Medication
Treatment for Stage 3 Melanoma: Stage III melanoma treatment varies greatly depending on whether the melanoma is completely resectable. When melanoma is completely resected, it has been removed entirely surgically. Melanoma that is unresectable cannot be removed completely through surgery alone.
Procedures
The average life expectancy for a stage IV melanoma patient is 6-22 months. How common is melanoma in 30s? The risk of melanoma increases as people age. The average age of people when it is diagnosed is 65. But melanoma is not uncommon even among those younger than 30.
Therapy
Yes: Stage 3 breast cancer is curable, but in addition to an operation most women will need chemotherapy and radiation therapy for the best chance of cure.... How dangerous is Stage 1 invasive DCIS cancer?
Nutrition
Stage III colon cancer is treatable and curable, although at a lower rate than earlier stages. Although it has spread to the lymph nodes, surgery can often cure between 30 and 50 percent of stage III colon cancer cases. The overall survival rate at five years for stage III colon cancer with treatment is between 43% and 83%.
Can Stage 3 melanoma be cured?
What is the life expectancy with melanoma Stage 4?
Is cancer curable in Stage 3?
Is colon cancer curable at Stage 3?
Can you be cured of stage 3 melanoma?
Stage III melanoma has multiple treatment options and can include surgery (including sentinel lymph node biopsy and possibly completion lymph node dissection), neo-adjuvant therapy, adjuvant therapy, radiation therapy, and clinical trials.
Is Stage 3 melanoma advanced?
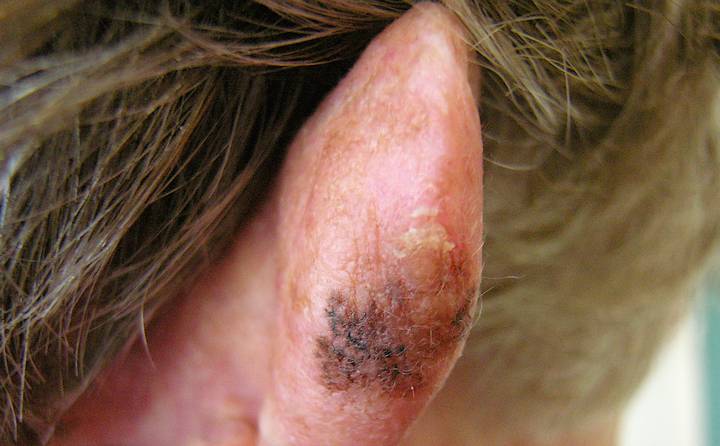
Stage 3 melanoma, also written as stage III, is an advanced form of skin cancer. Unlike in stages 1 and 2, the cancer in stage 3 melanoma has spread from the skin cells to the lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small tissues located in your neck, under your arms, and in other areas throughout the body.
How effective is immunotherapy for Stage 3 melanoma?
In a phase III study , scientists compared these treatments in people with unresectable stage 3 or stage 4 melanoma. They found that 55 percent of those who received Keytruda survived for at least 2 years. In comparison, 43 percent of those treated with Yervoy survived for 2 years or more.
What is the 10 year survival rate for stage 3 melanoma?
According to the IMDDP data, on which the survival calculations of the AJCCv8 classification of melanoma are based, the 5- and 10-year MSS rates in stage IIIA were 93% and 88%, and in stage IIIB, 83% and 77%.
Do you need chemo for stage 3 melanoma?
The typical treatment approach for stage III melanoma is a wide excision surgery to remove the primary tumor, as well as a dissection to remove the lymph node(s). Following surgery, further treatment may include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapies, or radiation therapy.
Do you feel sick with stage 3 melanoma?
hard or swollen lymph nodes. hard lump on your skin. unexplained pain. feeling very tired or unwell.
How serious is Stage 3C melanoma?
Stage 3C. Stage 3C melanoma can mean there is no sign of melanoma on the skin, and one of the following: The melanoma is in 2 to 3 lymph nodes. The melanoma is in 1 or more lymph nodes and has spread to the skin or lymphatic vessels near the melanoma.
