Medication
There is no known treatment or cure for neurofibromatosis or schwannomatosis. Medication can be prescribed to help with pain. In some cases, growths may be removed surgically or reduced with radiation therapy. Although surgery in these areas can cause further injury to nerves and additional neurological problems, it is usually well tolerated.
Procedures
· How is neurofibromatosis treated? Though there is no cure for either NF1 or NF2, there are ways to treat the effects the disease. Surgery may be helpful in removing tumors, though there is a risk of the tumors regenerating. For optic gliomas, treatment may include surgery and/or radiation.
Nutrition
· In April 2020 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved selumetinib (Koselugo) as a treament for children ages 2 years and older wth neurofibromatosis type 1. The drug helps to stop tumor cells from growing.
Is there any natural treatment for neurofibromatosis?
· There is no known treatment or cure for neurofibromatosis type 1 or 2. Treatments for both types are aimed at management of the condition and relief of symptoms and may include: Pain medication ; Surgical removal of growths ; Radiation therapy to reduce growths; Regular monitoring Children:
How do you treat neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Treatment While there is no treatment that can reverse NF1, its signs and symptoms can be addressed. Tumors, in particular, may warrant chemotherapy, radiation, surgery or a combination of treatments. In about 60% of people with NF1, symptoms are mild and can be monitored without the need for treatment.
How do medications treat neurofibromatosis?
· Once the type of neurofibromatosis is determined the treatment begins and it involves surgical methods to remove tumors, stereotactic radiosurgery, use of auditory brainstem and cochlear implants, radiotherapy and chemotherapy (if the patient is detected with malignant tumors). How is the treatment done?
How do you get rid of neurofibromas?
There are many ways to remove neurofibromas. Usually a neurofibroma is “excised”, meaning “cut out”, by a scalpel or other means; or they are “destroyed” by electrosurgery. The tumors may also be destroyed (ablated) by desiccation (dehydration or drying), or vaporized using electrosurgery.
Can neurofibromatosis be cured?
There isn't a cure for neurofibromatosis, but signs and symptoms can be managed. Generally, the sooner someone is under the care of a doctor trained in treating neurofibromatosis, the better the outcome.
How do you stop neurofibromas from growing?
There is no medication that can prevent neurofibromas from growing. And, there is nothing you can do that would make more neurofibromas develop. Neurofibromas often appear or grow in size during times of hormone changes such as puberty (which you can't avoid) and pregnancy.
What is the treatment for neurofibromatosis type 1?
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a genetic condition in which benign tumors arise along nerves anywhere in the body. Treatment for these tumors most often includes surgery; it sometimes also includes chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both.
Does neurofibromatosis worsen with age?
Neurofibromas may increase in number with age. Bone deformities. Abnormal bone development and a deficiency in bone mineral density can cause bone deformities such as a curved spine (scoliosis) or a bowed lower leg. Tumor on the optic nerve (optic glioma).
Can neurofibromatosis cause death?
Conclusions: The risk of developing malignant tumors and early death is increased in patients with neurofibromatosis, the most common malignancy being malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. These risks need to be recognized, and the families should be advised to seek genetic counseling and proper follow-up.
Should a neurofibroma be removed?
If the tumor is malignant, such as a malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) or other sarcoma (a neurofibroma that became cancerous), it may be necessary to remove the portion of the nerve that contains cancer cells, as well as some normal tissue around it to prevent the tumor from coming back.
How do you shrink neurofibroma?
An investigational drug called selumetinib can shrink tumors in children and young adults with a genetic syndrome called neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) and may improve symptoms such as pain and reduced mobility that result from tumors called plexiform neurofibromas, which develop in many people with NF1, according to ...
How long can you live with neurofibromatosis?
If there are no complications, the life expectancy of people with NF is almost normal. With the right education, people with NF can live a normal life. Although mental impairment is generally mild, NF1 is a known cause of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Learning disabilities are a common problem.
Is NF1 serious?
The symptoms of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) are often mild and cause no serious health problems. But some people will have severe symptoms. The symptoms of NF1 can affect many different areas of the body, but it's unlikely someone will develop all of them.
How is neurofibromatosis detected?
