How to treat cystitis naturally at home?
1. Heat / Cold Therapy...
2. Baking Soda...
3. Quercetin...
4. Turmeric...
5. Diet...
6. Colloidal Silver...
7. Pumpkin Seeds...
8. Probiotics...
Learn More...How to get rid of interstitial cystitis naturally?
Treatment - Cystitis
- Things you can try yourself. Some people believe drinking cranberry juice or using products that lowers the acidity of their urine (such as sodium bicarbonate or potassium citrate) reduces their ...
- Antibiotics. In some cases, a GP may prescribe a course of antibiotics. ...
- If cystitis keeps coming back. ...
What is the most effective treatment of interstitial cystitis?
- Boil two tablespoons of chamomile with 3 raw garlic cloves in a liter of water for 20 minutes. ...
- Drink three glasses of cranberry juice a day because this fruit has a substance that doesn’t allow bacteria to stick onto the urinary tract walls and to be eliminated by ...
- Make a stew with 4 onions and a liter of water. ...
What are the symptoms of radiation treatment?
Surgical options include:
- Fulguration. This minimally invasive method involves insertion of instruments through the urethra to burn off ulcers that may be present with interstitial cystitis.
- Resection. This is another minimally invasive method that involves insertion of instruments through the urethra to cut around any ulcers.
- Bladder augmentation. ...

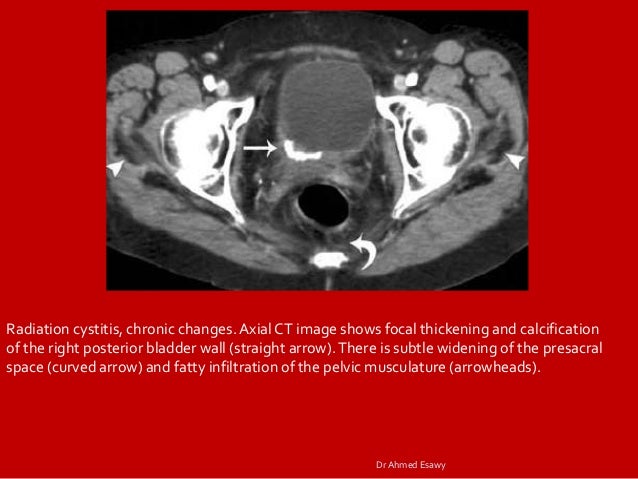
Does radiation cystitis go away?
Some symptoms of radiation cystitis may go away after radiation therapy has ended, but others may continue over time.
What is the fastest way to get rid of cystitis?
Antibiotics have been shown to be fast and effective in treating uncomplicated cystitis. The pain and burning usually get better within one to three days and then go away completely a short time later. But sometimes antibiotics aren't needed at all.
Is radiation cystitis progressive?
Radiation cystitis is an uncontrollable and unpreventable chronic alteration of the bladder due to any form of radiation therapy. This may occur at any point during follow-up (immediate to 20 years) and is progressive destruction of the bladder, ureter, and urethra.
How long does late radiation cystitis last?
This can range from a minimum of three months to a period of two to three years or more.
What is the best medicine for cystitis?
Antihistamines, such as loratadine (Claritin, others), which may reduce urinary urgency and frequency and relieve other symptoms. Pentosan polysulfate sodium (Elmiron), which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration specifically for treating interstitial cystitis.
What is the best antibiotic for cystitis?
Guidelines recommend three options for first-line treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis: fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (in regions where the prevalence of Escherichia coli resistance does not exceed 20 percent).
How do you stop the bleeding from radiation cystitis?
Intravesical astringents are medications put in the bladder that cause irritation and swelling around blood vessels to stop bleeding. These medications include silver nitrate, alum, phenol, and formalin.
How do you prevent radiation cystitis?
Other preventive measures. Data from a small pilot study of 20 patients undergoing radiotherapy for gynaecological malignancies indicate that prophylactic intravesical installations with 40 ml chondroitin sulphate 0.2% solution reduce the symptoms of acute radiation cystitis.
How do you diagnose radiation cystitis?
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION The diagnosis of hemorrhagic cystitis (HC) is based on a typical clinical presentation including hematuria and lower urinary tract symptoms, after excluding other potential causes of the signs/symptoms (such as urinary tract infection, bladder tumor, local tumor extension, and urolithiasis) via a ...
Why does it burn when I pee after radiation?