Which stages of melanoma has the best prognosis?
Melanoma can be treated most effectively in its early stages when it is still confined to the top layer of the skin (epidermis). The more deeply a melanoma grows into the lower layer of the skin (dermis), the greater the risk that it could spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
What is the new treatment for melanoma?
In a large clinical trial, people with advanced melanoma treated with nivolumab (Opdivo) and a new drug called relatlimab—which targets a protein called LAG-3—lived longer without their cancer getting worse than those treated only with nivolumab. Both nivolumab and relatlimab are immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Is melanoma a death sentence?
Metastatic melanoma was once almost a death sentence, with a median survival of less than a year. Now, some patients are living for years, with a few out at more than 10 years.
How long does it take for melanoma to spread to organs?
How fast does melanoma spread and grow to local lymph nodes and other organs? “Melanoma can grow extremely quickly and can become life-threatening in as little as six weeks,” noted Dr. Duncanson. “If left untreated, melanoma begins to spread, advancing its stage and worsening the prognosis.”
Can you live 50 years after melanoma?
Generally for people with melanoma in England: almost all people (almost 100%) will survive their melanoma for 1 year or more after they are diagnosed. around 90 out of every 100 people (around 90%) will survive their melanoma for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
What is Stage III Melanoma?
Stage III melanomas are tumors that have spread to regional lymph nodes or have developed in-transit deposits of disease, but there is no evidence of distant metastasis. Stage III melanoma is regional melanoma, meaning it has spread beyond the primary tumor (local) to the closest lymph nodes, but not to distant sites.
SINGLE AGENT IMMUNOTHERAPIES
Purpose: Keytruda is a humanized monoclonal antibody. It is designed to block a cellular target known as PD-1, which restricts the body’s immune system from attacking melanoma cells.
Combination Therapies
Purpose: Mekinist in combination with Tafinlar blocks a cellular pathway to inhibit the growth of melanoma metastases.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
Copyright © 2014-2021 - AIM at Melanoma Foundation. All rights reserved. Website by RED ZEPHYR DESIGN
What is the treatment for melanomas that can't be removed?
Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy . The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
How to treat melanoma in the brain?
Melanoma that comes back in the brain can be hard to treat. Single tumors can sometimes be removed by surgery. Radiation therapy to the brain (stereotactic radiosurgery or whole brain radiation therapy) may help as well. Systemic treatments ( immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemo) might also be tried.
What to do if SLNB found cancer?
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant (additional) treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs (if the melanoma has a BRAF gene mutation) might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back.
What is stage 0 melanoma?
It is usually treated by surgery (wide excision) to remove the melanoma and a small margin of normal skin around it. The removed sample is then sent to a lab to be looked at with a microscope.
What is the best treatment for cancer at the edges of the sample?
Some doctors may consider the use of imiquimod cream (Zyclara) or radiation therapy instead of surgery, although not all doctors agree with this.
Does melanoma spread to lymph nodes?
The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Because the melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , many doctors recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) as well. This is an option that you and your doctor should discuss.
Where does melanoma come back?
Almost any organ can be affected. Most often, the melanoma will come back in the lungs, bones, liver, or brain. Treatment for these recurrences is generally the same as for stage IV melanoma (see above).
How to treat early stage melanoma?
Treatment for early-stage melanomas usually includes surgery to remove the melanoma. A very thin melanoma may be removed entirely during the biopsy and require no further treatment. Otherwise, your surgeon will remove the cancer as well as a border of normal skin and a layer of tissue beneath the skin.
How to assign stage to melanoma?
To assign a stage to your melanoma, your doctor will: Determine the thickness. The thickness of a melanoma is determined by carefully examining the melanoma under a microscope and measuring it with a special tool. The thickness of a melanoma helps doctors decide on a treatment plan.
How to treat melanoma that has spread beyond the skin?
Treating melanomas that have spread beyond the skin. If melanoma has spread beyond the skin, treatment options may include: Surgery to remove affected lymph nodes. If melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes, your surgeon may remove the affected nodes.
What is the procedure to remove melanoma from lymph nodes?
