Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
A chronic digestive disease where the liquid content of the stomach refluxes into the esophagus.
What are the treatment options for esophageal motility disorders?
Medical treatment of esophageal motility disorders involves the uses of agents that either reduce (anti-cholinergic agents, nitrates, calcium antagonists) or …
What is ineffective esophageal motility?
Physical Therapy. Physical therapy exercises can address behavioral and functional issues, especially for chronic constipation. Children may be afraid of pain from a bowel movement and may not use the bathroom when they feel the urge to go. Our physical therapists work with your child to retrain the pelvic muscles.
What causes esophageal dysmotility?
Sep 16, 2020 · Drugs used in the management of intestinal motility disorders include parasympathomimetics, prokinetic agents, opioid antagonists, antidiarrheals, and antibiotics. The agents that are most useful...
What are motility issues?
Standard treatment of these motility disorders begins by ruling out GERD by empiric treatment with proton pump inhibitors. Once GERD is ruled out, different classes of smooth muscle relaxants are commonly used, including nitrates, calcium channel blockers, or phosphodiesterase inhibitors such as sildenafil (Viagra, Pfizer).
Can motility disorders be fixed?
There are many treatment options for motility disorders, including medication, diet modification and surgery. Your gastroenterologist will work closely with you to understand your diagnosis, symptoms and goals for treatment.
What causes intestinal motility disorder?
There are secondary causes of intestinal dysmotility. Examples of this include systemic Lupus erythematosus, amyloidosis, neurofibromatosis, Parkinson's disease, diabetes, scleroderma, thyroid disorders, and muscular dystrophies. Certain medications can also cause intestinal dysmotility.
Can bowel motility be improved?
Probiotics. Taking probiotic supplements has been shown to improve the transit time and regularity of bowel movements.
How do you treat intestinal dysmotility?
Medications for Dysmotility If there is a blockage in the intestine that needs to be expelled, doctors may recommend that patients take laxatives. This will help soften and propel any blockages in the intestinal tract and allow patients to digest food in a more normal manner.Feb 28, 2019
How can I restore my intestinal motility?
If your transit time is a concern, there are some steps you can take to speed things up.Exercise for 30 minutes a day. Food and digested material is moved through the body by a series of muscle contractions. ... Eat more fiber. ... Eat yogurt. ... Eat less meat. ... Drink more water.Mar 18, 2019
What slows down GI motility?
Certain medications that slow the rate of stomach emptying, such as narcotic pain medications. Scleroderma — a connective tissue disease. Nervous system diseases, such as Parkinson's disease or multiple sclerosis. Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)Oct 10, 2020
What drugs increase GI motility?
Medication Summary The agents that are most useful in the treatment of these disorders are neostigmine, bethanechol, metoclopramide, cisapride, and loperamide. Neostigmine appears to increase antral and intestinal motor activity in patients with hypomotility, including intestinal dysmotility.Sep 16, 2020
Is IBS a motility disorder?
IBS has also been called 'spastic colon,' implying a motility disorder. Some IBS patients may show altered motor patterns or transit depending on changes in stool patterns. Altered motility from abnormal gut contractions may result in IBS symptoms such as abdominal pain and discomfort.
Can a lazy bowel be fixed?
Dietary changes, such as increasing water and probiotic intake (i.e. yogurt or supplements) while limiting dairy, caffeine, and heavily processed foods may be an effective treatment for lazy bowel syndrome and chronic constipation.
Can Dysmotility be cured?
Many causes of dysmotility cannot be cured, meaning that treatment is focussed on the symptoms rather than the cause. This may involve dietary changes, medications to stimulate intestinal movements, or manipulation of the gut microbes. Only very rarely is surgery indicated and even then results are unpredictable.
What is motility disorder in adults?
Motility disorders are abnormal muscle and nerve contractions that cause spasms or lack of motion anywhere along your gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Your esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, as well as your colon and rectum may be unable to perform their functions in the digestive process.
Gastroenterology
At Boston Medical Center, our specialists will treat your esophageal conditions, such as motility disorders, with the compassion and expertise for which we are known.
