
Medication
Treatment - Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Lifestyle changes. In overweight women, the symptoms and overall risk of developing long-term health problems from PCOS can be greatly improved by losing excess weight.
- Medicines. A number of medicines are available to treat different symptoms associated with PCOS. ...
- Surgery. ...
- Pregnancy risks. ...
Procedures
– Yes, the answer is simple, PCOS can be cured permanently with diet and some simple in hand things which are explained as follows. The most important tip on diet for PCOS would be to cut down on simple sugars. Sugary foods bring about a surge in the blood sugar levels, which places undue stress on the body.
Self-care
Indulge Yourself In Some Recreational Activities Is The Best Way To Beat The Stress Levels
- Cook your favourite recipe
- Join a dance class or an aerobic session
- Learn swimming
- Practice gardening and grow new plants
- Go trekking or skiing
- Go for canoeing or rafting
Nutrition
There’s no cure for PCOS, and you’ll continue to experience symptoms after menopause. Women with PCOS may start menopause later than women who do have the condition. Careful attention to lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise can help you eliminate or improve some of the symptoms of PCOS and perimenopause.
How to cure polycystic ovary?
How to cure PCOS permanently?
How to treat PCOS and ovarian cysts naturally?
Does PCOS have a cure?
How can polycystic ovaries be cured?
How is PCOS treated?Birth control pills. These help to control menstrual cycles, lower androgen levels, and reduce acne.Diabetes medication. This is often used to lower insulin resistance in PCOS. ... A change in diet and activity. ... Medications to treat other symptoms.
How long does it take to treat polycystic ovaries?
It may take up to 6 months to determine whether treatment with birth control is effective. Antiandrogens also are sometimes used to treat PCOS. These medicines counter the effects of excess androgens on a girl's body, and can help clear up skin and hair growth problems.
What happens when you have polycystic ovaries?
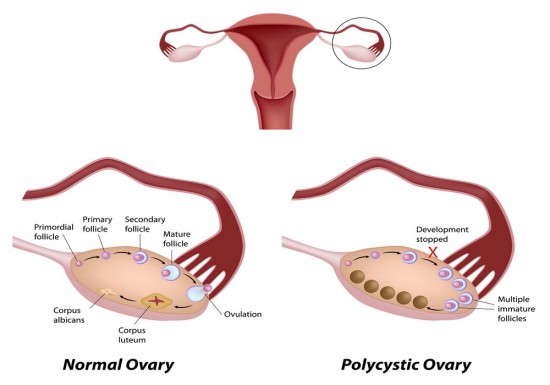
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may have infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods or excess male hormone (androgen) levels. The ovaries may develop numerous small collections of fluid (follicles) and fail to regularly release eggs.
Do polycystic ovaries need to be removed?
Myth: Women with polycystic ovaries have cysts that need to be removed surgically. Fact: The so-called 'cysts' are actually small follicles, each containing an egg. There is no need for surgery to remove the follicles from an ovary: they are a normal part of an ovulating ovary.
Is PCOS a serious problem?
Polycystic ovarian syndrome or PCOS is a common health condition affecting women of childbearing age. It is not a life-threatening or dangerous condition. It can, however, lead to various serious diseases, such as: Diabetes.
Can U Get pregnant with PCOS?
Can I still get pregnant if I have PCOS? Yes. Having PCOS does not mean you can't get pregnant. PCOS is one of the most common, but treatable, causes of infertility in women.
At what age PCOS starts?
It's common for women to find out they have PCOS when they have trouble getting pregnant, but it often begins soon after the first menstrual period, as young as age 11 or 12. It can also develop in the 20s or 30s.
What causes polycystic ovaries?
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown. There is evidence that genetics play a role. Several other factors also play a role in causing PCOS: Higher levels of male hormones called androgens: High androgen levels prevent the ovaries from releasing eggs (ovulation), which causes irregular menstrual cycles.
