What is the treatment for multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN)?
· Doctors may use chemotherapy, radiation therapy or hormone-based therapy for advanced cases. Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic By Mayo Clinic Staff Multiple endocrine neoplasia, type 1 (MEN 1) care at Mayo Clinic Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic Symptoms & causes Doctors & departments Oct. 29, 2021 Print Show references
How successful is surgery for multiple endocrine neoplasia?
Surgery is often the main therapy for MEN. Like all surgeries, surgery to treat multiple endocrine neoplasia is most successful when performed by a specialist with a great deal of experience in the particular procedure. MD Anderson surgeons are …
What is multiple endocrine neoplasia?
· INTRODUCTION. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is an autosomal dominant disorder classically characterized by predisposition to tumors of the parathyroid glands (which occur in the large majority of patients by age 50 years), anterior pituitary, and pancreatic islet cells ( figure 1 ). MEN1 also includes a predisposition to ...
What are the treatment options for neuroendocrine tumors?
· Other treatment options include surgery to remove the tumor(s), freezing or burning tumors that have spread to the liver without removing them, and, more rarely, systemic chemotherapy—treatment with anticancer drugs that travel through the …

What is the treatment for MEN1?
Surgery is often successful in removing MEN1-related tumors and curing related symptoms. But in some cases, the tumors may grow back or spread to lymph nodes link, the liver, or, more rarely, the bones. Your doctor may prescribe medicines to reduce the size of the tumor and treat related problems.
Is there a cure for endocrine neoplasia?
Genetic screening tests can be done to detect disease in family members of people who have multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes. No cure is available, but doctors treat the changes in each gland as they occur with surgery or with drugs to control excess hormone production.
Can MEN1 be cured?
MEN 1 can't be cured. But regular testing can detect problems, and doctors can provide treatment as needed. MEN 1 is an inherited disorder. This means people who have the gene mutation can pass it on to their children.
Can you live a normal life with MEN1?
Nevertheless, despite the advances in treatment of MEN1 tumors and associated functional syndromes, the life expectancy of patients remains shorter than normal population (death mean age: 55 years) (Norton et al. 2015a). MEN1 probands present a mean interval of survival of 18 years after the clinical diagnosis.
What organs are affected by multiple endocrine neoplasia?
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is a hereditary condition associated with tumors of the endocrine (hormone producing) glands. MEN1 was originally known as Wermer syndrome. The most common tumors seen in MEN1 involve the parathyroid gland, islet cells of the pancreas, and pituitary gland.
What is the most common cause of multiple endocrine neoplasia?
Multiple endocrine neoplasia is caused by gene mutations that are handed down in families.MEN1 is caused by gene mutations in the MEN1 gene.MEN2 is caused by gene mutations in the RET gene.
How do you know if you have multiple endocrine neoplasia?
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia SymptomsHyperparathyroidism, which means the parathyroid gland produces too much hormone. ... High levels of gastrin, ulcers, inflammation of the esophagus, diarrhea and abdominal pain.Headaches and changes in vision.Problems with sexual function and fertility.More items...
Is multiple endocrine neoplasia an autoimmune disorder?
Autoimmune Addison's disease (AAD) is a rare condition occurring either in isolation or associated with other autoimmune diseases as part of an autoimmune polyglandular syndrome (APS) type 1, 2 or 4. Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type 1, 2 or 4 is a hereditary autosomal dominant cancer syndrome.
Is there a blood test for MEN1?
Genetic testing of a blood sample can identify MEN1 gene mutations in many people with symptoms. A positive test result can confirm a diagnosis or identify family members at risk of developing MEN1.
What Is Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1?
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is a hereditary condition associated with tumors of the endocrine (hormone producing) glands. MEN1 was o...
What Are The Estimated Cancer Risks Associated With Men1?
Approximately 1 out of 3 islet cell tumors of the pancreas are cancerous. If the cancer has spread, the most common site of spread is the liver. A...
What Are The Treatment Options For The Endocrine Tumors?
Most of these tumors are treated with surgery or by taking a medicine that suppresses growth or function of the tumor. Parathyroid tumors, which ar...