What are Motility Disorders?
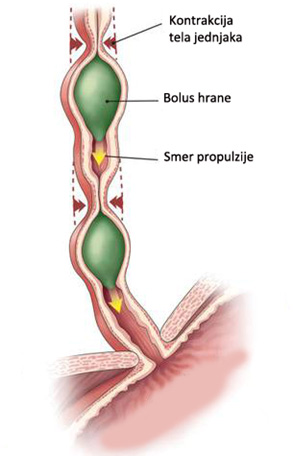
When you swallow, food travels down the esophagus by a series of muscular contractions called peristalsis. At the bottom of the esophagus is a muscular valve (the lower esophageal sphincter or LES) that opens to allow food to enter the stomach and then closes to prevent regurgitation of stomach contents back into the esophagus.
What are the Causes?
The causes of motility disorders are not completely understood, but researchers think infections and family history play a role.
How are Motility Disorders Diagnosed?
There are several ways that physicians may detect a motility disorder, after doing a medical history and physical examination.
How to help a child with constipation?
Physical therapy exercises can address behavioral and functional issues, especially for chronic constipation. Children may be afraid of pain from a bowel movement and may not use the bathroom when they feel the urge to go. Our physical therapists work with your child to retrain the pelvic muscles. Therapy involves teaching children how to recognize when they need to have a bowel movement. Our physical therapists provide balance and stability training for toilet posture, breathing exercises, and specific therapy to help children safely strain and relax the abdominal and pelvic muscles when using the toilet.
What is the purpose of a physical therapist?
Our physical therapists provide balance and stability training for toilet posture, breathing exercises, and specific therapy to help children safely strain and relax the abdominal and pelvic muscles when using the toilet.
What are the symptoms of a swollen stomach?
Motility disorders occur in the upper and lower sections of the digestive tract. They include: 1 Achalasia: Occurs when the esophagus cannot move correctly, leading to food backing up into the esophagus. This causes swallowing difficulties and vomiting. 2 Gastroparesis: A delay of food moving from the stomach into the intestines. This can cause severe nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and weight loss. 3 Pseudo-Obstruction: Can be caused by slow movement of the small intestines, leading to abdominal distention and difficulties with eating. 4 Chronic Constipation: When a child's inability to have regular bowel movements is severe, blocks can form and can cause them to leak stool.
Where to relax at Duke Children's?
If your child is staying at Duke Children’s, you can relax in the Ronald McDonald Family Room. You can grab a light meal, shower, do laundry, or use a computer with internet access.
Why does my child leak poop?
Chronic Constipation: When a child's inability to have regular bowel movements is severe, blocks can form and can cause them to leak stool.
What causes stomach pain and vomiting?
This causes swallowing difficulties and vomiting. Gastroparesis: A delay of food moving from the stomach into the intestines. This can cause severe nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and weight loss.
What is the tube used for upper endoscopy?
Upper Endoscopy. The doctor uses a thin, lighted tube with a camera to look inside the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine for damaged tissue. The tube is inserted through the mouth and down the throat. This can also be used to place other tubes needed for esophageal and small intestine manometry studies.
What are the drugs used to treat intestinal motility?
Drugs used in the management of intestinal motility disorders include parasympathomimetics, prokinetic agents, opioid antagonists, antidiarrheals, and antibiotics. The agents that are most useful in the treatment of these disorders are neostigmine, bet hanechol, metoclopramide, cisapride, and loperamide.
What is the best treatment for irritable bowel syndrome?
Cognitive interventions (eg, cognitive behavorial therapy, hypnotherapy) have been successful in managing abdominal pain in patients with irritable bowel syndrome; however, they have limited utility for routine use in daily practice owing to their labor intensiveness and tight availability.
Why are insoluble fibers important?
In addition, because insoluble fibers create a mass effect in the stomach, they may be helpful in weight control, prevent ing diseases related to obesity (eg, cardiovascular accidents and endocrine disturbances). Prescriptions of laxatives, diuretics, benzodiazepines, and anticholinergic drugs should be limited.