What happens if PCOS is left untreated?
Unmanaged PCOS can impact short and long term health. It's associated with type 2 diabetes, infertility, cardiovascular disease, obesity, sleep apnea (disrupted breathing in sleep), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and depression (9-11). Early diagnosis and treatment can help reduce these risks significantly.
What is the difference between polycystic ovaries and PCOS?
Poly Cystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) The difference between PCO and PCOS is that PCOS is associated with the production of too many male sex hormones from the ovaries and therefore often causes an imbalance. To diagnose PCOS, you must have at least 2 of these 3 symptoms: One or both ovaries must be polycystic.
What is the best treatment for PCOs?
Birth control is the most common PCOS treatment for women who don't want to get pregnant. Hormonal birth control -- pills, a skin patch, vaginal ring, shots, or a hormonal IUD (intrauterine device) -- can help restore regular periods.
What is PCOS treatment?
Treatments can help you manage the symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and lower your odds for long-term health problems such as diabetes and heart disease. You and your doctor should talk about what your goals are so you can come up with a treatment plan. For example, if you want to get pregnant and are having trouble, ...
How to deal with PCOs?
One of the best ways to deal with PCOS is to eat well and exercise regularly. Many women with PCOS are overweight or obese. Losing just 5% to 10% of your body weight may ease some symptoms and help make your periods more regular. It may also help manage problems with blood sugar levels and ovulation.
How to make your ovaries work better?
Surgery: A procedure called ovarian drilling might make your ovaries work better when ovulation medications don't, but it's being done less often than it used to. The doctor makes a small cut in your belly and uses a tool called a laparoscope with a needle to poke your ovary and wreck a small part of it.
Can PCOs cause hair growth?
Excessive hair growth. Sometimes PCOS causes unwanted hair growth, which your doctor can treat with medications and hair removal methods, such as: Depilatories: These are creams, gels, and lotions that break down the protein structure of hair so it falls out of the skin. Follow the directions on the package.
Does birth control stop hair growth?
Spironolactone ( Aldactone ): If birth control doesn't stop hair growth after 6 months, your doctor may prescribe this drug. It lowers the level of a type of sex hormone called androgens.
Can a doctor prescribe medication for weight loss?
When a healthy diet and regular exercise aren't enough, medications can make losing weight easier. Different drugs work in different ways. Your doctor will prescribe the medication they think will be the most successful for you. Options include:
What is the first step for women with polycystic ovary syndrome?
In many cases, the first action that health care providers recommend for women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is that they make specific lifestyle changes.
How do medications help with PCOs?
1, 11 In women with PCOS, these medications can help: Clear acne and reduce hair growth. Improve weight loss. Lower cholesterol levels. Make periods more regular.
How long does it take for a woman to ovulate with PCOs?
Slightly reduce infertility associated with PCOS 12. After 4 to 6 months of using these medications, women with PCOS may start ovulating naturally. 13. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved insulin-sensitizing medications, such as metformin (pronounced met-FAWR-min), specifically for treating PCOS.
What is the pill for PCOs?
Also called birth control pills or "the Pill," hormonal contraceptives can be used for the long-term treatment of women with PCOS who do not wish to become pregnant, 1 and in fact they are the primary treatment for these women. Oral contraceptive pills contain a combination of the hormones estrogen and progestin. In women with PCOS, these hormones: 1
What is the best treatment for acne?
Retinoids (pronounced RET-n-oids ), antibac terial agents, and antibiotics may be used to treat acne. These products may be available in pills, creams, or gels. The specific treatment depends on the severity of the acne and how long it has been visible.
How to prevent pregnancy with oral contraceptives?
Reduce excess hair growth. Help clear acne. Because anti-androgens can cause birth defects, they are often taken with oral contraceptives to prevent pregnancy. 15 Be sure to talk with your health care provider about the risks of these treatments, especially if you want to become pregnant.
What is the treatment for hair follicles?
