What is Pneumobilia and what causes it?
Pneumobilia, or air within the biliary tree of the liver, suggests an abnormal communication between the biliary tract and the intestines, or infection by gas-forming bacteria. Pneumobilia usually can be distinguished from air in the portal venous system by its appearance on computed tomography (CT) scan. The most common conditions associated ...
What is Pneumobilia in endoscopy?
Sep 09, 2017 · Pneumobilia Treatment There have been only two ways of treatment in Pneumobilia • Endoscopic biliary procedure • Biliary surgery In the 1st procedure, the patient swallow the endoscope and the physician will pass it through esophagus to the spot. Now a small plastic tube is inserted in the endoscope to view inside along with a dye.
What are the treatment options for pneumonia?
Aug 16, 2021 · If your pneumonia is so severe that you are treated in the hospital, you may be given intravenous fluids and antibiotics, as well as oxygen therapy, and possibly other breathing treatments. Recovering from Pneumonia It may take time to recover from pneumonia. Some people feel better and are able to return to their normal routines within a week.
How long does it take for Pneumobilia to go away?
In addition to CT, MRI/MRCP, especially with the combination of both T1-weighted and T2-weighted images, is highly sensitive and specific for intrahepatic pneumobilia. 83 Once identified on imaging, pneumobilia must be differentiated from portal venous air, as the two entities may have similar appearance on ultrasonography and may require CT scan with contrast to …

Does pneumobilia need to be treated?
Pneumobilia, gas within the biliary tract, is due to an abnormal connection between the gastrointestinal tract and the biliary tract and is considered a serious pathology usually requiring surgical intervention.
How long can pneumobilia last?
More benign causes of pneumobilia are post-cholecystectomy, post ERCP, or following percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC) [14,15]. However, these should resolve spontaneously in weeks to months unless the sphincter of Oddi is incompetent, in which case pneumobilia can persist for years as seen in our patient.Apr 14, 2021
Is pneumobilia an emergency?
Pneumobilia in a patient who is clinically unstable is an emergency. The etiologies are related to either some form of a biliary-enteric fistula or emphysematous cholecystitis [2,3].Apr 14, 2021
What does pneumobilia indicate?
Pneumobilia, or air within the biliary tree of the liver, suggests an abnormal communication between the biliary tract and the intestines, or infection by gas-forming bacteria.
What causes pneumobilia?
Pneumobilia almost always results from some type of communication between the bile ducts and intestine. One of the most common causes is a surgically created biliary enteric fistula such as a choledochojejunostomy or cholecystojejunostomy (seeFig. 12-13).
What organs does a HIDA scan show?
A HIDA, or hepatobiliary, scan is a diagnostic test. It's used to capture images of the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and small intestine to help diagnose medical conditions related to those organs. Bile is a substance that helps digest fat.
What is ERCP used to diagnose?
What is ERCP? Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, or ERCP, is a procedure to diagnose and treat problems in the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas.
What are the complications of pneumonia?
People who may be more likely to have complications from pneumonia include: 1 Older adults or very young children. 2 People whose immune system does not work well. 3 People with other, serious medical problems such as diabetes or cirrhosis of the liver.
What is ARDS in a lung?
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a severe form of respiratory failure. Lung abscesses, which are infrequent, but serious complications of pneumonia. They occur when pockets of pus form inside or around the lung. These may sometimes need to be drained with surgery.
How long does it take to recover from pneumonia?
Some people feel better and are able to return to their normal routines within a week. For other people, it can take a month or more. Most people continue to feel tired for about a month. Adequate rest is important to maintain progress toward full recovery and to avoid relapse.
Do antibiotics work against viruses?
If you stop, you risk having the infection come back, and you increase the chances that the germs will be resistant to treatment in the future. Typical antibiotics do not work against viruses. If you have viral pneumonia, your doctor may prescribe an antiviral medication to treat it. Sometimes, though, symptom management and rest are all ...
What is the best medicine for cough and fever?
Most people can manage their symptoms such as fever and cough at home by following these steps: Control your fever with aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen), or acetaminophen. DO NOT give aspirin to children.
How to get rid of an infection?
If your cough is preventing you from getting the rest you need, ask your doctor about steps you can take to get relief. Drink warm beverages, take steamy baths and use a humidifier to help open your airways and ease your breathing.
How to stop breathing when you smoke?
Contact your doctor right away if your breathing gets worse instead of better over time. Stay away from smoke to let your lungs heal. This includes smoking, secondhand smoke and wood smoke. Talk to your doctor if you are a smoker and are having trouble staying smokefree while you recover.
