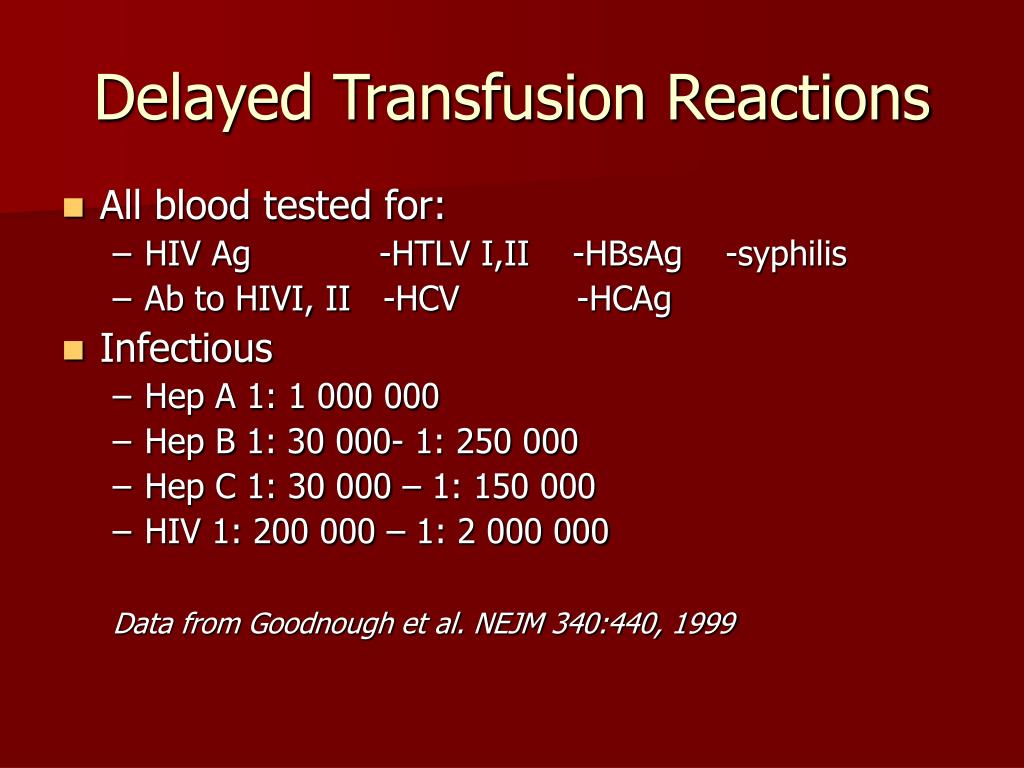
Acute reactions
| Reaction | Prevalence | Symptoms | Onset | Treatment |
| Simple allergic | 1–3% of all transfusions | Rash, itching, and hives | During or within 4 hours | Antihistamines |
| Anaphylactic | 1 in 20,000–30,000 transfusions | Flushed skin, itching, hives, swelling, ... | Seconds to minutes at the beginning of t ... | IV epinephrine, antihistamines, IV stero ... |
| Febrile nonhemolytic transfusion reactio ... | 1–3% per unit of blood transfused | Rise in temperature by at least 1% and c ... | Within 4 hours Trusted Source | Antipyretics |
| Acute hemolytic transfusion reaction | 2–8% per 10,000 units f blood transfused | Fever, flank pain, low blood pressure, r ... | During, immediately afterward, or within ... | Supportive therapy using IV fluids, dial ... |
When to stop a blood transfusion?
Reactions people experience may include:
- Breathing troubles.
- Fevers, chills or rashes.
- Hemolytic transfusion reaction (your immune system tries to destroy transfused red blood cells).
What can cause problems in a transfusion reaction?
What can cause problems in a transfusion reaction? In some cases transfusion reaction can occur due to over load of blood volume. Too much of blood overload can make harder for the heart to pump blood. Iron overload can occur if too much of iron is present in donor blood.
What is the transfusion reaction and why does it happen?
What is a blood transfusion reaction? A blood transfusion reaction is a harmful immune system response to donor blood. Reactions can occur right away or much later, and can be mild or severe. What causes a blood transfusion reaction? Your immune system can react to anything in the donor blood. One of the most serious reactions is called ABO incompatibility.
Why can a transfusion reaction be fatal?
