
Explore
Your doctor probably will recommend:
- Blood tests to measure the level of vitamin D in your body
- X-rays to look at your bone structure
- Bone mineral density scans to test the amount of calcium and phosphate in your bones
How do medications treat osteomalacia?
Treatment options depend on the diagnosis and severity. While osteomalacia can be cured after only a few weeks of supplements, osteoporosis treatment focuses on managing symptoms. Providers prescribe medications for osteoporosis but not osteomalacia. Prevention for both conditions starts with a proper intake of vitamins and minerals.
Can osteomalacia be cured?
The Natural Treatment For Osteoporosis
- Vitamin K in small doses (nearly fifty microgram/day) will help in the porosity of the bones. It is useful in osteoporosis cure.
- Avoid meat in the diet. This is to be replaced by the green leafy vegetables. ...
- Manganese (as present in pineapple) will be beneficial in the condition of osteoporosis.
What are the best natural remedies for osteoporosis?
People can try:
- jogging
- walking
- climbing stairs
- weight lifting
- bodyweight exercises
How to help osteoporosis naturally?
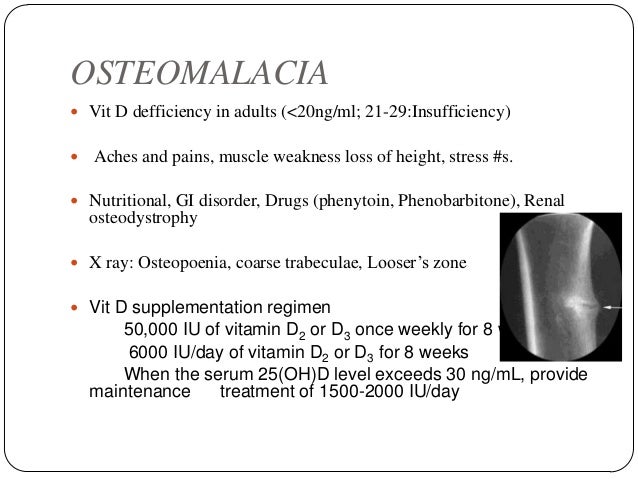
What medication is used to treat osteomalacia?
Drugs used to treat OsteomalaciaDrug nameRatingRx/OTCView information about Calciferol CalciferolRateRx/OTCGeneric name: ergocalciferol systemic Drug class: vitamins For consumers: dosage, interactions, side effectsView information about Calcidol CalcidolRateRx/OTC24 more rows
How long does osteomalacia take to cure?
If left untreated, osteomalacia can lead to broken bones and severe deformity. There are various treatment options available to help manage the conditions. You may see improvements in a few weeks if you increase your intake of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus. Complete healing of the bones takes about 6 months.
How do you recover from osteomalacia?
Treatment will cure osteomalacia in most cases, but easing bone pain, muscle weakness and cramps may take several months. If it's caused by a lack of vitamin D, you will probably need to take vitamin D supplements every day. Taking calcium supplements every day too may speed up bone healing.
Can soft bones be cured?
Treatment and Prevention. Osteomalacia is treatable, usually with vitamin and/or mineral supplements, and most people can be cured. It is generally treated by administration of vitamin D, calcium and, if needed, also phosphorus. If the osteomalacia is caused by an underlying condition, this will also need to be treated ...
What does osteomalacia feel like?
The most common symptoms of osteomalacia are pain in the bones and hips, bone fractures, and muscle weakness. Patients can also have difficulty walking.
How much vitamin d3 should I take daily?
The current recommendations suggest consuming 400–800 IU (10–20 mcg) of vitamin D per day. However, people who need more vitamin D can safely consume 1,000–4,000 IU (25–100 mcg) daily. Consuming more than this is not advised, as it is not linked to any extra health benefits.
How long does it take to recover from vitamin D deficiency?
“If you put people on 2,000-4,000 [milligrams] of vitamin D based on what their deficient value was, you can usually get them corrected in four to six weeks, which is when you are really going to need the vitamin D.
How can I boost my vitamin D?
Spend time in sunlight. Vitamin D is often referred to as “the sunshine vitamin” because the sun is one of the best sources of this nutrient. ... Consume fatty fish and seafood. ... Eat more mushrooms. ... Include egg yolks in your diet. ... Eat fortified foods. ... Take a supplement. ... Try a UV lamp.
What is the best treatment for osteomalacia?
Other treatments to relieve or correct osteomalacia symptoms may include: Wearing braces to reduce or prevent bone irregularities.
How to diagnose osteomalacia?
How is osteomalacia diagnosed? 1 The most important indicator is low levels of vitamin D, but low levels of calcium or a significant drop in phosphate levels may also indicate osteomalacia. 2 X-rays may be taken to see if there is any evidence of osteomalacia. 3 A bone mineral density scan may be helpful in evaluating the amount of calcium and other minerals present in a patient’s bone segment. These scans are not required to make the diagnosis of osteomalacia. However, they may give important information about a patient’s bone health.
