What causes foraminal stenosis and how is it treated?
Before we go into those, however, let’s talk about the types of surgeries that may relieve severe foraminal stenosis. Common surgical procedures for foraminal stenosis include: Foraminotomy : A minimally invasive procedure in which your surgeon removes a tiny piece of bone or soft tissue that is causing compression on a nerve.
How serious is foraminal stenosis?
A compressed nerve can be very painful and limit mobility. At that point, more advanced foraminal stenosis treatment, such as a surgical procedure, may be needed. Types of surgery for treating foraminal stenosis Traditionally, surgery to address foraminal narrowing has involved a highly invasive open neck or back procedure.
Does foraminal stenosis get better?
What is the treatment for severe Foraminal stenosis? Nonsurgical treatments, such as physical therapy, pain medication, activity modification, and/or epidural injections are typically tried first for cervical foraminal stenosis. What does impingement of …
Can medications be used to treat canal stenosis?
Treatment of severe foraminal narrowing generally starts out conservatively, with a variety of nonsurgical treatments that are designed to manage pain and improve mobility. Pain medication, epidural injections, vertebral manipulation, physical therapy and other conservative treatments have all been shown to be effective for many patients.
What can be done for severe foraminal stenosis?
How Is Neural Foraminal Stenosis Treated?Medicines. This may include prescription or over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), prescription pain medicines, muscle relaxers, and steroids.Correcting your posture. ... Modifying your activities. ... Physical therapy. ... Braces. ... Surgery.May 17, 2021
How serious is severe foraminal stenosis?
For some people, the condition doesn't cause any symptoms and doesn't require treatment. However, severe cases of neural foraminal stenosis can cause paralysis. If symptoms do occur, they typically happen on the side of the body where the nerve root becomes pinched.
Does severe foraminal stenosis require surgery?
Depending on the cause and extent of the cervical foraminal stenosis, multiple surgical options may be considered. When cervical foraminal stenosis is severe or causing problems at multiple spinal levels, more than one surgical technique may need to be performed during the procedure.
What happens if severe foraminal stenosis is left untreated?
Not every case of foraminal stenosis will result in even temporary paralysis. This symptom is most likely to occur if the foraminal stenosis is undiagnosed and/or untreated. If this condition is ignored or not detected, then afflicted nerves may die, which can lead to loss of bodily function.Aug 9, 2018
Will foraminal stenosis get worse?
While cervical foraminal stenosis tends to progress over time, the symptoms may not necessarily worsen. Most people can manage cervical foraminal stenosis symptoms with nonsurgical treatments, such as physical therapy, medication, rest, cervical traction, and minimally invasive injection therapies.
How fast does foraminal stenosis progress?
Symptoms generally develop slowly over time (again, most common with patients of age 50+), and they may come and go. Unfortunately, these symptoms can eventually become chronic and quite debilitating.
How successful is foraminal stenosis surgery?
Foraminotomy via the Wiltse approach is considered a gold standard for stenosis of the foraminal or extraforaminal area, and the success rate is reported to be approximately 80%. However, the Wiltse approach may lead to incomplete surgery due to limited visualization.Nov 21, 2018
What kind of doctor treats foraminal stenosis?
Preparing for your appointment If your primary care doctor thinks you have spinal stenosis, he or she may refer you to a doctor who specializes in disorders of the nervous system (neurologist). Depending on the severity of your symptoms, you may also need to see a spinal surgeon (neurosurgeon, orthopedic surgeon).Oct 24, 2020
How long is foraminal stenosis surgery?
Generally, this visit takes less than two hours and you will not need anyone to drive you.May 23, 2016
Is foraminal stenosis surgery painful?
Least Invasive Procedures for Foraminal Stenosis Treatment A laminectomy and/or facetectomy are performed to release the pressure on the spinal cord. Unfortunately, this technique is invasive and leads to significant post-operative pain and lengthy recovery.
Is foraminal stenosis a disability?
As the foramen close in, it can lead to those nerves becoming pinched. You can receive disability benefits for foraminal stenosis if you have supporting medical documentation.
Can foraminal stenosis be reversed?
Unfortunately, foraminal narrowing can't be reversed. While exercise and weight management can keep you healthy and pain-free for many years, your condition may progress to the point where pain and symptoms are affecting your quality of life and ability to perform daily tasks.
What is the term for the narrowing of the spinal canal?
Severe foraminal narrowing, or foraminal stenosis, occurs when one or more of the foraminal canals — the openings next to the vertebrae that allow the nerve roots to exit the spinal canal — narrow. This is usually related to a degenerative spine condition, like a herniated disc or spinal osteoarthritis, which can displace spinal anatomy ...