How does lubiprostone work?
Lubiprostone and linaclotide are secretagogues that work by increasing intestinal secretion of chloride, which is followed by secretion of water into the intestinal lumen. Both medications are approved in the treatment of treating chronic constipation and constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.
How old do you have to be to have a colonoscopy?
Any patients older than 50 years should be scheduled for colonoscopy, even if they are not symptomatic. Patients with a history of abdominal surgery who have recurrent bowel habit disorders should be carefully evaluated with an eye to detecting eventual adhesions.
Is surgery a palliative treatment?
Surgery for these patients is always palliative.
Is neostigmine a acetylcholinesterase inhibitor?
Neostigmine is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It is especially important in the treatment of intestinal pseudo-obstruction, particularly in patients in whom conservative treatment has failed and who have a cecal di lation measuring larger than 12 cm. [ 36] Intravenous neostigmine 2 mg is given slowly over 5 minutes.
What causes achalasia?
The cause of achalasia in unknown, but it is associated with many factors, including: 1 Family history 2 Abnormal immune system 3 Possible viral infection 4 Age (most frequently occurs in people ages 30 to 60)
What causes achalasia in the esophagus?
Achalasia is caused by nerve damage in the esophagus, specifically at the muscular valve that connects the bottom of the esophagus to the top of the stomach. The nerves don’t allow this area to relax, which prevents food from entering the stomach. This can lead to another motility symptom, dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing. It can also result in a variety of health complications, including chest pain, weight loss, malnutrition, aspiration pneumonia, esophageal cancer and perforation of the esophagus from the food buildup.
What is constipation in the colon?
Pandolfino. It affects four million Americans on a chronic basis. It’s defined broadly as having a bowel movement less than three times per week, but it can also be related to not feeling completely empty or having to strain to have a bowel movement. The complications of constipation can include:
Can esophageal cancer cause difficulty swallowing?
This can lead to another motility symptom, dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing. It can also result in a variety of health complications, including chest pain, weight loss, malnutrition, aspiration pneumonia, esophageal cancer and perforation of the esophagus from the food buildup.
What are the complications of constipation?
The complications of constipation can include: Hemorrhoids, or swollen veins in the rectum. Anal fissures, or tearing of the rectum. Diverticular disease. Rectal prolapse, when a piece of your intestinal lining pushes out of your anus due to strain. Fecal impaction, when stool gets stuck, causing a backup.
Can GERD cause heartburn?
You’ve likely experienced heartburn after a big, greasy meal. GERD is a more severe version of this , where the valve at the base of the esophagus either opens spontaneously or doesn’t close properly, allowing the acidic stomach juices to enter the esophagus. If left untreated, GERD can cause inflammation or narrowing of the esophagus, dysphagia, Barrett's esophagus, and rarely esophageal cancer.
Can spicy foods cause GERD?
Certain foods, including those that are highly acidic or spicy, can exacerbate GERD symptoms . “We’ve seen patients get their esophageal motility disorders under control with diet therapies,” says Dr. Pandolfino. “This approach has been effective for everything from heartburn to the more complex motility disorders.”.
What is motility clinic?
The Motility Clinic consists of physicians who have special training and interests in disorders of gastrointestinal motility. The major disorders that fall into this category of gastrointestinal conditions include: Functional bowel disorders, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), functional or nonulcer dyspepsia (NUD) ...
What are the different types of motility?
The Motility Clinic consists of physicians who have special training and interests in disorders of gastrointestinal motility. The major disorders that fall into this category of gastrointestinal conditions include: 1 Fecal incontinence 2 Functional bowel disorders, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), functional or nonulcer dyspepsia (NUD) 3 Gastroparesis (slow gastric emptying) that can be associated with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux, nausea, vomiting and anorexia 4 Intractable constipation due to either slow transit or disorders of evacuation 5 Pseudo-obstruction (disorders of gastric and intestinal motility) that can be associated with all of the above in addition to distension, bloating, abdominal pain, undernutrition, weight loss and constipation 6 Undiagnosed diarrheal syndromes
What is pseudo obstruction?