Why do my bones break down so fast?
Osteomalacia is a disease that weakens bones and can cause them to break more easily. It is a disorder of decreased mineralization, which results in bone breaking down faster than it can re-form. It is a condition that occurs in adults. In children, inadequate concentrations of vitamin D may cause rickets.
What are the indicators of osteomalacia?
The most important indicator is low levels of vitamin D, but low levels of calcium or a significant drop in phosphate levels may also indicate osteomalacia. X-rays may be taken to see if there is any evidence of osteomalacia.
Can osteomalacia be diagnosed with a bone biopsy?
These scans are not required to make the diagnosis of osteomalacia. However, they may give important information about a patient’s bone health. Rarely, the doctor may perform a bone biopsy, in which a sample of bone tissue is taken and examined.
How long does it take for osteomalacia to heal?
You may see improvements in a few weeks if you increase your intake of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus. Complete healing of the bones takes about 6 months.
Why is vitamin D important for osteomalacia?
A lack of vitamin D is the most common cause of osteomalacia. Vitamin D is an important nutrient that helps you absorb calcium in your stomach. Vitamin D also helps maintain calcium and phosphate levels to help your bones form properly. It’s made within the skin from exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays in sunlight.
How do you know if you have osteomalacia?
There are a few symptoms of osteomalacia. The most common is bones that fracture easily. Another is muscle weakness. This happens because of problems in the areas where muscle attaches to bone. A person with osteomalacia may have a hard time walking or may develop a waddling gait.
Is osteomalacia the same as osteoporosis?
Problems with bone formation or the bone-building process causes osteomalacia. This condition isn’t the same as osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a weakening of living bone that’s already formed and being remodeled.
Can osteomalacia cause bone fractures?
If you don’t treat the cause of your osteomalacia, there are complications. Adults can fracture bones easily such as rib, leg, and spine bones. Also, in children, osteomalacia and rickets often occur together, which can lead to bowing of the legs or premature tooth loss. Symptoms can return if not enough vitamin D is available.
What foods can help with osteomalacia?
If osteomalacia comes from not getting enough vitamin D, you can treat it by getting more of it in your diet through certain foods and supplements. Foods with vitamin D include: Cereal. Cheese. Eggs. Fish (tuna, salmon, swordfish, sardines) Liver. Milk.
What is it called when your bones are weak and break?
Causes. Symptoms. Diagnosis. Treatment. The word osteomalacia means “soft bones.”. The condition keeps your bones from mineralizing, or hardening, as they should. That makes them weak and more likely to bend and break. Only adults have it. When the same thing happens in children, it’s called rickets.
Can a seizure cause osteomalacia?
Over time, extra acid in your body fluids can slowly dissolve bone. It’s rare, but some people have a genetic condition that causes osteomalacia.
Is osteomalacia the same as osteoporosis?
Osteomalacia is more common in women and often happens during pregnancy. It’s not the same as osteoporosis. Both can cause bones to break. But while osteomalacia is a problem with bones not hardening, osteoporosis is the weakening of the bone.
How to fix osteomalacia?
Calcium is the other nutrient necessary for strengthening your bones and making them hard. Increasing your calcium intake, either through supplements or dietary changes, can help resolve osteomalacia. Luckily, many foods high in vitamin D are also high in calcium. Most dairy products are a good source of both. For individuals who were lucky enough to have had their doctor diagnose osteomalacia early, diet changes may be enough. Sometimes, doctors recommend taking a phosphate supplement along with calcium, as phosphate is important for bone metabolism. Without enough calcium and phosphate for proper bone metabolism, there will be insufficient bone mineralization.
Does vitamin D help with osteomalacia?
This is why individuals struggle with a deficiency in winter months. Those who live in areas with short days are also more at risk of developing a deficiency and potentially osteomalacia. Anyone who is restricted to being indoors is at risk as well. Spending a little more time outside in the sun can help with symptoms of osteomalacia, but proceed with caution. Wear plenty of sunscreen and follow any recommendations made by your doctor. Too much sun exposure can greatly increase your risk of skin cancer. Of all of the causes of osteomalacia, a lack of vitamin D is the number-one, worldwide.
Can braces help with osteomalacia?
When osteomalacia is severe, it may be time to consider braces and surgery. Braces are useful for both correcting and preventing abnormalities in bone formation. Supports and braces can also prevent you from experiencing a painful fracture or break. Although they can be awkward to wear, braces can be the best line of defense while trying to increase your calcium and vitamin D intake.
How to treat osteomalacia?
Treatment for osteomalacia will depend on the underlying cause. For someone with osteomalacia due to vitamin D deficiency, vitamin D therapy provides an effective treatment. This works well for the majority of people with osteomalacia. You may need to start out with a very high dose of vitamin D in the first weeks or couple of months after you are diagnosed. You might also need to take calcium supplements. 1
What does osteomalacia mean?