A physical examination by a doctor familiar with the disorder is usually performed. Doctors may use special lamps to examine the skin for café-au-lait spots. Doctors may also rely on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-rays, computerized tomography (CT scan) and blood tests to detect defects in the NF1 gene.
How is NF1 diagnosed?
Your child's doctor will look for signs of NF1 in your child's skin, eyes, bones or brain. The second method is genetic testing, also called a molecular or DNA diagnosis. Your child will need to give a blood sample. A lab will check the sample for a change (mutation) in the NF1 gene.
Can neurofibromatosis be treated?
Known growths are often imaged with periodic surveillance scans with treatment reserved for enlarging or symptomatic growths. There is no known treatment or cure for neurofibromatosis or schw annomatosis. Medication can be prescribed to help with pain.
Does the AANS endorse neurofibromatosis?
Children’s Tumor Foundation: Ending Neurofibromatosis Through Research. Neurofibromatosis Network. The AANS does not endorse any treatments, procedures, products or physicians referenced in these patient fact sheets. This information is provided as an educational service and is not intended to serve as medical advice.
What is NF1 in children?
Some people with this disorder have barely noticeable neurological problems, while others are affected profoundly. There are two major types: neurofibromatosis type I (NF1) and neurofibromatosis type II (NF2). NF1 manifests itself at birth or during early childhood.
What is a NF1?
There are two major types: neurofibromatosis type I (NF1) and neurofibromatosis type II (NF2). NF1 manifests itself at birth or during early childhood. NF1 is characterized by multiple light brown (café-au-lait) spots concentrated in the groin and underarms and benign tumors under the skin.
What is NF1 characterized by?
NF1 is characterized by multiple light brown (café-au-lait) spots concentrated in the groin and underarms and benign tumors under the skin. Enlargement and deformity of bones and curvature of the spine ( scoliosis) may also be present.
Can NF1 cause scoliosis?
Enlarge ment and deformity of bones and curva ture of the spin e ( scoliosis) may also be present. On occasion, people with NF1 may develop tumors in the brain, on the cranial nerves or involving the spinal cord . NF2 may appear during childhood, adolescence or early adulthood.
What is NF2 in the brain?
NF2 is primarily characterized by benign tumors of the nerves that transmit sound impulses and balance signals from the inner ears to the brain. Tumors commonly affect both the left and right (bilateral) hearing and balance (vestibulocochlear) nerves. A third related disorder, called schwannomatosis, has been recognized.
What is the most common form of neurofibromatosis?
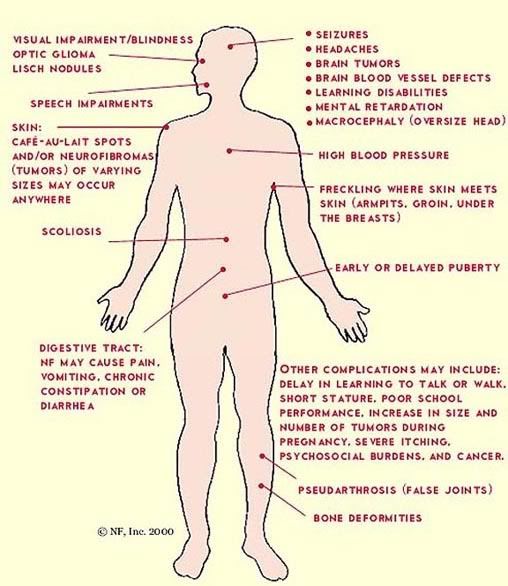
The most common form of neurofibromatosis (NF) is NF-1. It is a genetic disorder that causes tumors to form on nerves. These may occur anywhere in the body. NF is one of the most common genetic disorders. It occurs in every racial and ethnic group and affects both sexes equally. There are at least 100,000 people in the United States with NF. In a city the size of Chicago, as many as 2,300 people have NF. The symptoms and progression of NF is different for each person. Common complications are café au lait ("coffee with milk") spots on the skin, brownish-red spots called Lisch nodules in the colored part of the eye, benign skin tumors called neurofibromas and larger benign tumors of nerves called plexiform neurofibromas. Some signs of NF-1 are usually visible within the first year of life, while other signs of NF-1 may develop as people get older. NF-1 is a progressive disorder and complications are age-specific.