Pseudo-obstruction (disorders of gastric and intestinal motility) that can be associated with all of the above in addition to distension, bloating, abdominal pain, undernutrition, weight loss and constipation. Undiagnosed diarrheal syndromes.
Where can flexible catheters be positioned?
Flexible catheters can be positioned at different levels of the upper gut. By recording the contractions of the intestinal muscle, the strength and coordination of the muscle can be characterized.
What causes gastrointestinal motility?
Gastrointestinal motility can be impaired due to: 1 A problem within the muscles that control peristalsis 2 A problem with the nerves or hormones that govern the muscles' contractions
What is delayed gastric emptying?
Gastroparesis. Gastroparesis is also known as "delayed gastric emptying" (in other words, a stomach that's slow in emptying itself). Your stomach muscles govern the movement of partly digested food through your stomach and into your small intestine.
What happens when you have IBS?
When you have IBS, your digestive motility is altered, moving either too quickly or too slowly, leading to diarrhea or constipation, respectively. These abnormal muscle contractions also contribute to pain and the other symptoms of IBS. 5. What to Know About IBS.
What is Hirschsprung's disease?
Hirschsprung's Disease. Hirschsprung's disease is a congenital disorder in which poor digestive motility causes a blockage in the large intestine. It's far more common in boys than in girls, and it's sometimes linked to other major inherited conditions, such as Down syndrome. 7 . An Overview of Hirschsprung's Disease.
How does food move down the esophagus?
Once you swallow food, it is moved down the esophagus by peristalsis. The muscles in the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine then continue the process, keeping the food moving as it's digested by digestive juices, including stomach acids and bile, that are added along the way.
Is Verywell Health peer reviewed?
Verywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles . Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
What is chronic intestinal pseudo obstruction?
Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction is a rare condition with symptoms similar to those caused by an obstruction or blockage in the bowel. But upon examination, no blockage is found. Instead, the symptoms are due to nerve or muscle problems that affect the movement of food, fluid, and air through the intestines. 8.
What is bowel motility?
Problems With Bowel Motions. Bowel motility disorders (also called intestinal motility disorders), refer to conditions in which the bowel movements are abnormal. In rare cases, all motility may cease. However, in the majority of intestinal motility disorders, bowel motility happens either at an abnormally fast rate or at an abnormally slow rate.
What is the first line of treatment for bowel motility?
In acute cases that cause severe signs and symptoms, endoscopic decompression is the first line of treatment. Surgery is an option in chronic cases of bowel motility disorders. Surgical treatment may involve removal of a part of the intestine (also called intestinal resection).
How does bowel motility affect digestion?
Bowel motility disorders affect the processes of digestion, absorption, and movement of digested material through the intestine. Adverse effects on these processes causes a variety of signs and symptoms. Some of the common signs and symptoms of bowel motility disorders include:
Where do segmentation contractions occur?
Segmentation contractions: Segmentation contractions mainly occur in the small intestine, where the majority of digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs. Segmentation contractions churn the food and expose the broken down mush for absorption of nutrients and water by the cells in the intestinal wall.
What are the symptoms of malnutrition?
Malnutrition caused by inefficient digestion and absorption. Loss of appetite. Weight loss. Not all of the above mentioned signs and symptoms are present in all cases. The exact signs and symptoms present in an individual depends on the underlying cause of bowel motility disorder.
Is small bowel resection a surgical procedure?
Both small bowel resection and large bowel resection are possible surgical options. In cases of intestinal resection in which the remaining cut ends of the bowels are not close enough to be joined, an opening is made in the abdominal wall to connect the end of the bowel and provide an outlet for waste.
What causes peristaltic waves in the gut?
The segmentation contractions and peristaltic waves in the gut are a result of coordination between the smooth muscles and the nerves of the gut. Therefore, nerve and muscle disorders may compromise bowel motility. In fact, bowel motility disorders are seen in some degenerative conditions of the nerve and the muscle.