Questions to Ask The Doctor
If you are concerned about your risk of cancer, talk with your doctor. Consider asking the following questions of your doctor: 1. What is my risk o...
Our Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Treatments
If you are diagnosed with multiple endocrine neoplasia, your doctor will discuss the best options to treat it. This depends on several factors, including the type of disease and your general health. Your treatment for MEN will be customized to your particular needs.
Clinical Trials
MD Anderson patients have access to clinical trials offering promising new treatments that cannot be found anywhere else.
Knowledge Center
Find the latest news and information about multiple endocrine neoplasia in our Knowledge Center, including blog posts, articles, videos, news releases and more.
myCancerConnection
Talk to someone who shares your cancer diagnosis and be matched with a survivor.
Prevention and Screening
Many cancers can be prevented with lifestyle changes and regular screening.
What is the most common manifestation of a MEN1?
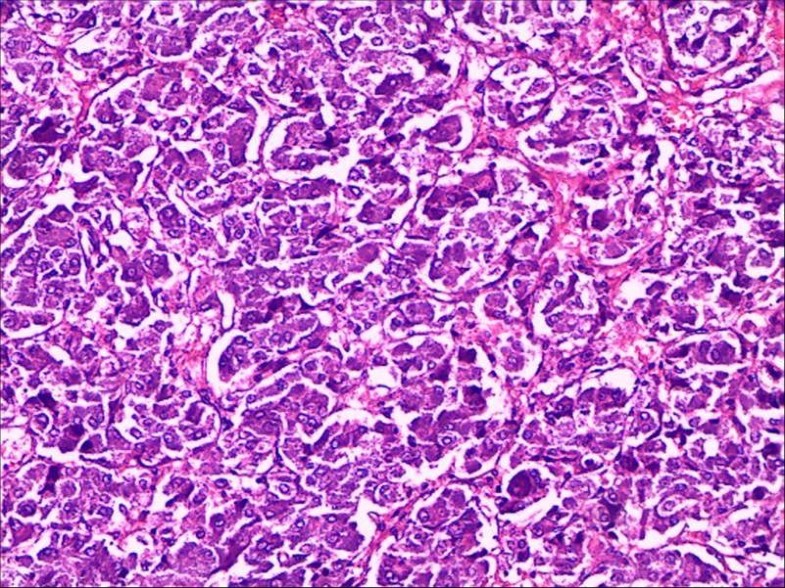
Multiple parathyroid tumors causing primary hyperparathyroidism are the most common manifestation of MEN1, with over 90 percent penetrance by age 50 to 70 years [ 1-3 ]. Pathologic hypercellularity of multiple glands is common in these patients and, given sufficient time, perhaps universal. Patients with classical MEN1 are at high risk of recurrent hyperparathyroidism after apparently successful subtotal parathyroidectomy.
What is a MEN1?
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is an autosomal dominant disorder classically characterized by predisposition to tumors of the parathyroid glands (which occur in the large majority of patients by age 50 years), anterior pituitary, and pancreatic islet cells ( table 1 ). MEN1 also includes a predisposition to gastrinomas in the duodenum, carcinoids, adrenal adenomas, angiofibromas, lipomas, and other tumors ( table 2 ). The most common types of tumors in MEN1 are generally benign, but malignancy of some carcinoid, islet cell, and gastrointestinal tract tumors are important causes of mortality in MEN1. Treatment of MEN1 can differ markedly from that of more common sporadic forms of the relevant endocrine tumors, and referral to centers with major experience and multidisciplinary expertise in MEN1 is strongly recommended.
What is MEN1 tumor?
MEN1 causes tumors to develop in endocrine glands and other parts of the body. Although most of these tumors are noncancerous, they can cause the affected glands to increase in size and become overactive, producing too much hormone.
What are the most common pituitary tumors?
In people with MEN1, the two most common pituitary tumors are. Prolactinomas. The most common pituitary tumor in people with MEN1, prolactinomas produce the hormone prolactin. Normally, this hormone signals women’s breasts to produce milk during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
What is a MEN1?