Can foraminal stenosis cause pain?
Because severe foraminal stenosis is often caused by age or degeneration of the spine, the symptoms can often worsen over time ...
What causes neural foraminal stenosis?
Most causes of neural foraminal stenosis are degenerative, which means they happen over time as you age. It can also be caused by injuries. Some causes of foraminal stenosis include: Osteoarthritis, which can cause bone spurs to grow into the foramen. Paget's disease, which also causes bone overgrowth.
How to tell if you have cervical foraminal stenosis?
Cervical foraminal stenosis. Symptoms can include: 1 Neck pain 2 Balance problems 3 Loss of bowel or bladder control 4 Trouble using your hands 5 Numbness or tingling in the hand, arm, foot, or leg 6 Weakness in the hand, arm, leg, or foot#N#
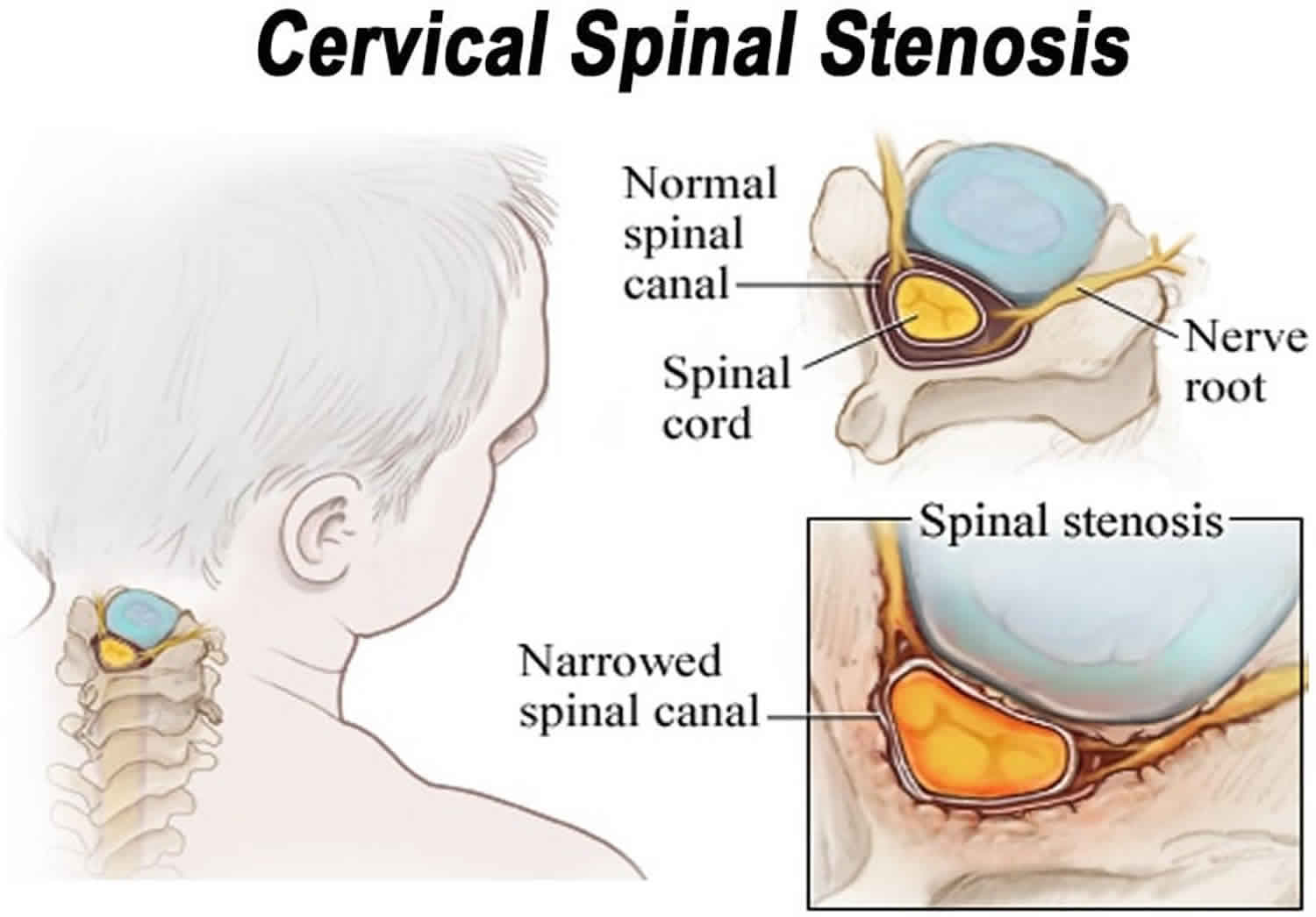
What is spinal stenosis?