What is NF-2 in the brain?
NF-2 is sometimes referred to as central neurofibromatosis or bilateral acoustic neuroma disease. Much like NF-1, the symptoms and progression of NF-2 is different for each person. NF-2 causes tumors along the nerves leading to the brain or spinal cord, as well as tumors of the covering of the brain and spinal cord, and the spinal cord itself. Because of this, NF-2 can cause serious disabilities. Patients may develop multiple tumors on nerves associated with swallowing, speech, eye movements and facial sensation, and on the spinal nerves going to the arms and legs. Signs of NF-2 are usually not present until people are teenagers or older. The most common symptoms of NF-2 are tinnitus (ringing in the ears), hearing loss and loss of balance.
Is NF a serious disease?
The NF-related disorders include NF-1, NF-2 and schwannomatosis, each with distinguishing symptoms. NF can be a serious and unpredictable disease, however many people with NF live a normal and productive life.
Can NF-1 be passed on to a child?
NF-1 and NF-2 are genetic disorders that may be passed from parent to child, but can also develop due to a spontaneous change in a gene. About half of those with NF-1 and NF-2 do not have a parent with the disorder and represent new genetic changes. The risk of an affected pregnancy for a patient with NF-1 or NF-2 is 50 percent for each pregnancy. The gene that causes NF-1 is different than the one that causes NF-2. Schwannomatosis is predominantly a sporadic condition, which means the risk of passing this disorder on to children is substantially less than in NF-1 and NF-2.
What is Schwannomatosis?
Schwannomatosis is a rare condition defined by the presence of multiple benign tumors of nerves that are frequently very painful. In addition to pain, weakness is a common problem. Symptoms usually begin in young or mid-adult years.
What is neurofibromatosis?
About Neurofibromatosis. Neurofibromatosis is a genetic neurological disorder that can affect the brain, spinal cord, nerves and skin.
Is neurofibromatosis genetic?
However, the genetic cause of this form of NF has not been found. What is neurofibromatosis? Neurofibromatosis (NF) is a genetic neurological disorder that can affect the brain, spinal cord, nerves and skin. Tumors, or neurofibromas, grow along the body's nerves or on or underneath the skin.
What are the symptoms of neurofibromatosis type 2?
Symptoms for neurofibromatosis type 2 include: Tumors along the eighth cranial nerve (schwannomas). Meningiomas and other brain tumors. Ringing noises inside the ear (tinnitus), hearing loss and/or deafness.
What is the most common type of tumor?
Tumors, or neurofibromas, grow along the body's nerves or on or underneath the skin. Scientists have classified NF into two distinct types: neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) and NF2. NF1, formerly known as von Recklinghausen's NF, is the more common of the types. It occurs in approximately 1 in 4,000 births.
How many births are there in NF1?
NF1, formerly known as von Recklinghausen's NF, is the more common of the types. It occurs in approximately 1 in 4,000 births. NF2, also referred to as bilateral acoustic NF, central NF or vestibular NF, occurs less frequently- 1 in 40,000 births.
How often does NF2 occur?
NF2, also referred to as bilateral acoustic NF, central NF or vestibular NF, occurs less frequently- 1 in 40,000 births. Occurrences of NF1 and NF2 are present among all racial groups and affect both sexes equally. The tumors arise from changes in the nerve cells and skin cells.
When does NF1 appear?
Symptoms for NF1 vary for each individual. Those that are skin-related are often present at birth, during infancy and by a child's tenth birthday. From ages 10 to 15, neurofibromas may become apparent.
What You Need to Know
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a condition caused by a change in a specific gene, and therefore can be inherited and passed on.
What is NF1?
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (also called Von Recklinghausen’s disease, Von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis and peripheral NF) is one of the most commoninherited disorders and affects about one in every 3,000 people. NF1 ranges from mild to severe, and can cause more symptoms in some people than in others.
NF1 Symptoms and Diagnosis
Neurofibromatosis type 1 symptoms can involve many different parts of the body. A doctor with expertise in NF1 can provide an accurate diagnosis based on the symptoms, family history, as well as genetic testing and other imaging tests or biopsy.