Electrolysis (pronounced ih-lek-TROL-uh-sis ), laser hair removal, and intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy are other options, but they are often expensive and may require multiple treatments. 1 Electrolysis uses an electric current applied to each hair follicle to destroy its root.
What are the best ways to treat PCOs?
Home Remedies and Lifestyle. Lifestyle modifications are the first line of treatment for PCOS. Not only do they address the reproductive problems in PCOS, but they also reduce the risks of common complications such as metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
How to treat PCOs?
The single most important PCOS treatment is to lose weight if you are overweight. 1 By reducing calories and simple sugars, increasing lean protein and fiber, and beginning a regular exercise routine, you can help your body increase its response to insulin, and possibly decrease androgen production.
What is the best diet for PCOs?
A healthy diet is important in PCOS even if you are at a normal weight. Enjoy limited fruits (too many may negatively affect insulin resistance due to high fructose levels) and plenty of vegetables, moderate amounts of high-fiber, unprocessed, low-glycemic index grains (such as oats and quinoa), and foods rich in omega-3 fats such as fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), nuts , seeds, and avocados. 2
What is the best medicine for androgen secretion?
Medications that suppress androgen secretion are one option that your doctor may consider. Oral contraceptives may help with this, or you may be prescribed an antiandrogenic medication, such as Spironolactone (aldactone). 1
What is the pill for women?
The pill contains a combination of estrogen and progesterone which aids in regulating a woman’s hormones. This will help normalize your cycle, thereby making your periods more regular.
Does PCOs have a cure?
An Overview of PCOS & Infertility. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) does not have a cure, but there are treatments that can address its symptoms and complications. For example, medications can be used to help regulate menstruation, while lifestyle approaches (like exercise) can help reduce related risks like metabolic syndrome.
Does metformin help with ovulation?
By increasing the body’s response to insulin, it is thought that the ovary may not make as many androgens, which increases the likelihood that ovulation will occur. Metformin may also reduce the levels of circulating androgens. This will help regulate your menstrual cycle and may help you lose weight. 1 .
What is PCOS in gynecology?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which the ovaries produce an abnormal amount of androgens, male sex hormones that are usually present in women in small amounts.
How to reduce hair growth in PCOs?
Diabetes medication. This is often used to lower insulin resistance in PCOS. It may also help reduce androgen levels, slow hair growth, and help you ovulate more regularly. A change in diet and activity. A healthy diet and more physical activity can help you lose weight and reduce your symptoms.
How do you know if you have PCOs?
The symptoms of PCOS may include: Missed periods, irregular periods, or very light periods. Ovaries that are large or have many cysts. Excess body hair, including the chest, stomach, and back (hirsutism) Weight gain, especially around the belly (abdomen) Acne or oily skin. Male-pattern baldness or thinning hair.
What is the test for PCOs?
Some of the symptoms of PCOS are like those caused by other health problems. Because of this, you may also have tests such as: Ultrasound. This test uses sound waves and a computer to create images of blood vessels, tissues, and organs. This test is used to look at the size of the ovaries and see if they have cysts.
What to do if you don't plan to get pregnant?
It can cause symptoms such as abdominal bloating and pelvic pain. If you do not plan to become pregnant, your treatment may include: Birth control pills. These help to control menstrual cycles, lower androgen levels, and reduce acne. Diabetes medication. This is often used to lower insulin resistance in PCOS.
What are the health problems of PCOs?
These include type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, problems with the heart and blood vessels, and uterine cancer. Women with PCOS often have problems with their ability to get pregnant (fertility).
Can PCOs cause insulin resistance?
The exact cause of PCOS is not clear. Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance. This means the body can't use insulin well. Insulin levels build up in the body and may cause higher androgen levels. Obesity can also increase insulin levels and make PCOS symptoms worse. PCOS may also run in families.
What is the best medication for PCOs?
