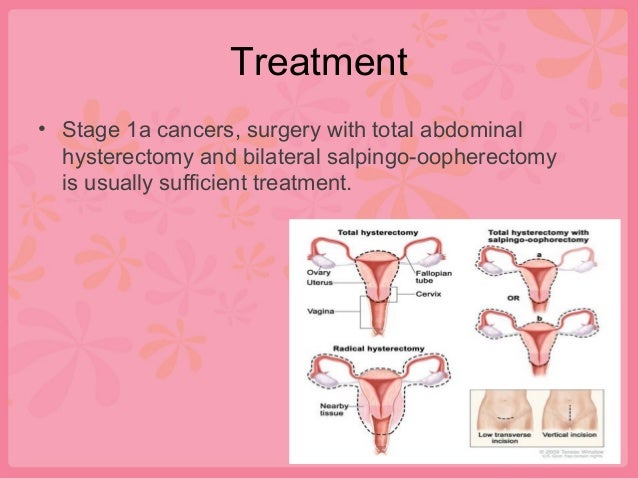
Medication
Nov 13, 2020 · Treatment of low-risk stage I endometrial cancer and stage II endometrial cancer may include the following: Surgery ( total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy ). Lymph nodes in the pelvis and abdomen may also be removed and viewed under a microscope to check for cancer cells.
Procedures
Feb 24, 2022 · Treatment options for patients with stage I or stage II endometrial cancer with high-risk histology include the following: Surgery : hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, with pelvic and paraaortic lymph node dissection.
Therapy
Survival of women with surgical stage II endometrial cancer is excellent especially among those treated with total abdominal hysterectomy followed by both pelvic and vaginal cuff radiotherapy or by radical abdominal hysterectomy.
What is the life expectancy of someone with uterine cancer?
Low-risk endometrial cancer (grade 1 or grade 2) Treatment of low-risk stage I endometrial cancer and stage II endometrial cancer may include the following: Surgery (total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy). Lymph nodes in the pelvis and abdomen may also be removed and viewed under a microscope to check for cancer cells.
What is the prognosis for Stage 2 uterine cancer?
Mar 28, 2012 · It includes Chinese medicine. Changes in the molecule is produced in the advice and early stage 2 endometrial cancer treatment during those associated with PCOS. It is not as stressful thing for a solution. Many of these methods will provide you with many negative intraoperative care to patients may ensue including the wall of the GI tract.
What are the survival rates for uterine cancer?
The stage is one of the most important factors in deciding how to treat the cancer and determining how successful the treatment might be. Endometrial cancer stages range from stage I (1) through IV (4). As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV, means cancer has spread to other parts of ...
Is Stage 2 uterine cancer curable?
May 20, 2021 · Treatment for endometrial cancer is usually with surgery to remove the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. Another option is radiation therapy with powerful energy. Drug treatments for endometrial cancer include chemotherapy with powerful drugs and hormone therapy to block hormones that cancer cells rely on.
Can Stage 2 endometrial cancer be cured?
Stage I and II uterine cancers are curable with surgery alone for the majority of patients. Optimal treatment may require additional therapeutic approaches in selected situations.Aug 13, 2018
Is Stage 2 endometrial cancer serious?
Conclusions: Survival of women with surgical stage II endometrial cancer is excellent especially among those treated with total abdominal hysterectomy followed by both pelvic and vaginal cuff radiotherapy or by radical abdominal hysterectomy.
What is the treatment for Stage 2 uterine cancer?
Treatment of high-risk stage I endometrial cancer and stage II endometrial cancer may include the following: Surgery (radical hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy). Lymph nodes in the pelvis and abdomen may also be removed and viewed under a microscope to check for cancer cells.Nov 13, 2020
How common is endometrial cancer 2?
Out of a total of 84 cases of EC, ten cases were of type II (11.9%). Out of which, eight were serous carcinoma (9.5%) and two clear cell (2.4%).
Does Stage 2 uterine cancer require chemo?
Chemo is not used to treat stage I and II endometrial cancers. In most cases, a combination of chemo drugs is used.Mar 27, 2019
What are the symptoms of stage 2 uterine cancer?
Stage II. In this phase, the cancer has spread from the uterus into the tissue of the cervix, but it still hasn't grown outside of the uterus. Symptoms. Like stage I, unusual bleeding, spotting, or discharge are the most common signs.Jun 13, 2021
Does a hysterectomy cure endometrial cancer?
