
Which drug is used for treating neurogenic bladder?
Medicine for Neurogenic Bladder Your health care provider may suggest: Overactive bladder medicines that relax the bladder such as oxybutynin, tolterodine, or solifenacin, as well as mirabegron. Bladder muscle injections to relax the bladder, such as injection of Botulinum toxin.
How do they treat neurogenic bladder?
How is neurogenic bladder treated?Medicines.Emptying the bladder with a catheter at regular times.Preventive antibiotics to reduce infection.Placing an artificial cuff around the neck of the bladder which can be inflated to hold urine and deflated to release it.Surgery to remove stones or blockages.More items...
Can you recover from a neurogenic bladder?
There's no cure for neurogenic bladder, but you can manage your symptoms and get control. If you have OAB, you may need to: Train your bladder. You can do this by squeezing your pelvic floor muscles during the day or when you need to pee (Kegel exercises).
What is the prognosis for neurogenic bladder?
Answer. The prognosis of patients with incontinence from neurogenic bladder is excellent with modern health care. With improvement in information technology, well-trained medical staff, and advances in medical knowledge, patients who are incontinent should not experience the morbidity and mortality of the past.
What is the most common complication of a neurogenic bladder?
Bladder infections are the most common complication of neurogenic bladder.
Is neurogenic bladder life threatening?
Neurogenic bladder is not curable, but it is manageable. It's important to see a doctor as soon as the condition develops, however. Left untreated it can lead to kidney failure, which can be life threatening.
Can nerve damage to the bladder be repaired?
Surgical Treatments If lifestyle or medical treatments do not work, your health care provider may suggest surgery. For patients with overactive bladder symptoms, a surgery called sacral neuromodulation (SNS) is the only surgery available. SNS targets the nerves carrying signals between the spinal cord and the bladder.
What is the most common cause of a neurogenic bladder?
Neurogenic bladder is the name given to a number of urinary conditions in people who lack bladder control due to a brain, spinal cord or nerve problem. This nerve damage can be the result of diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), Parkinson's disease or diabetes.
Can neurogenic bladder cause kidney failure?
If untreated, a neurogenic bladder can cause renal failure and urinary incontinence.
Is there surgery for neurogenic bladder?
Surgeries for neurogenic bladder include: Artificial sphincter. Electrical device implanted near the bladder nerves to stimulate the bladder muscles. Sling surgery.
What are the 2 types of neurogenic bladder?
There are two types of neurogenic bladder.Overactive bladder causes you to have little or no control over your urination. It can also cause you to feel a sudden or frequent need to urinate. ... Underactive bladder occurs when your bladder muscles lose their ability to hold your urine.
Can your bladder repair itself?
The bladder is a master at self-repair. When damaged by infection or injury, the organ can mend itself quickly, calling upon specialized cells in its lining to repair tissue and restore a barrier against harmful materials concentrated in urine.
What Is Neurogenic Bladder?
When neurological (nervous system) conditions affect the bladder, it is called neurogenic bladder. There are two major types of bladder control pro...
What Causes Neurogenic Bladder?
Neurogenic bladder can be congenital (present at birth). Birth defects that can cause neurogenic bladder include: 1. Spina bifida (myelomeningocele...
What Are The Symptoms of Neurogenic Bladder?
The most common symptom of neurogenic bladder is being unable to control urination. Other symptoms include: 1. A weak or dribbling urinary stream 2...
What is neurogenic bladder?
Neurogenic bladder is a condition in which problems with the nervous system affect the bladder and urination. Conditions like stroke and Parkinson’s disease can result in neurogenic bladder. Treatment options include drug therapy and surgery. Appointments & Access. Contact Us.
What causes a bladder to leak?
Leakage can occur if the bladder cannot empty (overflow incontinence), if the sphincter controlling urination doesn’t work (stress incontinence), or if bladder spasms cause the bladder to shrink before the person reaches the toilet (urge incontinence).