Bladder inflammation (cystitis) Inflammation of the bladder (radiation induced cystitis) is when your bladder is irritated and becomes swollen because of radiotherapy. Bladder inflammation can cause the following symptoms: a burning feeling or pain when you pass urine.
How many hyperbaric treatments are needed for radiation cystitis?
A retrospective review of 60 patients who received an average of 33 hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) treatments showed that 80% of patients had total or partial resolution of hematuria. When HBOT was started within six months of hematuria onset, 96% had total or partial resolution of symptoms.
What is the best treatment for radiation cystitis?
Analgesics help with pain management in radiation cystitis. Surgeries like bladder augmentation which increases bladder volume and urinary diversion to channel urine through an alternate pathway. Surgical removal of the bladder known as a cystectomy is reserved as the last option in radiation cystitis.
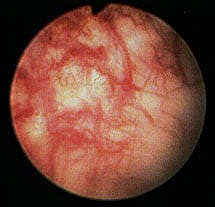
What is radiation cystitis?
Radiation cystitis is condition where the bladder become inflamed because of exposure to radiation. It is rare for most people to be exposed to radiation for other than medical reasons. The bladder itself may be targeted in radiation therapy (radiotherapy) or the other pelvic organs may be irradiated for cancer at these sites with ...
What is the cause of urinary cystitis?
Most cases of cystitis are due to urinary tract infections where the causative microbes enter through the urethra and ascend the urinary tract to the bladder.
What is radiation treatment?
Radiation treatment is used for the treatment of cancer. When directed at the pelvis, it can cause radiation cystitis. Radiation is used to destroy cancerous cells. Ideally the target area is only irradiated but the surrounding tissue is often affected as well.
What is radiation therapy used for?
Picture from Wikimedia Commons. In pelvic tumors, radiation therapy is used for treating cancers of the bladder, colon and rectum. In men, it is also used for prostate cancer and among women for uterine, ovarian and vaginal cancers.
Can radiation cystitis be diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Radiation Cystitis. There are a number of investigations that can be conducted to diagnose radiation cystitis. The patient’s history of radiation treatment is one of the most important indicators that the presenting urinary tract symptoms are a result of radiation cystitis.
Is radiation cystitis a symptomatic disease?
The prognosis for radiation cystitis is dependent on a multitude of factors. Most cases are acute and only symptomatic treatment is necessary. It resolves spontaneously but may recur. Chronic cystitis is more difficult to manage and can be persistent or episodic.
How to treat bacterial cystitis?
Treating bacterial cystitis. Antibiotics are the first line of treatment for cystitis caused by bacteria. Which drugs are used and for how long depend on your overall health and the bacteria found in your urine. First-time infection. Symptoms often improve significantly within a day or so of antibiotic treatment.
How to treat cystitis in the bladder?
Take a sitz bath. Soak in a bathtub of warm water (sitz bath) for 15 to 20 minutes to help relieve pain or discomfort. For recurrent bladder infections, work with your doctor to develop a strategy to reduce recurrences and the discomfort that cystitis can cause.
What is a cystoscope?
Cystoscopy allows your doctor to view your lower urinary tract to look for abnormalities, such as a bladder stone. Surgical tools can be passed through the cystoscope to treat certain urinary tract conditions.
How to treat bladder distention?
Procedures that manipulate your bladder to improve symptoms, such as stretching the bladder with water or gas ( bladder distention) or surgery. Nerve stimulation, which uses mild electrical pulses to relieve pelvic pain and, in some cases, reduce urinary frequency.
What is the procedure to check for bacterial culture in urine?
If so, he or she may request a urine bacterial culture. Cystoscopy. During this test, your doctor inserts a cystoscope — a thin tube with a light and camera attached — through the urethra into your bladder to view your urinary tract for signs of disease.
Why are bladder infections so difficult to treat?
Hospital-acquired bladder infections can be a challenge to treat because bacteria found in hospitals are often resistant to the common types of antibiotics used to treat community-acquired bladder infections. For that reason, different types of antibiotics and different treatment approaches may be needed.
How to prepare for a cystitis appointment?
To prepare for your appointment: Ask if there's anything you need to do in advance, such as collect a urine specimen. Write down your symptoms, including any that seem unrelated to cystitis. Make a list of all the medications, vitamins or other supplements that you take.
What is the Radiation Cystits Foundation?
