
What causes thickening of the walls of the heart?
If the cause of the heart wall thickening is an aortic valve stenosis, the treatment is carried out depending on the severity of the disease. With a slight form of valve narrowing without symptoms, it may be sufficient if the affected person avoids physical exertion and …
What is the treatment for thickening of the heart?
Nov 16, 2020 · Alcohol septal ablation (nonsurgical procedure) – In this procedure, ethanol (a type of alcohol) is injected through a tube into the small artery that supplies blood to the area of heart muscle thickened by HCM. The alcohol causes these cells to die. The thickened tissue shrinks to a more normal size.
Can thickening of the heart muscle be reversed?
Thick heart muscle reduces blood flow to the aorta What is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)? Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a complex type of heart disease that affects your heart muscle. It can cause: Thickening of your heart muscle (especially the ventricles or lower heart chambers). Left ventricular stiffness. Mitral valve changes.
What causes thin heart walls?
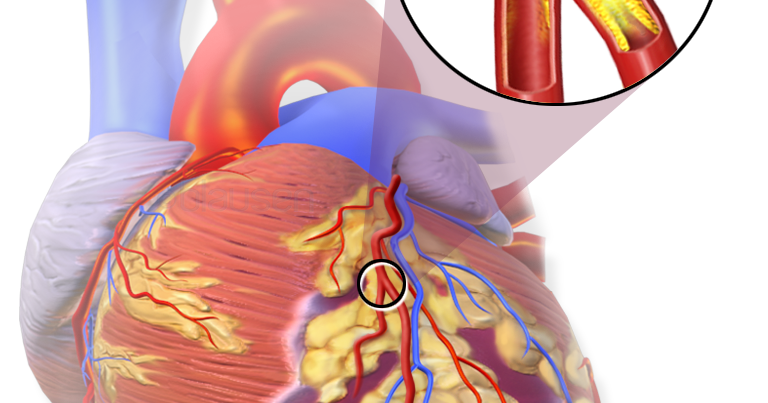
How serious is thickening of the heart?
The thickened heart muscle can eventually become too stiff to effectively fill the heart with blood. As a result, your heart can't pump enough blood to meet your body's needs. Sudden cardiac death. Rarely, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can cause heart-related sudden death in people of all ages.Jun 2, 2020
How is thickening of the heart treated?
Septal myectomy. During this surgical procedure, the surgeon removes a small amount of the thickened septal wall of the heart to widen the outflow tract (the path the blood takes) from the left ventricle to the aorta.Jun 14, 2021
Can thickening of the heart muscle be reversed?
There is no treatment which can reverse the changes of the heart muscle. Treatment aims to ease symptoms if they occur and to prevent complications. If you do not have any symptoms or you only have mild symptoms then you may not need any treatment.Jan 25, 2021
What causes the heart to thicken?
What is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is most often caused by abnormal genes in the heart muscle. These genes cause the walls of the heart chamber (left ventricle) to contract harder and become thicker than normal. The thickened walls become stiff.Nov 17, 2020
Can high blood pressure cause thickening of the heart?
High blood pressure means the pressure inside the blood vessels (called arteries) is too high. As the heart pumps against this pressure, it must work harder. Over time, this causes the heart muscle to thicken. Because there are often no symptoms with high blood pressure, people can have the problem without knowing it.
What is the life expectancy of someone with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Mean age at HCM death was 56 years (range, 7-87 years); 21 deaths (72%) were considered premature, occurring before age 75 years (Figure 1). The other 8 patients (28%) died of HCM at age 76 to 87 years and, therefore, achieved statistical life expectancy (Figure 1).
Does exercise help enlarged heart?
Exercise may reduce more than your waist size. It also may help shrink a thickened and enlarged heart. Regular exercise can be at least as beneficial as blood pressure medication when treating an enlarged heart.Sep 22, 2004
What medications should be avoided with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Agents to reduce pre- or afterload (such as nitrate, ACE inhibitors, nifedipine-type calcium antagonists) are contraindicated with HOCM due to possible aggravation of the outflow tract obstruction.Apr 1, 2011
Can you live a normal life with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Research has shown that with proper treatment and follow-ups, most people with HCM live a normal life. A database of 1,297 patients with HCM from the Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation identified that 2% of the patients can live past 90 years, and 69% of them were women.Mar 2, 2021
Can HCM be cured?
There is no cure for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).Jan 3, 2020
What causes a thickening of the heart wall?
