
Full Answer
What causes pain in the L5 S1?
May 15, 2019 · What is the treatment for severe Foraminal stenosis L5 S1? Conservative treatment includes medication, rehabilitation, and spinal nerve block. Surgery should be considered when the pathology is refractory to conservative treatment and requires direct decompression of the exiting nerve root, including the dorsal root ganglia.
What is L5 on S1?
Treatment options include both conservative and surgical approaches. Conservative treatment includes medication, rehabilitation, and spinal nerve block. Surgery should be considered when the pathology is refractory to conservative treatment and requires direct decompression of the exiting nerve root, including the dorsal root ganglia.
What is a mild hypertrophic facet change at L5 S1?
Before we go into those, however, let’s talk about the types of surgeries that may relieve severe foraminal stenosis. Common surgical procedures for foraminal stenosis include: Foraminotomy : A minimally invasive procedure in which your surgeon removes a tiny piece of bone or soft tissue that is causing compression on a nerve.
What does offset of L5 over S1 means?
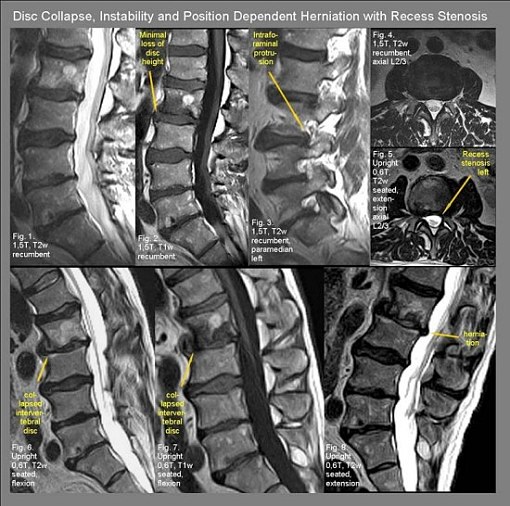
What is lumbar foraminal stenosis?
Lumbar foraminal stenosis, the hidden stenosis including at L5/S1. In patients with lower back and leg pain, lumbar foraminal stenosis (LFS) is one of the most important pathologies, especially for predominant radicular symptoms. LFS pathology can develop as a result of progressing spinal degeneration and is characterized by exacerbation ...
What is LFS in the spine?
LFS pathology can develop as a result of progressing spinal degeneration and is characterized by exacerbation with foraminal narrowing ca …. In patients with lower back and leg pain, lumbar foraminal stenosis (LFS) is one of the most important pathologies, especially for predominant radicular symptoms. LFS pathology can develop as ...
What is LFS pathology?
LFS pathology can develop as a result of progressing spinal degeneration and is characterized by exacerbation with foraminal narrowing caused by lumbar extension (Kemp's sign). However, there is a lack of critical clinical findings for LFS pathology.
What causes L5 radiculopathy?
The lumbosacral junction can cause L5 radiculopathy with greater incidence than other lumbar levels as a result of anatomical and epidemiological factors, which should be better addressed when treating clinical lower back pain.
What is conservative treatment?
Conservative treatment includes medication, rehabilitation, and spinal nerve block. Surgery should be considered when the pathology is refractory to conservative treatment and requires direct decompression of the exiting nerve root, including the dorsal root ganglia.
What is the most common form of foraminal stenosis?
Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis: When foraminal stenosis occurs in the lower back, it affects your lower body. The symptoms can spread throughout your leg, buttocks, and even the feet. Lumbar sten osis is the most common form of foraminal stenosis.
What tests are done to check for spinal stenosis?
During this exam, your doctor will check your reflexes, muscle strength, and any pain associated with movements in the body. Diagnostic tests will help your doctor rule out any other spinal conditions. These tests can include imaging techniques such as x-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. Foraminal Stenosis Treatment.
What is the procedure called when a nerve is compressed?
Foraminotomy: A minimally invasive procedure in which your surgeon removes a tiny piece of bone or soft tissue that is causing compression on a nerve. This enlarges the openings of the foramina. As a result, the nerve has more space and is no longer pinched.