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Treatment
While there is no treatment that can reverse NF1, its signs and symptoms can be addressed. Tumors, in particular, may warrant chemotherapy, radiation, surgery or a combination of treatments. In about 60% of people with NF1, symptoms are mild and can be monitored without the need for treatment.
Does neurofibromatosis cause headaches?
The treatment of neurofibromatosis does not generally have major side effects. However, in case some major side effects are seen to occur, then the patient must immediately consult his/her doctor. Some of the side effects of the treatment of neurofibromatosis include headache, nausea, skin rash, impaired wound healing, irregular menstrual cycle, ...
When should neurofibromatosis be treated?
It is recommended that the treatment of neurofibromatosis should begin at a young age, when the symptoms of this problem first appear, in order to get effective results.
What are the different types of neurofibromatosis?
There are mainly three types of neurofibromatosis. These are neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), and schwannomatosis. The symptoms of NF1 involve occurrence of flat light brown spots on the skin, ...
What tests are used to diagnose neurofibromatosis?
The physical examinations for the treatment of neurofibromatosis includes monitoring of blood pressure of the patient, growth and development, eye and ear examination, checking for skeletal deformities and imaging tests such as Xray imaging, CT scan and MRI to detect bone deformity and formation of tumors in brain and/or spinal cord.
Is neurofibromatosis benign or non-cancerous?
The tumors that form in this case are usually non-cancerous (benign). However, a few cases, though rare, has been reported regarding the development of malignant tumors. This problem is generally diagnosed within a person in their childhood or during early adulthood. There are mainly three types of neurofibromatosis.
What is the treatment for neurofibromatosis?
Once the type of neurofibromatosis is determined the treatment begins and it involves surgical methods to remove tumors, stereotactic radiosurgery, use of auditory brainstem and cochlear implants, radiotherapy and chemotherapy (if the patient is detected with malignant tumors).
Can neurofibromatosis be surgically removed?
In cases of severe symptoms, the doctor might even recommend for surgical treatments if necessary. For patients having neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) and experiencing complete or partial hearing loss or tumor growth, the doctors might recommend for surg ical treatments to remove the tumors that were causing the problem .
What is the best treatment for neurofibroma of the skull base?
At UPMC, the preferred surgical treatment for neurofibroma of the skull base is the Endoscopic Endonasal Approach (EEA).
How do surgeons remove neurofibroma?
Surgeons then remove the neuro fibroma through the nose and nasal cavities.
What is a neurofibroma?
Neurofibromas are benign tumors of peripheral nerves. They arise from the cells that form and support the nerve sheath: Schwann cells, fibroblasts, and perineural cells. These tumors infiltrate the nerve and disrupt the sheaths of individual fibers. The most commonly affected nerve is the vestibulocochlear nerve, ...
Which nerve is most commonly affected by neurofibroma?
The most commonly affected nerve is the vestibulocochlear nerve, which transmits sound and balance information to the brain from the inner ear. Neurofibromas can be single or multiple. When multiple, they are associated with neurofibromatosis type I, a genetic disorder also known as von Recklinghausen disease.
Can a neurofibroma be single?
Neurofibromas can be single or multiple. When multiple, they are associated with neurofibromatosis type I, a genetic disorder also known as von Recklinghausen disease. Symptoms depend on the location and size of the tumor. Neurofibromas typically are painless, slow-growing masses, and may cause no symptoms.
How to diagnose neurofibroma?
Diagnosing Neurofibroma. To diagnose neurofibroma, your doctor will: Perform a physical exam. Ask about any symptoms you are experiencing. Symptoms of neurofibroma and neurofibromatosis. Symptoms depend on the location and size of the tumor. Neurofibromas typically are painless and slow-growing.
Can neurofibroma be diagnosed with MRI?
Imaging and radiology tests to diagnose neurofibroma and neurofibromatosis. Your doctor may order an MRI to diagnose neurofibroma because it has a characteristic appearance on the scan.
What are the signs of neurofibromatosis?
Signs and symptoms of neurofibromatosis may vary from person to person.
Can neurofibromatosis be cured?
Presently, there is no cure for any type of neurofibromatosis. Conditions, however, can be treated and managed for an improved quality of life. Treatment generally focuses on managing symptoms (such as pain, headache, and seizures) and preventing complications.