A so-called “aortic valve stenosis” can also lead to thickening of the heart wall. In this heart valve disease, the outflow opening of the valve is narrowed, which means that it cannot open as far as it should. As a result, it is difficult to eject blood from the left ventricle and there is blood congestion that can reach the lungs. This leads to an increased pressure load on the wall of the heart, which the heart tries to balance by strengthening the muscles. Depending on the severity of the valve constriction, those affected often suffer from shortness of breath and tiredness even with slight exertion; dizziness, chest pain or feelings of oppression (angina pectoris), a pronounced feeling of weakness and fainting are also possible.
Why do athletes have enlarged hearts?
Since the heart is a muscle, it can - like any other muscle - grow through training. Competitive athletes often have an enlarged heart, which is therefore also referred to as the "athlete heart" or "athlete heart". The change is caused by the thickening of the muscles as a result of regular exercise - however, in contrast to the pathological enlargement of the heart, this is usually not a cause for concern. Instead, it is a natural response to the training stimulus that is, in principle, reversible. Whether someone develops an athlete's heart or not depends on the training time and intensity, and obviously there must also be a certain genetic disposition.
Why is heart disease so late?
Due to the reduced pumping capacity due to the pathological thickening of the heart wall, there is typically a decrease in performance at the beginning, especially during physical exertion. Likewise, the disease can initially be completely symptom-free, which is why it is often discovered relatively late.
Can angina cause shortness of breath?
Likewise, the disease can initially be completely symptom-free, which is why it is often discovered relatively late. From a certain level, sufferers often suffer from short ness of breath or shortness of breath, chest pain (angina pectoris), irregular heartbeat, dizziness or even fainting spells. Likewise, the resulting weakness of the heart is often shown by chronic fatigue, thick legs (edema) and frequent urination. If the disease has already progressed, the symptoms mentioned not only occur when you are exerting yourself, but also at rest, which makes physical activity almost impossible. In addition, there is an increased risk of a heart attack.
What is the best medicine to slow down your heart rate?
Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and digoxin are examples of medicines that slow the heart rate. Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers also are used to lower blood pressure. Keep your heart beating with a normal rhythm. These medicines, called antiarrhythmics, help prevent arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats).
What are the medicines that help prevent arrhythmias?
These medicines, called antiarrhythmics, help prevent arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats). Balance electrolytes in your body. Electrolytes are minerals that help maintain fluid levels and the acid-base balance in your body. Electrolytes also help muscle and nerve tissues work properly.
What is a heart transplant?
Heart Transplant – In a heart transplant surgery, a person’s diseased heart is replaced with a healthy donor heart. A heart transplant is a last resort for people who have end-stage heart failure. (“End-stage” means that all other treatment options have been explored, without success.)
How to lower blood pressure?
Choose and prepare foods with little salt (sodium). Too much salt can raise your risk of high blood pressure. Studies show that following a Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating plan can lower blood pressure. Choose foods and beverages that are low in added sugar. Avoid drinking alcohol.
What are the goals of cardiomyopathy?
When treating cardiomyopathy, objectives include: Stopping the disease from getting worse. Managing any conditions that cause or contribute to the disease. Reducing complications and the risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) Controlling symptoms so that you can live as normally as possible.
Can you prevent cardiomyopathy?
You cannot prevent inherited types of cardiomyopathy. But you can take steps to lower your risk for conditions that may lead to (or complicate) cardiomyopathy, such coronary heart disease, high blood pressure and heart attack . Cardiomyopathy can be precipitated by an underlying disease or condition.
Does dilated cardiomyopathy go away?
Sometimes, dilated cardiomyopathy that comes on suddenly may even go away on its own. In other instances, treatment is needed. Treatment hinges on a few factors: the type of cardiomyopathy, the severity of your symptoms and complications as well as your age and overall health.
What is the name of the disease that affects the heart muscle?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a complex type of heart disease that affects the heart muscle. It causes thickening of the heart muscle (especially the ventricles, or lower heart chambers), left ventricular stiffness, mitral valve changes and cellular changes. Thickening of the heart muscle (myocardium) occurs most commonly at the septum.
What is the term for the abnormal heart rhythm?
Through a microscope, the cells appear disorganized and irregular (called “disarray”) instead of being organized and parallel. This disarray may cause changes in the electrical signals traveling through the lower chambers of the heart and lead to ventricular arrhythmia (a type of abnormal heart rhythm).
What is the HOCM?
This type of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may be called hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM). HCM also may cause thickening in other parts of the heart muscle, such as the bottom of the heart called the apex, right ventricle, or throughout the entire left ventricle. Normal Heart. Stiffness in the left ventricle occurs as a result ...