If there's a risk that the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, your doctor may recommend a procedure known as a sentinel node biopsy. During a sentinel node biopsy, a dye is injected in the area where your melanoma was removed. The dye flows to the nearby lymph nodes.
How to cope with melanoma?
Here are some ideas to help you cope: Learn enough about melanoma to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor about your cancer, including your treatment options and, if you like, your prognosis. As you learn more about cancer, you may become more confident in making treatment decisions. Keep friends and family close.
What is the stage of melanoma?
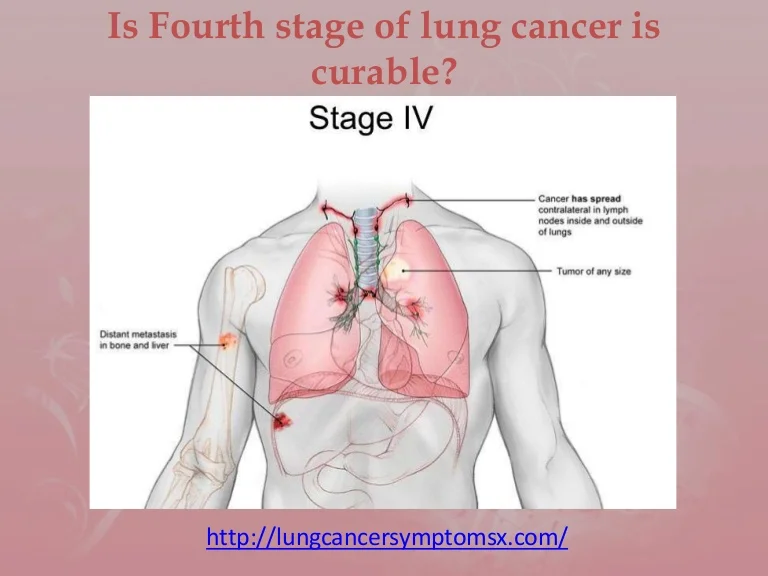
Melanoma is staged using the Roman numerals 0 through IV. At stage 0 and stage I, a melanoma is small and has a very successful treatment rate. But the higher the numeral, the lower the chances of a full recovery. By stage IV, the cancer has spread beyond your skin to other organs, such as your lungs or liver.
How does thickness affect melanoma?
The thickness of a melanoma helps doctors decide on a treatment plan. In general, the thicker the tumor, the more serious the disease. Thinner melanomas may only require surgery to remove the cancer and some normal tissue around it.
What is stage 3 melanoma?
Stage 3 Melanoma. Stage III melanoma, also known as regional melanoma, has metastasized (spread) to nearby lymph nodes, lymph vessels, or skin. Lymph nodes are an important part of the lymphatic system, which is a vast network of tissues and organs that helps rid the body of waste, toxins, and other unwanted materials.
What is the follow up for stage 3 melanoma?
Follow-Up Care for Stage 3 Melanoma: After achieving No Evidence of Disease (NED) following treatment for Stage III melanoma, you should conduct monthly self exams of your skin and lymph nodes and have an annual, full-body skin exam performed by a trained dermatologist for the rest of your life.
How many lymph nodes does melanoma spread to?
The melanoma has spread to four or more lymph nodes detected by biopsy of the sentinel lymph node; OR. The melanoma has spread to four or more lymph nodes, at least one of which was detected clinically, the presence of any number of nodes that are clumped together; OR.
How does melanoma spread?
The melanoma has spread to one lymph node detected clinically or by biopsy of the sentinel lymph node; AND the melanoma has spread to very small areas of skin near the primary tumor, sometimes called “satellite tumors” or has begun to travel through lymph channels toward lymph nodes but has not yet reached them; OR.
What is a high risk melanoma?
High-risk melanoma usually is defined as melanoma that is deeper or thicker (more than 4 millimeters thick) at the primary site or involves nearby lymph nodes.
What system is involved in melanoma?
The lymphatic system also helps support the immune system by transporting infection-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Stage III melanoma is divided into four subgroups based on ulceration of the primary tumor and the extent of growth into the lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and nearby skin:
How thick is a melanoma?