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is a rare genetic disorder that mainly affects the endocrine glands. Located in different parts of the body, these glands control the production of hormones that direct many body processes, including growth, digestion, and sexual function. MEN1 can affect the parathyroids, pancreas, and pituitary glands.
What is MEN1 in biology?
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is a rare genetic disorder that mainly affects the endocrine glands. Located in different parts of the body, these glands control the production of hormones that direct many body processes, including growth, digestion, and sexual function. View full-sized image.
Where is the parathyroid gland located?
The parathyroid glands are located on or near the thyroid gland in the neck. Hyperparathyroidism. MEN1-related tumors cause the parathyroid glands to become overactive, producing too much parathyroid hormone. This condition, called hyperparathyroidism, is the most common complication associated with MEN1.
Where do tumors form?
Over time, some of these tumors may become cancerous. Insulinomas. These tumors form only in the pancreas, in cells that produce the hormone insulin. Insulin controls levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) by moving glucose into the cells, where it can be used for energy.
What are some examples of MEN1?
MEN1 can also cause tumors in other parts of the body. Examples include. tumors in other endocrine glands, such as the adrenal glands. carcinoid tumors —slow-growing tumors most often found in the stomach, thymus, and lungs.
What is the treatment for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor?
Patients with a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor that has spread to the liver may be treated with a somatostatin analogue or a drug that regulates signaling in the pancreatic islet cell, everolimus. Other neuroendocrine tumors are typically removed by surgery and other treatments may be recommended.
Where do neuroendocrine tumors spread?
A small percentage of mediastinal neuroendocrine tumors are cancerous and spread to local (nearby) lymph nodes or to the liver, lung, or other locations.
What is a MEN1?
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is a hereditary condition associated with tumors of the endocrine (hormone producing) glands. MEN1 was originally known as Wermer syndrome. The most common tumors seen in MEN1 involve the parathyroid gland, islet cells of the pancreas, and pituitary gland. Other endocrine tumors seen in MEN1 include ...
What are the most common tumors in men1?
The most common tumors seen in MEN1 involve the parathyroid gland, islet cells of the pancreas, and pituitary gland. Other endocrine tumors seen in MEN1 include adrenal cortical tumors, neuroendocrine tumors (previously called carcinoid tumors), and rare pheochromocytomas, as well as tumors in other parts of the digestive tract.
Is ependymoma a tumor?
ependymoma, which is a tumor from nervous system tissue; uncommon. The majority of tumors in people with MEN1 are benign (noncancerous). However, approximately 1 out of 3 pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and mediastinal neuroendocrine tumors are cancerous, meaning the tumor can spread to other parts of the body.
Can pancreatic cancer spread to other parts of the body?
However, approximately 1 out of 3 pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and mediastinal neuroendocrine tumors are cancerous, meaning the tumor can spread to other parts of the body. These tumors can also cause problems by producing high amounts of hormones. There is a wide variety of symptoms that can occur due to this increased hormone production by ...
What are the symptoms of a breast cancer?
There is a wide variety of symptoms that can occur due to this increased hormone production by this type of tumor. These include increased production of: Prolactin, which causes abnormal milk production by the breast, lack of menstruation in women, and lowered testosterone production in men.
How Do Doctors Diagnose MEN-1?
If your child is showing symptoms of MEN-1, one or more of the following are used to diagnose MEN-1:
What Treatments Are Available for MEN-1?
There is currently no cure for MEN1. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and remove tumors. Without proper treatment, MEN-1 can be life-threatening.
Appointments and Referrals
Request an appointment or second opinion, refer a patient, find a doctor or view test results with MGHfC's secure online services.
What is multiple endocrine neoplasia?
Collapse Section. Multiple endocrine neoplasia is a group of disorders that affect the body's network of hormone-producing glands called the endocrine system. Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream and regulate the function of cells and tissues throughout the body.
What are the different types of endocrine neoplasia?
The major forms of multiple endocrine neoplasia are called type 1, type 2, and type 4. These types are distinguished by the genes involved, the types of hormones made, and the characteristic signs and symptoms. Many different types of tumors are associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia. Type 1 frequently involves tumors ...
Is endocrine neoplasia type 1 autosomal dominant?