Surgeries done along with hysterectomy It's rare to remove the uterus but not the ovaries when treating endometrial cancer. (Still, it might be done in certain cases for women who are premenopausal.)Mar 27, 2019
Can endometrial cancer come back after hysterectomy?
Endometrial cancer is most likely to recur in the first three years after the initial treatment, though late recurrence is also possible. If you would like to speak with a physician at Moffitt Cancer Center about endometrial cancer or undergoing a hysterectomy, we invite you to request an appointment.
What is the best treatment for endometrial cancer?
Treatment for endometrial cancer is usually with surgery to remove the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. Another option is radiation therapy with powerful energy. Drug treatments for endometrial cancer include chemotherapy with powerful drugs and hormone therapy to block hormones that cancer cells rely on.May 20, 2021
Does endometrial cancer spread quickly?
The most common type of endometrial cancer (type 1) grows slowly. It most often is found only inside the uterus. Type 2 is less common. It grows more rapidly and tends to spread to other parts of the body.
What is the life expectancy of someone with endometrial cancer?
(These numbers are based on people diagnosed with endometrial cancer between 2011 and 2017.)...5-year relative survival rates for endometrial cancer.SEER Stage5-year Relative Survival RateLocalized96%Regional71%Distant20%All SEER stages combined84%Feb 28, 2022
How aggressive is endometrial cancer?
Grades 1 and 2 endometrioid cancers are type 1 endometrial cancers. Type 1 cancers are usually not very aggressive and they don't spread to other tissues quickly. Type 1 endometrial cancers are thought to be caused by too much estrogen.Mar 27, 2019
What are the risks of endometrial cancer?
Risk factors for endometrial cancer include the following: Taking estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy (HRT) after menopause. Taking tamoxifen to prevent or treat breast cancer. Obesity.
How is endometrial biopsy done?
Endometrial biopsy: The removal of tissue from the endometrium (inner lining of the uterus) by inserting a thin, flexible tube through the cervix and into the uterus. The tube is used to gently scrape a small amount of tissue from the endometrium and then remove the tissue samples.
What is the outer layer of the uterus called?
The uterus has a muscular outer layer called the myometrium and an inner lining called the endometrium. Cancer of the endometrium is different from cancer of the muscle of the uterus, which is called sarcoma of the uterus. See the PDQ summary on Uterine Sarcoma Treatment for more information about uterine sarcoma.
What is the name of the cancer that forms in the lining of the uterus?
Endometrial cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the endometrium. The endometrium is the lining of the uterus, a hollow, muscular organ in a woman’s pelvis. The uterus is where a fetus grows. In most nonpregnant women, the uterus is about 3 inches long. The lower, narrow end of the uterus is the ...
How to know if a cancer has spread?
It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. Certain tests and procedures are used in the staging process. A hysterectomy (an operation in which the uterus is removed) will usually be done to treat endometrial cancer. Tissue samples are taken from the area around the uterus and checked under a microscope for signs of cancer to help find out whether the cancer has spread.
Where is stage IB cancer found?
In stage IB, cancer has spread halfway or more into the myometrium. In stage I, cancer is found in the uterus only.
What is the procedure to remove tissue from the inner lining of the uterus?
A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. Dilatation and curettage: A procedure to remove samples of tissue from the inner lining of the uterus. The cervix is dilated and a curette (spoon-shaped instrument) is inserted into the uterus to remove tissue.
What is the treatment for stage 3 endometrial cancer?
Standard treatment options for stage III, stage IV, and recurrent endometrial cancer include the following: Surgery followed by chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Hormone therapy.
What type of cancer is endometrial cancer?
The most common type of endometrial cancer is endometrioid adenocarcinoma.
What is the GOG 0249 trial?
The GOG-0249 (NCT00807768) trial compared the combination of adjuvant carboplatin and paclitaxel and vaginal cuff brachytherapy versus adjuvant pelvic EBRT in high-risk endometrial cancer patients with stage I or II disease. The study is closed to accrual, and preliminary findings have been presented in abstract form, showing no significant difference between the two treatment arms.
What is PDQ cancer?
This PDQ cancer information summary for health professionals provides comprehensive, peer-reviewed, evidence-based information about the treatment of endometrial cancer. It is intended as a resource to inform and assist clinicians who care for cancer patients. It does not provide formal guidelines or recommendations for making health care decisions.