#N#The Radiation Cystits Foundation supports the development of a new Radiation Cystits Patient Registry. The goal is to create a resource to help doctors better recognize severe complications that arise long after pelvic radiation treatments.#N##N#The potential uses of this registry about radiation cystitis (and cancer survivorship post-radiotherapy) include: improving the scientific understanding of radiation cystitis, discovering trends and common needs of registry participants, describing the aggregate personal characteristics of patients within the registry, documenting registry patient medical histories, and contacting registry participants to inform them of new studies. This registry has been created and developed within the published guidance of the National Institute of Health Rare Diseases Registry Program (RaDaR).#N##N#Signup is easy. The form takes less than 5 minutes to complete.
What is radiation cytosis?
What is Radiation Cystitis? Radiation Cystitis (also known as Irradiation Cystitis or “RC”) is a rare and serious side effect that arises from anticancer radiation therapy for pelvic malignancies including prostate, rectal, endometrial and cervical cancers . Symptoms include hematuria (urinary bleeding) and other voiding symptoms such as urinary ...
Where is the hemorrhagic cystitis trial?
As of November '20, a clinical trial for hemorrhagic cystitis testing a new experimental drug is open for enrollment for qualifying patients at sites in the Pittsburgh, PA and Detroit, MI areas.
Is RC a life threatening condition?
Patients with RC and often experience variations or flares of these symptoms over time. RC can be a life threatening condition and there are no definitive treatments or cures for RC. Existing options are costly and limited. The condition represents a significant unmet medical need worldwide.
Is hemorrhagic cystitis the same as RC?
Hemorrhagic cystitis is a closely related condition and is often used synonymously with RC. Hemorrhagic cystitis refers to the same urinary symptoms as RC which result from of either anticancer radiation therapy and/or certain types of anticancer chemotherapy.
What is radiation cystitis?
Radiation cystitis is the inflammation of the urinary bladder caused by radiation. Cancer therapy applied to the pelvis causes damage to the bladder. Radiation cystitis is one of the most feared radiation health effects in this type of therapy. So, if your doctor diagnosed radiation cystitis, you probably were under treatment for tumors in ...
What is the most feared complication of hemorrhagic cystitis?
Hemorrhagi c cystitis is the most feared complication because bleeding can cause shock and death when a large volume of blood is lost (2). As mentioned above, the most severe complication of this condition includes hemorrhagic cystitis and necrosis of the bladder.
What are the symptoms of necrosis of the bladder?
Necrosis of the bladder: The symptoms of necrosis of the bladder are usually non-specific. The most common symptom is pelvic pain. Patients may have pyuria along with other urinary symptoms common in radiation cystitis (6). Hydronephrosis: It causes flank pain and back pain, which is often unilateral.
What is the name of the infection of the bladder?
Cystitis is the clinical name of the Inflammation of the urinary bladder. The most common cause is infections of the urinary tract. Bacteria typically travel upwards through the urethra and irritate the bladder. Other causes of cystitis are certain drugs and radiation.
What is the dose rate of radiation?
In a dose rate below 0.8 Gy/hour, there are fewer chances of suffering from radiation cystitis. When the doses exceed 2 Gy/hour, the risk of toxicity becomes even higher, and the patient can develop cystitis. “Gy” means gray, which is the unit of the ionizing radiation that is administered to the patient.
How do radiations affect tumor cells?
Radiations used to treat tumor cells acts on the intracellular level by producing free radicals. These free radicals interfere with DNA synthesis and cause cell death and radiation injuries. Among other things, there are gene mutations, cell membrane damage, and alterations in the cell cycle. Inflammation is the initial process in this chain ...
Is radiation cystitis the same as infectious cystitis?
The symptoms of radiation cystitis are not always the same as infectious or interstitial cystitis. Bladder problems in cystitis usually include a burning sensation in the urinary tract. This is common in infectious cystitis and radiation cystitis.
What is the best treatment for radiation cystitis?
Pharmacologic therapy for radiation cystitis is primarily aimed at relief of symptoms. Symptomatic frequency and urgency are best treated with anticholinergic agents. Once all other causes of dysuria have been ruled out, phenazopyridine can be used to provide symptomatic relief. If the symptoms of radiation cystitis are not severe ...
Does pentoxifylline help with radiation fibrosis?
Pentoxifylline has been shown to relieve pain due to radiation fibrosis. Pentoxifylline and its metabolites improve the flow properties of blood by decreasing its viscosity. This increases blood flow to the affected microcirculation and enhances tissue oxygenation.