What is it called when you can't control your urine?
Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the flow of urine. The storage of urine can be a problem if the bladder is unable to empty fully or if it begins to empty itself before the person reaches the bathroom (a condition known as overactive bladder).
What is the purpose of urodynamic studies?
Urodynamic studies: These bladder function tests measure how much urine the bladder can hold, the pressure within the bladder, how well urine flows, and how well the bladder empties when it is full.
What is botox injection?
Injections of botulinum A toxin (Botox®): A doctor injects Botox into the bladder or urinary sphincters. Bladder augmentation (augmentation cystoplasty): This is a surgery in which segments of the intestine (sigmoid colon) are removed and attached to the walls of the bladder.
What is the bowel used for in urine?
This reduces the bladder's internal pressure and increases its ability to store urine. Ileal conduit: Part of the small bowel is used to make a urine stoma. This stoma drains to a bag attached to the outside of the body.
Where is the bladder located?
The bladder is a hollow organ located in the pelvis, or lower abdomen. The bladder has two important functions: It stores urine. It removes urine from the body through a complex communication circuit in the spinal cord and brain. Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the flow of urine.
What is neurogenic bladder?
Neurogenic bladder affects many Americans and occurs when there is a problem with the way your brain communicates with your bladder. People who have a neurogenic bladder usually experience a bladder that is either overactive (spastic) or underactive (flaccid).
How do neurogenic bladders work?
Many people with neurogenic bladders use a catheter to control their bladder. A catheter is a thin tube that is inserted into the urethra and then into the bladder to allow urine to drain from the bladder. While using a catheter may sound a little intimidating at first, most people are able to master the process quickly and it can provide a great deal of freedom for those struggling with bladder control.
What is the procedure to make the bladder bigger?
If all else fails, there are different surgeries available to treat neurogenic bladder. Bladder augmentation is a surgical procedure to make the bladder larger. This helps reduce the pressure in the bladder, and reduce leaks.
How to control bladder pressure?
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help ease pressure placed on the bladder and also strengthen the pelvic floor muscles used to control bladder function.
Can neurogenic bladder be treated?
Treatments For Neurogenic Bladder. Having a neurological condition, such as Multiple Sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease can be overwhelming, both physically and emotionally. But one thing many people may not realize is how it will affect their bladder. Luckily, there are treatments available that can help to minimize symptoms ...
How to determine if you have neurogenic bladder?
In addition to reviewing your medical history and conducting a physical exam, your doctor may recommend a variety of diagnostic tests to determine if you have neurogenic bladder. These may include: a cystometrogram to test bladder function and capacity. an electromyography to test bladder muscle tone and coordination. spinal and brain imaging.
What are the symptoms of neurogenic bladder?
Neurogenic bladder symptoms include: a dribbling stream when urinating. an inability to fully empty your bladder. straining during urination. a loss of bladder control. increased urinary tract infections (UTIs) leaking urine. difficulty determining when your bladder is full.
How to prevent bladder from becoming full?
Your doctor will likely recommend a variety of treatments. They may suggest that you urinate at regular intervals, which will prevent your bladder from becoming too full. Your doctor may also ask you to keep a journal to record any leakage incidents. This can help you determine the best intervals for urinating.
What are some ways to help with bladder control?
Other surgical options include bladder reconstruction surgery which may help with bladder control. Medical manufacturers are continuing to release new inventions, such as bladder slings, to reduce symptoms and help improve bladder control.
Why does my bladder not empty?
Because this condition causes you to lose the sensation to urinate, your bladder can fill beyond typical capacity and leak. But your bladder may not empty fully. This is called urinary retention. Urinary retention increases your risk of a UTI.
What is the procedure to release urine?
Catheterization. In some instances, your doctor may recommend catheterization to ensure complete bladder emptying. This painless process involves inserting a thin plastic tube into the bladder to release urine. However, this procedure carries the risk for increased UTIs.
What diseases affect the bladder?