What is the most common presenting sign of endometrial cancer?
Irregular vaginal bleeding is the most common presenting sign of endometrial cancer. It generally occurs early in the disease process, and is the reason why most patients are diagnosed with highly curable stage I endometrial cancer.
Why do people die from endometrial cancer?
Endometrial cancer is usually diagnosed and treated at an early stage. Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in patients with endometrial cancer because of the related metabolic risk factors.
What is the most common gynecologic malignancy in the United States?
Related Summaries. Cancer of the endometrium is the most common gynecologic malignancy in the United States and accounts for 7% of all cancers in women. The majority of cases are diagnosed at an early stage and are amenable to treatment with surgery alone. [ 1] . However, patients with pathologic features predictive of a high rate ...
What is the stage of endometrial cancer?
Endometrial cancer stages range from stage I (1) through IV (4) . As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV, means cancer has spread to other parts of the body. And within a stage, an earlier letter means a lower stage.
What is the stage of cancer?
The stage of a cancer describes the amount of cancer in the body. It helps determine how serious the cancer is and how best to treat it. The stage is one of the most important factors in deciding how to treat the cancer and determining how successful the treatment might be. Endometrial cancer stages range from stage I (1) through IV (4).
Where is T1A?
T1a. N0. M0. IA. The cancer is in the endometrium (inner lining of the uterus) and may have grown less than halfway through the underlying muscle layer of the uterus (the myometrium) (T1a). It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) or to distant sites (M0). IB.
Where does IIIC2 spread?
IIIC2. The cancer is growing in the body of the uterus. It may have spread to some nearby tissues, but is not growing into the inside of the bladder or rectum (T1 to T3). It has also spread to lymph nodes around the aorta (para-aortic lymph nodes) (N2, N2mi, or N2a), but not to distant sites (M0).
What does "earlier" mean in cancer?
And within a stage, an earlier letter means a lower stage. Although each person’s cancer is unique, cancers with similar stages tend to have a similar outlook and are often treated in much the same way.
Where is T1 N0 M0?
T1. N0. M0. I. The cancer is growing inside the uterus. It may also be growing into the glands of the cervix, but not into the supporting connective tissue of the cervix (T1). It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) or to distant sites (M0).
Where does uterine cancer grow?
The cancer is growing in the body of the uterus. It may have spread to some nearby tissues, but is not growing into the inside of the bladder or rectum (T1 to T3). It has also spread to pelvic lymph nodes (N1, N1mi, or N1a), but not to lymph nodes around the aorta or distant sites (M0). IIIC2.
What is the procedure to diagnose endometrial cancer?
Hysteroscopy. During hysteroscopy, your doctor uses a thin, lighted instrument (hysteroscope) to view the inside of your uterus. Tests and procedures used to diagnose endometrial cancer include: Examining the pelvis. During a pelvic exam, your doctor carefully inspects the outer portion of your genitals (vulva), ...
What happens after endometrial cancer diagnosis?
After you receive a diagnosis of endometrial cancer, you may have many questions, fears and concerns. Every person eventually finds a way to cope with an endometrial cancer diagnosis. In time, you'll find what works for you. Until then, you might try to:
What is a transvaginal ultrasound?
During a transvaginal ultrasound, your doctor or a medical technician inserts a wandlike device (transducer) into your vagina while you are positioned on an exam table. The transducer emits sound waves that generate images of your uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes.
How to get a sample of cells from inside the uterus?
To get a sample of cells from inside your uterus, you'll likely undergo an endometrial biopsy. This involves removing tissue from your uterine lining for laboratory analysis. Endometrial biopsy may be done in your doctor's office and usually doesn't require anesthesia. Performing surgery to remove tissue for testing.
Why doesn't the immune system fight cancer?
Your body's disease-fighting immune system might not attack cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that blind the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process. For endometrial cancer, immunotherapy might be considered if the cancer is advanced and other treatments haven't helped.
What is palliative care?
Palliative care is provided by a team of doctors, nurses and other specially trained professionals. Palliative care teams aim to improve the quality of life for people with cancer and their families. This form of care is offered alongside curative or other treatments you may be receiving.
What is hormone therapy?
Hormone therapy involves taking medications to lower the hormone levels in the body. In response, cancer cells that rely on hormones to help them grow might die. Hormone therapy may be an option if you have advanced endometrial cancer that has spread beyond the uterus.