What is HCM screening?
Screening. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a medical condition that may be passed on from generation to generation. It is important for you or your family members to have screening if you have a first-degree relative with the condition. First-degree relatives are your parents, siblings and children.
How many people are affected by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy affects an estimated 600,000 to 1.5 million Americans, or one in 500 people. It is more prevalent than multiple sclerosis, which affects one in 700 people.
What causes a narrowing of the septum?
The thickened septum may cause a narrowing that can block or reduce the blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta - a condition called “outflow tract obstruction.”.
What causes blood to go back into the left atrium?
The obstruction is the result of the mitral valve striking the septum. When this occurs, the mitral valve frequently leaks, causing the blood to go back into the left atrium. Cellular changes, or changes in the cells of the heart muscle, occur with HCM.
What is it called when the heart wall is thicker than normal?
In most people with hypertrop hic cardiomyopathy , the muscular wall (septum) between the two bottom chambers of the heart (ventricles) becomes thicker than normal. As a result, the thicker wall may block blood flow out of the heart. This is called obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. If there's no significant blocking of blood flow, ...
What is it called when the heart is not pumping blood?
If there's no significant blocking of blood flow, the condition is called nonobstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. However, the heart's main pumping chamber (left ventricle) may become stiff. This makes it hard for the heart to relax and reduces the amount of blood the ventricle can hold and send to the body with each heartbeat.
What causes a person to die suddenly?
As a result, your heart can't pump enough blood to meet your body's needs. Sudden cardiac death. Rarely, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can cause heart-related sudden death in people of all ages.
How is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy passed down?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is usually passed down through families (inherited). If you have a parent with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, you have a 50% chance of having the genetic mutation for the disease.
What are the complications of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
But complications of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can include: Atrial fibrillation. Thickened heart muscle, as well as the abnormal structure of heart cells, can cause changes in the heart's electrical system, resulting in fast or irregular heartbeats.
How to know if you have HCM?
It's important to get a prompt, accurate diagnosis and appropriate care. See your doctor if you have a family history of HCM or any symptoms associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Call 911 or your local emergency number if you have any of the following symptoms for more than a few minutes: Rapid or irregular heartbeat.
What are the symptoms of a symtom?
Call 911 or your local emergency number if you have any of the following symptoms for more than a few minutes: 1 Rapid or irregular heartbeat 2 Difficulty breathing 3 Chest pain
Diagnosis
Treatment
- The goal of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment is to relieve symptoms and prevent sudden cardiac death in people at high risk. Your specific treatment depends on the severity of your symptoms. Together, you and your doctor will discuss the most appropriate treatment for your condition.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- Being diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can cause a range of difficult emotions. Like many people with this condition, you may experience feelings of grief, fear and anger. These responses are appropriate to the lifestyle changes that come with your diagnosis. To cope with your condition: 1. Reduce your stress.Find ways to reduce your stress. 2. Get support.Get suppor…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You may be referred to a doctor trained in diagnosing and treating heart conditions (cardiologist). Here's some information to help you prepare for your appointment.
Overview
Symptoms
- Signs and symptoms of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may include one or more of the following: 1. Chest pain, especially during exercise 2. Fainting, especially during or just after exercise or exertion 3. Heart murmur, which a doctor might detect while listening to your heart 4. Sensation of rapid, fluttering or pounding heartbeats (palpitations) 5. Shortness of breath, especially during e…
Causes
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is usually caused by abnormal genes (gene mutations) that cause the heart muscle to grow abnormally thick. In most people with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the muscular wall (septum) between the two bottom chambers of the heart (ventricles) becomes thicker than normal. As a result, the thicker wall may block blood flow out of the heart. This is ca…
Risk Factors
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is usually passed down through families (inherited). If you have a parent with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, you have a 50% chance of having the genetic mutation for the disease. Parents, children or siblings of a person with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy should ask their doctors about screening for the disease.
Complications
- Many people with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) don't have significant health problems. But complications of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can include: 1. Atrial fibrillation.Thickened heart muscle, as well as the abnormal structure of heart cells, can cause changes in the heart's electrical system, resulting in fast or irregular heartbeats. Atrial fibrillation can also increase you…
Prevention
- There is no known prevention for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. But it's important to identify the condition as early as possible to guide treatment and prevent complications. If you have a first-degree relative — a parent, sibling or child — with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, doctors may recommend genetic testing to screen for the condition. However, not everyone with HCMhas a c…