Alzheimer’s disease. tumors of the brain or spinal cord. multiple sclerosis. Parkinson’s disease. injury to the spinal cord. spinal cord birth defects, such as spina bifida. stroke . Conditions that affect the bladder muscles include: diabetes, which can cause nerve damage.
What is neurogenic bladder?
What is a neurogenic bladder? The muscles and nerves of the urinary system work together to hold and release urine at the right time. Nerves carry messages between the bladder and the spinal cord and brain. The messages tell the muscles of the bladder to either tighten or release. In neurogenic bladder, these nerves don’t work the way they should.
What tests are done to determine if you have neurogenic bladder?
He or she will review your health history and do a physical exam. Other tests may include: X-rays of the skull and spine.
Why does urine keep coming back?
Urine retention happens if the muscles holding urine in do not get the message that it is time to pass urine. Damage to the tiny blood vessels in the kidney may happen if the bladder becomes too full and urine backs up into the kidneys. This causes extra pressure and may lead to blood in the urine.
What is the treatment for kidney failure?
It may include medicine, urinary catheters, antibiotics to reduce the chance of infection, and, in severe cases, surgery. Some complications of include urine leakage, inability to pass urine, kidney damage, and kidney or urinary tract infections.
How to get rid of bladder stones?
Emptying the bladder with a catheter at regular times. Preventive antibiotics to reduce infection. Placing an artificial cuff around the neck of the bladder which can be inflated to hold urine and deflated to release it. Surgery to remove stones or blockages. Botox injections into the bladder muscle.
What is the UTI in kidney stones?
Urinary tract infection (UTI) Kidney stones. Urinary incontinence (unable to control urine) Small urine volume during voiding. Urinary frequency and urgency. Dribbling urine. Loss of feeling that the bladder is full. The symptoms of neurogenic bladder may look like other conditions.
How to treat neurogenic bladder?
Potential surgical treatments for neurogenic bladder include: Electrical device implanted near the bladder nerves to stimulate the bladder muscles. Creation of an opening (stoma) in which urine flows into a special pouch (this may include diverting urine away from the bladder, a "urinary diversion")
What medicine can help with neurogenic bladder?
Medicine for Neurogenic Bladder. Medicines may help manage symptoms. Your health care provider may suggest: Overactive bladder medicines that relax the bladder such as oxybutynin, tolterodine, or solifenacin, as well as mirabegron. Bladder muscle injections to relax the bladder, such as injection of Botulinum toxin.
What are the complications of neurogenic bladder?
Complications of neurogenic bladder may include: Constant urine leakage can cause skin to break down and lead to pressure sores. Kidney damage can occur if the bladder becomes too full, or if excess pressure in the bladder causes urine back up to the kidneys. Urinary tract infections.
What supplements are used for urinary infections?
Supplements and suppressive medications to prevent urinary infections, such as cranberry-based supplements, mandelamine (a medication to prevent bacterial growth) or specific vitamins may be considered for patients who are susceptible to infection. Some patients with neurogenic bladder may need to use a urinary catheter.
What is the best treatment for an overactive bladder?
Other types of medication that can affect the nervous system such as GABA supplements and anti-epileptic drugs. Most of these treatments help to calm an overactive bladder. Unfortunately, there are few, if any, treatments to improve the strength of the bladder muscle.
What is pelvic floor therapy?
Pelvic floor therapy - teaching patients skills or techniques to control the muscles and nerves involved in urinating. Exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles (Kegel exercises) Biofeedback to provide training to learn how to do the above with the aid of a computer.
What is neurogenic bladder?
Neurogenic bladder is when a problem in your brain, spinal cord, or central nervous system makes you lose control of your bladder. You may pee too much or too little. You could have symptoms of both overactive bladder (OAB) and underactive bladder (UAB). You may not be able to fully empty it.
How to get rid of a swollen bladder?
Things like caffeine , alcohol, spicy foods, dairy, artificial sweeteners , chocolate, and citrus fruit can irritate your system. Use electrical stimulation. A device under your skin sends electricity to the nerve that controls your bladder.
What is the name of the test that checks for bladder problems?
They may also put dye into your bladder (cystography). EEG or EMG. An electroencephalograph (EEG) checks to see if there's a problem in your brain. An electromyograph (EMG) checks the nerves and muscles in your bladder. Neurogenic Bladder Complications.
Can you empty your bladder?
You may not be able to fully empty it. It’s normal to have some stress and anxiety if you can’t control when you urinate. Talk to your doctor about what’s going on as soon as possible so you can start on a treatment to help manage your symptoms.
Can UAB cause bladder leakage?
With UAB, your brain may not get the signal that it’s time to pee. Or, your urinary muscles may be too tight to let urine pass (obstructive bladder). You could also leak urine when your bladder gets too full ( overflow incontinence ). Other symptoms of neurogenic bladder include:
What Is a Neurogenic Bladder?
Neurogenic bladder is a term that refers to the changes that can occur due to any type of nerve-related injury or disease. The muscles and nerves of the urinary system work together to hold and release urine at the right times.
What Causes Neurogenic Bladder?
Neurogenic bladder can be triggered by a number of disorders, including:
How Is Bladder Dysfunction Diagnosed?
If your physician thinks you may have neurogenic bladder, he or she will review your health history, do a physical exam, and check your brain, spinal cord, and bladder. Other tests may include:
What Treatment Is Available for Neurogenic Bladder?
Treatment for neurogenic bladder depends on the cause. It is aimed at preventing kidney damage and may include:
What Kind of Specialist Handles Patients Who Have a Neurogenic Bladder?
A urologist or urogynecologist can diagnose and treat neurogenic bladder.
What is it and types of neurogenic bladder
When neurological damage occurs to the nervous system , it can affect the bladder. There are several muscles and nerves that work together so that we can hold urine until we go to urinate and empty it.
Neurogenic bladder symptoms
The symptoms of a neurogenic bladder will depend on whether it is an overactive bladder that does not stop contracting or, on the contrary, an underactive bladder, which has no movement at all.
Causes of neurogenic bladder
The causes of neurogenic bladder are disorders in the nervous system or injuries to it, either in the brain or in the spinal cord. Some of the disorders and injuries that can cause this condition are:
Neurogenic bladder: drug treatment
The medical treatment for neurogenic bladder does not solve the problem but tries to improve symptoms. However, early treatment can prevent kidney damage.
Neurogenic bladder: natural treatment
Your doctor may ask you to do certain things like exercises to strengthen your pelvic muscles or keep a urine diary to know when you are going to urinate and thus avoid overflowing. They are good natural remedies. We are going to tell you how these and other natural remedies for neurogenic bladder work.
What is bladder training?
Bladder training: A non-surgical approach helps patients learn the skills and exercises (such as Kegels) needed to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Some patients might be asked to keep a diary recording the time of urination and amount passed, so the patient can establish a more manageable pattern for urination.
What are the symptoms of an underactive bladder?
Symptoms of an underactive bladder include: Full bladder and urine leakage. Inability to tell when the bladder is full. Problems starting to urinate or emptying all the urine from the bladder. Urinary retention.
What is it called when the bladder is not communicating properly with the brain?
One condition your doctor may look into is called neurogenic bladder. It results when the bladder's muscles and nerves are not communicating properly with the brain. Nerve damage from conditions such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, or spina bifida can break down communication between the bladder and the brain.
How to treat a swollen pelvic floor?
Some common treatments include: 1 Bladder training: A non-surgical approach helps patients learn the skills and exercises (such as Kegels) needed to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Some patients might be asked to keep a diary recording the time of urination and amount passed, so the patient can establish a more manageable pattern for urination. 2 Catheterization: In this treatment, patients are taught how to self-insert a small catheter tube in order to empty the bladder at regular intervals. 3 Sacral Neuromodulation: In this relatively new approach, small electrodes and a stimulator are inserted near nerves related to bladder function. The stimulator delivers the electrical impulses that the body would normally receive if the nerves were undamaged.