The melanoma has not yet spread to distant sites. OR. The melanoma tumor is more than 1.0 millimeter and less than 2.0 millimeters thick (the size of a new crayon point) with broken skin (ulceration) or more than 2.0 to 4.0 millimeters thick without broken skin (ulceration) when looked at under a microscope; AND:
Stages IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC
In order to better describe these variable factors, stage III melanoma is further divided into the following three categories:
Treatments for Stage III Melanoma
The typical treatment approach for stage III melanoma is a wide excision surgery to remove the primary tumor, as well as a dissection to remove the lymph node (s). Following surgery, further treatment may include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapies, or radiation therapy.
What stage of melanoma is metastatic?
Metastatic melanoma. Once it spreads, or metastasizes, the disease is known as metastatic melanoma. This type of melanoma may typically occur during stage III or stage IV. Common sites for metastases include the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones and brain.
How do you know if you have metastatic melanoma?
Metastatic melanoma symptoms and signs may include: Fatigue. Swollen or painful lymph nodes. Weight loss. Loss of appetite. Trouble breathing or a cough that doesn’t go away. Bone pain. Headaches.
How does immunotherapy help with melanoma?
The newest, most common type of immunotherapy used in patients with melanoma is called checkpoint inhibitors. Checkpoint inhibitors work by blocking a checkpoint in the immune system, thus allowing immune system T cells to better kill melanoma cells that have been left behind after surgery. The keys to turning on this immune process are the checkpoint proteins CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4), PD-1 (programmed death receptor-1), and PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1), with PD in the last 2 proteins an abbreviation for “programmed death.”
What is the staging system for melanoma?
Melanoma staging is based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system, which uses 3 key pieces of information to stage a cancer: the extent of the T umor thickness (abbreviated T ), whether the melanoma has spread to local lymph N odes ( N ), and whether the cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes or other organs, or M etastasized ( M ). Combining these 3 metrics, the TNM system is then used to classify the stage of a cancer.
How are immunotherapies administered?
Immunotherapies are administered in an infusion center by a healthcare team. Targeted therapies such as BRAF and MEK inhibitors, however, are taken orally. Although oral medications are understandably preferred by patients, the absence of daily medical supervision means that the responsibility for taking these medications rests with the patient and his or her caregivers. With BRAF/MEK targeted therapies used in patients with melanoma, dabrafenib is taken twice daily, whereas trametinib is taken only once daily. 26,27 Dosing calendars, pillboxes, smartphone alarms, and other types of reminders may help patients and their caregivers follow dosing schedules.
What are the biomarkers of melanoma?
For patients with melanoma, the biomarkers that physicians look for include mutations in the genes BRAF (pronounced bee-raff), NRAS (pronounced en-rass), NF-1 (pronounced en-eff-1), and KIT (pronounced like the word “kit”).
How is cancer staged?
Cancer staging is a process that evaluates the amount of cancer that is present. Staging allows physicians to categorize cancers from different patients into groups that are likely to have similar features, therapeutic options, and response to treatment. Melanoma is staged by looking at the biopsy sample and reporting the depth of the tumor, whether tissue breakdown (ulceration) is present, and whether the tumor has spread to other parts of the body (metastasized). Melanoma can range from stage 0 (also known as melanoma in situ) to stage IV, with higher numbers indicating that the tumor has penetrated more deeply in the skin and spread farther in the body (see Figure 2 ). Some stages are further subdivided by using capital letters (A, B, C, and D), with the later letters in the alphabet representing a higher stage of cancer.
How many people will die from melanoma in 2020?
Nevertheless, it has been estimated that 6850 individuals in the United States will die of melanoma in 2020. 2. Although anyone can develop melanoma, it is generally more common among individuals born with light skin, light-colored hair, and blue or green eyes.
What is the role of melanoma cells?
Melanocytes are specialized cells that produce the pigment (melanin) that gives our skin and hair their color. High amounts of sun exposure or exposure to other sources of ultraviolet (UV) light (such as tanning beds) can play a role in the development of melanoma.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment