
What does it mean if you have precancerous cells?
Your doctor may use a loop electrosurgical excision procedure, also known as LEEP, to manage precancerous growths on the surface or in the canal of the cervix, which connects the vagina and uterus. In this procedure, the doctor inserts a thin wire loop into the vagina. The loop carries a small electrical current that removes the precancerous tissue.
Can chemical peels remove pre-cancerous cells?
Precancerous conditions of the cervix occur in an area called the transformation zone. This is where one type of lining (glandular, columnar cells) is constantly being changed into another type of lining (squamous cells). The transformation of columnar cells into squamous cells is a normal process, but it makes the cells more sensitive to the ...
How to spot a precancerous growth on your skin?
Treatment for precancerous skin depends on the location and severity of the lesions, and can range from active surveillance to local treatment and removal of the affected area. In order to prevent further development of precancerous skin, adequate sun …
Are all colon polyps precancerous or worse?
Sep 23, 2021 · 1 Main Treatments for precancerous HPV cells. 1.1 Cryotherapy; 1.2 Electrosurgical extraction by loop; 1.3 Cold conization with scalpel; 1.4 Steps of the procedure
How serious are precancerous cells?
How serious are precancerous cells? Precancerous cells may or may not turn into cancer over time. Because those cells are abnormal, it's important to have them monitored or sometimes removed to help reduce your risk of cancer down the road.Nov 5, 2021
How do you get rid of precancerous cells?
Treatment for precancerous cells identified during a Pap test can vary. In serious cases, it can mean surgery to remove abnormal cells, cryosurgery to freeze the cells, or laser therapy to burn away the cells.Jan 29, 2019
Can precancerous cells go away?
“ No one dies of pre-cancer," says Justin Chura, MD, Chief of Surgery & Director of Gynecologic Oncology and Robotic Surgery at our Philadelphia hospital. "It's a very treatable condition, if it even needs treatment at all. A pathology report may indicate carcinoma in situ.Dec 19, 2018
Should I be worried if I have precancerous cells?
Often, precancerous lesions are not invasive and a person will not develop cancer. In some cases these precancerous cells, if left alone, may go on to become “invasive” cancer cells. Sometimes, it may take these cells a few years, or even decades to progress.Dec 19, 2018
How long before precancerous cells become cancerous?
These aren't cancer cells, but cells that may turn cancerous if left untreated for many years. It takes 10-15 years for pre-cancer to progress to cancer.Jan 10, 2018
Can abnormal cells go back to normal?
Abnormal cervical cells may also return to normal even without treatment, especially in younger women. LSIL and HSIL are two types of abnormal changes to cervical squamous cells.Mar 22, 2022
What is Stage 3 precancerous cells mean?
Listen to pronunciation. Severely abnormal cells are found on the surface of the cervix. CIN 3 is usually caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) and is found when a cervical biopsy is done. CIN 3 is not cancer, but may become cancer and spread to nearby normal tissue if not treated.
What are the symptoms of precancerous cells?
SymptomsVaginal bleeding after intercourse, between periods or after menopause.Watery, bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and have a foul odor.Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse.Jun 17, 2021
What are the two main types of cervical cancers?
The main types of cervical cancers are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Most (up to 9 out of 10) cervical cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. These cancers develop from cells in the exocervix. Squamous cell carcinomas most often begin in the transformation zone (where the exocervix joins the endocervix).Jul 30, 2020
Should I get a hysterectomy if I have precancerous cells?
If the precancerous disease is more extensive or involves adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), and the woman has completed childbearing, a total hysterectomy may be recommended. 1 During a total hysterectomy, the entire uterus (including the cervix) is removed.
What are symptoms of HPV in females?
HPV can infect cells in the vagina and around the vulva. If a female has low risk HPV, they may see warts on the vulva. These warts may present as: a cluster that looks like a cauliflower....Some symptoms of vaginal cancer include :bleeding after sex.unusual discharge.a lump in the vagina.pain while having sex.Jan 28, 2021
When do you need a cone biopsy?
Cone biopsy is done to detect cervical cancer or early changes that lead to cancer. A cone biopsy is done if a test called colposcopy cannot find the cause of an abnormal Pap smear. Cone biopsy may also be used to treat: Moderate to severe types of abnormal cell changes (called CIN II or CIN III)
What is precancerous skin?
Precancerous skin consists of various premalignant changes in the skin cells that increase the likelihood of developing into skin cancer. These cha...
What does precancerous skin cancer look like?
Precancerous skin growths can have a variety of colors, shapes, and textures depending on the types of lesion. Some have a characteristic appearanc...
What causes precancerous skin?
The most common cause of precancerous skin is damage to the DNA inside skin cells. Damage to DNA can cause changes in various genes that usually co...
What are the risk factors for precancerous skin?
A wide variety of genetic and environmental risk factors can lead to DNA damage and consequent development of precancerous skin. These can include...
How do you diagnose precancerous skin?
To diagnose precancerous skin, a detailed medical history and examination of the skin is necessary. When physical examination cannot clarify the di...
What do precancerous skin cells look like?
Under a microscope, the appearance of precancerous skin cells depends on the specific type of lesion. When looking at non-precancerous skin, one wi...
How do you treat precancerous skin?
Treatment options for precancerous skin growths usually depend on the number and location of affected areas. Most mild cases require the watch-and-...
What are the most important facts to know about precancerous skin?
Precancerous skin consists of several changes to the DNA of skin cells that can potentially lead to skin cancer. It can arise from personal charact...
What are the different types of dysplasia?
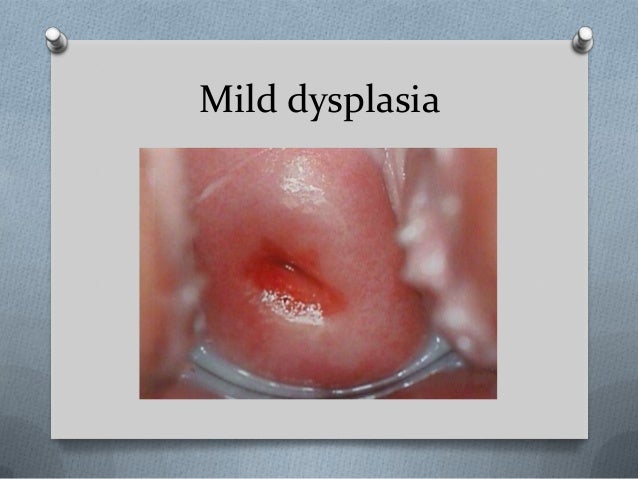
Dysplasia can range from mild to severe: 1 Mild dysplasia : Mild dysplasia refers to cells that are just slightly abnormal. These cells do not usually progress to cancer. 2 Moderate dysplasia : These cells are moderately abnormal and have a higher risk of developing into cancer. 3 Severe dysplasia : This is the most extreme abnormality seen before a cell would be described as cancerous. Severe dysplasia is much more likely to progress to cancer. 2
What is a precancerous cell?
Precancerous cells (also called premalignant cells) are defined as abnormal cells that could turn into cancerous cells, but which, by themselves, are not invasive. 1 . The concept of precancerous cells is confusing because it isn’t a black-and-white issue.
Can inflammation lead to cancer?
Chronic inflammation in tissue can lead to precancerous changes that may in turn progress to cancer. An example is in people who have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) for a prolonged period of time. Chronic inflammation of the esophagus by stomach acids can result in a condition known as Barrett’s esophagus.
What is a CIN?
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN): A precancerous state of cervical cancer 2 . Barrett's esophagus: Abnormal esophageal cells which may go on to become esophageal cancer 3 . Actinic keratoses: Abnormal changes in the skin which may develop into squamous cell skin cancer 6 .
How to describe precancerous changes in cervical cells?
Another way to describe the severity of precancerous changes in cells is by grades. With cervical cells, these classifications are usually used when a biopsy is done after finding dysplasia on a pap smear. Low-grade dysplasia : Low-grade changes are unlikely to progress to cancer.
Which type of cancer begins in epithelial cells?
Cancers which begin in epithelial cells (roughly 85% of cancers) may have a precancerous state. This is in contrast to cancers, such as sarcomas, which begin in mesothelial cells. Some precancerous states include:
Can precancerous cells be invasive?
They may stay the same—that is, remain abnormal but not invasive—or they may even become normal again. It’s important to emphasize again that cells that are precancerous are not cancer cells. This means that left alone, they're not invasive—that is, they will not spread to other regions of the body.
What is loop excision?
Your doctor may use a loop electrosurgical excision procedure, also known as LEEP, to manage precancerous growths on the surface or in the canal of the cervix, which connects the vagina and uterus. In this procedure, the doctor inserts a thin wire loop into the vagina.
How does a loop procedure work?
The loop carries a small electrical current that removes the precancerous tissue. This procedure is usually performed in the doctor’s office with a local anesthetic. Following the procedure, doctors continue to monitor you using Pap tests to make sure there are no additional precancerous changes.
What is the procedure to remove a cone shaped piece of tissue from the cervix called?