It's a type of spinal stenosis. Your spinal cord is a bundle of nerves that runs down the center of your spine. Nerves branch off of your spinal cord and connect to your arms, legs, and other body parts. Cervical foraminal stenosis. This occurs in your cervical vertebrae, which are the spinal bones in your neck.
How many vertebrae are there in the spine?
Your spine is made up of 33 vertebrae. Each one has openings to let nerves that branch off the spinal cord pass through to other parts of the body. When these openings, called neural foramen, narrow or get blocked, they can press on your nerves. This is called neural foraminal stenosis.
Where does foraminal narrowing occur?
This occurs in your cervical vertebrae, which are the spinal bones in your neck. Your neck is one of the most mobile parts of your spine and has to support your head, so it's a common place for foraminal narrowing to occur. Thoracic foraminal stenosis. This is the least likely type of foraminal stenosis.
Where is the thoracic spine located?
Your thoracic spine is located in your upper back area. Thoracic foraminal stenosis can affect your shoulders and ribcage. . Lumbar foraminal stenosis. This is another common type of foraminal stenosis. The lumbar spine is located in your lower back. This is another very mobile area of your spine.
What is the pain in the lower back?
Weakness in the leg or foot. Pain in the lower back that may come and go. Numbness or tingling in the buttock, leg, or foot.
What to do if stenosis is pinching nerve root?
The type of surgery will depend on the location of the stenosis and what’s causing it. If a herniated disk is pinching your nerve root, then surgery to remove the bulging disk may be the solution .
What is the term for a spinal stenosis?
Foraminal stenosis is a specific type of spinal stenosis. Nerves pass though the foramen from your spinal cord out to the rest of your body. When the foramen close in, the nerve roots passing through them can be pinched. A pinched nerve can lead to radiculopathy — or pain, numbness, and weakness in the part of the body the nerve serves.
Why does my arm feel numb?
Your arm and hand may feel weak and numb with “pins and needles.”. Thoracic stenosis develops when the foramen in the upper portion of your back narrow. Pinched nerve roots in this part of your back can cause pain and numbness that wrap around to the front of your body.
How to prevent back pain?
Using good posture and technique when sitting, playing sports, exercising, and lifting heavy objects can also help prevent injury to your back. Injuries can lead to stenosis and pinched nerves. Keep reading to learn about the symptoms, treatment options, and more.
Can pinched nerves come and go?
But not everyone with foraminal stenosis will experience symptoms. Some people may have symptoms that come and go.
What is the term for a numbness in the lower back?
This can be felt as pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in the buttock, leg, and sometimes the foot. Sciatica is a term you may have heard for this type of pain.
Can arthritis cause stenosis?
Arthritis and the wear and tear of daily living often lead to changes in your spine that narrow the foramen. But injury can cause stenosis as well, especially in younger people. For example, one cause of foraminal stenosis is a bulging or herniated disk.
What is the best medication for spinal stenosis?
Pain relievers. Pain medications such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), naproxen (Aleve, others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) may be used temporarily to ease the discomfort of spinal stenosis. They are typically recommended for a short time only, as there's little evidence of benefit from long-term use. Antidepressants.
How to diagnose spinal stenosis?
To diagnose spinal stenosis, your doctor may ask you about signs and symptoms, discuss your medical history, and conduct a physical examination. He or she may order several imaging tests to help pinpoint the cause of your signs and symptoms.
Where is laminoplasty performed?
While shown here on the neck, it can also be performed in the lumbar spine. Laminoplasty is performed only on the vertebrae in the neck (cervical spine). It opens up the space within the spinal canal by creating a hinge on the lamina. Metal hardware bridges the gap in the opened section of the spine.
Can spinal stenosis cause muscle weakness?
It's common for people who have spinal stenosis to become less active, in an effort to reduce pain. But that can lead to muscle weakness, which can result in more pain. A physical therapist can teach you exercises that may help:
What is the purpose of MRI?
An MRI uses a powerful magnet and radio waves to produce cross-sectional images of your spine. The test can detect damage to your disks and ligaments, as well as the presence of tumors. Most important, it can show where the nerves in the spinal cord are being pressured. CT or CT myelogram.
How to reduce back pain?
If you're overweight or obese, your doctor may recommend that you lose weight. Losing excess weight can reduce pain by taking some stress off the back, particularly the lumbar portion of the spine.
Can corticosteroid injections help with stenosis?
Your nerve roots may become irritated and swollen at the spots where they are being pinched. While injecting a steroid medication (corticosteroid) into the space around impingement won't fix the stenosis, it can help reduce the inflammation and relieve some of the pain.