
What are symptoms of third nerve palsy?
- Sudden onset of a droopy eyelid and an inability to open the eye.
- If the eyelid is not completely closed the patient will have horizontal and vertical double vision.
- Very limited movement of the eye upwards, downwards or inwards, with the eye being deviated downwards and outwards.
- The pupil on the affected side may be enlarged. ...
Can sixth nerve Palsey be cured?
In some cases, sixth nerve palsy will disappear without treatment. If inflammation of the sixth nerve is suspected, medications called corticosteroids may be used. Until the nerve heals, wearing an eye patch can help with double vision. Prism spectacles can also help to realign eyesight.
What are the different treatments for cranial nerve palsy?
- Alternate an eye patch on each eye, to treat double vision
- Special prism glasses, to help align the eye
- Botulinum toxin, to temporarily paralyze the muscle on the other side of the eye and help eye alignment
- Surgery, if other treatment options have not worked
Can acupuncture help third nerve eye paralysis?
therapy, eye patching, botulinum toxin injections, and strabismus surgery. Acupuncture has also been reported as a therapeutic option for oculomotor nerve palsy as well as electroacupuncture combined with acupoint injection.10-12 Our patient presented with oculomotor nerve palsy that was
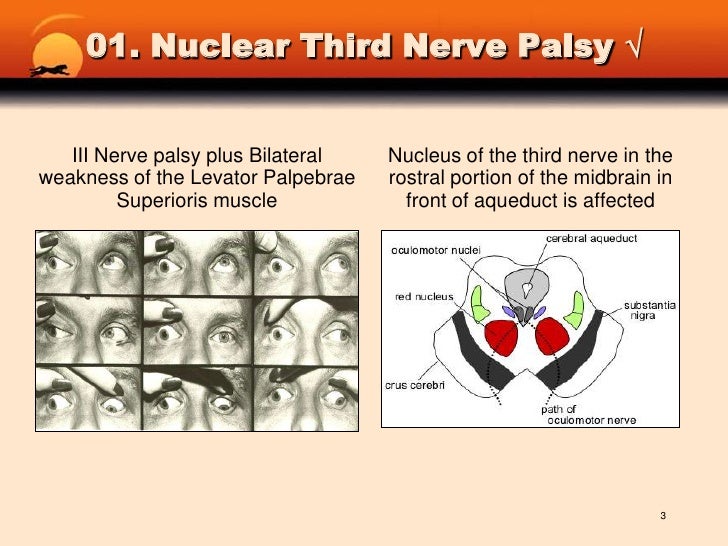
How long does it take for 3rd nerve palsy to heal?
Most patients with ischemic third-nerve palsy demonstrate improvement within 1 month and complete recovery in 3 months. In cases of diplopia, the affected eye can be occluded with the help of an eye patch or opaque contact lens.
How is 3rd nerve palsy treated?
Treatment can be both nonsurgical and surgical. As nonsurgical modalities are not of much help, surgery remains the main-stay of treatment. Surgical strategies are different for complete and partial third nerve palsy. Surgery for complete third nerve palsy may involve supra-maximal recession - resection of the recti.
What is the most common cause of third nerve palsy?
The most common causes of acquired third nerve palsy were:Presumed microvascular (42 percent)Trauma (12 percent)Compression from neoplasm (11 percent)Post-neurosurgery (10 percent)Compression from aneurysm (6 percent)
How is nerve palsy treated?
Minor palsies may be treated with a more conservative approach, including corticosteroid injections and splinting. This may help reduce swelling and inflammation from peripheral nerve paralysis. If this doesn't work or stops working, surgery might be necessary for a peripheral nerve paralysis.
Can third nerve palsy get worse?
The pupil is often affected when the cause is compression of the 3rd cranial nerve. When the pupil is not affected, the cause is often inadequate blood flow to the nerve. The disorder causing the palsy may worsen, resulting in a serious, life-threatening condition.
Is 3rd nerve palsy an emergency?
A third nerve palsy is an ocular emergency that requires an urgent referral. Paresis of the third nerve can occur anywhere along its course from the midbrain to the orbit. Underlying etiologies can be life threatening and immediate neuroimaging is warranted to ensure there is no intracranial mass or aneurysm.
Is 3rd nerve palsy a stroke?