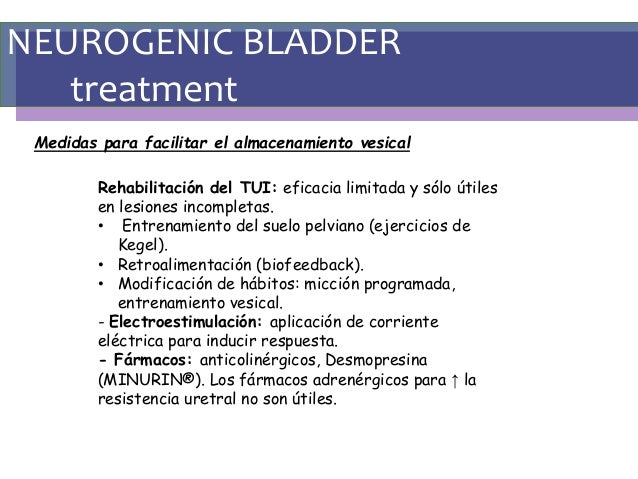
Treatment
- The treatment depends on the cause of NBD. The primary physician may involve a bladder specialistsuch as a urologist, nephrologist, or urogynecologist to coordinate patient care throughout treatment. When bladder dysfunction is caused by a spinal nerve root compression, spine surgery is performed to decompress (take pressure off) the nerves (eg, discectomy). In so…
- Depending on the etiology, various techniques can be employed to maintain renal function and prevent urinary tract infections. Self catheterization, medication or surgical interventions including cystoplasty or sphincterotomy can be employed.
- Neurogenic bladder can be treated with: 1. Medication 2. Urinary catheter 3. Preventive antibiotics 4. Bladder cuff 5. Botox injections 6. Electrical stimulationWhen medical therapy for neurogenic bladder fails, surgery remains as one viable option. Surgery may enhance patient safety or quality of life to a greater extent than nonsurgical approaches. For example, in patients with neurogeni…
Clinical Presentation
- Overflow incontinence is the primary symptom in patients with a flaccid or spastic bladder. Patients retain urine and have constant overflow dribbling. Men typically also have erectile dysfunction. Patients with spastic bladder may have frequency, nocturia and urgency or spastic paralysis with sensory deficits.A full clinical history and examination should be taken, including …
- Depending on the location of the injury in the nervous system, patients typically present with increased frequency, nocturia, urinary incontinence/urgency, urinary tract infection and urinary retention. Bladder may be hyperreflexic, hyporeflexic or areflexic with impaired to no sensation 3. A number of classification schemes exist for neurogenic bladders, including the Lapides class…
Complications
- These include: 1. Reduced quality of life - with social isolation and embarrassment. 2. Increased frequency of urinary tract infections (UTIs) and urinary calculi. 3. Hydronephrosis with vesico-ureteral reflux may occur because the large urine volume puts pressure on the vesico-ureteral junction, causing dysfunction with reflux and, in severe cases, nephropathy. 4. Patients with hig…
- People with neurogenic bladder are prone to complications. Those include frequent urinary tract infections and urinary calculi (solid particles), kidney swelling (hydronephrosis), backward flow of urine from the bladder to the kidneys (vesicoureteral reflux), as well as kidney disease.Over the long term, untreated lower urinary tract dysfunction can lead to the loss of renal function. Risk fa…
Classification
- Several classification systems are available based on neuro-urological criteria or bladder and urethral function.A popular system based on urodynamic findings is as follows:
Function
Epidemiology
Management
- Patients and carers need adequate support and education. Do not underestimate the effect on relationships and quality of life.
Prognosis
- Prognosis is good if the disorder is diagnosed and treated before kidneys are damaged. But it will lead to a significant impact on the lives of patients and carers.