Diabetes drugs are commonly used to treat insulin resistance in women with PCOS, the options of which include: 6. Glucophage (metformin), the first-line oral drug of choice that can control diabetes while promoting weight loss. Actos (pioglitazone), an oral drug used to reduce high blood sugar. Avandia (rosiglitazone), an oral drug ...
What is the best fertility medicine for PCOs?
Clomid (clomiphene citrate), the most commonly used fertility drug that works better in some women with PCOS than others. Femara (letrozole) ., a medication mainly used to treat breast cancer that has also been shown to stimulate ovulation as well. Glucophage (metformin), a commonly prescribed diabetes drug that may enhance the effectiveness ...
What is PCOs and testosterone?
Hyperandrogenism. Women with PCOS often have elevated levels of male hormones ( androgens ), including testosterone. The condition, referred to as hyperandrogenism, can lead to lead to the onset of secondary male characteristics in such as male-pattern hair loss and hirsutism (excessive facial and body hair growth). 9.
How many women with PCOs are overweight?
Roughly half of women with PCOS are overweight or obese. 7 Not only does PCOS contribute to weight gain, but it also makes it far more difficult for women to lose weight. In addition to exercise and diet, drug therapies are sometimes used to assist with weight loss.
How many women with PCOs develop diabetes?
Around 50% to 70% of women with PCOS will develop diabetes or prediabetes by the age of 40 due to the onset of insulin resistance (a condition influenced by imbalances in estrogen production). These women are also at greater risk of gestational diabetes, a condition caused by the impairment of glucose metabolism during pregnancy. 5. ...
What is PCOs in women?
PCOS is characterized by hormonal abnormalities that can result in infrequent periods ( oligomenorrhea) or absent periods ( amenorrhea ). These and other hormonal irregularities can undermine a woman's ability to get pregnant. Drug therapies are aimed at regulating hormones to better restore a normal menstrual cycle .
What is the best pill for PCOs?
Inositol, a natural supplement used to improved egg quality in women with PCOS can also promote weight loss. Qsymia (phentermine/topiramate), an appetite suppressant that works similarly to Contrave. Saxenda (liraglutide), used to treat insulin resistance and obesity. Wegovy (semaglutide), a once-weekly injection that helps suppress appetite ...
What is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), also known as polycystic ovarian syndrome, is a common health problem caused by an imbalance of reproductive hormones. The hormonal imbalance creates problems in the ovaries. The ovaries make the egg that is released each month as part of a healthy menstrual cycle.
Who gets PCOS?
Between 5% and 10% of women between 15 and 44, or during the years you can have children, have PCOS. 1 Most women find out they have PCOS in their 20s and 30s, when they have problems getting pregnant and see their doctor. But PCOS can happen at any age after puberty. 2
What are the symptoms of PCOS?
Irregular menstrual cycle. Women with PCOS may miss periods or have fewer periods (fewer than eight in a year). Or, their periods may come every 21 days or more often. Some women with PCOS stop having menstrual periods.
What causes PCOS?
The exact cause of PCOS is not known. Most experts think that several factors, including genetics, play a role:
Can I still get pregnant if I have PCOS?
Yes. Having PCOS does not mean you can't get pregnant. PCOS is one of the most common, but treatable, causes of infertility in women. In women with PCOS, the hormonal imbalance interferes with the growth and release of eggs from the ovaries (ovulation). If you don't ovulate, you can't get pregnant.
Is PCOS linked to other health problems?
Diabetes. More than half of women with PCOS will have diabetes or prediabetes (glucose intolerance) before the age of 40. 4 Learn more about diabetes on our Diabetes page.
Will my PCOS symptoms go away at menopause?
Yes and no. PCOS affects many systems in the body. Many women with PCOS find that their menstrual cycles become more regular as they get closer to menopause. However, their PCOS hormonal imbalance does not change with age, so they may continue to have symptoms of PCOS.
How to treat PCOs?