An isolated third nerve palsy is a rare presentation of stroke. Historical features and risk factors can help distinguish the cause of third nerve palsy. A detailed neurological examination with attention to 'neighboring' signs is essential during the evaluation of individuals presenting with third nerve palsy.
How do you test for third nerve palsy?
Diagnosis of Third Cranial Nerve Palsy Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) of the brain is done to identify the cause. If the pupil is affected or if symptoms suggest a serious underlying disorder, brain MRI or CT is done immediately.
What are the signs and symptoms of complete third nerve palsy?
Third cranial nerve disorders can impair ocular motility, pupillary function, or both. Symptoms and signs include diplopia, ptosis, and paresis of eye adduction and of upward and downward gaze. If the pupil is affected, it is dilated, and light reflexes are impaired.
Can nerve palsy be cured?
If your condition is caused by viral illness or an unknown cause, it's likely to completely disappear. You may never fully recover, though, if your sixth nerve palsy is due to trauma. Some people may have permanent vision changes.
How do you fix facial nerve palsy?
Surgery to Correct Facial Paralysis Facial reanimation microsurgery -- sometimes referred to as "smile surgery" -- can restore your ability to smile spontaneously after a damaged facial nerve has caused facial paralysis. It can take two forms: muscle transfer or nerve transfer.
How long does it take for facial nerves to heal?
Within three months, most people have recovered full motion and function of their face. A delay in recovery is often accompanied by some form of abnormal facial function. But if facial paralysis from Bell's palsy doesn't get better, there are effective treatment options.
How long does it take for a third nerve palsy to heal?
Blood tests will also be carried out to investigate other causes of a third nerve palsy. Most (80%) microvascular third palsies will resolve within 3-6 months. However spontaneous recovery is less likely to occur if the third nerve palsy has been caused by an aneurysm.
What causes a third nerve to be damaged?
This is known as a microvascular palsy. Direct pressure on the third nerve caused by swelling of neighbouring blood vessels known as an aneurysm, or tumours can damage the third nerve.
What muscle is used to reduce divergent and vertical strabismus?
To restore an area of single vision. Weakening the lateral rectus muscle and strengthening the medial rectus muscle are the mainstays of surgery. Sometimes the superior oblique muscle can be moved to a new position to help centralise the eye.
Can a third nerve palsy be ruled out?
Once a serious cause for the third nerve palsy has been ruled out the patient can be seen in the eye clinic where specific tests will be carried out to measure the strabismus and assess the range of eye movements. Blood tests will also be carried out to investigate other causes of a third nerve palsy. Most (80%) microvascular third palsies will ...
What is the cause of third cranial nerve palsy?
Third cranial nerve palsy from ischemia in the nerve trunk is believed to result from insufficiency of the vasa nervosa or small vessels that supply the nerve. [ 30] Third cranial nerve palsy is most frequent in persons older than 60 years and in those with prominent or long-standing atherosclerotic risk factors, such as diabetes or hypertension.
How long does it take for a patient to go into remission from palsy?
Fortunately, nearly all patients undergo spontaneous remission of the palsy, usually within 6-8 weeks.
What is the treatment for ptosis?
Treatment during the symptomatic interval is directed at alleviating symptoms, mainly pain and diplopia. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the first-line treatment of choice for the pain. Diplopia is not a problem when ptosis occludes the involved eye.
Is diplopia a problem with ptosis?
Diplopia is not a problem when ptosis occludes the involved eye. When diplopia is from large-angle divergence of the visual axis, patching one eye is the only practical short-term solution. When the angle of deviation is smaller, fusion in primary position often can be achieved using horizontal or vertical prism or both.
Can diplopia patients drive?
Patients who are monocular from either ptosis or ocular patching and patients with diplopia should not climb on high places, drive a vehicle, or operate heavy machinery. Patients should avoid any other activity where limitation of peripheral vision poses danger.
What causes the sixth nerve to be affected?
Determine cause: The sixth nerve can be affected by many disorders of the nervous system. The cause must be determined. Many cases improve with time as long as the cause is not tumor or other mass. Surgery and glasses do not help.
What nerve is responsible for double vision?
Double vision: The fourth cranial nerve is the trochlear nerve. This coordinates the downward and inward rotation of the eye. Thus, a palsy leads to double vision particularly when looking downward. Patients have problems when going down stairs as this worsens the diploplia.