Doctors remove a cone-shaped piece of tissue from the cervix in a procedure called conization . They may use conization to remove precancerous tissue high up in the cervical canal, along with a border of surrounding healthy tissue, to help ensure that all of the precancerous cells have been taken out.
How long does it take for a precancerous condition to develop?
If left untreated, it may take 10 years or more for precancerous conditions ...
Can you get HPV from more than one partner?
Having more than one sex partner increases your risk of getting HPV. The following risk factors increase the chance that an HPV infection will not go away on its own and can develop into a precancerous condition of the cervix: — smoking. — having a weakened immune system.
What is the transformation zone of the cervix?
Precancerous conditions of the cervix occur in an area called the transformation zone. This is where one type of lining (glandular, columnar cells) is constantly being changed into another type of lining (squamous cells).
Can a Pap test show abnormal cervix?
But sometimes there may be spotting or bleeding after sex. An abnormal Pap test result is often the first sign that some cells in the cervix are abnormal. This is why it is important to have regular Pap tests.
What is XP skin cancer?
XP is a rare, autosomal recessive condition that results from a genetic mutation affecting one’s ability to repair DNA damage. Individuals with XP also experience intolerance to light (photophobia), severe solar sensitivity, pigmentary changes on the skin, and skin dryness (xerosis). Because of their inability to repair sun damaged DNA, individuals with XP often develop cancers on sun-exposed areas of their skin and eyes.
Is smoking a risk factor for leukoplakia?
Additionally, smoking is the most common risk factor for the development of leukoplakia in and around the mouth. Individual and family history of various types of skin cancer can also increase the likelihood of developing precancerous skin. Although it can affect anyone, precancerous skin occurs most commonly in older adults.
Is tanning bed harmful?
Sunlight is the main source of UV radiation exposure, so all individuals with increased sun exposure are potentially at risk for developing sun damaged and resultant precancerous skin. Indoor tanning beds tend to be even more dangerous, however, as they expose individuals to higher levels of radiation. When UV rays reach the skin’s inner layer, they can damage the DNA. If the body is unable to repair this damage, the cells can begin to divide and grow uncontrollably.
Can a virus cause precancerous skin?
Certain viral infections, such as the human papiloma virus, can also lead to the development of precancerous skin . Such viruses have genes that affect growth-regulating proteins of infected skin cells. This can cause skin cells to grow uncontrollably and stay alive for longer than usual, resulting in precancerous skin .
Why is sun protection important?
They often think that the damage is done, so what’s the point.#N#If you have a precancerous skin growth, protecting your skin from the sun offers two big benefits: 1) It helps to prevent the sun from causing further damage to your skin, which could lead to more precancerous growths or skin cancer , and 2) It gives your body a chance to repair some of the damage to your skin. #N#If you’re unsure about how to protect your skin, you can learn what to do at Prevent skin cancer.
How to treat AKs?
To treat both the visible and hidden AKs, your dermatologist may recommend that you have more than one type of treatment. Your treatment plan many involve going to your dermatologist’s office for a treatment, such as cryotherapy or a specialized light treatment called photodynamic therapy (PDT).
Can you prevent skin cancer?
If you’re unsure about how to protect your skin, you can learn what to do at Prevent skin cancer. Lifelong skin cancer exams can be life-saving. Having just one precancerous skin growth means that the sun, indoor tanning, or both have badly damaged your skin. As such, you have an increased risk of developing skin cancer.
Why is it important to protect your skin from the sun?
If you have a precancerous skin growth, protecting your skin from the sun offers two big benefits: 1) It helps to prevent the sun from causing further damage to your skin, which could lead to more precancerous growths or skin cancer , and 2) It gives your body a chance to repair some of the damage to your skin.
What does precancerous mean?
So what does this mean? “Precancer means there isn’t cancer there yet, but if you don’t monitor or do something about it, it may develop into cancer,” noted Dr. Stephanie Angela King, surgical oncologist at Fox Chase Cancer Center.
Treatment of precancerous lesions
Treatment can range from simply watching the patient closely, having minor surgery, starting a medication that helps prevent growth, or possibly a major surgery. Every organ is different in how we manage these “precancer” lesions, so each patient needs to meet with a specialist in this area to come up with a plan to follow up and treat.

Definition
Types of Precancerous Conditions
Dysplasia Meaning
Causes
Latency and Progression
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
- The treatment of precancerous cells also depends on where in the body they are located. In some cases, close monitoring is all that is recommended to see if the level of dysplasia progresses or if it goes away without any treatment. Often, the precancerous cells will be removed by a procedure such as cryotherapy (freezing the cells) or surgery to r...
Summary
A Word from Verywell