What is the cause for most fatal transfusion reactions? misidentification Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction associated with the infusion of incompatible RBC's Non Hemolytic Transfusion Reactions involves all other types of reactions that don't involve the hemolysis of rbc's Acute Hemolytic Reaction
Which medications are used for mild transfusion reaction?
Premedication with acetaminophen and diphenhydramine is the most commonly used approach to reduce the incidence of FNHTR and allergic reactions to blood products; it is used in 50% to 80% of transfusions in the US and Canada.
What is the first thing you do if the patient develops a reaction to a transfusion?
Transfusion reactions require immediate recognition, laboratory investigation, and clinical management. If a transfusion reaction is suspected during blood administration, the safest practice is to stop the transfusion and keep the intravenous line open with 0.9% sodium chloride (normal saline).
How do you treat a non hemolytic transfusion reaction?
Stop the transfusion immediately and follow other steps for managing suspected transfusion reactions. Treat the fever with an antipyretic. However, avoid aspirin in thrombocytopenic and paediatric patients. Consider and exclude other causes, as fever alone may be the first manifestation of a life-threatening reaction.
Do you remove IV after transfusion reaction?
If a reaction is suspected, the transfusion should be immediately stopped, blood products and tubing removed, and the intravenous line kept open with normal saline.
Why is normal saline given after a blood transfusion reaction?
Background: It is standard practice at many hospitals to follow blood component transfusions with a normal saline (0.9% NaCl) flush. This serves the dual purpose of administering to the patient any residual blood left in the administration set (up to 40 mL), and it flushes the line for later use.
Which would the nurse do first if an allergic reaction to a blood transfusion occurs?
When a transfusion reaction is suspected, the transfusion should be immediately stopped, and the intravenous line should be kept open using appropriate fluids (usually 0.9% saline). A clerical check should be performed by examining the product bag and confirming the patient's identification.
How is a delayed transfusion reaction treated?
Symptomatic patients experiencing DHTR can be immediately treated with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg), adding erythropoietin (EPO) if the DHTR is also associated with reticulocytopenia. Prophylactic anticoagulation is administered to lower the risk of thrombosis associated with EPO administration.
Can medication be given during blood transfusion?
Safety considerations: No medications may be added to blood units or through IV tubing. Specific blood administration tubing is required for all blood transfusions. Blood tubing is changed every 4 hours or 4 units, whichever comes first.
What Is A Blood Transfusion reaction?
A blood transfusion reaction is a harmful immune system response to donor blood. Reactions can occur right away or much later, and can be mild or s...
What Causes A Blood Transfusion reaction?
Your immune system can react to anything in the donor blood. One of the most serious reactions is called ABO incompatibility. The 4 main blood type...
What Increases My Risk For A Blood Transfusion reaction?
1. You had a blood transfusion before. Your immune system will attack donor blood the next time you get a transfusion. 2. You have been pregnant. Y...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of An Immediate reaction?
Healthcare providers will stop the transfusion if you have any of the following: 1. A strong feeling of dread or that something is wrong 2. Faintin...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of A Delayed reaction?
A delayed blood transfusion reaction can begin within 3 to 10 days. You may also have a reaction the next time you receive blood. 1. A high fever a...
How Is A Blood Transfusion Reaction Diagnosed and Treated?
Your blood and urine will be tested for signs of kidney failure or destroyed red blood cells. You may need any of the following to treat a reaction...
How Can I Help Prevent Another Blood Transfusion reaction?
1. Give complete health information. Tell your healthcare providers about your health conditions, transfusions, and pregnancies. 2. Alert your heal...
Call 911 For Any of The Following
1. You have a skin rash, hives, swelling, or itching. 2. You have trouble breathing, shortness of breath, wheezing, or coughing. 3. Your throat tig...
When Should I Seek Immediate Care?
1. You have a seizure. 2. You have a headache or double vision. 3. You are lightheaded, confused, or feel like you are going to faint. 4. You have...
What is blood transfusion?
Blood transfusions are most commonly done for blood components, such as red blood cells, platelets, or plasma. Before a blood transfusion, a medical provider will draw your blood. This sample will be sent to a laboratory for typing and crossmatching. Typing is when the lab determines blood type.
How long does it take for a transfusion to react?
Transfusion reaction symptoms include: In some instances, however, transfusion reactions take place days after the transfusion.
What happens if you give too much blood?
