
Treatment of SCID
- Bone marrow transplant. The most common treatment for SCID is an allogeneic bone marrow transplant, which will introduce normal infection-fighting cells into your child’s body.
- Enzyme therapy. ...
- IVIG. ...
- Gene therapy. ...
Is there a cure for SCIDs?
Most children with SCID are treated with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, or HSCT, also known as a bone marrow transplantation. In this treatment, hematopoietic stem cells are taken from a donor. The hematopoietic stem cells that are …
What are the treatments for X-linked SCID?
Most children with SCID are treated with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, or HSCT, also known as a bone marrow transplantation. In this treatment, hematopoietic stem cells are taken from a donor. The hematopoietic stem cells that are …
What is the treatment for SCID in newborns?
Hematopoietic (blood-forming) stem cell transplantation is the standard treatment for infants with SCID. Ideally, infants with SCID receive stem cells from a sibling who is a close tissue match. Transplants from matched siblings lead to the best restoration of immune function, but if a matched sibling is not available, infants may receive stem cells from a parent or an unrelated …
What is the prognosis of SCID?
Treatment of SCID Bone marrow transplant. The most common treatment for SCID is an allogeneic bone marrow transplant, which will introduce... Enzyme therapy. For children with ADA SCID, enzyme replacement therapy may be used to repair the defective adenosine... IVIG. Immunoglobulin replacement (also ...
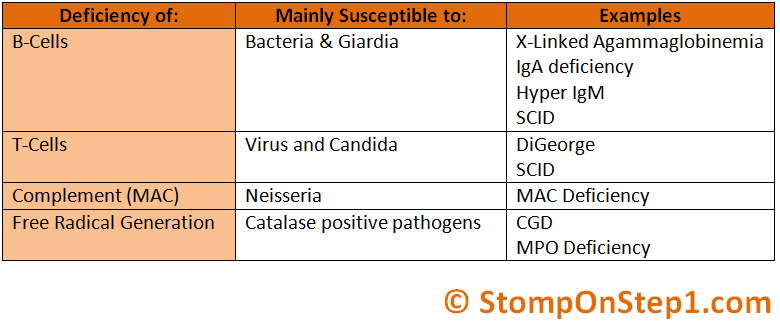
What is the treatment for ADA-SCID?
Prior to these treatments, a child with SCID will begin the treatment process by taking antibiotics, antivirals and antifungals to ward off infection. The child will also receive immunoglobulin therapy, or Ig, an infusion of antibodies designed ...
What is hematopoietic stem cell transplant?
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Most children with SCID are treated with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, or HSCT, also known as a bone marrow transplantation. In this treatment, hematopoietic stem cells are taken from a donor. The hematopoietic stem cells that are taken from the donor are infused into a child with SCID.
What is the best treatment for SCID?
Studies also have shown that gene therapy can be an effective treatment for some types of SCID, including X-linked SCID.
What are the symptoms of SCID?
Symptoms of SCID occur in infancy and include serious or life-threatening infections, especially viral infections, which may result in pneumonia and chronic diarrhea. Candida (yeast) infections of the mouth and diaper area ...
What is a severe immunodeficiency?
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a group of rare disorders caused by mutations in different genes involved in the development and function of infection-fighting immune cells. Infants with SCID appear healthy at birth but are highly susceptible to severe infections.
What is the cause of SCID?
The best-known form of autosomal recessive SCID is caused by adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency , in which infants lack the ADA enzyme necessary for T-cell survival.
What is the test for Candida?
Candida (yeast) infections of the mouth and diaper area and pneumonia caused by the fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii also are common. The SCID newborn screening test, originally developed at NIH, measures T cell receptor excision circles (TRECs), a byproduct of T-cell development.
What is the best treatment for SCID?
The most common treatment for SCID is an allogeneic bone marrow transplant , which will introduce normal infection-fighting cells into your child’s body. Allogeneic transplants use stem cells from a relative or an unrelated donor from the National Marrow Donor Program.
When is SCID treated?
Children diagnosed with SCID in infancy, treated in the first three months of life, and those who receive a bone marrow transplant from the donor-matched sibling have the highest success rates. Children who receive parent or non-relative transplants also have generally good outcomes if diagnosed and treated promptly
What causes thrush in the throat?
Persistent thrush in the mouth or throat. Repeated cases of pneumonia or bronchitis. Repeated bouts of diarrhea. Deep infections that affect the entire lung or liver. Failure to grow normally or gain weight appropriately. Family history of immunodeficiency or infant deaths from infections.
What is combined immunodeficiency?
Severe combined immunodeficiency is a group of hereditary disorders linked to defects of at least 17 different genes. These defects affect lymphocytes, a type of white blood cells, that become T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. T cells are the helper cells in the blood stream that encourage other cells in the body to respond ...
What was Audrey's diagnosis?
Audrey was diagnosed with severe combined immunodeficiency at birth and underwent a bone marrow transplant at CHOP when she was just 4 weeks old. Following an abnormal newborn screen, blood testing to measure the number of the T, B and NK cells is needed to see if the newborn actually has SCID.
What do B cells do?
B cells produce antibodies that attack foreign substances such as viruses and bacteria. NK cells, like their name implies, are typically involved in the direct killing of diseased cells. In SCID, the immune-protecting skills of both T cells and B cells are affected.
When does SCID become apparent?
Symptoms of SCID usually become apparent within the first year of life and generally include repeated infections — both common and serious — that do not to respond to medications in a typical manner.
What is the most common type of SCID?
The most common type of SCID is called X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (XSCID).
What is a severe combined immunodeficiency?
Severe combined immunodeficiencies (SCID) are inherited immune system disorders characterized by abnormalities with responses of both T cells and B cells ( specific types of white blood cells needed for immune system function). Common signs and symptoms include an increased susceptibility to infections including ear infections;
What is a registry in research?
A registry supports research by collecting of information about patients that share something in common, such as being diagnosed with Severe combined immunodeficiency. The type of data collected can vary from registry to registry and is based on the goals and purpose of that registry.
What is compassionate allowance?
The Social Security Administration has included this condition in their Compassionate Allowances Initiative. This initiative speeds up the processing of disability claims for applicants with certain medical conditions that cause severe disability. More information about Compassionate Allowances and applying for Social Security disability is available online.
Why is research important?
Research helps us better understand diseases and can lead to advances in diagnosis and treatment. This section provides resources to help you learn about medical research and ways to get involved.
What is the HPO database?
People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. This information comes from a database called the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) . The HPO collects information on symptoms that have been described in medical resources.
Can you inherit SCID?
SCID can be inherited in an X-linked recessive or autosomal recessive manner depending on the genetic cause of the condition. X-linked SCID is the most common type of SCID and is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner.