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 usually has an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. People with this condition are born with one mutated copy of the MEN1 gene in each cell. In most cases, the altered gene is inherited from an affected parent.
What is the name of the tumor that causes high blood pressure?
Some people with this disorder also develop a pheochromocytoma, which is an adrenal gland tumor that can cause dangerously high blood pressure. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 is divided into three subtypes: type 2A, type 2B (formerly called type 3), and familial medullary thyroid carcinoma (FMTC).
What is the function of menin?
Although the exact function of menin is unknown, it is likely involved in cell functions such as copying and repairing DNA and regulating the activity of other genes. When mutations inactivate both copies of the MEN1 gene, menin is no longer available to control cell growth and division.
What happens if you have a MEN1 mutation?
Almost everyone who is born with one MEN1 mutation acquires a second mutation in certain cells, which can then divide in an unregulated way to form tumors. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 and type 4 are also inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
What is the RET gene?
Mutations in the RET gene cause multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2. This gene provides instructions for producing a protein that is involved in signaling within cells. The RET protein triggers chemical reactions that instruct cells to respond to their environment, for example by dividing or maturing.
What are the symptoms of multiple endocrine neoplasia?
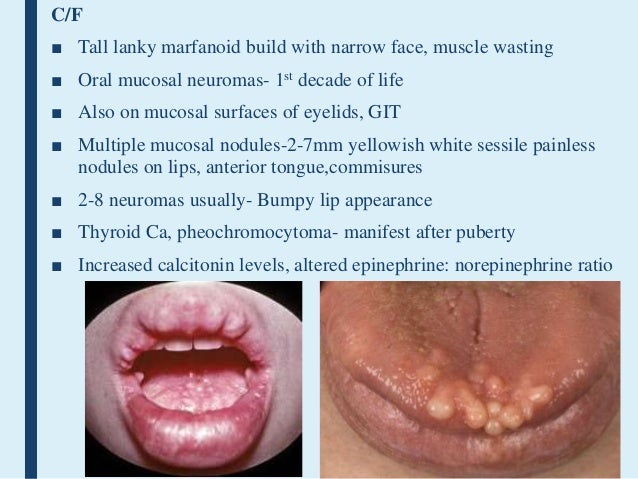
Symptoms of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 include: Symptoms of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B include: Growths around nerves (neuromas) of mucous membranes, such as the lips and tongue.
How to treat hyperparathyroidism?
Hyperparathyroidism caused by MEN1 is usually treated with surgical removal of three-and-a-half of the four parathyroid glands (though sometimes all four glands are removed) with a portion of the parathyroid gland inserted into the forearm. Medications to help balance hormone levels or treat symptoms.
What is a MEN1 tumor?
Multiple endoc rine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) (also called multiple endocrine adenomatoses or Wermer's syndrome) Tumors usually are benign but can cause problems by releasing too much hormone or growing against other parts of the body. About half of people with MEN1 eventually develop cancer. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2)
Can a tumor cause cancer?
Tumors usually are benign but can cause problems by releasing too much hormone or growing against other parts of the body. About half of people with MEN1 eventually develop cancer. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2) MEN2 is divided into three types: Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2A (MEN2A)
What are the symptoms of acromegaly?
Enlargement of bones ( acromegaly) Cushing’s syndrome. Excess production of breast milk. Symptoms of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B include: Growths around nerves (neuromas) of mucous membranes, such as the lips and tongue. Thickening of eyelids and lips. Abnormalities of the bones of the feet and thighs.
What are the symptoms of Cushing's syndrome?
Cushing’s syndrome. Excess production of breast milk. Symptoms of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B include: Growths around nerves (neuromas) of mucous membranes, such as the lips and tongue. Thickening of eyelids and lips. Abnormalities of the bones of the feet and thighs. Spinal curvature.
What is MEN1 and MEN2?
Multiple endocrine neoplasia is caused by genetic mutations passed down in families. MEN1 is caused by gene mutations in the MEN1 gene. MEN2 is caused by gene mutations in the RET gene. Children of parents who have MEN syndrome have a 50% chance of developing the disease.