Giving this contaminated blood to a recipient can lead to infection, shock, and death. A transfusion reaction can also occur if a person receives too much blood. This is known as transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO).
How long does it take for a lungs reaction to occur?
This reaction usually occurs within six hours of receiving blood.
What is crossmatching blood?
Crossmatching is testing to determine if your blood is compatible with a donor’s blood of the same type. A number of blood types exist, including: Knowing your blood type is important because red blood cells contain antigens, or protein markers, corresponding to these blood types.
Why is blood mixed with donor blood?
A sample of recipient blood is often mixed with potential donor blood to ensure compatibility. Before the blood is given to you, the blood label and your identity will be thoroughly checked. This ensures the doctor or nurse is giving the proper blood products to the right recipient.
Should blood transfusions be stopped?
If you or your medical provider observes blood transfusion reaction symptoms, the transfusion should be immediately stopped. A laboratory representative should come and draw blood from you and take the donated blood for testing to ensure they were matched appropriately. Transfusion reactions can vary in severity.
What is a transfusion reaction?
Transfusion Reactions: Adverse Effects, Causes and Treatment. A blood transfusion or putting donated blood into a patient’s bloodstream is a procedure used to save lives. It is performed in people undergoing surgery, or in cases of serious loss of blood. A blood transfusion is a delicate procedure that should involve matching blood types ...
What is the most common type of blood transfusion reaction?
Immune-related reactions include: Nonhemolytic fever is the most common type of blood transfusion reactions and is likely to recur with a patient who has had more than one blood transfusion. The reaction does not destroy the red blood cells.
What happens when the immune system mistakenly identifies transfused blood components as harmful and begins to attack them
This reaction is combated by thorough screening before transfusion. Hemolytic transfusion reactions involve the destruction of red blood cells.
Why does hemolytic transfusion cause a reaction?
This causes the recipient body’s immune system to attack the transfused blood, destroying the red blood cells, Mild hemolytic transfusion reactions are caused by a mismatch in one or more of the 100 minor blood types. They are not as serious as a mismatch between blood types or rhesus factors. ...
Why does blood transfusion take longer?
The procedure can take longer if more blood is needs to be transfused. A blood transfusion is stopped immediately if the following adverse reactions occur: A large swelling at the point of transfusion. Apart from the large swelling, the transfusion point will be painful, and you have a burning sensation.
Why do non-immune blood transfusions happen?
Nonimmune blood transfusion reactions usually happen because there is too much fluid caused by transfusion. It mostly happens to first-time patients of a blood transfusion. The condition is treated by putting the patient on medication to increase urination and thereby rid the body of the excess fluid.
What are the symptoms of delayed blood transfusion?
Watch out for the following symptoms: Headaches, blurred vision, and seizures. Yellowish eyes and skin. Fatigue and body weakness. Difficulty in breathing.
What are the ATRs in blood transfusion?
Allergic transfusion reactions (ATRs) occur in up to 3% of transfusions, with rates being highest in platelet and plasma products. 1 Most of these reactions are mild and do not progress in severity. 2 Severe ATRs occur at a lower rate, 7.7% of ATRs or 1 in 20,000 to 47,000 products transfused, but represent 4% of transfusion-related mortalities. 1, 3 As such, great care must be taken in evaluating these patients, although symptoms encountered during severe ATRs typically have more rapid onset compared with symptoms of mild ATRs that rarely evolve to anaphylaxis. 1, 2 It is therefore allowable for the transfusion associated with mild ATRs to be restarted after pausing and administering treatment with an antihistamine medication, usually diphenhydramine, if the patient’s symptoms resolve. 2
Why are transfusions aborted?
Transfusions are often needlessly aborted after occurrence of a mild allergic transfusion reaction ( ATR), leading to wastage and reexposure of recipients to additional blood products (with potential alloimmunization).
How to stop a transfusion?
Alert your healthcare providers about any problems. Tell your healthcare providers right away if something feels wrong. They will stop the transfusion and treat your symptoms.
What is a blood transfusion reaction?
A blood transfusion reaction is a harmful immune system response to donor blood. Reactions can occur right away or much later, and can be mild or severe.
What does it mean when you feel like you have a blood transfusion?
A strong feeling of dread or that something is wrong. Fainting or breathing problems. Fever and chills. Itching, hives, or swelling. Pain or burning in your abdomen, chest, or back, or at the transfusion site. Swelling and a large bruise at the transfusion site. Blood in your urine. Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Why do you stop a blood transfusion?
