmics. Most of these will stretch out the QT interval even further!
Is Torsades easy to control?
Torsades is generally fairly easy to control with a combination of high-dose magnesium, heart rate augmentation, and occasionally some lidocaine. Failure to respond to these interventions suggests an alternative diagnosis (e.g. polymorphic VT due to ischemia or catecholaminergic ventricular tachycardia).