Lifestyle interventions are the first treatments doctors recommend for PCOS, and they often work well. Weight loss can treat PCOS symptoms and improve the odds of getting pregnant. Diet and aerobic exercise are two effective ways to lose weight. Medications are an option if lifestyle changes don’t work.
What is PCOS in pregnancy?
Diet and lifestyle. Medical treatments. When to see a doctor. Bottom line. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition that affects a woman’s hormone levels. Women with PCOS produce higher-than-normal amounts of male hormones.
What are the reproductive organs that regulate the menstrual cycle?
Trusted Source. ). PCOS affects a woman’s ovaries, the reproductive organs that produce estrogen and progesterone — hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle. The ovaries also produce a small amount of male hormones called androgens. The ovaries release eggs to be fertilized by a man’s sperm.
What age group is PCOs?
PCOS is a problem with hormones that affects women during their childbearing years (ages 15 to 44). Between 2.2 and 26.7 percent of women in this age group have PCOS ( 1, 2. Trusted Source. ). Many women have PCOS but don’t know it. In one study, up to 70 percent of women with PCOS hadn’t been diagnosed ( 2.
Why is it hard to get pregnant with PCOs?
This hormone imbalance causes their body to skip menstrual periods and makes it harder for them to get pregnant . PCOS also causes hair growth on the face and body, and baldness. And it can contribute to long-term health problems like diabetes and heart disease.
What is PCOS in Italian?
Italian physician Antonio Vallisneri first described its symptoms in 1721 ( 3. Trusted Source. ). Summary. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) affects up to almost 27 percent of women during their childbearing years ( 4 ). It involves cysts in the ovaries, high levels of male hormones, and irregular periods.
What are the symptoms of PCOs?
PCOS is a “syndrome,” or group of symptoms that affects the ovaries and ovulation. Its three main features are: cysts in the ovaries. high levels of male hormones. irregular or skipped periods. In PCOS, many small, fluid-filled sacs grow inside the ovaries. The word “polycystic” means “many cysts.”. These sacs are actually follicles, each one ...
How to help PCOs?
The symptoms associated with PCOS can cause stress. Stress reduction techniques, which help calm the mind and let you connect with your body, can help. These include yoga and meditation. Speaking with a therapist or other medical professional may also be beneficial.
How to reduce insulin resistance in PCOs?
Other lifestyle changes to consider. PCOS, like many disorders, responds positively to proactive lifestyle choices. This includes exercise and daily physical movement. Both can help to reduce insulin resistance, especially when coupled with a limited intake of unhealthy carbohydrates.
What is PCOs in women?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is typically earmarked by irregular periods or by no menstruation at all. Women with PCOS typically have multiple cysts in their ovaries, caused by an overproduction of hormones called androgens. of women with the disorder are overweight or obese.
How does diet affect PCOs?
How does my diet affect PCOS? Women with PCOS are often found to have higher than normal insulin levels. Insulin is a hormone that’s produced in your pancreas. It helps the cells in your body turn sugar ( glucose) into energy. If you don’t produce enough insulin, your blood sugar levels can rise.
Why is it so hard to lose weight with PCOs?
A diet high in refined carbohydrates, such as starchy and sugary foods, can make insulin resistance, and therefore weight loss, more difficult to control.
Can PCOs be managed?
Women with PCOS, particularly when its symptoms are not managed, may also be at greater risk for: Many women with PCOS find they’re able to manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of other medical concerns by controlling their diet and lifestyle choices.

Home Remedies and Lifestyle
Over-The-Counter (OTC) Therapies
Surgeries and Specialist-Driven Procedures
Fertility Treatment
Specialist to consult
Complementary Alternative Medicine
- There's no test to definitively diagnose PCOS. Your doctor is likely to start with a discussion of your medical history, including your menstrual periods and weight changes. A physical exam will include checking for signs of excess hair growth, insulin resistance and acne. Your doctor migh…
A Word from Verywell