Pain, nausea, itching, or a large bruise at the transfusion site are good reasons to stop the transfusion. Ask if you can use your own blood. You may be able to get your own blood during surgery. Your blood will need to be drawn and stored a few weeks before a scheduled surgery. Carry medical alert identification.
How long does it take for a delayed blood transfusion to occur?
A delayed blood transfusion reaction can begin within 3 to 10 days. You may also have a reaction the next time you receive blood. Yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes.
Why do you need medicine for a fever?
You may also need medicine to relax muscles in your throat and chest to help you breathe, or to raise your blood pressure. Medicine may also be given to lower a fever. Fluids may be given through your IV to prevent your blood pressure from falling too low.
Can you refuse treatment?
You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
How long does it take for diuresis to resolve?
In febrile, nonhemolytic reactions, fever usually resolves in 15-30 minutes without specific treatment.
Can you take acetaminophen with fever?
If fever causes discomfort, oral acetaminophen (325-500 mg) may be administered. Avoid aspirin because of its prolonged adverse effect on platelet function. In allergic reactions, diphenhydramine is usually effective for relieving pruritus that is associated with hives or a rash. The route (oral or intravenous) and the dose (25-100 mg) ...
What are immune-mediated transfusion reactions?
This topic will mainly address immune-mediated transfusion reactions, which comprise an array of distinct adverse clinical responses to transfusion. They are mediated by the interaction of recipient antibodies to foreign antigens contained in any allogeneic blood products. Acute immune-mediated transfusion reactions occur immediately following, or within 24 hours of, transfusion. They include acute hemolytic, febrile nonhemolytic, allergic (with or without anaphylaxis), and transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI). Delayed immune-mediated transfusion reactions occur within days to weeks of transfusion and include delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction, graft-versus-host disease, and post-transfusion purpura.
How long after a transfusion do you have a reaction?
Immune-mediated transfusion reactions can be classified as acute or delayed. Acute reactions occur within 24 hours of transfusion and include acute hemolytic, febrile nonhemolytic, allergic, and transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI). Delayed reactions occur days to weeks after the transfusion and include delayed hemolytic transfusion ...
What should every patient receiving blood products be placed on?
Every patient receiving blood products should be placed on cardiac monitoring and continuous pulse oximetry. If a reaction is suspected, stop the transfusion and discontinue any plans for future transfusions. If applicable, alerting the blood bank of the reaction as immediately as possible will prevent incorrect transfusion ...
Is TACO treated with furosemide?
Hypoxemia from pulmonary edema can be improved with bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP) in the short term, and diuretics such as furosemide can help with fluid management in the less immediate management.
When is a transfusion needed?
It may be necessary if there is severe loss of blood from the body or if the blood and its components are not produced enough. Blood loss usually occurs after an injury or an accident or during the surgical procedure. Production of blood may be affected in illness, ...
What is the reaction to blood transfusion?
The reaction is characterized by fever and rigors. A mild allergic reaction may occur during the blood transfusion. It is related to plasma proteins found in the transfused components. Usually the patient suffers from localized wheels and itching. In some cases fever and rigor may develop.
Why does iron overload occur in transfusions?
In some cases transfusion reaction can occur due to over load of blood volume. Too much of blood overload can make harder for the heart to pump blood. Iron overload can occur if too much of iron is present in donor blood. Iron overload can affect liver and heart functions. Rapid infusion of refrigerated blood components can lead to hypothermia.
How long does it take for a transfusion reaction to develop?
In some cases the symptoms of transfusion reaction may develop after few days of transfusion. The signs and symptoms of transfusion reaction may be as follows: Fever. Chills.
What happens if blood type and recipient's blood do not match?
Transfusion reaction can occur if the donor’s blood type and recipient’s blood do not match. Although not common, transfusion reaction can sometimes lead to severe health consequences.
Why is blood transfusion done?
Blood transfusion is done mainly to replenish the lost blood volume or deficiency of its components such as hemoglobin , plasma or platelets. Blood grouping and cross matching is the first step before blood transfusion.
What happens if the blood group of a donor is not compatible with that of recipient patient's blood group type
If the blood group of donor is not compatible with that of recipient patient’s blood group type, the antibodies of recipient’s blood will attack the donor’s blood. The donor’s red blood cells are attacked. It is a hemolytic reaction.