The word “osteomalacia” comes from the Greek roots “osteon” and “malakia,” meaning “bone” and “soft.”. The medical condition may cause pain, muscle weakness, difficulty walking, and an increased risk of bone fracture.
Why is vitamin D important for osteomalacia?
Vitamin D is important for proper mineralization of new bone matrix. So it’s not surprising that vitamin D deficiency is a major cause of osteomalacia. Vitamin D deficiency might be caused by some of the following: Very low vitamin D in the diet. Decreased exposure to sunlight.
What is the difference between osteoporosis and osteomalacia?
In contrast, in osteoporosis, more bone is broken down than normal compared to the normal amount of new bone being formed, and mineralization is normal or just a little reduced.
What causes osteomalacia?
Osteomalacia can also be caused by a deficiency in some of the minerals needed to harden bones. So deficiencies of phosphate can lead to osteomalacia. Some of the causes of hypophosphatemia include: 1 Certain genetic hereditary syndromes affecting phosphate 2 Certain rare kinds of tumors 3 Excess intake of antacids 4 Certain rare genetic kidney problems 1
Why are new bones so soft?
Another way to put it is that there is a decrease in the amount of calcium and other minerals for a given unit of underlying protein bone matrix. That makes the bones too soft. 3 .
What happens to the bone matrix in osteomalacia?
In osteomalacia, some of the existing underlying bone matrix becomes unmineralized.
What is the best treatment for osteomalacia?
The best natural treatment for osteomalacia is vitamin D. Your doctor will often prescribe this as the first treatment option, and daily supplements can help reduce bone cracks and fractures. When combined with phosphorus and calcium supplements, your overall bone health can improve.
What is the cause of osteomalacia?
Osteomalacia is a condition characterized by weakened bones. The leading cause of this, like many bone diseases, is a lack of vitamin D. Early detection and treatment are necessary steps in preventing serious fractures. Learn more with this guide.
Why does osteomalacia weaken bones?
Osteomalacia causes your bone to weaken as they develop, and the main cause of this is a lack of vitamin D. Vitamin D is essential for absorbing calcium, which is an important mineral for healthy bone development. A lack of vitamin D can also result from little to no sun exposure as the sun’s rays allow the vitamin to be made in the skin.
How long does it take for osteomalacia to heal?
♦ The incidence of osteomalacia is about 1 in 1000 people.#N#♦ Almost 15 percent of the world’s population is vitamin D deficient.#N#♦ It can take up to six months for bones to fully heal after treatment begins.#N#♦ Osteomalacia affects 1 in every 2000,000 children.
What foods can you eat to prevent osteomalacia?
To increase your dietary intake of vitamin D and calcium, be sure to eat the following foods: ♦ Greens, such as spinach, kale, and collards. ♦ White beans. ♦ Fish, such as salmon, trout, tuna, and sardines.
Is osteomalacia a disability?
Osteomalacia and Disability. While osteomalacia is treatable, if left untreated, bone deformities can be severe. If this happens, the pain and lack of mobility can be debilitating. The worse the condition gets, the more at risk you are for severe fractures, which can keep you from daily activities.
Is osteomalacia the same as osteoporosis?
Osteomalacia is commonly confused with osteoporosis as both involve weak bones, but the two conditions are different. Osteoporosis is the weakening of bones that have already been formed, and osteomalacia affects bones as they are forming.
What is the best treatment for osteomalacia?
Osteomalacia treatments. If osteomalacia is found early enough, your doctor may recommend vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate supplements. Sometimes vitamin D is also given intravenously, or through an injection into the vein.
What blood test is used to diagnose osteomalacia?
For osteomalacia, a blood test can typically yield a diagnosis. The blood test measures: calcium. phosphorus. vitamin D levels. Other blood tests may be ordered as well, including those to check for: alkaline phosphatase, which is made by cells that make bone and is elevated in those with osteomalacia.
Why is bone health important?
Bone health is important for a healthy body. Osteoporosis and osteomalacia are two diseases that affect the bones. While they both weaken the bones, they act in different ways. Knowing the difference between the two can help you talk with a medical professional about your symptoms and get the appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
What are the two different conditions that affect the bones?
Osteomalacia and osteoporosis are two different conditions that affect the bones.
What is the term for a bone that has a reduced bone density?
Osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is when your bone mineral density and bone mass decreases, or when the quality or structure of the bone changes. Over time, this can cause a reduction in bone strength, increasing the risk of fractures. The inside of a bone typically has spaces akin to a honeycomb structure.
How is osteoporosis diagnosed?
Osteoporosis is usually diagnosed during a routine screening for the condition. Routine screenings are done for women over age 65 years or women of any age who have certain risk factors. Tools used in making a diagnosis include: medical history, including previous fractures, lifestyle behaviors, and family history.
Why is menopause a risk factor for bone loss?
Menopause can also be a risk factor because changes in hormone levels lead to quicker bone loss. Other risk factors can include: family history of osteoporosis. poor nutrition.