Can 3rd nerve palsy be acquired?
Third nerve palsy: can have multiple etiologies (congenital or acquired). Some causes do not need intervention and time may resolve the signs and symptoms. Some require intervention (such as those caused by mass effect). Ask your ophthalmologist what the cause of your 3rd nerve palsy is and he /she can give you treatment options.
How to tell if you have third cranial nerve palsy?
Symptoms of Third Cranial Nerve Palsy. The affected eye turns slightly outward and downward when the unaffected eye looks straight ahead, causing double vision. The affected eye may turn inward very slowly and may move only to the middle when looking inward. It cannot move up and down.
What nerves are involved in palsy?
Third Cranial Nerve (Oculomotor Nerve) Palsy 1 These palsies can occur when pressure is put on the nerve or the nerve does not get enough blood. 2 People have double vision when they look in a certain direction, the eyelid droops, and the pupil may be widened (dilated). 3 Doctors do a neurologic examination and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) of the brain. 4 Treatment depends on the cause.
Why does the 3rd cranial nerve droop?
It cannot move up and down. Because the 3rd cranial nerve also raises the eyelids and controls the pupils, the eyelid droops. The pupil may be normal or be widened (dilated) and may not narrow (constrict) in response to light. The pupil is often affected when the cause is compression of the nerve.
What is the term for paralysis of the brain?
Palsy refers to paralysis, which can range from partial to complete. Herniation occurs when the brain is forced downward through a small natural opening in the sheets of tissue that separate the brain into compartments.
What causes a herniated brain?
Herniation may result from bleeding (sometimes caused by a head injury ), a tumor, or another mass in the brain. Inadequate blood flow is more common and usually less serious. It typically results from. Diabetes.
Can palsy cause a headache?
The disorder causing the palsy may worsen, resulting in a serious, life-threatening condition. For example, a severe headache may occur suddenly, or a person may become increasingly drowsy or less responsive. In such cases, the cause may be a ruptured aneurysm, which then bleeds. People may go into a coma.
What causes third nerve palsy?
Acquired third nerve palsy can be associated with head injury, infection, vaccination, migraine, brain tumor, aneurysm, diabetes, or high blood pressure.
What nerve controls the position of the upper eyelid?
The third cranial nerv e also controls constriction of the pupil, the position of the upper eyelid, and the ability of the eye to focus. A complete third nerve palsy causes a completely closed eyelid and deviation of the eye outward and downward. The eye cannot move inward or up, and the pupil is typically enlarged and does not react normally ...
What nerve controls the movement of the eye?
The third cranial nerve controls the movement of four of the six eye muscles. These muscles move the eye inward, up and down, and they control torsion (rotating the eye downward and toward the ear on the same side). The third cranial nerve also controls constriction of the pupil, the position of the upper eyelid, and the ability of the eye to focus. A complete third nerve palsy causes a completely closed eyelid and deviation of the eye outward and downward. The eye cannot move inward or up, and the pupil is typically enlarged and does not react normally to light. A partial third nerve palsy affects, to varying degrees, any of the functions controlled by the third cranial nerve.
Can you use both eyes together with third nerve palsy?
The more severe the third nerve palsy, the more difficult it is to re-establish eye movements and single vision when the patient is attempting to use both eyes together . Residual diplopia can be quite bothersome for some patients.
Can a child with third nerve palsy have binocular vision?
Children with severe third nerve palsy often do not have binocular vision (simultaneous perception with both eyes), and stereopsis (three-dimensional vision) is often absent. An abnormal head posture may allow binocular vision. A partial palsy can be associated with the development of binocular vision.
The causes of acquired 3rd nerve palsy
Among all cases of ocular misalignment from cranial nerve palsies, third nerve palsies are the most worrisome, because a subset of these cases is caused by life-threatening aneurysms. There is significant disagreement, however, regarding the true incidence of third nerve palsies and the relative incidence of the various etiologies.
Pupil involvement
Ten patients (17 percent) with microvascular third nerve palsies had pupil involvement, while pupil involvement was seen in 16 patients (64 percent) with compressive third nerve palsies. "Our primary goal was to confirm incidence and etiologies of third nerve palsies," says Dr. Chen.
For more information
Fang C, et al. Incidence and etiologies of acquired third nerve palsy using a population-based method. JAMA Ophthalmology. 2017;135:23.