What causes pneumobilia in the biliary system?
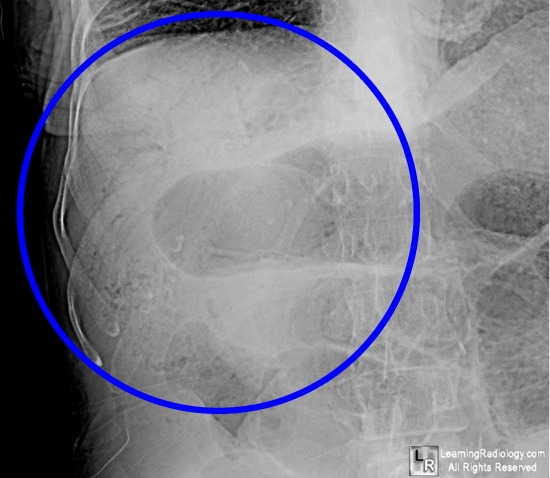
The most common cause of pneumobilia is previous diverting surgery for biliary obstruction, such as choledochojejunostomy or choledochoduodenostomy (Box 6-6 ). In patients who have had previous sphincterotomies during ERCP, air may reflux from the duodenum into the biliary system. Any condition that undermines the competence of the sphincter of Oddi, whether it be traumatic, inflammatory, neoplastic, or iatrogenic, can result in air in the biliary system. On plain abdominal films, the air is seen as linear branching lucencies ( Fig. 6-33 ), and during UGI studies barium also may be seen within the biliary system. The air collections within the biliary system are generally centralized as a result of the centripetal flow of bile ( Fig. 6-34 ). This observation helps distinguish air in the biliary system from air in the portal venous system, which is carried peripherally.
Where is gas in the bile ducts?
Gas in the bile ducts, or pneumobilia, is characterized radiographically by thin, branched, tubular areas of lucency in the central portion of the liver (Fig. 16-13 ). This central location can be explained by the flow of bile from the periphery of the liver toward the porta hepatis.
What is axial T2WI?
Axial T2WI MR shows an air-fluid level within the bile ducts as a signal void with a linear interface with the high-signal bile in the dependent position of the bile duct.
What causes biliary fistula?
Other unusual causes of biliary fistula include Crohn's disease and neoplasms and rarely biliary-pancreatic fistula ( Fig. 6-36 ). In most inflammatory conditions of the duodenum, even the more severe peptic processes, the biliary system is unaffected.
What is pneumobilia in the biliary system?
Pneumobilia is defined as air within the biliary system. It is usually caused by an abnormal connection between the biliary gastrointestinal tracts. Persistent asymptomatic pneumobilia is a rare occurrence and is generally considered a benign finding on imaging.
Is pneumobilia iatrogenic or non-iatrogenic?
Most cases of pneumobilia are iatrogenic and easily identified on imaging. Some of the non-iatrogenic causes include emphysematous cholecystitis, ascending cholangitis (usually with gas-forming organisms), spontaneous biliary-enteric fistula, biliary bronchopleural fistula, incompetent sphincter of Oddi, and visceral blunt trauma [1]. Timely awareness of pneumobilia etiology is imperative to enable prompt accurate treatment to avert catastrophic sequelae. We present a unique case of a patient developing acute cholangitis in the setting of long-standing spontaneous pneumobilia and increased intraabdominal pressure. This has not been previously reported in the literature.
what is pneumobilia?
Air in Bile Ducts: As you can guess, air does not belong in the bile ducts. The most common cause is following an ercp/sphincterotomy, where air refluxes back into the b ... Read More
who am i?
A little more: Your question will need to have a little more context in order to receive a meaningful answer. If it was meant to check if questions are answered here ... Read More
medication?
Just don't know?: Please re-ask your question? Medication prescribing, use, management, monitoring, educating and keeping them straight and properly used is the most d ... Read More
am i dying?
We all are: A 3-word question with no details... well, life is short on Earth, regardless of whether a person lives 3 days, 3000 days, or 30,000 days. It is not l ... Read More
whats brat?
Bland diet: Brat stands for bananas, rice, applesauce and toast. It has been recommended for years for various stomach issues, especially gastroenteritis. However ... Read More
Causes
In a healthy individual with normal anatomy, there is no air within the biliary tree. When this finding is present, it may be secondary to:
Further reading
Sherman SC, Tran H (February 2006). "Pneumobilia: benign or life-threatening". The Journal of Emergency Medicine. 30 (2): 147–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2005.05.016. PMID 16567248.